Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technical Information About Advantages of Used Nozzles
Uploaded by
apostolulOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical Information About Advantages of Used Nozzles
Uploaded by
apostolulCopyright:
Available Formats
TECHNICAL INFORMATION ABOUT ADVANTAGES OF NOZZLE
APPLICATIONS FOR USED NOZZLE(TYPE 19A OR 37) The advantages of Nozzles( type 19A or 37) are well known for towing vessels such as tugs and fishing boats, however significant improvements in performance can be achieved on vessels such as coasters, inland waterways craft and bulk carriers using designs optimized for each vessel type. Tugs, trawlers, dredgers and offshore supply vessels are typical of the application where a nozzles (TYPE 19A or 37) can provide up to 25-30% improvement in thrust at low speed. This allows a reduction in installed power for a given performance. A fishing vessel, for example, can work larger gear in deeper waters or maintain speed in bad weather as proven by the many thousands of of trawlers fitted with Nozzles worldwide.
Below have the very nice example for see the difference about used open propeller and used nozzle
TESTS Two recent conversions prove that the increased trawling thrust from a Nozzle system can reduce fuel consumption.
Vessel 1: 500 bhp engine: 500 litres/day! Vessel 2: 270 bhp engine: 270 litres/day!
These are average figures from weekly trips and show a reduction of 20% in fuel consumption/hour when trawling. Overall it is not uncommon to see a 15% reduction in annual fuel bills taking steaming into account. A Nozzle system gives 20-25% increase in thrust when towing. A vessel with 800 bhp and 2000mm open propeller achieves 8.6 tonnes. 8.6 tonnes can be achieved using 640 bhp with a Nozzle system. A 20% reduction in engine power for the same towing thrust! Comparison @ 3 Knots Towing Take this example of a vessel having BHP 170 19A(37) Nozzle(t) 2.68 2.90 Open Screw(t) 2.30 2.48 295 bhp 190 3.10 2.65 engine with 1300 210 230 3.30 3.55 2.83 3.02 mm fixed pitch propeller. 250 270 285 3.75 3.95 max. 3.20 max.
An open propeller gives 3.20t @ 270bhp. 3.2t can be be achieved at 220bhp with the Nozzle system! 3.92t max. with the Nozzle System, a 22% improvement! For the same power the Nozzle system gives 17% more thrust! The increases in performance apply for all engine sizes.
The Importance of Propeller diameter Propeller Diameter(mm) 1300 1600 1900 2200 2500 Shaft RPM 400 280 210 160 130 19A Nozzle 3.92 4.45 5.00 5.50 6.00
A significant improvement by increasing propeller diameter using the same 295bhp engine! In fact the Nozzle system provides more thrust with either fixed pitch or CP propellers has been proved beyond doubt. Whether a 10m vesel with 100 hp or a 40m vessel with 2000 hp the benefits of the Kort Nozzle are the same.
The HT type or HR type nozzle compare to 19A and 37
Nozzles are aerofoil shaped rings placed around the propeller. Nozzles have found their application in ships for decades with good results. The main advantage of the nozzle is that it increases the thrust on the propeller. Comparing propellers with and without nozzles shows that the nozzle propeller offers about 25% more total thrust (nozzle and propeller) than an open propeller at zero ship speed (bollard condition). At high ship speeds this difference becomes less up to the point where the nozzle generates drag instead of thrust. For decades all nozzles have been of the 19A or 37 type. The 37 nozzle has been applied in cases where astern thrust is needed, such as in harbor tugs. The 19A nozzle is usually applied to all other cases. Recent developments in computational tools have accelerated the application and use of new types of nozzles. A good example of this is the HT o HR nozzle. The HT or HR nozzle is very useful for improving the performance of the propulsion unit of tugs and dredgers. This nozzle generates more thrust at dredging conditions in combination with more thrust at free-sailing speed, compared with conventional nozzles such as the 19A and 37 Marin nozzles. This is made possible by the specially shaped profile of the nozzle(the shaped is like fish!!). About testing with this shape have this:. Extensive CFD analysis was carried out in order to understand the basic flow properties causing this difference. (CFD stands for Computational Fluid Dynamics; these are new tools which enable flow phenomena to be calculated including the effects of friction and flow separation). It appeared that at the model scale the flow at the trailing edge of the HR nozzle showed local flow separation, which affected the lift on the nozzle profile. CFD analysis carried out for the full-scale Reynolds number showed that in those conditions the flow separation is not present.
The shift in the local separation point at the trailing edge creates additional lift on the HT or HR nozzles, which is then manifest at full scale. This has set a basis for detailed prediction of the performance of the HT or HR nozzle.
