Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5 Word Meaning and Semantic Feature
Uploaded by
Anastasiya RudenkoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 Word Meaning and Semantic Feature
Uploaded by
Anastasiya RudenkoCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 Word meaning and semantic feature
. Conventionalityand Motivation: ()@ --- A. Conventionality: It refers that words are conventional, arbitrary symbols; that is,there is no intrinsic() relation between the sound symbol and its sense. There is no way to explain why this or that sound-symbol has this or that meaning beyond the fact that the people of a given community have agreed to use one to designate the other.For instance,the English call what Chinese call fangzi in house,the French call it Maison and the Russian dom.All these symbols are totally different from one another,yet they all signify the same thing. B. Motivation: It refers to the connection between word-symbol and its sense. Though the great majority of English words are conventional and arbitrary symbols, there is a group of words that can be described as motivated, that is there is a +direct connection between the symbol and its sense. For example, onomatopoeic words such as roar, bang and clash,derived words and compound words such as readable, kilgram and daydream, etc. A. phonetic motivation: Words motivated phonetically are called echoic words or onomatopoeic words, whose pronunciation suggests the meaning. b. Morphological motivation: Most of the derivational affixes have a specific meaning,when added to a base, they derive a new word. We say the word is morphologically motivated, for a direct connection can be observed between the morphemic structure of the word and its meaning. c. Semantic motivation: It refers to motivation base on semantic factors. It is a kind of mental association. Main types of word meaning
1 A Grammatical meaning: Grammatical meaning is indispensable in determining the
position a word occupies in a sentence. a. word-class: when a dictionary lists the function of a word,the definition does at least two things: it describes the words lexcal meaning and also gives what is traditionally known as the part of speech of the word,which modern linguists call the wors-class.the word-class is essential , for when we use a word in a sentence, we have to take into consideration two factors: its specific lexical meaning and the position it normally occupies in a sentence, which is determinded by the word-class to which the word belongs. B. Lexical meaning: which is different from grammatical meaning is two respects: first the lexical meaning of a word is the same in all the forms of one and the same word while the grammatical meaning varies from one word-form to another, second,every word has a different lexical meaning, whereas the grammatical meaning is the same in identical sets of individual forms of different meaning.
1.
How are the sound and meaning of most words related? Give examples to illustrate your point?
1
2.
What do we mean by phonetic motivation
Phonetic/Onomatopoeic motivation: Indicates the relatinship between sound and meaning of word.Its sound suggests its meaning. e.g. , cuckoo,squeak,quack,etc.@ ping-pang
3. 4. 5.
Quote a short poem or a passage tha shows the literary effect of onomatopoeic words what is meant by grammatical meaning? Grammatical meaning:refer to that part of the meaning of the word which indicates grammatical concept or relationships, such as part of speech of words, singular and plural meanings of nouns, tense meaning of verbs and their inflectional forms.
It consists of word-class and inflectional paradigm() 1)Word-class: It describe the words lexicological meaning and also gives what is traditonally known as the part of speech of the word. e.g. modern will be marked as a noun. 2)Inflectional paradigm:It refers to thegrammatical forms ()of a word which appear the different forms when used in actual speech. e.g. cat-cats; to walk,walks etc.
6.
What is the difference between grammatical meaning ()and lexical meaning( )?
Lexical meaning -- is constant in all the words within or without context related to the notion that the word conveys. It has two components conceptual meaning 1) Denotative meaning()/ Conceptual meaning(): 2) associative meaning.() Lexical meaning and grammatical meaning make up the word-meaning. Grammatical meaning surfaces only in use. Conceptual meaning (denotative meaning) the meaning given in the dictionary and forms the core of word-meaning. It is constant and relative stable. Conceptual meaning forms the basis for communication. e.g. The sun rises in the East. the sun Associative meaning the secondary meaning supplemented to the conceptual meaning. It is open-ended and indeterminate 7. Why should we give primary importations to conceptual/denotative meaning of word? Conceptual meaning (denotative meaning) the meaning given in the dictionary and forms the core of word-meaning. It is constant and relative stable. Conceptual meaning forms the basis for communication.-- give three or five words which have connotation varying from one speech community to another speech commnunity ,or from era to era
2
8.
