Professional Documents
Culture Documents
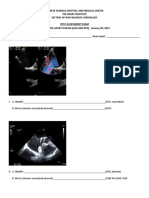
Quantitative β-HCG Discriminatory level: <15 K: th th th
Uploaded by
Reda SoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantitative β-HCG Discriminatory level: <15 K: th th th
Uploaded by
Reda SoCopyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy is protective from PID.
ECTOPIC PREGGERS o CORNERSTONE Dx Quantitative -HCG Discriminatory level: <15 K mIU/ml o TRIAD Vaginal bleeding Abdominal pain amenorrhea o Use Methotrexate if EP < 3.5 cm (-) intra-abdominal hemorrhage 6 weeks AOG If (+) of fetus should be dead o MC RF PID Previous tubal pregnancy IUD Previous tubal surgery MgSO4 has a hygroscopic property that decreases edema. BISHOPS SCORE: >5 SASSONE: 9 Be pregnant o NSD: after 2 years o ABORTION: 3-6 months After pregnancy: EARLIEST o Ovulation: 3 months o Menses: 6 months Uterus: o Size: enlargement due to HPY and HPL o Position: dextrorotated o HEGARS SIGN: 1st Trimester o LAYERS Endometrium Decidua basalis Decidua vera Decidua parietalis Myometrium External, middle, internal Serosa o Contractions: Braxton-Hicks vs. TRUE labor CERVIX
o GOODELLS Sign: 4 weeks o Mucus plug made up of (3) OVARIES o Corpus luteum vs. CL of pregnancy: up to 8 weeks o Luteoma of pregnancy vs. hyperreactio luteinalis SKIN o Striae gravidarum o Diastasis recti o Palmar erythema o Linea nigra, chloasma Assoc. with estrogen not with MSH; 2nd trimester FALLOPIAN TUBES: elongated VAGINA o CHADWICKs SIGN: 6 weeks o Increase pH BREAST o (+) Montgomery tubercles, secondary areola, colostrums Weight gain: 12.5 kg/ 27.5 lbs; Williams: 25-35 lbs, for overweight teenagers: 15 llbs LAYERS OF THE ABDOMINAL WALL o Skin o subQ o Campers o Scarpas o Anterior Rectus o Rectus Abdominis o Posterior rectus o Pre-peritonial fat o Parietal fascia Nausea/vomiting: 2-3 months Disturbance of urination: 2-3 months PROGESTERONE causes: o Increase in body temp o Fatigue and drowsiness ESTROGEN causes: breast tenderness o FERNING o Estrogen is associated with INCREASED NaCl which causes the cervical mucus to fern 16-32 weeks: FU = AOG 28 weeks: B-H 24 weeks: Leopolds Maneuver Pregnancy Test o Serum 8-9 days o Urine: 2-3 weeks after fertilization
HCG: PEAKS at 60th -70th day, plateaus at 100-120th day FETAL HEART TONE o UTZ: 4-5 weekssd o ECG: 6-8 weeks o DOPPLER: 10-12 weeks o Stet: 17-18 weeks Fetal movement: felt by examiner: 20 weeks o Felt by mother N: 16-17 weeks M: 18-19 weeks Lightening: ONLY in primiparas EDC = o Coitus + 266 days o Ovulation 3 months o Naegeles o Quickening + 24 M/22 N weeks Kessler index: measures preconception care Quetelet Index = Body Mass Index CRL = AOG at 12 weeks PRENATAL CARE: every . . . o 4 weeks: 28 weeks AOG o 2 weeks 36 weeks AOG o 1 week END o ADEQUATE: #5 PNCUs LMP: EDC +/- 2 weeks UTZ: EDC +/- 2 days Iron o Started at 16 weeks AOG o Exacerbates nausea and vomiting o Total: 1000 = 300 (baby) + 500 (mother) o (+) maternal dilutional anemia at 2nd trimester Increase by 450 ml of blood (+) 1.1 mg Fe/RBC o At 3rd trimester: increase transport of iron to fetus Folate o Given 1 month before (CPG: 3 months) and at 1st trimester o Needed for - - - WILLIAMS o 0.4 mcg (?) Given 1 month before (CPG: 3 months) and at 1st trimester And if with prior history of neural tube defect PLACENTA o 185 mm (dm) x 23 mm (thickness) o 497 ml in volume o
o o o o BPS o o o o o
508 g COTYLEDON: 10-38 Umbilical cord: 55-60 cm; longest recorded: 300 cm (check na lang) 6:1, ratio or birth weight to placental weight Fetal breathing Fetal tone Fetal movement Amniotic fluid volume Non-stress test Usually done if the score for the first 4 is low If with normal score: MCCOD: Maternal and fetal hemorrhage Umbilical cord accidents Abruption placenta 10/10: normal, 8/10: normal or suspected, 6: possible, 4: probable, 0-2: almost certain
