Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micro Respi Skin Infect 1 and 2 Revised1
Uploaded by
Maebritt TibubosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Micro Respi Skin Infect 1 and 2 Revised1
Uploaded by
Maebritt TibubosCopyright:
Available Formats
***Note: Mukha lng pong mahaba kasi table form at saka ung pictures hahaha.
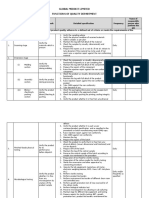
Pero maiksi lng yan, promise! Hahaha =] pls take note yung mga nakabold at underlined kasi un ang usually inemphasized ni Dra. Padla :3 Systemic Mycosis Are inherently virulent Orginate primarily in the lungs; can spread to different body organs Caused by dimorphic fungi Broad distribution, however, is confined in the body and the absence of animal-to human horizontal transmission typifies this.
A. Endemic Respiratory Mycoses Have restricted geographical locations Exhibit thermal dimorphism (2 forms: mold and yeast; depends on temperature) Acquired through inhalation of conidia (asexual spores) from the soil Portal of entry: Respiratory tract Lungs are the main focus of infection Usually asymptomatic or of very short duration Accompanied by a high degree of specific resistance to reinfection Affect otherwise healthy individuals At rm temp, molds persist, but at 37OC, molds transforms into yeast. Disease Characteristics Geographical Distribution/Transmision Clinical Disease Laboratory Diagnosis Identification/Lab Test Exoantigen test; nucleic acid probe Skin test Serology (cf test); Antigen (Ag) detection Treatment and prevention Usually not required, Lungs: Itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole
Histoplasmosis
to North Aka darlings dse; Endemic Locally cavers dse, America, spelunkers dse, N. distributed American histoplasmosis; Habitat: Grow in soil Caused by contaminated with bat
Asymptomatic infection (90-95%) [self limiting flu-like illness; Pulmonary infection -inhaled microconidia taken
GMS/Giemsa/PA S show small round to oval intracellular and extracellular yeast cell KOH not
histoplasma capsulatum
and bird excreta
Transmission: soil An ascomycte with infections, bat, avian habitat; can be controlled telemorphic by occupational exposure (ajellomyces capsulatus = sexual Not transmissible from state) human to human or animal to human. Thermally dimorphic; facultative intracellular
Infectious particle: Microconidia Tissue form: intracellular yeast cell
up by alveolar macrophage; mimics PTB (acute/chronic); Disseminated infection (includes RES and mucocutaneous; skin lesions); primary sign is splenomegaly (assoc w. immunosuppressio) Primary cutaneous is rare Mimics Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) because homogenous appearance at the hilar H. capsulate var duboisii is large, thick walled yeast causing a variant form of histoplasmosis prevalent in Africans that preferentially involves the skin, subcutaneous tissues, lymphatics and bones
applicable Rm Temp Culture: fine septate hyphae, large tuberculate macroconidia and small microcondia (therefore highly infectious) Tuberculate macroconidia dx of the organism Invitro/Cuture at BHIA: 37OC: appear single budding yeast cell
Systemic: Amphotherici nB Others: Surgical debridement Prevention: Wearing protecting clothing, mask, soil decontaminati on with 3-5% formalin
Blastomycosis B for Broad Based Bud!
Aka N. American blastomycosis; Chicago dse, gilchrist;s dse; suppurative granulomatous mycosis of the lungs, skin and subcutaneous tissue caused blastomyces dermatitidis ascomycyte, thermally dimorphic
found in N. America, Africa, Asia
outbreaks associated with activities with moist soil enriched with organic debris and rotting wood
Natural disease that is common in cats and dogs therefore not by and transmissible from these animals.