You might also like
- Choosing A Pump SicDocument6 pagesChoosing A Pump Sicchipora3No ratings yet
- Lightnin Impeller Technology PDFDocument8 pagesLightnin Impeller Technology PDFNaila TheExplore HorisonNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of A New Cross Flow Type Hydraulic Turbine For High Head and Low Flow RateDocument18 pagesNumerical Analysis of A New Cross Flow Type Hydraulic Turbine For High Head and Low Flow RateephremNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Fluid Mixing Impeller TechnologyDocument6 pagesInnovations in Fluid Mixing Impeller Technologybosh_422No ratings yet
- Oerlikon Leybold Roots Blower Vacuum Pump CatalogDocument40 pagesOerlikon Leybold Roots Blower Vacuum Pump CatalogYasir Ali100% (1)
- Engineering Data IndexDocument11 pagesEngineering Data IndexphaindikaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Motor For Coiled Tubing ApplicationsDocument8 pagesTurbine Motor For Coiled Tubing ApplicationsEspion BenNo ratings yet
- 2012 Paper Screw CompressorsDocument25 pages2012 Paper Screw CompressorsravisankarNo ratings yet
- New Aerzen Rotary Lobe Compressor Packages Offer Volume Flows from 110 to 4,100 m3/hDocument20 pagesNew Aerzen Rotary Lobe Compressor Packages Offer Volume Flows from 110 to 4,100 m3/hJazmany OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Agitator DesignDocument6 pagesAgitator DesignGLENDA CASINONo ratings yet
- DC Nov07 DeepReservoirsDocument5 pagesDC Nov07 DeepReservoirsAbraham Montes HumanezNo ratings yet
- 9 - Propulsion Systems PDFDocument36 pages9 - Propulsion Systems PDFJosé Edwin RoldánNo ratings yet
- Propulsion and ShaftingDocument31 pagesPropulsion and ShaftingPriscila KImNo ratings yet
- Bombas CornellDocument12 pagesBombas CornellGabo Cabezas NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Medium and Highspeed Diesel Engines For Marine Service 1938Document11 pagesMedium and Highspeed Diesel Engines For Marine Service 1938Merrel RossNo ratings yet
- Nacelle Design and SizingDocument34 pagesNacelle Design and SizingIan Kelly100% (1)
- Optimization of Screw Compressor Design: SynopsisDocument11 pagesOptimization of Screw Compressor Design: SynopsisDustyn Deakins100% (1)
- Expandable Liner Hangers reduce pressure drop in Ecuador wellsDocument22 pagesExpandable Liner Hangers reduce pressure drop in Ecuador wellsHosam Ali100% (1)
- 9 Propulsion SystemsDocument36 pages9 Propulsion SystemsBegan GurungNo ratings yet
- Rig DesginDocument25 pagesRig Desginriobm100% (1)
- Rig DesginDocument25 pagesRig DesginImam PranadipaNo ratings yet
- At Turbo TechDocument20 pagesAt Turbo Tech1mmahoney100% (1)
- Screw Compressors: Misconception or Reality? A Concise Guide to Oil Flooded Rotary Screw CompressorsDocument16 pagesScrew Compressors: Misconception or Reality? A Concise Guide to Oil Flooded Rotary Screw CompressorsAditya BansodNo ratings yet
- Understanding Specific and Suction Specific SpeedDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Specific and Suction Specific Speedmurugan1984No ratings yet
- Micro-Scale Radial-Flow Compressor Impeller Made of Silicon Nitride - Manufacturing and PerformanceDocument10 pagesMicro-Scale Radial-Flow Compressor Impeller Made of Silicon Nitride - Manufacturing and PerformanceKerrie SpenceNo ratings yet
- Reynolds AirfoilDocument24 pagesReynolds Airfoilcv cvNo ratings yet
- Thruster OffshoreDocument2 pagesThruster OffshoreVipul KumarNo ratings yet
- New High Efficiency Steam TurbineDocument6 pagesNew High Efficiency Steam TurbineGunjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Press Design CalculationsDocument11 pagesHydraulic Press Design CalculationsSherif AdelNo ratings yet
- Efficient Screw Compressors for Dry Air DeliveryDocument10 pagesEfficient Screw Compressors for Dry Air DeliverySaeedAkbarzadehNo ratings yet
- Model 3196 ANSI B73.1M Process Pump: Engineered Performance For Increased Plant ReliabilityDocument74 pagesModel 3196 ANSI B73.1M Process Pump: Engineered Performance For Increased Plant Reliabilityscottt_84No ratings yet
