Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Bredd Eng Vt96
Uploaded by
Epic WinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Bredd Eng Vt96
Uploaded by
Epic WinCopyright:
Available Formats
Np MaA vt 1996
Directions
Test period Test time Weeks 18 - 22 1996. According to the local school, but at least 60 minutes (during normal lesson time). Decided locally by the school. The test material should be handed in with your solutions. Write your name, gymnasium programme/adult education and date of birth on the papers you hand in. Test The Open-Solutions part contains two alternate problems of which you should choose one problem. The questions in the problem can be such that you will have to decide between the possible interpretations. You should present the assumptions which form the basis for your computations and conclusions. A partial, but not completed, solution can provide a basis for positive assessment. For each problem, there is a description of what the teacher will consider during the evaluation of your work. If anything is unclear, ask your teacher.
Resources Test material
Working methods
The teacher responsible will inform you of the different working methods which are allowed for the Open-Solutions part of the test. The presentation of the solutions to the problem will be done individually.
Np MaA vt 1996
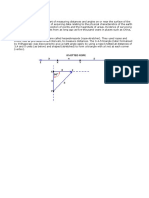
1. The Courtyard
In the tenants association, Renen, there are a total of 30 apartments. Up until now, they have had a fairly boring courtyard. Now the residents want to do something nice with their courtyard. They want to have a nice green area between the buildings and a sand-covered playground with an area of 40 - 50 m2. They already have the swing sets and other equipment for the playground. The association needs help with a drawing in an appropiate scale, as well as an extensive cost analysis. In the drawing, the green area, walkways, trees, and bushes should be drawn. The residents do not want to pay more than 1500 crowns per apartment. The work they can do themselves. The courtyard has the form of a rectangle with the measurements shown in the sketch below. MAKE A SUGGESTION!
PRESENT YOUR SUGGESTION WITH THE HELP OF A SCALED DRAWING AND
A COST ANALYSIS
20 m 35 m 35 m
20 m
Price Trees 300 kr each Bushes 80 kr each Asphalt 180 kr/m2 115 kr/ m3 2 kr/ m2 175 kr/ m3
Topsoil Grass seeds Sand Playground equipment
Preconditions There should be at least 5 m between each tree. There should be 2-3 m between each bush. All of the walkways should be covered with asphalt. For 180 kr/m2, a firm will do the whole job. A layer of topsoil, 10 - 20 cm thick, is needed to get a nice grass area. A layer of sand, approximately 20 cm thick, is needed for the playground. Old equipment can be reused.
When evaluating your work, the teacher will consider the following: how you perform your computations how you present your work and motivate your results how appropiate your suggestion is for the final goal how you construct and present your drawing if your suggestion follows the given preconditions which mathematical knowledge you present
Np MaA vt 1996
2. Coordinate Geometry
In computer aided drawing, one is often interested in depicting geometric figures. This can be done in different ways. Two such methods are shown here. Method I: Reflection When the segment AB is reflected in the xaxis, we get the line segment CD.
A B 1 1 D C
Method II: Dilation A line L1 has been drawn through the point A and the origin. On that line, point E is placed so that the distance between point E and the origin is double the distance between point A and the origin. On the corresponding side, point F is set with the help of line L2.
1
L1 E L2
A B
x
1
Solve the problems on the next side!
Np MaA vt 1996
Draw a coordinate system on your answer sheet. Use the same scale as in the figures above. Draw a triangle with corners at the points (1,4), (5,1), and (8,5).
a)
Draw a new triangle by reflection in the x-axis (according to method 1).
Describe how you worked when you constructed the reflected figure and state the coordinates of the corners of the new triangle.
Describe everything else you know and can find out about the two triangles you have drawn. Show your computations and reasoning.
b)
Draw a new triangle by applying method 2 to the first triangle.
Compare the new triangle with the first one. Describe the differences and the similarities.
In the description of method 2, the new points distance to the origin is found by multiplying the distance of the old point to the origin by a factor of 2 (doubling). Investigate what happens when you use another factor
In the description of method 2, the origin was the starting point for L1 and L2 when the new figure was constructed. Investigate what happens if you use another point.