Asymptomatic (50%) Pulmonary infection (50%) TB like Disseminated infection Chronic cutaneous infection (verrucous/ulcerative crusty, elevated lesions with microabscesses that weeps) Primary cutaneous (rare)
KOH shows thick walled yeast cells with single broad based bud At Rm temperature: White, cottony Mycelia form, Pyriform conidia borne singly on septate hyphae Culture at 37C: Double walled yeast cells with single broad based bud attached to a parent by a wide base which are pathognomic of blastomycosis
Exoantigen test; nucleic acid probe Others: Skin test Serology Immunofluorescence (IF) Ag detection
Ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconaole Disseminated: Ampho b Exicision for skin lesion
inhabits decaying wood, soil saprophyte
Infectious particle: conidia Tissue form:broad based yeast cells Aka Posadas dse, San Joaquin Valley Fever, Desert Rheumatism Caused by
Coccidiomycosis
Endemic in western hemisphere; desert; Dust storm; Soil tillage; California; Sonoran desert
Highly infectious, acute, self limited nd usually benign respiratory disease
KOH shows thick walled spherules filled with nonbudding small endospores
Exoantigen; nucleic acid probe, demonstration of spherule production in animals
Acute Respi Disease not necessary to treat
coccidiooides immitis Deutoremycete (imperfect fungi thus reproduce asexually) Thermally dimorphic
Infectious particle: arthroconidia -very resistant to heat, dryness, salinity -asexual spore which can be divided thallic (fragmentation of septate hyphae and blastic yeast cells)
Tissue form: spherules (filled with endospore w.o budding)
Infections involving the Highest endemicity in skin, bone, joints, lymph Spherules (370C are semi-arid regions with nodes, adrenals and CNS not yeast cells; they alkaline soils are parasitic form; has lots of endospore Asymptomiatic Outbreaks occur inside which can Evident hair following dust storms, develop into adenopathy on earthquakes and earth individual spherules. xrays excavation Pulmonary infection Culture at RT: (38-40%) Transmission: Inhalation Hyphae bearing - PTB like; egg of arthroconidia barrel shaped shell cavity on (Rectangle conidia) atroconindia xray; acute, self trapped in alveolar space separated by limited usu. where they develop into Benign respi dse dysjunctor cells spherules filled with Disseminated infect endospores -Infection involving CNS, Culture at 37: not routinely done joints, bones, skin because it is highly -Meningitis (cause of infectious and death) - mortality is higher in requires stringent dark-skinned ethnic conditions group
Itraconazole, Other test: ketoconazole, Skin test ampothericin (coccidiodin, B spherulin), serology, IF Meningitis: Fluconazole Surgery: Reduce exposure to dust in endemic areas; Vaccine devt in progress
Paracoccidiomyc osis P for Pulmonary dse!!!
Aka pulmonary dse; South American Blastomycosis; LutzSplendore-Almeidas Dse Caused by Paracoccidiooides braziliensis Deuteromycete Thermally dimorphic
Habitat: unknown but found to reside in humid soil rich in proteins; cultivated in fruit bats and armadillos
Infectious particle: Conidia
Higher incidence ratio in Clinical specimens: Males because estrogen sputum, pus, crusts inhibits conversion of from lesions mycelium to yeast. KOH shows yeast cells with multiple Asymptomatic narrow based buds infection Pulmonary infection (blasto kasi is broad based) Dissemination infect (oral/nasal mucosa) KOH shows mariners - Chronic wheel appearance Granulomatous lesions formed by stimulation of alpha- Culture rm temp: septate hyphae with glucan [cell wall no typical pattern of polysaccharide] - Mulberry Lesions @ sporulation GIT mucosa Cutlture at 37OC - Facial skin most - Thick Yeast cells common site of with ships or infection mariners - Triad of sxs in steering wheel endemic areas: appearance Pulmonary lesions, - Cells are large, edentulous mouth, spherical to cervical pyriform and lymphadenopathy with thick walls Affects both healthy and immunosuppressed individuals who have traveled or lived in endemic areas
Exoantigen Dna proble ID: Skin test Serology
Itraconazole, ketoconazole, ampothericin B, sulfa drugs Others: surgical excision localized lesion
of
Penicilosis
caused by Penicilloisis marneffei Only Penicillum species that is
Bamboo rat (reservoir); endemic in SEA; Portal of entry: lungs
KOH shows small Exoantigen test yeast cells with Conversion to yeast transverse septum forms Culture at RT:
Itraconazole and ketoconazole For serious
thermally dimorphic Produces red pigments around the colony (kasi other penicillium produces yellow) Reproduce: transverse fission/schizogony
Infectious Conidia
particle:
Conidiophore branch Indicator of HIV infection into metullae which in endemic areas support the phialides that bear chains of conidia (brush like or Pulmonary infection finger like) Disseminated infection -similar to histoplasmosis; Colonies produce affects many internal diffusible red organs; exhibits as skin pigment around the lesion such as those seen colony (very characteristics) in AIDS patients Culture @ 37OC: Round to oval yeast cell with cross walls