HEMA o Hemoglobin: 11-12.5 mg/dl o WBC: Labor and puerperium: 16-26 K Ultrasound: reliable for EDC until the 20th week AOG LABOR o Regular, painful contractions every 3-5 cm that leads to cervical change ACTIVE LABOR o 3-4 cm with uterine contractions ENGAGEMENT o Descent of BPD below the level of pelvic inlet; lowest point is at the level of the ischial spines; 5 cm: from PELVIC INLET ISCHIAL SPINES FIXATION o Descent through the pelvic inlet to a depth PADAKAR: Uterine height = fundic height 3 (cervix)
Gestational hypertension BP 140/90 mm Hg for first time during pregnancy No proteinuria BP returns to normal < 12 weeks' postpartum Final diagnosis made only postpartum May have other signs or symptoms of preeclampsia, for example, epigastric discomfort or thrombocytopenia Preeclampsia Minimum criteria BP 140/90 mm Hg after 20 weeks' gestation Proteinuria 300 mg/24 hours or 1+ dipstick Increased certainty of preeclampsia BP 160/110 mg Hg Proteinuria 2.0 g/24 hours or 2+ dipstick Serum creatinine > 1.2 mg/dL unless known to be previously elevated Platelets < 100,000/mm3 Microangiopathic hemolysis (increased LDH) Elevated ALT or AST Persistent headache or other cerebral or visual disturbance Persistent epigastric pain Eclampsia Seizures that cannot be attributed to other causes in a woman with preeclampsia Superimposed Preeclampsia (on chronic hypertension) New-onset proteinuria 300 mg/24 hours in hypertensive women but no proteinuria before 20 weeks' gestation A sudden increase in proteinuria or blood pressure or platelet count < 100,000/mm3 in women with hypertension and proteinuria before 20 weeks' gestation Chronic Hypertension BP 140/90 mm Hg before pregnancy or diagnosed before 20 weeks' gestation not attributable to gestational trophoblastic disease OR Hypertension first diagnosed after 20 weeks' gestation and persistent after 12 weeks' postpartum
You might also like
- OBGYN Student Study GuideDocument39 pagesOBGYN Student Study GuideGoffo13100% (4)
- Ob Ati StudyDocument22 pagesOb Ati Studylpirman0580% (5)
- Study Guide For OBGYNDocument34 pagesStudy Guide For OBGYNFiorellaBeatriz100% (1)
- ATI Maternal Newborn Proctored Study Guide (2018)Document8 pagesATI Maternal Newborn Proctored Study Guide (2018)Emma Lilly100% (6)
- Case Report: Friday, 19 Ma7 2017Document23 pagesCase Report: Friday, 19 Ma7 2017Gunawan Efri SNo ratings yet
- I. Skenario B Blok 17Document37 pagesI. Skenario B Blok 17Kadek MarthaNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes in PregnancyDocument13 pagesPhysiologic Changes in PregnancyLauren Levy100% (1)
- Family Medicine PresentationDocument53 pagesFamily Medicine PresentationNancy BaggaNo ratings yet
- P A Partus Maturus With Caesarea Section E.C Breech Position With Ebw 3500 + SC HistoryDocument59 pagesP A Partus Maturus With Caesarea Section E.C Breech Position With Ebw 3500 + SC HistoryDema Syah FadliNo ratings yet
- Primary ObstetricsDocument62 pagesPrimary ObstetricsGill Bulanan - PeñaNo ratings yet
- Adaptasi Fisiologis KehamilanDocument57 pagesAdaptasi Fisiologis KehamilannafisaaNo ratings yet
- Obgyn Notes Uwise QbankDocument11 pagesObgyn Notes Uwise QbankLaura Lopez Roca0% (1)
- Ob Gyn Notes - UWorld 2018Document17 pagesOb Gyn Notes - UWorld 2018Fake person0% (1)
- Pregnancy ChangesDocument20 pagesPregnancy ChangesMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument22 pagesFetal DistressIrwin FitriansyahNo ratings yet
- Obgyn UWISE Notes (And Master The Boards)Document8 pagesObgyn UWISE Notes (And Master The Boards)Laura Lopez Roca100% (5)
- Previous CS Due To Contracted PelvicDocument23 pagesPrevious CS Due To Contracted PelvicIrwin FitriansyahNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument40 pagesAbortionSholen SamaritaNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes Accdg To LocationDocument6 pagesPhysiologic Changes Accdg To LocationMadayag, Mary Faith U.No ratings yet
- Pregnancy and LaborDocument9 pagesPregnancy and LaborkurapotaNo ratings yet
- Ob Revalida Review 2017 PDFDocument71 pagesOb Revalida Review 2017 PDFMara Medina - BorleoNo ratings yet
- Apgo & World Study Guide - TPDocument16 pagesApgo & World Study Guide - TPxx_caligurl_93xxNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Mission NEETPGDocument142 pagesDay 1 Mission NEETPGKalyan SagarNo ratings yet
