Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unctional AND Roject Rganizations
Uploaded by
Paresh KharadiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unctional AND Roject Rganizations
Uploaded by
Paresh KharadiCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
2 FUNCTIONAL AND PROJECT ORGANIZATIONS
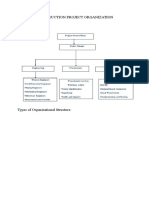
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION Functional organization is structure in which authority rests with the functional heads; the structure is sectioned by departmental groups. What are some advantages of the functional structure? Simple and clear; coordination left to top management Reduces overhead Provides clearly marked career paths for hiring and promotion Employees work alongside colleagues who share similar interests What are some disadvantages of the functional structure? Coordination of functional tasks is difficult; little reward for cooperation with other groups since authority resides with functional supervisor. Provides scope for different department heads to pass-off company project failures as being due to the failures of other departments. PROJECT TEAM STRUCTURE Project team structure consists of an autonomous project team, existing independently of the rest of the organization. The project team is assembled for a specific project under the action of the product manager. The team is thus temporary and will be disbanded when its project is complete. Sometimes we can find design or products with special requirements that are not encompassed within one or more of the functions. This will lead to a cooperative efforts of marketing, production, engineering, and others as appropriate; as well as assistance from the accounting legal, and contracting staffs. When it is an important new effort, a dynamic and capable person from the upper levels of middle management is selected to take responsibility for this unique activity. A project is organized around this project manager, and then a few specialized assistants are provided and a project team is formed. The project manager exercises direct and autonomous control over the various discipline groups and is responsible for the coordination and monitoring of the effort of the team. Since most major organizational functions will be affected by this team, it is typically removed from the functional organizations structure. A multiple project organization is needed when the number of projects increases. There is a definite limit to the number of major projects any traditional organization can support. As the number of projects increases the managerial load on the general manager increases to the point where he can no longer cope. Advantages of project team structures Good at responding well to an immediate project need. Flexibility Responsibility for success of project clearly identified. Releases top management from micromanaging operations, so that the management can focus on the overall company strategy rather than detailed nuts and bolts.
12
Disadvantages of project team structures The actual organizational power and authority of the team manager may be a delicate issue. Greater administrative overhead. In-group vs. Out-group mentality may develop. MATRIX STRUCTURE In the matrix structure, the personnel and other resources that a project manager requires are not permanently assigned to the project, but are obtained from a pool controlled and monitored by a functional manager. Personnel required to perform specific functions in a particular project are detailed for the period necessary, and are then returned to the control of he functional manager for reassignment. Discipline supervisors are responsible for the efforts of the groups constituting assigned project personnel and for other required resources. The members of the groups and their supervisors are charged with the timely completion of the different tasks and are responsible to the project manager and the functional manager. Example: An engineer assigned for a specific period to design a subsystem of a project is responsible to the functional manager for completing the task as scheduled, and to the project manager for providing an acceptable design. The two managers report to a matrix executive. The project manager in the matrix works with the functional manager to establish the resource requirements and their timetable utilization on the project, and to work out the revisions required as the project effort proceeds. The functional manager is responsible for assuring that resources are utilized in the manner best serving the interests of the organization. The formal role of the matrix executive or top-level management is similar to the top subordinate to the position. The general manager is literally on top of or outside the basic matrix structure and therefore should have a clear perspective of all activities and personnel within the matrix. Here, however, the similarity ends. The general manager leads a dual command structure, the functional and the project hierarchies, which must be balanced through a careful blend of autocratic and cooperative managerial styles. Participation is required, for example, in the arbitration of technical disputes and in resource allocations. Autocracy is essential to the establishment, enforcement, and revision of priorities among and between the functional and project entities within the matrix. This role involve the three major managerial concerns:
balancing power - The balance of power involves allocating both project and functions budgets, orchestrating personnel assignments, and applying schedule pressures and others. managing the decision context - Management of the decision context is accomplished by establishing strategy, policy, and control systems to assure that decisions are made to benefit the overall organization rather than the individual functional department or project. setting standards - High performance standards start at the top. They must established and enforced by the general manager, since his is the only position in the matrix with the perspective and power to require top quality performance.
Advantages of the matrix organization It attempts to retain the benefits of both structures ( functional organization and project team structure ).
13
FUNCTIONAL
AND
CONCURRENT ENGINEERING PROJECT ORGANIZATIONS MODULE 2
Coordinates resources in a way that applies them effectively to different projects. Staff can retain membership on teams and their functional department colleagues.