When evaluating your work, the teacher will consider the following: how you apply the basic geometric concepts and theorems how you present your work and motivate your results how you understand and apply the given instructions which mathematical knowledge you present how you describe, compare, and discuss the different triangles how you perform your investigations in the problem
You might also like
- D Bredd Eng vt99Document3 pagesD Bredd Eng vt99Epic WinNo ratings yet
- D Bredd Eng ht97Document3 pagesD Bredd Eng ht97Epic WinNo ratings yet
- NpMaA Bredd Eng Ht98Document12 pagesNpMaA Bredd Eng Ht98Epic WinNo ratings yet
- National Test in Mathematics Course D SPRING 2005 DirectionsDocument7 pagesNational Test in Mathematics Course D SPRING 2005 DirectionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Surface AreaDocument36 pagesSurface AreaMary Belle Peraren Estores100% (1)
- National Test in Mathematics Course B SPRING 2002 DirectionsDocument7 pagesNational Test in Mathematics Course B SPRING 2002 DirectionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Math Formulas with GeoGebraDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Math Formulas with GeoGebraVarzaru SimonaNo ratings yet
- 7 Amalgamation PDFDocument8 pages7 Amalgamation PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Deriving PiDocument8 pagesDeriving Piapi-373103187No ratings yet
- Ed321 VideoDocument2 pagesEd321 Videoapi-242145065No ratings yet
- Have Students Put Home Link Page 71 Into Mailboxes. - 1:30 P.MDocument5 pagesHave Students Put Home Link Page 71 Into Mailboxes. - 1:30 P.MJulieNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Document20 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Nik NabihahNo ratings yet
- Geometrygardenminiproject-Myah Simon Dd-E ModelDocument9 pagesGeometrygardenminiproject-Myah Simon Dd-E Modelapi-627011822No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Verbal Test QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 9: Verbal Test Questionsapi-214017049No ratings yet
- AssureplanDocument2 pagesAssureplanapi-315989751No ratings yet
- Introduction To Algebra Tiles AlgebraDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Algebra Tiles Algebrajes74No ratings yet
- National Test in Mathematics Course D SPRING 2002 DirectionsDocument9 pagesNational Test in Mathematics Course D SPRING 2002 DirectionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- 09D - 8.99 Volume and Surface Area Project v2Document9 pages09D - 8.99 Volume and Surface Area Project v2Zai SulaimanNo ratings yet
- AS1 5 SOUP v2Document5 pagesAS1 5 SOUP v2Liz FoxNo ratings yet
- MCT4CE Culminating Task PracticeDocument3 pagesMCT4CE Culminating Task Practiceledmabaya23No ratings yet
- Micro Teach Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMicro Teach Lesson Planapi-316460590No ratings yet
- Measuring Area and PerimeterDocument4 pagesMeasuring Area and PerimeterjenniyanceyNo ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter: Reporting Category Geometry Topic Primary SOL MaterialsDocument5 pagesArea and Perimeter: Reporting Category Geometry Topic Primary SOL Materialssangita bediyaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Module 2Document10 pagesCalculus Module 2Karl AngcananNo ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter: Reporting Category Geometry Topic Primary SOL MaterialsDocument5 pagesArea and Perimeter: Reporting Category Geometry Topic Primary SOL Materialssangita bediyaNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMath 105 Lesson Planapi-250245193No ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3WINDOWS 10No ratings yet
- Inverse Sine Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesInverse Sine Lesson PlanMolly FrantzNo ratings yet
- Math 6 PPT Q3 Week 6Document58 pagesMath 6 PPT Q3 Week 6Julie SungaNo ratings yet
- Math - Oct. 26-30 PDFDocument11 pagesMath - Oct. 26-30 PDFJulieNo ratings yet
- LessonPlanL1 Geometric Shapes Area and PerimeterDocument9 pagesLessonPlanL1 Geometric Shapes Area and PerimeterArtchell MabandingNo ratings yet
- TCNJ Lesson Plan: Aim/Focus QuestionDocument12 pagesTCNJ Lesson Plan: Aim/Focus Questionapi-253005231No ratings yet
- Lattice Multiplication Kenesha HardyDocument6 pagesLattice Multiplication Kenesha Hardyapi-267389718No ratings yet
- Measurement Year 6 7Document10 pagesMeasurement Year 6 7api-419109401No ratings yet
- Offset SurveyDocument10 pagesOffset SurveygladysNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series ScenariosDocument9 pagesSequences and Series ScenariosManisah Mohd ShahNo ratings yet
- 9MA0 32 Que 20211019Document20 pages9MA0 32 Que 20211019John HarrodNo ratings yet