- And Dyspareunia - Only: Painful Sex During MenstruationDocument47 pagesAnd Dyspareunia - Only: Painful Sex During MenstruationActeen MyoseenNo ratings yet
- L9 FixDocument37 pagesL9 FixAlpascaFirdausNo ratings yet
- OBgyn ShelfDocument10 pagesOBgyn ShelfHassan R. G.100% (1)
- Maternity Ati Key PointsDocument28 pagesMaternity Ati Key PointsVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (2)
- ObGyn Case FilesDocument27 pagesObGyn Case Filesyanks1120100% (3)
- OB Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesOB Final Exam Study GuideMarissa SolanoNo ratings yet
- CASE DISCUSSION Subgroup 1 1Document112 pagesCASE DISCUSSION Subgroup 1 1Kartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument48 pagesDiagnosis of PregnancyMukesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- English Case Ectopic PregnancyDocument29 pagesEnglish Case Ectopic PregnancyJonathan GnwNo ratings yet
- Total Placenta Previa + Acreta Suspected + Previous CS 141118Document26 pagesTotal Placenta Previa + Acreta Suspected + Previous CS 141118fritaNo ratings yet
- Skenario KasusDocument16 pagesSkenario KasusRetno TharraNo ratings yet
- Case Study Missed Miscarriage Dilation and CurettageDocument48 pagesCase Study Missed Miscarriage Dilation and CurettageEsther Ellise AbundoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument54 pagesEctopic Pregnancypatriciaatan1497No ratings yet
- RECT," "ALWAYS," and "NEVER." If You Find One of These Words, Cir-Evaluate Each Answer As Being Either True or False. ExampleDocument4 pagesRECT," "ALWAYS," and "NEVER." If You Find One of These Words, Cir-Evaluate Each Answer As Being Either True or False. ExampleRescueMomNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument37 pagesCase ReportKarina SurakusumaNo ratings yet
- Pages From First - Aid.for - The.obstetrics - And.gynecology - Clerkship.3rd - Ed-Ublog - TKDocument6 pagesPages From First - Aid.for - The.obstetrics - And.gynecology - Clerkship.3rd - Ed-Ublog - TKMahmoud MohsenNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Study Guide 1Document48 pagesOBGYN Study Guide 1Dayana FrazerNo ratings yet
- Case Report - G1P0A0 Parturian 40-41 Weeks + Severe PE + ROMDocument29 pagesCase Report - G1P0A0 Parturian 40-41 Weeks + Severe PE + ROMsurbakti_christineNo ratings yet
- MSC Zahraa Abdul Ghani M.A: Done byDocument9 pagesMSC Zahraa Abdul Ghani M.A: Done byFahima SekandaryNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Study Guide 3: Mitra Ahmad Soltani 2008Document172 pagesObstetrics Study Guide 3: Mitra Ahmad Soltani 2008Anonymous N2PHMnTIYLNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document45 pagesUnit 3Soni KhatoonNo ratings yet
- CC 19 Feb 2018 PEBDocument63 pagesCC 19 Feb 2018 PEBShinta Retno WulandariNo ratings yet
- SC Oligo + IUGRDocument21 pagesSC Oligo + IUGRIrwin FitriansyahNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Yousef Hassan Basman BazarDocument76 pagesCase Presentation: Yousef Hassan Basman BazarYousef Hassan BazarNo ratings yet
- At I Maternal NewbornDocument24 pagesAt I Maternal NewbornEunice Cortés100% (2)
- High Risk PregnancyDocument141 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancyesthereugenia100% (1)
- SC Dengan R LaparatomiDocument21 pagesSC Dengan R LaparatomiIrwin FitriansyahNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics PDFDocument48 pagesObstetrics PDFLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Clinical Obstetrics/Gynecology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2From EverandClinical Obstetrics/Gynecology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]From EverandNo Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (24)
- Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center Department of Medical Education and Research Research Ethics Review Board (Rerb)Document11 pagesChinese General Hospital and Medical Center Department of Medical Education and Research Research Ethics Review Board (Rerb)Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Name: - Year LevelDocument6 pagesName: - Year LevelReda SoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 55 - Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument1 pageCHAPTER 55 - Percutaneous Coronary InterventionReda SoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 27 - Heart Failure With A Preserved Ejection FractionDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 27 - Heart Failure With A Preserved Ejection FractionReda SoNo ratings yet
- Braunwald Chapter KeypointersDocument6 pagesBraunwald Chapter KeypointersReda SoNo ratings yet
- Ward Reflection PaperDocument1 pageWard Reflection PaperReda SoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Genetic Cardiac ArrythmiasDocument7 pagesChapter 32 - Genetic Cardiac ArrythmiasReda SoNo ratings yet
- CH 50 - Approach To Patient With Chest PainDocument1 pageCH 50 - Approach To Patient With Chest PainReda SoNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors in Developing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Among Patients in DM Foot Clinic at East Avenue Medical Center From January 2013 To January 2015Document7 pagesRisk Factors in Developing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Among Patients in DM Foot Clinic at East Avenue Medical Center From January 2013 To January 2015Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key-Mitral ValveDocument6 pagesAnswer Key-Mitral ValveReda SoNo ratings yet
- EXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoDocument5 pagesEXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoReda SoNo ratings yet
- Private Ward Admission Census 1Document6 pagesPrivate Ward Admission Census 1Reda SoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11: The History and Physical Examination: An Evidence Based ApproachDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 11: The History and Physical Examination: An Evidence Based ApproachReda SoNo ratings yet
- Tilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APDocument1 pageTilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APReda SoNo ratings yet
- Aortic ExamDocument3 pagesAortic ExamReda SoNo ratings yet
- Coronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Document3 pagesCoronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Rapid Response Team and Cardiac Arrest/Resuscitation TeamDocument11 pagesRapid Response Team and Cardiac Arrest/Resuscitation TeamReda SoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 61: Diabetes and The Cardiovascular System: Ma. Arnee V. Anico-Tondo, M.D., FPCP (CGH)Document1 pageCHAPTER 61: Diabetes and The Cardiovascular System: Ma. Arnee V. Anico-Tondo, M.D., FPCP (CGH)Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Trials SummaryDocument12 pagesTrials SummaryReda SoNo ratings yet
- Coronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Document3 pagesCoronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Reda SoNo ratings yet
- 2011 PadDocument19 pages2011 PadReda SoNo ratings yet
- Vascular Conference: JUNE 2018 - MARCH 2019Document2 pagesVascular Conference: JUNE 2018 - MARCH 2019Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Team BLDG LetterDocument1 pageTeam BLDG LetterReda SoNo ratings yet
- ECHO CensusDocument9 pagesECHO CensusReda SoNo ratings yet
- Case Protocol 3Document5 pagesCase Protocol 3Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities 2019Document1 pageDaily Activities 2019Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Marijuana LegalizationDocument5 pagesMarijuana LegalizationMatt ImpellusoNo ratings yet
- Tilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APDocument1 pageTilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APReda SoNo ratings yet
- Case Protocol 3Document2 pagesCase Protocol 3Reda SoNo ratings yet
- Compu Ted Tomogra Phy: (M90Us - LiDocument1 pageCompu Ted Tomogra Phy: (M90Us - LiReda SoNo ratings yet
- FR Cayat Vs COMELEC PDFDocument38 pagesFR Cayat Vs COMELEC PDFMark John Geronimo BautistaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Master Schedule - ACMP 4.0, Summar 2020 - 28 Aug 2020Document16 pages4.2 Master Schedule - ACMP 4.0, Summar 2020 - 28 Aug 2020Moon Sadia DiptheeNo ratings yet