Disadvantages of the matrix organization Potential for conflict between functional vs. project groups. Greater administrative overhead. Increase in managerial overhead MAJOR ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Advantages: Better customer relations Shorter product development time Lower program costs Better control of projects Improved quality and reliability Higher profit margins Better control over program security Better project visibility and focus on results Improves coordination among company divisions doing work on the project Accelerated development of managers due to breadth of project responsibilities Better control over program security Disadvantages: More complex internal operations Inconsistency in application of company policy Lower utilization of personnel Higher program costs More difficult to manage Tendency for functional groups to neglect their job Too much shifting of personnel from project to project
ACTIVITY 2.1 SPACE SURVIVAL TEAM BUILDING 3 SPACE SURVIVAL In the following situation, your life and death will depend upon how well your team can share its present knowledge of a relatively unfamiliar situation so that the team can make
3
Teams in Engineering Education, Arizona University Tempe, Arizona 85287, March 1994, Section II - 4. 14
decisions that will lead to your survival. This problem is fictional, although the ranking to which you will compare your results was done by a number of space experts. Read the situation and do Step 1 without discussing it with your other team members. THE SITUATION You are a member of a lunar exploration crew originally scheduled to rendezvous with a mother ship on the lighted surface of the moon. Due to mechanical difficulties however, your ship was forced to land at a spot some 320 kilometers (200 miles) from the rendezvous point. During the re-entry and landing, much of the equipment aboard was damaged, and, since survival depends on reaching the mother ship, the most critical items available must be chosen for the 320 km trip. YOUR TASK In this page are listed the 15 items left intact and undamaged after landing. Your task is to rank these items according to their importance in aiding you to reach the mother ship, starting with 1 the more important, to 15 the least important. You should assume the number in the crew is the same as the number on your team, you are the actual people in the situation, the team has agreed to sick together, and all 15 items are in good condition. SPACE SURVIVAL TEAM BUILDING EXERCISE STEP 1: (Do this step now) Each person is to individually rank each item. 1 is most important; 15 is least important. Do not discuss the situation or the task until each member finished the individual ranking. STEP 2: (To be done after the following mini-lecture on team roles.) Rank order the 15 items as a team. Once discussion begins dont change your individual ranking.
15
FUNCTIONAL
AND
CONCURRENT ENGINEERING PROJECT ORGANIZATIONS MODULE 2
Items Box of matches Food concentrate 20 meters of nylon rope Parachute silk Portable heating unit Two .45 caliber pistols One case dehydrated milk Two 50 kg tanks of oxygen Stellar map (of the moons constellations) Life raft Magnetic compass 25 liters of water Signal flares First aid kit w/hypodermic needle Solar-power. FM receiver/transmitter
Step 1 Individual Ranking
Step 2 Team Ranking
Step 3 Expert Ranking
Step 4 Difference Ranking (1-3)
Step 5 Difference Ranking (2-3)
Your score
Team Score
16
You might also like
- Chapter 7 Projects Implementation and ControlDocument51 pagesChapter 7 Projects Implementation and ControlfekadeNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument41 pagesProject ManagementJochie TeruelNo ratings yet
- Types of OrganizationDocument10 pagesTypes of Organizationahmedabad ahmedabadNo ratings yet
- Describe The Main Project Organisation Structures and Give Their Advantages and Disadvantages. Functional Organizational StructureDocument12 pagesDescribe The Main Project Organisation Structures and Give Their Advantages and Disadvantages. Functional Organizational StructurePres GunaNo ratings yet
- Understanding OrganizationsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding OrganizationsUmar ArshadNo ratings yet
- PM-ORG-STRUCTDocument24 pagesPM-ORG-STRUCTshawar69No ratings yet
- Management of Project Based OrganizationsDocument42 pagesManagement of Project Based OrganizationsUmair MansoorNo ratings yet
- Project Management Topic: Project Organizational Structure Types Uot AcademyDocument19 pagesProject Management Topic: Project Organizational Structure Types Uot AcademyHAMZA ALINo ratings yet
- Construction Project OrganizationDocument34 pagesConstruction Project OrganizationKarl TimtimNo ratings yet
- 1.project Organization Structure-1Document17 pages1.project Organization Structure-1Asano NyekhaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Organizational Structure and Gantt ChartDocument44 pagesProject Management Organizational Structure and Gantt ChartKha Ren100% (1)
- Understanding the Difference Between Goals and ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnderstanding the Difference Between Goals and Objectivesjayadarsini21130% (1)
- Project Management Organization Structures and Crashing ExplainedDocument7 pagesProject Management Organization Structures and Crashing ExplainedKiran BhattNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project Management Organizational Structure, PALANOGSUMILONGDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Project Management Organizational Structure, PALANOGSUMILONGKrissia Mae Palanog100% (1)
- Project Management MethadologiesDocument7 pagesProject Management MethadologiesLyricalNo ratings yet