- MylessonplanDocument3 pagesMylessonplanapi-313400286No ratings yet
- Exploring Dilations and ProportionsDocument49 pagesExploring Dilations and ProportionseclecticOTANo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Trapezoid, Integration, & Geogebra RubricDocument6 pagesAP Calculus AB Trapezoid, Integration, & Geogebra Rubricapi-261139685No ratings yet
- Algebra Old Exam Papers 91027Document106 pagesAlgebra Old Exam Papers 91027sajith_senanayake_1100% (2)
- Specmath1and2 Samp WDocument39 pagesSpecmath1and2 Samp WpappadutNo ratings yet
- Lesson 66.estimating The Area of A Parallelogram, Triangle, and A TrapezoidDocument21 pagesLesson 66.estimating The Area of A Parallelogram, Triangle, and A TrapezoidBrielle Lagasca100% (1)
- MAT1F1 Lesson on Perimeter and AreaDocument7 pagesMAT1F1 Lesson on Perimeter and AreaCt HusnaNo ratings yet
- Painting Polynomials Up For ConferenceDocument6 pagesPainting Polynomials Up For Conferenceapi-247455001No ratings yet
- HL Portfolio WorkDocument76 pagesHL Portfolio WorksnipripNo ratings yet
- Puzzle Cube ProjectDocument19 pagesPuzzle Cube Projectapi-260953119No ratings yet
- Problembased 2 1Document6 pagesProblembased 2 1cynthiaaa sNo ratings yet
- LessonPlanL2 Area Perimeter VolumeDocument10 pagesLessonPlanL2 Area Perimeter VolumeVishesh VatsNo ratings yet
- Example of Assessments in MathematicsDocument4 pagesExample of Assessments in MathematicsEna ElisabethNo ratings yet
- Mccoy Decision Making LessonDocument11 pagesMccoy Decision Making Lessonapi-256995276No ratings yet
- Year: 10 Subject: Maths - Week 1: Circle Theorems and Fractions (See Below)Document3 pagesYear: 10 Subject: Maths - Week 1: Circle Theorems and Fractions (See Below)anon_155205867No ratings yet
- Appendix D 1Document3 pagesAppendix D 1api-457394590No ratings yet
- 2018 Test 1 CADocument10 pages2018 Test 1 CARaghav GanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7-Fundamental Operation On Integers - Addition of IntegersDocument6 pagesGrade 7-Fundamental Operation On Integers - Addition of IntegersSer Nap83% (6)
- Find The Volume of A Cone: Mathematics/ Grade 8 Objective: Students Will Analyze Formulas For The Volumes of A Cone by Classifying TheDocument8 pagesFind The Volume of A Cone: Mathematics/ Grade 8 Objective: Students Will Analyze Formulas For The Volumes of A Cone by Classifying Theapi-314454587No ratings yet
- System of Equations Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSystem of Equations Lesson Planapi-489866539No ratings yet
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4From EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4No ratings yet
- Mathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLDocument6 pagesMathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- FogDocument5 pagesFogEpic WinNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument192 pagesInequalitiesEpic Win100% (2)
- Warning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsDocument12 pagesWarning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- FaithDocument8 pagesFaithceceph354No ratings yet
- Nelson BibDocument5 pagesNelson BibEpic WinNo ratings yet
- RomeDocument7 pagesRomeEpic WinNo ratings yet
- The Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsDocument18 pagesThe Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Syntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument7 pagesSyntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- IstDocument34 pagesIstEpic WinNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument7 pagesOutlineEpic WinNo ratings yet
- ElemDocument101 pagesElemEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Ram RecDocument8 pagesRam RecEpic WinNo ratings yet
- New 18Document5 pagesNew 18Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- HopeDocument4 pagesHopeEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Zhang TDocument4 pagesZhang TEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Hilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityDocument27 pagesHilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityEpic WinNo ratings yet
- J. P. MayDocument17 pagesJ. P. MayEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Zhang QDocument15 pagesZhang QEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Edward NelsonDocument1 pageEdward NelsonEpic WinNo ratings yet
- EDocument9 pagesEEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Internal Set TheoryDocument26 pagesInternal Set TheoryEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WoolfDocument9 pagesWoolfEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WeinerDocument6 pagesWeinerEpic WinNo ratings yet