- Tax Compliance, Moral..Document52 pagesTax Compliance, Moral..PutriNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Board of Directors in Corporate GovernanceDocument12 pagesThe Role of The Board of Directors in Corporate GovernancedushyantNo ratings yet
- System of Units: Si Units and English UnitsDocument7 pagesSystem of Units: Si Units and English UnitsJp ValdezNo ratings yet
- JawabanDocument12 pagesJawabanKevin FebrianNo ratings yet
- Sand Cone Method: Measurement in The FieldDocument2 pagesSand Cone Method: Measurement in The FieldAbbas tahmasebi poorNo ratings yet
- TRIAD: A Sustainable Approach To ForestryDocument25 pagesTRIAD: A Sustainable Approach To ForestryInstitut EDSNo ratings yet
- SSoA Resilience Proceedings 27mbDocument704 pagesSSoA Resilience Proceedings 27mbdon_h_manzano100% (1)
- The Cornerstones of TestingDocument7 pagesThe Cornerstones of TestingOmar Khalid Shohag100% (3)
- B Blunt Hair Color Shine With Blunt: Sunny Sanjeev Masih PGDM 1 Roll No.50 Final PresentationDocument12 pagesB Blunt Hair Color Shine With Blunt: Sunny Sanjeev Masih PGDM 1 Roll No.50 Final PresentationAnkit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lista Destinatari Tema IDocument4 pagesLista Destinatari Tema INicola IlieNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Suhu Pengeringan Terhadap Karakteristik Kimia Dan Aktivitas Antioksidan Bubuk Kulit Buah Naga MerahDocument9 pagesPengaruh Suhu Pengeringan Terhadap Karakteristik Kimia Dan Aktivitas Antioksidan Bubuk Kulit Buah Naga MerahDika CodNo ratings yet
- Bebras2021 BrochureDocument5 pagesBebras2021 BrochureJeal Amyrrh CaratiquitNo ratings yet
- 05 CEE2219 TM2 MidExam - 2018-19 - SolnDocument8 pages05 CEE2219 TM2 MidExam - 2018-19 - SolnCyrus ChartehNo ratings yet
- LGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemDocument24 pagesLGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemMuhammad Syazwan Ahmad Fauzi100% (1)
- Hamlet Test ReviewDocument3 pagesHamlet Test ReviewAnonymous 1iZ7ooCLkj100% (2)
- The Apollo Parachute Landing SystemDocument28 pagesThe Apollo Parachute Landing SystemBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Food Security: Its Components and ChallengesDocument9 pagesFood Security: Its Components and ChallengesSimlindile NgobelaNo ratings yet
- List of Holidays 2019Document1 pageList of Holidays 2019abhishek ranaNo ratings yet
- Lynker Technologies LLC U.S. Caribbean Watershed Restoration and Monitoring Coordinator - SE US Job in Remote - GlassdoorDocument4 pagesLynker Technologies LLC U.S. Caribbean Watershed Restoration and Monitoring Coordinator - SE US Job in Remote - GlassdoorCORALationsNo ratings yet
- Short StoriesDocument20 pagesShort StoriesPatrick Paul AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- MANILA HOTEL CORP. vs. NLRCDocument5 pagesMANILA HOTEL CORP. vs. NLRCHilary MostajoNo ratings yet
- I. Lesson Plan Overview and DescriptionDocument5 pagesI. Lesson Plan Overview and Descriptionapi-283247632No ratings yet
- Bennett Et Al 2019 Towards A Sustainable and Equitable Blue EconomyDocument3 pagesBennett Et Al 2019 Towards A Sustainable and Equitable Blue Economynaomi 23No ratings yet
- The List of Official United States National SymbolsDocument3 pagesThe List of Official United States National SymbolsВікторія АтаманюкNo ratings yet
- RetrofitDocument4 pagesRetrofitNiket ShahNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilDocument28 pagesTwo Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilMinilik Tikur SewNo ratings yet
- Ijara-Based Financing: Definition of Ijara (Leasing)Document13 pagesIjara-Based Financing: Definition of Ijara (Leasing)Nura HaikuNo ratings yet
- NASA: 45607main NNBE Interim Report1 12-20-02Document91 pagesNASA: 45607main NNBE Interim Report1 12-20-02NASAdocumentsNo ratings yet

























































![No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/591540228/149x198/6ba6cc3b38/1713999276?v=1)