Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Router Vs Switch
Uploaded by
Kaustubh ParkerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Router Vs Switch
Uploaded by
Kaustubh ParkerCopyright:
Available Formats
Router vs Switch
Routers and switches are both computer networking devices. They allow one or more computers to be connected to other computers, networked devices, or to other networks. However, the functions of a hub, switch and router are quite different, even if at times they are integrated into a single device. Routers connect two or more logical subnets, which do not necessarily map one-to-one to the physical interfaces of the router. The term layer 3 switch often is used interchangeably with router, but switch is really a general term without a rigorous technical definition. In marketing usage, it is generally optimized for Ethernet LAN interfaces and may not have other physical interface types.
Comparison chart
Router NAT (Network Can Perform NAT Address Translation): Routing Decision: Take faster Routing Decision Bandwidth sharing is Dynamic (Enables either static or dynamic bandwidth sharing for modular cable interfaces. The default percent-value is 0. The percent-value range is 1-96.) 1-10 Mbps(Wireless) 100 Mbps (Wired) LAN . WAN Store IP address in Routing table and maintain address at its own. Switch Switches can Not perform NAT Take more time for complicated routing Decision If speed of switch is 10/100 Mbps then bandwidth of each and every one of its ports gets 10/100 Mbps. 10/100Mbps, 1Gbps LAN Store MAC address in lookup table and maintain address at its own Uses MAC address
Bandwidth sharing:
Speed: Used in (LAN/MAN/WAN): Table:
Address used for data Uses IP address tramsmission: Data Transmission Packet form: Technical Specifications: Device Type: Layer: Ports:
Frame (L2 Switch) Frame & Packet (L3 switch) Network switches operate at Routers operate at Layer 3 (Network) of the layer two (Data Link Layer) OSI model. of the OSI model. internetworking device networking device Data Link Layer Network Network Layer Layer 2/4/8 8/16/24/48
Used for: Price: Latest Models:
Features:
Faster:
Switch Connecting two or more Connecting Two or more networks. nodes. Starts from 2500/-Rs (L2) 20,000 /- Rs (appx.) 15,000/- Rs (L3) (appx.) Alcatel's OmniSwitch 9000; Linksys WRT54GL Juniper MX & EX Cisco Catalyst switch 4500 series Cisco 3900,2900,1900 and 6500(10 Gbps), Priority rt range On/Off Firewall VPN Dynamic hadling of setting of port VLAN Port Bandwidth mirroring In a LAN environment L3 In a different network environment (MAN/ switch is faster than Router WAN) Router is faster than L3 Switch. (built in switchning hardware)
Router
Function of a router vs. switch
A router is a more sophisticated device than a switch. Traditional routers are designed to join multiple area networks (LANs and WANs). Routers serve as intermediate destinations for network traffic. They receive TCP/IP packets, look inside each packet to identify the source and target IP addresses, then forward these packets as needed to ensure the data reaches its final destination. A network switch is a small hardware device that joins multiple computers together within one local area network (LAN). Switches are incapable of joining multiple networks or sharing an Internet connection. A home network with a switch must designate one computer as the gateway to the Internet, and that device must possess two network adapters for sharing, one for the home LAN and one for the Internet WAN. With a router, all home computers connect to the router equally, and it performs the equivalent gateway functions.
Router vs. Switch for wireless networks
Routers can connect wired or wireless (WiFi) networks. A switch is used for wired networking connections.
Intelligence in a router vs. switch
Routers are more sophisticated devices that can have software to increase network throughput using techniques such as caching.