- J-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationDocument9 pagesJ-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionDocument17 pagesProbability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WaddleDocument10 pagesWaddleEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WalijiDocument6 pagesWalijiEpic WinNo ratings yet
- VParticipantsDocument1 pageVParticipantsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Functions and SequenceDocument13 pagesFunctions and SequenceVanshika WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- New Aspects of Caputo-Fabrizio Fractional Derivative: Progress in Fractional Differentiation and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesNew Aspects of Caputo-Fabrizio Fractional Derivative: Progress in Fractional Differentiation and ApplicationsQamar Abbas 189No ratings yet
- Interacción Tabique PórticoDocument225 pagesInteracción Tabique Pórticodalex_tauro93No ratings yet
- Brave New Universe Illuminating The Darkest Secrets of The CosmosDocument281 pagesBrave New Universe Illuminating The Darkest Secrets of The Cosmosgalici2002No ratings yet
- Textbook of Heat Transfer - S. P. Sukhatme PDFDocument122 pagesTextbook of Heat Transfer - S. P. Sukhatme PDFVineet Mathew50% (6)
- Non-Destructive Testing of A Building Wall by Studying Natural Thermal SignalsDocument7 pagesNon-Destructive Testing of A Building Wall by Studying Natural Thermal SignalsyamiyuugiNo ratings yet
- Euler Elements of Algebra PDFDocument2 pagesEuler Elements of Algebra PDFDawn0% (1)
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- 3.11 Inequalities: N A A B A A ADocument10 pages3.11 Inequalities: N A A B A A ANethra SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - MsDocument4 pagesFurther Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Mswa030waNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PANDocument3 pagesGrade 5 PANletletNo ratings yet
- Che 312 Notebook DistillationDocument19 pagesChe 312 Notebook DistillationUGWU MARYANNNo ratings yet
- Petrophysics in Horizontal WellsDocument13 pagesPetrophysics in Horizontal WellsusuarioNo ratings yet
- Trig integrals & trig subsDocument6 pagesTrig integrals & trig subsjunaidadilNo ratings yet
- Inde 2156 HW 2Document6 pagesInde 2156 HW 2Emre ParlakNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Nature of StatisticsDocument47 pagesModule 1: Nature of StatisticsHannah Bea LindoNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 1Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 1villanuevaparedesaracely4No ratings yet
- Choosing A Statistical Test: © Louis Cohen, Lawrence Manion & Keith MorrisonDocument16 pagesChoosing A Statistical Test: © Louis Cohen, Lawrence Manion & Keith MorrisonMarko JelavićNo ratings yet
- Control of Smps A Refresher Part 3Document13 pagesControl of Smps A Refresher Part 3Alvaro Javier Baños RiveraNo ratings yet
- Q-Learning Based Link Adaptation in 5GDocument6 pagesQ-Learning Based Link Adaptation in 5Gkalyank1No ratings yet
- Physics CalaDocument7 pagesPhysics CalaMunazNo ratings yet
- QPCSEON16Document929 pagesQPCSEON16Farhan Sheikh MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Tool Radius Compensation For 5-Axis Machining SpecificationsDocument61 pagesTool Radius Compensation For 5-Axis Machining SpecificationsmikeNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency - Mean, Median, Mode ExplainedDocument8 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency - Mean, Median, Mode ExplainedNor HidayahNo ratings yet
- 02 - Sistem Penunjang Keputusan Dalam Optimalisasi Pemberian Insentif Terhadap Pemasok Menggunakan Metode TOPSISDocument8 pages02 - Sistem Penunjang Keputusan Dalam Optimalisasi Pemberian Insentif Terhadap Pemasok Menggunakan Metode TOPSISAries putraNo ratings yet
- 1D Box ApplicationsDocument2 pages1D Box Applicationsarpan palNo ratings yet
- Amc8 - Aops - Basic Math - Toc PDFDocument5 pagesAmc8 - Aops - Basic Math - Toc PDFkrish100% (1)
- (Signal Processing and Communications 13) Hu, Yu Hen - Programmable Digital Signal Processors - Architecture, Programming, and App PDFDocument386 pages(Signal Processing and Communications 13) Hu, Yu Hen - Programmable Digital Signal Processors - Architecture, Programming, and App PDFGururaj BandaNo ratings yet
- Voice Based Application As Medicine Spotter For Visually ImpairedDocument5 pagesVoice Based Application As Medicine Spotter For Visually ImpairedCh.pranushaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Univariate Linear RegressionDocument64 pagesBahan Univariate Linear RegressionDwi AstitiNo ratings yet