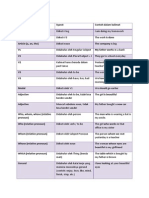
Connotative meaning(): refers to the emotional association which a word or phrase sugests in one's mind;it is the supplementary value which is added to the purely denotative meaning of a word@ Explain the following terms with example 9. Semantic feature The analysis of word meaning is often seen as a process of breaking down the sense of word into its minimal components, which are known as semantic feature or sense components
10. Componential Analysis()p.156:
It refers to the analysis of breaking down the conceptual meaning into its minimal distinctive components which are known as semantic features.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 05 ML Upper-Intermediate Test File 2006 PDFDocument36 pages05 ML Upper-Intermediate Test File 2006 PDFAnastasiya Rudenko80% (5)
- Greek Enchiridion - William G.MacDonaldDocument100 pagesGreek Enchiridion - William G.MacDonaldThe Apostle of Albion100% (1)
- 11+ Vocabulary Root Words, Prefixes and Suffixes Test Paper 3Document9 pages11+ Vocabulary Root Words, Prefixes and Suffixes Test Paper 3GuitargirlMimiNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument3 pagesBullyingAnastasiya RudenkoNo ratings yet
- World PuzzelDocument3 pagesWorld PuzzelAnastasiya RudenkoNo ratings yet
- FoodDocument3 pagesFoodAnastasiya RudenkoNo ratings yet
- Innovative Methods of Teaching EnglishDocument1 pageInnovative Methods of Teaching EnglishAnastasiya RudenkoNo ratings yet
- Innovative Method of TeachingDocument16 pagesInnovative Method of TeachingAji Handoko100% (1)
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English On YouTubeDocument24 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English On YouTubeEA Spoken English100% (6)
- Subject and Object PronounsDocument3 pagesSubject and Object Pronounsyaki70No ratings yet
- Assignment N3Document6 pagesAssignment N3Mỹ Linh Võ Thị0% (1)
- Passé Composé Avec Être: Remember Which Verbs Use Être? Continue ReadingDocument3 pagesPassé Composé Avec Être: Remember Which Verbs Use Être? Continue ReadingAshutosh HNo ratings yet
- 1 Grammar Book A1Document24 pages1 Grammar Book A1clafer15No ratings yet
- Internal ChangeDocument3 pagesInternal ChangejjlesterjjNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Education and Lifelong Learning: 1°medi oDocument11 pagesUnit 2: Education and Lifelong Learning: 1°medi oAlexis CortesNo ratings yet
- Tabel Error RecognitionDocument4 pagesTabel Error RecognitionNurPiter ThiodorisNo ratings yet
- Basic 01 Student BookDocument78 pagesBasic 01 Student BookMoises Enoc Perez AquinoNo ratings yet
- (Empirical Approaches To Language Typology 54) Silvia Luraghi., Tuomas Huuomo (Eds.) - Partitive Cases and Related Categories-De Gruyter Mouton (2014) PDFDocument585 pages(Empirical Approaches To Language Typology 54) Silvia Luraghi., Tuomas Huuomo (Eds.) - Partitive Cases and Related Categories-De Gruyter Mouton (2014) PDFSilvia LuraghiNo ratings yet
- Spectrum TRD1 GV U2 1Document1 pageSpectrum TRD1 GV U2 1MARIA TERESA LOPEZ CINTASNo ratings yet
- Adjectives: Definition, Types, Degrees, Position and MoreDocument12 pagesAdjectives: Definition, Types, Degrees, Position and MoreGothicAnkhNo ratings yet
- Language Test Score SheetDocument1 pageLanguage Test Score SheetAndré Raffael MoellerNo ratings yet
- Adjectives + PrepositionsDocument5 pagesAdjectives + Prepositionscristianomar63No ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative SentencesDocument6 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative SentencesHéctor HerediaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Modern GreekDocument432 pagesHandbook of Modern GreekMusa şen53% (15)
- Quick Death of A SalesmanDocument11 pagesQuick Death of A Salesmanmayumi leonardoNo ratings yet
- Madina Book1 Notes Abdurrahman OrgDocument77 pagesMadina Book1 Notes Abdurrahman OrgereelotNo ratings yet
- 88 Verb Tense Review 1 The Simple Tenses US StudentDocument12 pages88 Verb Tense Review 1 The Simple Tenses US StudentVincent Hicks100% (1)
- Adjective ClausesDocument8 pagesAdjective ClausesBaggins SilvanabagginsNo ratings yet
- Imperative (Imperativo)Document4 pagesImperative (Imperativo)miomirmNo ratings yet
- 8th Class English Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument5 pages8th Class English Grammar Parts of SpeechstephanrazaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Year 6 All Purpose GTMJ - WritingDocument3 pages2012 Year 6 All Purpose GTMJ - WritingbibNo ratings yet
- Frequency of Modal Verbs in English Language CorporaDocument6 pagesFrequency of Modal Verbs in English Language Corporaapi-515559766No ratings yet
- The Difference Between Act and ActionDocument4 pagesThe Difference Between Act and ActionlearnafrenNo ratings yet
- Insisted: The Irish Man Was Determined To Pay For Our DrinksDocument3 pagesInsisted: The Irish Man Was Determined To Pay For Our DrinksprppecheNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Unit 1 I VOCABULARY: Complete The Sentences With Countries and Capital CitiesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Unit 1 I VOCABULARY: Complete The Sentences With Countries and Capital CitiesnapimveNo ratings yet
- ErosionDocument15 pagesErosionSreedhar Reddy SajjalaNo ratings yet