infection: Ampho B
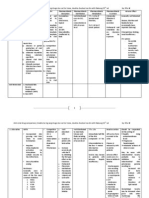
B. Opportunistic Mycoses Portal of entry: respiratory, mucocutaneous (for Candidiasis) Infectious particle: conidia, mycelia Widely distributed as saprophytes or as members of normal flora (in comparison with endemic na restricted and distribution) Invade only in the presence of underlying predisposition Invade mainly those who are immunosuppressed Disease Characteristics Geographical Distribution/ Transmission Endogenously acquired Clinical Disease Laboratory Diagnosis Gramstain/KOH shows small budding yeast cell and pseudohyphae (meaning no true Identification/Lab Test Germ Tube Test (GTT) (+) for C. albicans Other test: Assimilation Treatment and Prevention Cutaneous: Topical Nystatin, ketoconazole, fluconazole
Candidiasis
Caused by Candida spp Mostly C. albicans Normal flora
Most common systemic/opportunistic fungal infection Normally found worldwide; clinical in Normal flora spectrum: extremely of skin, mouth, diverse
of GIT Ascomycete Dimorphic [lang! not thermally] Exist as pseudohypha e or hyphjae Reproduce by budding
Infectious/tissue form: yeast cell and pseudohyphae
vagina, mucous septation) membranes, Leading fungal infection stool patients with HIV-AIDS Culture at RT and 37: Major -Pseudophyae Cutaneous and colonizing with clusters of Subcutaneous habitat: GIT Systemic/disseminated round blastoconida /invasive - Chlamydospore, - Candidemia yeast cells and (catheter related) pseudohyphae - Acute chronic produced on disseminated chlamydospore - Deep organ candidiasis (pulmo on cornmeal agar candidiasis) Predisposing factors: Physiological (pregnancy and age) Trauma (burn, infection) Hematological (neutropenia, cellular immunodeficiency) Endocrinological (DM, Hypothyroidism, Addisons dse) Iatrogenic (chemotherapeutics, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, catheters, etc) Others: IV drug addiction, malnutrition
test Biotyping IF Immunohistochemistry DNA probes, PCR Mannan antigen detection (RIA, ELISA, LAT)
Systemic: Ketoconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, flucytosine, ampho B Prevention: Avoid disturbing the normal balance of microbial flora and intact host defense
Aspergillosis A for ABPA! A for Acute Angle!
KOH show Allergic form: soil 1. wide septate Allergic dichotomousl Bronchopulmonary y branching Aspergillosis (ABPA) frequent hpyhae may give rise to laboratory (45deg or asthma or hay contaminants acute angle); fever 2. condial colonizing heads form/pulmonary Transmission: supports aspergilloma or inhalation of swollen fungus ball conidia vesicle with Invasive or Infectious particle: rows of disseminated (for Asexual spore: phialides immunocompromised) conidia bering radial Mycotoxicosis chains of (ingestion of food Tissue form: conidia. products with toxin) hyphae ***so take note niyo to ung diff kasi zygomycomycete kamuka nia*** Caused by Aspergillus spp ( commonly fumigates and flavus) Ascomycte; Ubiquitous; freq lab contaminants
Natural reservoir: and air
Serology Immunohistochemistry Galactomannan antigen detection in serum
Allergic form: itraconazole; corticosterioid Aspergilloma: Surgery & ampho B Diseminated: Itraconazole, fluconazole, ampho B Prevention: Avoid or minimize exposure to conidia; prophylactic low-dose ampho B or itraconazole
Cryptococcosis [has 3 biotypes]
[singit ko dito ang virulence factors ah? Wala ng box eh :P ]
Aka bussebuschke dse; Torulosis Caused by Filobasidella neoformans Sexual phase: Basidiomycete (the spores are produced
Widespread in nature; soil saprophyte and abundanct in avian habitats Transmission: Inhalation of nonencapsulated
Biochemical test: (+) Urease Test: fuschia pink in One of the most life color threatening infection with (+) caffeic acid AIDS Culture 37OC: test due to -Creamy, mucoid phenoloxidase production Pulmo (acute/chronic) yeast colonies usually -Brown to blkack on Others: asymptomatic; mx: colonies
Primary site of infection: Lungs
KOH/India ink shows yeast cells with wide capsule
Ampho B; ampho B 5 FC combination; fluconazole prophylaxis ff primary treatment (for AIDS patients)
Virulence factors: 1)Capusule: -wide -Antiphagocytic -Serotype A,B,C,D and AD 2.Production of phenoloxidase convert phenoilic compounds to melanin; survival mechanism within phagocytes
externally, on Or minimally the end of encapsulated specialized yeast cells cells called basidia.) Specifically Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii Encapsulated yeast Replicate by budding 0nly fungal species with well-defined virulence factor
Infectious particle: nonencapsulated yeast (at 27 and 37 C); basidiospore C Neoformans var neoformans [1st biotype] Serotype D