- Vane Pumps PDFDocument120 pagesVane Pumps PDFAndi IshakaNo ratings yet
- Design of A New Improved Intake Manifold For F-Sae Car: January 2016Document6 pagesDesign of A New Improved Intake Manifold For F-Sae Car: January 2016İlker EnesNo ratings yet
- Rule of ThumbDocument8 pagesRule of ThumbHima Bindu Kolli100% (1)
- PCP VenezuelaDocument6 pagesPCP VenezuelakurtbkNo ratings yet
- Cylinder head porting guide: Improve engine efficiency through port modificationsDocument10 pagesCylinder head porting guide: Improve engine efficiency through port modificationsdebugevdo75% (8)
- Rules of Thumb For Pumps 2-7: Pump BasicsDocument5 pagesRules of Thumb For Pumps 2-7: Pump BasicsYinka AkinkunmiNo ratings yet
- LUF617 - DW - 8Hx11 - F Gas WellDocument10 pagesLUF617 - DW - 8Hx11 - F Gas WellJosé TimanáNo ratings yet
- Suction Specific Speed (Why Worry)Document8 pagesSuction Specific Speed (Why Worry)Tasawwur TahirNo ratings yet
- Faure Herman TurbineDocument3 pagesFaure Herman TurbinedidikosanNo ratings yet
- FlowLabEOC2e CH14Document2 pagesFlowLabEOC2e CH14Nathan100% (1)
- RR-B Propulsion 0612 Singlepages LR10 250512 Tcm92-8664Document28 pagesRR-B Propulsion 0612 Singlepages LR10 250512 Tcm92-8664dondo1004No ratings yet
- SUBJECT: The Difference Between Specific Speed and Suction Specific Speed 9-12Document3 pagesSUBJECT: The Difference Between Specific Speed and Suction Specific Speed 9-12jgarciablancoNo ratings yet
- Nacelle Design and SizingDocument34 pagesNacelle Design and SizingSandeep BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Hydropower BalanceDocument7 pagesHydropower BalanceDarío GuardatiNo ratings yet
- Screw Gas Compression IntroDocument24 pagesScrew Gas Compression IntroClaudioNo ratings yet
- ImpellerDocument10 pagesImpellerelchevere_5No ratings yet
- Pump Clinic 43Document3 pagesPump Clinic 43fnahas_bhNo ratings yet
- SOHC Head Flow Data + CarburetorsDocument62 pagesSOHC Head Flow Data + CarburetorsVincenzo SepeNo ratings yet
- Agitator DesignDocument6 pagesAgitator Designप्रमोद रणपिसेNo ratings yet
- HE Nozzle DevDocument21 pagesHE Nozzle DevJonathan MooreNo ratings yet
- 10 HP M2a Right Angle ManualDocument21 pages10 HP M2a Right Angle ManualSonthiMNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor GuidenceDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Compressor GuidenceChem.Engg100% (1)
- Catálogo General UPA 50 HZ 2 PARTEDocument20 pagesCatálogo General UPA 50 HZ 2 PARTENao Oi OiNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Capuchon Sy 0001 13Document1 pageCapuchon Sy 0001 13apostolulNo ratings yet
- A-01-Main and Second Floor PlanDocument1 pageA-01-Main and Second Floor PlanapostolulNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System MV 0079 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageHydraulic System MV 0079 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Unit MV 0078 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageHydraulic Power Unit MV 0078 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Abs Rules & RegulationsDocument55 pagesAbs Rules & RegulationsRENGANATHAN PNo ratings yet
- Bridge Control Panel MV 0073 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageBridge Control Panel MV 0073 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of CPP MV 0072 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageArrangement of CPP MV 0072 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Outline Drawing of Azimuth Thruster-mv-0080-10-Pusher VesselDocument1 pageOutline Drawing of Azimuth Thruster-mv-0080-10-Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- CPP System Diagram MV 0074 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageCPP System Diagram MV 0074 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System MV 0079 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageHydraulic System MV 0079 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Azimuth Rudder System Diagram (Port) MV 0075 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageAzimuth Rudder System Diagram (Port) MV 0075 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Unit MV 0078 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageHydraulic Power Unit MV 0078 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of CPP and Azimuththruster-mv-0071-10-Pusher VesselDocument1 pageArrangement of CPP and Azimuththruster-mv-0071-10-Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