- Organizational Influences and Project Life Cycle Process English VersionDocument74 pagesOrganizational Influences and Project Life Cycle Process English VersiongalihNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration - MBA Semester 4 "Project Management" Specialization Pm0017 - Project Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesMaster of Business Administration - MBA Semester 4 "Project Management" Specialization Pm0017 - Project Quality Managementmreenal kalitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. 4 Team FormationsDocument8 pagesLesson 1. 4 Team FormationsCharlaine MaurilloNo ratings yet
- Project Management Quiz01Document7 pagesProject Management Quiz01ray.lazare28No ratings yet
- PMCH 03Document32 pagesPMCH 03RockyLagishettyNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument19 pagesProject ManagementAsmaul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Project Management SlidesDocument88 pagesProject Management SlidesSam SaimNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter-3Document6 pagesPM Chapter-3GolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- The Organisational Context ContinuedDocument32 pagesThe Organisational Context ContinuedKerica HenryNo ratings yet
- Construction Project OrganizationDocument7 pagesConstruction Project OrganizationAnonymous cQHVRleTv100% (2)
- Garcia - Organizing Group Teams and StructuresDocument47 pagesGarcia - Organizing Group Teams and StructuresGarcia Shella MarieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part ADocument17 pagesUnit 4 Part AWasim RezaNo ratings yet
- Project OrganisationDocument3 pagesProject Organisationswathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- KJ Somaiya College of Arts & Commerce Sanket Sanjay Pawar Tybms/B Roll No - 134 Subject: Project Work Assignment 1: Types of Organizational StructureDocument8 pagesKJ Somaiya College of Arts & Commerce Sanket Sanjay Pawar Tybms/B Roll No - 134 Subject: Project Work Assignment 1: Types of Organizational StructureSANKET PAWARNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Chapter-3Document34 pagesProject Management: Chapter-3Zohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Organization Structure Staffing and ManagementDocument8 pagesTopic 2 Organization Structure Staffing and ManagementNazaree tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Project Managment Matrix OrganisationDocument5 pagesProject Managment Matrix OrganisationJaggu JrzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document55 pagesChapter 3assemtharwat1960No ratings yet
- Group 2: Construction Project OrganizationDocument27 pagesGroup 2: Construction Project OrganizationUdat Hakeem Malang AmirNo ratings yet
- Types of Matrix Organizational StructuresDocument3 pagesTypes of Matrix Organizational StructuresadrianeNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument18 pagesOrganization StructureAmir Reza Ahmadi MotlaghNo ratings yet
- Developing Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Document5 pagesDeveloping Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Sergio Olvera GNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structures and Project ManagementDocument27 pagesOrganizational Structures and Project ManagementrojanNo ratings yet
- Pure Project OrganizationDocument4 pagesPure Project Organizationnitu11100% (3)
- Roject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDDocument22 pagesRoject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDKandagatla KamalNo ratings yet
- External stakeholders and organizational structureDocument30 pagesExternal stakeholders and organizational structureÈm DâwgNo ratings yet
- A Project Is A Planned Set of Interrelated Tasks To Be Executed Over A Fixed Period and Within Certain Cost and Other LimitationsDocument9 pagesA Project Is A Planned Set of Interrelated Tasks To Be Executed Over A Fixed Period and Within Certain Cost and Other LimitationsSaksham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Government Project MGMTDocument11 pagesCase Study For Government Project MGMTMuktar Edris100% (1)
- Organizational Structures & Project ManagementDocument20 pagesOrganizational Structures & Project ManagementSalah Ud DinNo ratings yet
- Project Management and General Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesProject Management and General Operations Managementdeehimura2No ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Module 1Document21 pagesQuarter 2 Module 1pyong jNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Slide 1: Project Human Resource Management & Communication SkillsDocument34 pagesHuman Resources Slide 1: Project Human Resource Management & Communication SkillsMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Project OrganizationDocument24 pagesProject OrganizationHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- MBA Full Time (CBCS) Project Management (Fourth Semester) Lecture 1 NotesDocument8 pagesMBA Full Time (CBCS) Project Management (Fourth Semester) Lecture 1 NotesDrMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- Cons Method IbaratDocument22 pagesCons Method Ibaratshedilyn ibaratNo ratings yet
- Proj MGT TJDocument15 pagesProj MGT TJMD.Tahjibul AlamNo ratings yet
- CH 3-Project ManagementDocument57 pagesCH 3-Project ManagementAmani Al MqadmaNo ratings yet
- PM Ch 3 Organizing Staffing Projects TeamsDocument37 pagesPM Ch 3 Organizing Staffing Projects TeamsChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Define Project Organization and Explain Its Importance?Document9 pagesDefine Project Organization and Explain Its Importance?sapnaa11No ratings yet
- Project Success and FailureDocument18 pagesProject Success and FailureaviNo ratings yet
- Project Management - Notes-2Document17 pagesProject Management - Notes-2Maximillan LobuinNo ratings yet
- Project Management Structure Chapter OverviewDocument33 pagesProject Management Structure Chapter OverviewdanishsayedNo ratings yet
- Project Management Quiz03Document10 pagesProject Management Quiz03ray.lazare28No ratings yet
- Organization Structures and Theories ExplainedDocument5 pagesOrganization Structures and Theories ExplainedRenz NgohoNo ratings yet