Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE337 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 20O6
Uploaded by
sateesh83Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE337 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 20O6
Uploaded by
sateesh83Copyright:
Available Formats
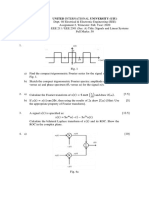
H-8287
CEMBER2006. DEGREEEXAMINATION,NOVEMBER/DE B.E./8.TECh.
Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 337 - DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Time : Three hours Answer ALL questions. PART A - (10 x2 = 20 marks) 1. 2. 3. Maximum : 100 marks
What are the disadvantagesof analog signal processing?
ft) 4. 5. 6.
Parallel?
Define Z-transform and its ROC?
What is the differencebetween Fourier transform of the continuous signal r(/) and the FT of the sampledsignal r(n). Let x(n) andX(jw) is fourier transform pair. What is the Fourier transform of of and odd sequence x(n) in terms of X$w)? even sequence What is aliasing?
7. 8. L 10.
What is the need for Hold circuit? Draw the basic structure of FIR filter. Is bilinear transformation ]inear or not? What is the merit and demerit of bilinear transformation? PARTB-(5x16=80marks)
ww
w.
aa na
va
x(n) = {I,2,3,2,1} xo(n)=
(a)
Seriesand in
N.
What is the resultant impulse response of the two systems whose impulse responsesare hr(n) and hr(n ) when they are in
co m
What are the basic operating involved in convolution process?
11. (a)
(i)
Let
, \
Find
and
xoh)=T'obtainx@)tntermsofx"(n)andro(n).(8) (ii) Discuss the merits and demerits of Digital signal processing over (8) analog signal process. Or
x(n\-x(-n)
^, ,
\ j-- r^-^-
(b)
(i) (ii)
Explain multichannel signals and multidimentional signals.
(g)
Explain the operation of frequency-division multiplexing and demultiplexing. (g) what is the output of the system wit]n h(n)= fl,1,1,] for the input x(n) = {-L,2, -I}? (g) state and prove that the product of the two sequencesrr(n) and xr(n) is equivalent to the convolution of their respective Z-transforms. i.e. Xr(z) @ Xr(z). (g)
12. (a)
(i)
(ii)
Or (b) (i) Find the z-transform xr(n)={8,b,7} of and, xr(n)={8,0,s,0,7}. what
is the relation between X,(z) and X,()? (ii) 13. (a) (i) (ii) (6) Find the inverse - Z transform of H(Z)=Z(Z+2)/(Z-0.2)(Z+0.6). (10)
(b)
(i) (ii)
Draw the flow chart of 8 point FFT.
and explain.
ww
L4.
(a)
(i)
Draw the block diagram of successive approximation A./D converter
w.
Define DFT. Explain how to compute DFT in matrix form.
aa na
Or
va
Derive the Fourier transform of a rectangular pulse whose amplitude is A and width is 2T and draw the amplitude spectrum. (8)
N.
Derive the equation of the first stage of FFT.
co m
(g)
( 10)
(ii)
What are the factors to be consideredfor A,/Dconverter?Explain. (6) Or
(b)
(i) (ii)
What is sampling?Explain.
(6)
Explain in detail how sampling in time domain results its spectrum
to be periodic.
( 10)
R 8287
15.
(a)
(i) (ii;
Draw the direct form - II of an IIR system.
(6)
ConvertH(.s)=(2s-1)/(s2 +5s+ 4) Lo H(z), usingimpulseinvariant
method with sampling period = 0.5 sec.
(10)
Or (b) (i) In IIR filter, Is it a unique cascade structure? Why? With an example implement a cascadestructure. (8) Convert the Bessel filter II(s)=3/s2+3s+3 transformation with Ts = 0.5 sec. using bilinear (8)
(ii)
ww
w.
aa na
va
N.