You might also like
- Difference between Modem, Router and switch and hubDocument35 pagesDifference between Modem, Router and switch and hubSonia ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exam Questions ExplainedDocument95 pagesCCNA Exam Questions ExplainedzaidzzNo ratings yet
- Switch and Router ConfigurationDocument41 pagesSwitch and Router ConfigurationBroot KalNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.3.5 Configuring Basic Routing and SwitchingDocument12 pagesLab 2.3.5 Configuring Basic Routing and SwitchingPanic Teuku Ryan Francis100% (1)
- CCNA1 v5.0 NB - ITN Practice Skills Assessment - PT - CLI Command AnswersDocument19 pagesCCNA1 v5.0 NB - ITN Practice Skills Assessment - PT - CLI Command AnswersnilocNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer Sample PDFDocument89 pagesPacket Tracer Sample PDFYidnekachewNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 Quiz 2 ThsootDocument10 pagesCCNPv7 Quiz 2 ThsootClaudio Aliste Requena100% (1)
- CCNA 2 Final Exam QuestionsDocument67 pagesCCNA 2 Final Exam Questionsradek1911No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Document14 pagesChapter 6 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Eddie83100% (14)
- OSI Seven Layers Model Explained With ExamplesDocument10 pagesOSI Seven Layers Model Explained With ExamplesHammad Nisar100% (1)
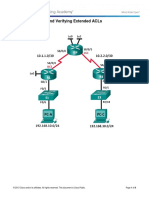
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDocument8 pages9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaNo ratings yet
- It 242 Week 6 Router and Switch ConfigurationDocument3 pagesIt 242 Week 6 Router and Switch Configurationhello_kitty4545No ratings yet
- Certkiller 300-101 Exam GuideDocument101 pagesCertkiller 300-101 Exam GuideKAy Cee100% (4)
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Document19 pagesCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxNo ratings yet
- CCNA Answers - CCNA Exam - CCNA ExamsDocument30 pagesCCNA Answers - CCNA Exam - CCNA ExamsMihai Gheorghe100% (1)
- Week10-Lab-build A Network With Switch and Observe MAC Addresses and ARPDocument9 pagesWeek10-Lab-build A Network With Switch and Observe MAC Addresses and ARPAdnan AliNo ratings yet
- Determining IP Routes: © 2000, Cisco Systems, IncDocument40 pagesDetermining IP Routes: © 2000, Cisco Systems, Incmadagoneraju100% (1)
- CCNA Training CCNA - Access List Questions 2Document12 pagesCCNA Training CCNA - Access List Questions 2dauzayl3529100% (1)
- Lab8 Sequential Lab Router ConfigDocument6 pagesLab8 Sequential Lab Router ConfigmedjacNo ratings yet
- 19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMDocument8 pages19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMjohannachicaNo ratings yet
- Addressing The Network - IPv4 and Subnetworking (IP Adressing and Subnetting)Document54 pagesAddressing The Network - IPv4 and Subnetworking (IP Adressing and Subnetting)Sunny100% (1)
- ROUTE Chapter 1 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document5 pagesROUTE Chapter 1 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (7)
- TCP/IP Suite Error and Control MessagesDocument28 pagesTCP/IP Suite Error and Control MessagesbaraynavabNo ratings yet
- 9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting ChallengeDocument5 pages9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting ChallengeOrlyn Valencia100% (5)
- CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Document20 pagesCCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxNo ratings yet
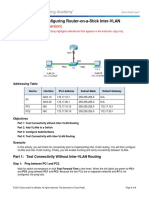
- (Instructor Version) : Packet Tracer - Configuring Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument4 pages(Instructor Version) : Packet Tracer - Configuring Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN RoutingAhmad Mustafa AbimayuNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Discovery 4.0 Final ExamDocument27 pagesCCNA 3 Discovery 4.0 Final ExamMamoona1680% (5)
- 20-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services IIDocument19 pages20-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services IImansoorali_afNo ratings yet
- En ENetwork IPTM v4040Document38 pagesEn ENetwork IPTM v4040abdelhf1No ratings yet
- Ccna Quick Revision NotesDocument49 pagesCcna Quick Revision NotesPaul100% (3)
- Shortnote LabDocument22 pagesShortnote LabSamiNo ratings yet
- Basic Router Cmmds Shortcut KeysDocument5 pagesBasic Router Cmmds Shortcut KeysMr.GoneNo ratings yet
- How To Set SSH-Telnet-HTTP Connection Timeout Using MPF For ASA 8.3 and LaterDocument12 pagesHow To Set SSH-Telnet-HTTP Connection Timeout Using MPF For ASA 8.3 and LaterCassandra ShafferNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocument4 pagesCisco Router Configuration CommandsTine ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Understanding subnetting with a cheat sheetDocument3 pagesUnderstanding subnetting with a cheat sheetsaed218No ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2019 (v5.1+v6.0) Introduction To NetworksDocument67 pagesCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2019 (v5.1+v6.0) Introduction To NetworksJamal ZaghmoutNo ratings yet
- CCNA Answers Chapter 1Document14 pagesCCNA Answers Chapter 1Brandon ScottNo ratings yet
- IP Subnet CalculationsDocument27 pagesIP Subnet Calculationsrajasekr1No ratings yet
- Eigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Document47 pagesEigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Sándor PetrócziNo ratings yet
- Routing and Switching Essentials Practice Skills Assessment Part IDocument7 pagesRouting and Switching Essentials Practice Skills Assessment Part IPierre Cantillo67% (3)
- Cisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Document54 pagesCisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Paul100% (2)
- Configure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN Routing ExplainedDocument2 pagesConfigure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN Routing ExplainedQuang AnhNo ratings yet
- Cisco Cli Analyzer Help Guide v3.2.1Document51 pagesCisco Cli Analyzer Help Guide v3.2.1Ritesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsFrom EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesFrom EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- XII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesDocument30 pagesXII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesLakshya NayakNo ratings yet
- Difference between router, switch and hubDocument2 pagesDifference between router, switch and hubMel Maravillas0% (1)
- Experiment No. 1: Problem DefinitionDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1: Problem DefinitionAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC 2000 Networking 2020Document30 pagesDell EMC 2000 Networking 2020abdulmuizzNo ratings yet
- Hanshin Service Manual For Hs-1321 Hs-2519 Hs-9041Document11 pagesHanshin Service Manual For Hs-1321 Hs-2519 Hs-9041Kaustubh Parker67% (3)
- DerivativesDocument1 pageDerivativesniniamicanNo ratings yet
- Sem IDocument1 pageSem IKaustubh ParkerNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BIOM Sem 7 Rev.Document12 pagesSyllabus BIOM Sem 7 Rev.Kaustubh ParkerNo ratings yet
- Am FMDocument28 pagesAm FMAnonymous 3smLyf6vEwNo ratings yet
- 10 Programming Foundations - Netwroks Part IDocument18 pages10 Programming Foundations - Netwroks Part IHammami SalahNo ratings yet
- Network Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Document86 pagesNetwork Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Tariq EhsanNo ratings yet
- T270 User ManualDocument41 pagesT270 User Manualafrian syahNo ratings yet
- Telecom, Internet & Wireless Tech ChapterDocument51 pagesTelecom, Internet & Wireless Tech ChapterAFIFAH KHAIRUNNISA SUBIYANTORO 1No ratings yet
- Computing: Pearson Higher Nationals inDocument70 pagesComputing: Pearson Higher Nationals inMaster GamerNo ratings yet
- EoS EoL Notice c1900Document7 pagesEoS EoL Notice c1900Anonymous k2SY4zdI3No ratings yet
- LAN Switching and WAN NetworksDocument29 pagesLAN Switching and WAN NetworksMin LwinNo ratings yet
- Christian Narine EDPM SbaDocument35 pagesChristian Narine EDPM SbaRajendra Persaud60% (5)
- ch18-SLIDE - (2) Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz A.ForouzanDocument38 pagesch18-SLIDE - (2) Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz A.ForouzanXP2009100% (3)
- Immaculate Conception High School Information Technology - Grade 11Document2 pagesImmaculate Conception High School Information Technology - Grade 11Zonya Kelly KaeNo ratings yet
- Sixnet BT Modem User GuideDocument70 pagesSixnet BT Modem User GuideknightxiiNo ratings yet
- LFS211 CHAPTER Revised PDFDocument53 pagesLFS211 CHAPTER Revised PDFbudiNo ratings yet
- Ata S2Document3 pagesAta S2Emir SosaNo ratings yet
- Christopher ChampagneDocument4 pagesChristopher ChampagneChristopher ChampagneNo ratings yet
- WAN TechnologiesDocument8 pagesWAN TechnologiesNyamache LamechNo ratings yet
- 10 GbeDocument181 pages10 Gbealeksandar7No ratings yet
- Sample Network Design ProposalDocument23 pagesSample Network Design Proposalajmcrae100% (1)
- EMS Guangxi Grid China SCADA PDFDocument3 pagesEMS Guangxi Grid China SCADA PDFDustin Soria VNo ratings yet
- Case Study Google, Apple, and Facebook Struggle For Your Internet ExperienceDocument13 pagesCase Study Google, Apple, and Facebook Struggle For Your Internet ExperienceAL-LadziNo ratings yet
- CirataDocument4 pagesCirataHeber Farid Fabrica QuispeNo ratings yet
- Prospectus: BRAC UniversityDocument298 pagesProspectus: BRAC UniversityMd. Aftabur Rahman100% (1)
- TCP IP Protocol Suite Chap-03 Underlying TechnologyDocument54 pagesTCP IP Protocol Suite Chap-03 Underlying TechnologyRahul RajNo ratings yet
- 15357158-CCNA4e Case StudyDocument14 pages15357158-CCNA4e Case StudySamuel GetachewNo ratings yet
- Quick setup guide for HooToo TripMate SithDocument1 pageQuick setup guide for HooToo TripMate Sithpradhish100% (1)
- HCIA (Datacom) V1.0 WEEKEND SESSION COURSE OUTLINEDocument4 pagesHCIA (Datacom) V1.0 WEEKEND SESSION COURSE OUTLINEjunaid ahmedNo ratings yet
- LMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking ConceptsDocument53 pagesLMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking Conceptslakshay187No ratings yet
- COMPUTER NETWORKS OVERVIEWDocument24 pagesCOMPUTER NETWORKS OVERVIEWDjordje OrasaninNo ratings yet
- DCN-unit-1 ModifiedDocument112 pagesDCN-unit-1 ModifiedMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 IntroductionDocument45 pages1.1 IntroductionJUGRAJ SINGHNo ratings yet
- Telindus 1421 SHDSL RouterDocument394 pagesTelindus 1421 SHDSL RouterPedro Luis Loredo SánchezNo ratings yet