- Arangement of Azimuth Thruster MV 0070 10 Pusher VesselDocument1 pageArangement of Azimuth Thruster MV 0070 10 Pusher VesselapostolulNo ratings yet
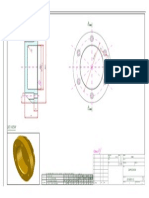
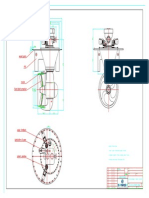
- Steps For Construction Nozzle (1) - S1Document1 pageSteps For Construction Nozzle (1) - S1apostolulNo ratings yet
- SVR Nandgi eDocument20 pagesSVR Nandgi eapostolulNo ratings yet
- Twin Screw Ice Class 3000Document1 pageTwin Screw Ice Class 3000apostolulNo ratings yet
- List of Paris MoU Deficiency CodesDocument11 pagesList of Paris MoU Deficiency CodesLito VertziniNo ratings yet
- PART-1 (Ship Types)Document24 pagesPART-1 (Ship Types)MohamedMostafaNo ratings yet
- Tommi CV 1 PDFDocument1 pageTommi CV 1 PDFAnaNo ratings yet
- Ocean Bill of LadingDocument1 pageOcean Bill of Ladingthanhphong3005No ratings yet
- Jascon 26 WAVDocument1 pageJascon 26 WAVVlad DemoNo ratings yet
- Application of Air Cavities On High-Speed Ships in RussiaDocument10 pagesApplication of Air Cavities On High-Speed Ships in RussiaMahdiNo ratings yet
- Sea Pearl 21 Owner's Manual GuideDocument9 pagesSea Pearl 21 Owner's Manual GuideJohn WalkerNo ratings yet
- Beneteau Survey PDFDocument101 pagesBeneteau Survey PDFChet Stephens100% (2)
- Instruction Manual: Quick Start GuideDocument14 pagesInstruction Manual: Quick Start GuideJeff ScottNo ratings yet
- All - Emy.p.2.03 Safety Message (GMDSS)Document2 pagesAll - Emy.p.2.03 Safety Message (GMDSS)Robin TetreNo ratings yet
- RNP APCH Down To LPV Minima: Flight Crew Basic Theoretical Training ForDocument102 pagesRNP APCH Down To LPV Minima: Flight Crew Basic Theoretical Training ForAleš Štimec100% (1)
- N06 Sea Passage PlanDocument5 pagesN06 Sea Passage Planاahmed Amer100% (1)
- Mensuration ProblemDocument6 pagesMensuration ProblemGeorge CarinoNo ratings yet
- Ironclad Armada ShipsDocument122 pagesIronclad Armada ShipsPaul Kent PolterNo ratings yet
- A View From Aloft (Vol. 1, Iss. 4)Document3 pagesA View From Aloft (Vol. 1, Iss. 4)BaySail - Appledore Tall ShipsNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Marine Structural EngineeringDocument46 pagesIntroduction of Marine Structural EngineeringFandy SipataNo ratings yet
- Ukcm PamphletDocument2 pagesUkcm PamphletgupenninjaNo ratings yet
- Crowdmanagement On ShipsDocument80 pagesCrowdmanagement On ShipsSamir Walavalkar100% (3)
- CV Deck Officer with ANT III & experience seeks new opportunityDocument1 pageCV Deck Officer with ANT III & experience seeks new opportunityGara HirayamaNo ratings yet
- Interpretations of SOLASDocument478 pagesInterpretations of SOLASVanessa Borges100% (4)
- Maintainence of Lsa EquipmentDocument5 pagesMaintainence of Lsa Equipmentsidadams2No ratings yet
- 4 Undewater Work PermitxDocument1 page4 Undewater Work PermitxMatt RHSRNo ratings yet
- Naval Repair Facility Sava Kovacevic TivatDocument2 pagesNaval Repair Facility Sava Kovacevic Tivatdoc.dr. Marinko AleksicNo ratings yet
- ECDIS LP Briefing PDFDocument5 pagesECDIS LP Briefing PDFJairie GagtanNo ratings yet
- IAMSARDocument13 pagesIAMSARatinder1375% (4)
- Executive Summary Damen RHIB Range 04 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesExecutive Summary Damen RHIB Range 04 2016 PDFhalim100% (1)
- Livro Completo Navigation Rules o BomDocument229 pagesLivro Completo Navigation Rules o BomQueridoHenriqueNo ratings yet
- The Propulsion & Manoeuvring Concept of The BCF-Super C - Class Double End FerriesDocument8 pagesThe Propulsion & Manoeuvring Concept of The BCF-Super C - Class Double End FerriesLelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- Sample-Masters Standing OrdersDocument6 pagesSample-Masters Standing Orderssinghal.ns4497100% (2)