R 8287
co m
You might also like
- 67 Important GIS Applications and UsesDocument28 pages67 Important GIS Applications and Usessateesh83No ratings yet
- Training Course: MODEL 2100 Instument Landing System (ILS)Document59 pagesTraining Course: MODEL 2100 Instument Landing System (ILS)Ruben AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- EC8352 - Signals & SystemsDocument3 pagesEC8352 - Signals & Systemssyed1188No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentsugesh98No ratings yet
- EC2314Document3 pagesEC2314Rakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- cs2403-DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING PDFDocument0 pagescs2403-DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING PDFvelkarthi92No ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Ysurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 7Document2 pages7049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- X (N) (F U (N)Document2 pagesX (N) (F U (N)049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- Cusat DSP Question PaperDocument14 pagesCusat DSP Question PaperSabith PockerNo ratings yet
- EC1307Document12 pagesEC1307Subbiah Siva SubramanianNo ratings yet
- r05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesr05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingBharath LudiNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ece, Eie)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ece, Eie)vinod chittemNo ratings yet
- R13 - December, 2014 - Regular ExaminationsDocument3 pagesR13 - December, 2014 - Regular ExaminationsmushahedNo ratings yet
- DSP CT SolutionDocument15 pagesDSP CT SolutionSougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- 8Document2 pages8049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.DhariniJeevanandamNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Electronics and Communication Engineering)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Electronics and Communication Engineering)mushahedNo ratings yet
- DSP QuestionsDocument8 pagesDSP Questionsjjshree79No ratings yet
- Ec2314 DSP Nov 2011 QPDocument3 pagesEc2314 DSP Nov 2011 QPRama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Roll NoDocument2 pagesRoll No049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems SyllabusDocument4 pagesSignals & Systems SyllabusShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems EC403Document2 pagesSignals & Systems EC403Shashank M ChanmalNo ratings yet
- r05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesr05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- WWW - Vidyarthiplus.In: Digital Signal Processing - Question BankDocument8 pagesWWW - Vidyarthiplus.In: Digital Signal Processing - Question Bankanon_303873446No ratings yet
- AE06Document3 pagesAE06Sanjeev PanwarNo ratings yet
- CS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2005Document4 pagesCS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2005Chandru Sekar100% (1)
- r05221902 Signals and SystemsDocument10 pagesr05221902 Signals and SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- EC2314 DSP Nov 2010 PDFDocument3 pagesEC2314 DSP Nov 2010 PDFSyed MusthafaNo ratings yet
- DSP PaperDocument3 pagesDSP PaperParth ShahNo ratings yet
- R5 210404 Signals & SystemsDocument1 pageR5 210404 Signals & SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKDocument5 pagesDigital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKSaran SekaranNo ratings yet
- QMF FilterDocument17 pagesQMF FilterShilpa Badave-LahaneNo ratings yet
- CS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2003Document3 pagesCS331 Digital Signal Processing Nov Dec 2003Chandru SekarNo ratings yet
- PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document5 pagesPART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)dhakaruNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument10 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingRakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument7 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingAhsan MalikNo ratings yet
- Assignment For B.Tech ECE: X N X KDocument3 pagesAssignment For B.Tech ECE: X N X KTanmay GoelNo ratings yet
- DE57J12Document4 pagesDE57J12tutulkarNo ratings yet
- 203 EEE 2301 Assignment 2Document2 pages203 EEE 2301 Assignment 2Faizur Rahman PaponNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumenthafizrahimmitNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - IETE AMIETE ET-CS-IT (Old Scheme) Signals and Systems Sample Paper 1Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - IETE AMIETE ET-CS-IT (Old Scheme) Signals and Systems Sample Paper 1Jonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitled9710190524No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis in S-DomainDocument22 pagesCircuit Analysis in S-Domainshreyas_stinsonNo ratings yet
- Ec2314 DSP Nov 2010 QPDocument3 pagesEc2314 DSP Nov 2010 QPRama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Rr410201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 pageRr410201 Digital Signal ProcessingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- CS331 Digital Signal Processing Apr May 2004Document3 pagesCS331 Digital Signal Processing Apr May 2004Chandru SekarNo ratings yet
- DSPDocument95 pagesDSPAbdulhafeez ShaikNo ratings yet
- R5310206-Linear and Discrete Systems AnalysisDocument4 pagesR5310206-Linear and Discrete Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing - Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument12 pagesDigital Signal Processing - Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringBizura SarumaNo ratings yet
- EEE 2519 CAT I Nov 2020Document2 pagesEEE 2519 CAT I Nov 2020Margaret IrunguNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing (Old) April2013Document1 pageDigital Signal Processing (Old) April2013avinashavi93No ratings yet