soilatary pulmo niger/bird seed nodulein the agar due to mediastinum phenoloxidase mimicking a carcinoma Disseminated Predilection for the CNS Meningitis: most frequent diagnosed form [difference ke cocciodiomycosis naman cause of death] Neutropism related to phenoloxidase activity Cutaneous (rare) mx: nodule in the lungs
Direct IF Ag detection test Differential Growth on Lcanavarine glycine bromtymol blue - appear in cobalt blue for C. Gatti (blue) - Yellow on C. neofromans
Found in soil Affects contaminated immunocompromised Virulence factor: with pigeon Capsule + 37 + droppings (rich phenoloxidase nitrogen and production alkaline pH of the droppings favors survival
of the yeast) Globally distributed (predominantly in N. Europe and N. America Found in Affects immunocompetent eucalyptus tree Clinica Mx: Pneumonia specifically: caladunensis (river red gum tree, and teretucornic s (forest red gum tree), decaying wood forming hollows in living trees; Worldwide distribution; Common on tropical/sub trop climates; (predominantly in SEA, S. California,
C neoformans var gattii [2nd biotype]
Serotype B and C Telemorphic name of filbasidiella bacillispora Infectious particle: basidiospores
***B = more prevalent and pathogenic
C neoformans var grubii [3rd biotype]
Serotype A
Zygomycosis
Aka mucormycosis /phycomycosis Caused by filamentous fungi namely: rhizopus, mucor, absidia Order: mucorales, Class: zygomycetes Non-septate Asexual form: sporangispore Sexual form: zygospore
Australia, Africa Biological, ecological and epidemiological characteristics not yet clearly defined; Acquired by Primary Site of Infection: exposure to Lungs sporangiospores Rhinocerebral Natural Most common; reservoir: soil cotton like fungus air and water Pulmonary Cutaneous Ubiquitous; GIT frequently Disseminated encountered as -aggresive angiocontaminants invaised and (e.g bread predominantly mold) infarctive. Risk factors: Diabetic acidosis Immunosuppression
KOH shows wide ribbon like aseptate hyphae branching of right angle (ung narrow or acute angle is aspergillus) Culture @ RT: Cotton candy appearance of colonies Morphologic features identify species Caution in interpreting results because they are common contaminants
Rhizopus: sporangia round; sporangiospore unbranched and at nodal;
Ampho B Surgical debridement Control of predisposing factors
Mucor: sporangia round; branch and at intermodal; columellae round to oval; rhizoid absent Absidia: Rudimentary, collumellae conical;branch; in between nodes
Characteristics of Species Causing Zygomycosis Characteristics Sporangia Sporangiospores Collumellae Rhizoids Collarettes Rhizopus Round Unbranched, nodal Hemi-spherical Well developed None remains when sporangial wall is dissolved Mucor Round Branched, intermodal Round to oval Absent Present when sporangial wall is dissolved Absidia Pyriform Branched, intermodal Conical Rudimentary ===
Endemic Respiratory Mycosis 1. Histoplasmosis H. Capsulatum
GMS/giems/PAS show small round to oval intra and extracell yeast cell Culture at rm tem: fine septate hyphae, large tuberculate macroconidia and small microcondia (therefore highly infectious) Invitro/Cuture at 37: ppear single budding yeast cell
2. Blastomycosis B. dermatitidis
KOH shows thick walled yeast cells with single broad based bud (3rd pic) At Rm temperature: White, cottony Mycelia form, Pyriform conidia borne singly on septate hyphae (1st pic) Culture at 37C: Double walled yeast cells with single broad based bud attached to a parent by a wide base which are pathognomic of blastomycosis (2nd pic) 3. Coccidiomycosis C. immitis
4.
Koh shows thich walled endospore spherules Culture at RT: Hyphae bearing barrel shaped atroconindia separated by dysjunctor cells (2nd pic) Culture at 37: not routinely done Paracoccidiomycosis P. braziliensis
KOH shows yeast cells with multiple narrow based buds (blasto kasi is broad based) [2nd pic] KOH shows mariners wheel appearance [1st pic] Culture rm temp: septate hyphae with no typical pattern of sporulation Cutlture at 37OC: Thick Yeast cells with ships or mariners steering wheel appearance [or sometimes mickey mouse]; Cells are large, spherical to pyriform and with thick walls 5. Pencillosis P. marneffei
KOH shows small yeast cells with transverse septum (2nd pic) Culture at RT: Conidiophore branch into metullae which support the phialides that bear chains of conidia (brush like or finger like) [1st and 3rd pic] Culture: Colonies produce diffusible red pigment around the colony (very characteristic ) [3rd pic] Culture at 37OC temp : Round to oval yeast cell with cross walls
Opportunistic Mycoses
1. Candidiasis C. albicans Gramstain/KOH shows small budding yeast cell and pseudohyphae (meaning no true septation) Culture at RT and 37: Pseudophyae with clusters of round blastoconida; Chlamydospore, yeast cells and pseudohyphae produced on chlamydospore on cornmeal agar 2. Aspergillosis Aspergillus spp.