- rr320201 Analysis of Linear SystemsDocument11 pagesrr320201 Analysis of Linear SystemsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems EC403Document3 pagesSignals & Systems EC403Shashank M ChanmalNo ratings yet
- EC Con-2Document8 pagesEC Con-2Prabhu SakinalaNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Influence of GenderDocument10 pagesInfluence of Gendersateesh83No ratings yet
- MFCC CodeDocument8 pagesMFCC Codesateesh83No ratings yet
- Design of Low-Cost Manual Cum Electric Powered Wheelchair For Disabled Person's To Use in IndoorDocument18 pagesDesign of Low-Cost Manual Cum Electric Powered Wheelchair For Disabled Person's To Use in Indoorsateesh83No ratings yet
- Design of Touch Screen Based Robot With Obstacle Detection Module For Autonomous Path NavigationDocument5 pagesDesign of Touch Screen Based Robot With Obstacle Detection Module For Autonomous Path Navigationsateesh83No ratings yet
- Program Booklet IEEE TENCON2017Document69 pagesProgram Booklet IEEE TENCON2017sateesh83No ratings yet
- Pre Requisite Area of Research 2015Document4 pagesPre Requisite Area of Research 2015sateesh83No ratings yet
- Malaysia SITIS 437 PDFDocument7 pagesMalaysia SITIS 437 PDFsateesh83No ratings yet
- Éç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.. Éç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.. Éç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.Document1 pageÉç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.. Éç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.. Éç-öÀ-™ - É ©' Æuç - Éç-Aç-û É - Ü¿-SS ÷.sateesh83No ratings yet
- Southern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh LimitedDocument1 pageSouthern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh Limitedsateesh83No ratings yet
- Sro: Gannavaram-614: About Us Organization ACTS & Rules Faqs Values & Rates Rti Act Document Templates PublicationsDocument1 pageSro: Gannavaram-614: About Us Organization ACTS & Rules Faqs Values & Rates Rti Act Document Templates Publicationssateesh83No ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and SystemsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Signals and Systemssateesh83No ratings yet
- Autumn Sem Pospectus 2015Document40 pagesAutumn Sem Pospectus 2015sateesh83No ratings yet
- Gate Ece 2004Document11 pagesGate Ece 2004sateesh83No ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2013 Signals and SystemsDocument7 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2013 Signals and Systemssateesh83No ratings yet
- CatdecDocument28 pagesCatdecsateesh83No ratings yet
- IntroToBluetoothHacking CarolinaCon2012Document50 pagesIntroToBluetoothHacking CarolinaCon2012HaQueXNo ratings yet
- Book - 11 - Radio NavigationDocument448 pagesBook - 11 - Radio NavigationCosmin Alexandru GrosariuNo ratings yet
- IPT Satellite CommunicationDocument89 pagesIPT Satellite CommunicationKifaru Micro-electronicsNo ratings yet
- Albania IPTV Free Codes November 2022Document2 pagesAlbania IPTV Free Codes November 2022Anderson Fernando100% (1)
- Global Sources - Telecom Products 05.11Document165 pagesGlobal Sources - Telecom Products 05.11Felipe MarschallNo ratings yet
- S3900 Command Manual PDFDocument1,159 pagesS3900 Command Manual PDFYezenia Cabello LazaroNo ratings yet
- Instructivo Usuario HGU Mitrastar GPT-2541 v1Document44 pagesInstructivo Usuario HGU Mitrastar GPT-2541 v1Rodrigo Chacana AhumadaNo ratings yet
- VOIP Protocols and StandardsDocument11 pagesVOIP Protocols and StandardsClarence Philip SantosNo ratings yet
- 5000 200 EMOR Order FormDocument1 page5000 200 EMOR Order FormNguyễn Văn TrungNo ratings yet
- Powerwave PDFDocument2 pagesPowerwave PDFRyan ArdyansyahNo ratings yet
- Case Study Free MobileDocument2 pagesCase Study Free MobilehayetNo ratings yet
- Quickstart Guide of OpenVox GSM Gateway WGW1002G Connect With Asterisk ServerDocument4 pagesQuickstart Guide of OpenVox GSM Gateway WGW1002G Connect With Asterisk ServergermanNo ratings yet
- airOS UGDocument148 pagesairOS UGPlamenNo ratings yet
- Camara Zavio D520EDocument2 pagesCamara Zavio D520ETecnoSmartNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik BGP Security: Rofiq FauziDocument27 pagesMikrotik BGP Security: Rofiq FauziRenaldyOktavianoNo ratings yet
- Thorax BrochureDocument6 pagesThorax BrochureeajNo ratings yet
- A6j MB - 0103 R2.2 0118Document63 pagesA6j MB - 0103 R2.2 0118Thịnh TúNo ratings yet
- E131525 1650995324013 157617 Shobikah - NWDocument133 pagesE131525 1650995324013 157617 Shobikah - NWVivekan VivekNo ratings yet
- Network Cabling Workshop PresentationDocument24 pagesNetwork Cabling Workshop Presentationjolopez1611No ratings yet
- Data Acquiring and Storing Functions For Iot/M2M Devices Data and MessagesDocument32 pagesData Acquiring and Storing Functions For Iot/M2M Devices Data and MessagesJayasree BaluguriNo ratings yet
- OSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFDocument52 pagesOSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFplinio_de_paulaNo ratings yet
- NakDocument37 pagesNakAnonymous vVedXyYNo ratings yet
- Inside The Social Network's (Datacenter) NetworkDocument49 pagesInside The Social Network's (Datacenter) NetworkVamsi Krishna PatchamatlaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues: ObjectiveHamzaSpahijaNo ratings yet
- Giachetti 2010Document29 pagesGiachetti 2010pharssNo ratings yet
- Offline Charging SystemDocument6 pagesOffline Charging SystemVivek PandeyNo ratings yet
- YapeDocument3 pagesYapeJordy RamosNo ratings yet
- IV ECE ESS Question BankDocument3 pagesIV ECE ESS Question BankVeerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- 07Document15 pages07vinodNo ratings yet