KOH show a) wide septate dichotomously branching hpyhae (45deg or acute angle); (3rd pic) b) condial heads supports swollen vesicle with rows of phialides bering radial chains of conidia. (2nd pic) ***so un ang diff this to zygo kasi magkamuka cla***
3. Cryptococcosis C. neoformans
KOH/India ink shows yeast cells with wide capsule Culture 37OC:Creamy, mucoid yeast colonies;Brown to blkack colonies on niger/bird seed agar due to phenoloxidase
4.Zygomycosis filamentous fungi namely: Rhizopus, Mucor, Absidia
KOH shows wide ribbon like aseptate hyphae branching of right angle (ung narrow or acute angle is aspergillus) Culture @ RT: Cotton candy appearance of colonies; Morphologic features identify species Rhizopus: sporangia round; sporangiospore unbranched and at nodal (1st row); Mucor: sporangia round; branch and at intermodal; columellae round to oval; rhizoid absent (2nd row) Absidia: Rudimentary, collumellae conical;branch; in between nodes (3rd row)
Further differentiation:
Penicillium brush like, finger like Aspergillus swollen head na may fingerlike din ang dulo Rhizopus round sporangia, unbranched
A. Rhizopus B. Mucor C. Absidia
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Sample Motion To Strike For Unlawful Detainer (Eviction) in CaliforniaDocument5 pagesSample Motion To Strike For Unlawful Detainer (Eviction) in CaliforniaStan Burman91% (11)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Functions of Quality DepartmentDocument5 pagesFunctions of Quality DepartmentsachinNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Sermon Notes: "True Greatness" (Luke 9:46-50)Document3 pagesSermon Notes: "True Greatness" (Luke 9:46-50)NewCityChurchCalgary100% (1)
- Electional AstrologyDocument9 pagesElectional AstrologyValentin ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Complaint Affidavit Rape CaseDocument3 pagesComplaint Affidavit Rape CaseMa Krissa Ellaine Bundang100% (1)
- GRAMMAR POINTS and USEFUL ENGLISHDocument197 pagesGRAMMAR POINTS and USEFUL ENGLISHMiguel Andrés LópezNo ratings yet
- According To Taxonomic Classification: TREMATODES-FlukesDocument4 pagesAccording To Taxonomic Classification: TREMATODES-FlukesMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- IM - Approach To HeadacheDocument2 pagesIM - Approach To HeadacheMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Nematodes GenDocument3 pagesNematodes GenMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Cestodes GenDocument5 pagesCestodes GenMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Patho Eso and Stomach RevisedDocument10 pagesPatho Eso and Stomach RevisedMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Surgery FinalDocument6 pagesSurgery FinalMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmia TranxDocument7 pagesAnti Arrhythmia TranxMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Blood Flukes and Flagellates TranxDocument6 pagesBlood Flukes and Flagellates TranxMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral TableDocument8 pagesAnti Viral TableMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal TableDocument4 pagesAnti Fungal TableMaebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Revised Table Part2Document7 pagesTetracycline Revised Table Part2Maebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline and Quinolones Revised Part1Document8 pagesTetracycline and Quinolones Revised Part1Maebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Assoc W. Lymphatic & Cvs Part 2 and 4Document10 pagesBacteria Assoc W. Lymphatic & Cvs Part 2 and 4Maebritt TibubosNo ratings yet
- 2022 P6 Maths Prelim NanyangDocument52 pages2022 P6 Maths Prelim NanyangAlbert Hein Nyan HtetNo ratings yet
- G O Ms NoDocument2 pagesG O Ms NoMuralidhar MogalicherlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Pronouns Substitution and Ellipsis - Oxford Practice Grammar - AdvancedDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Pronouns Substitution and Ellipsis - Oxford Practice Grammar - AdvancedKev ParedesNo ratings yet
- TimeOut Magz - 50 Sexiest Songs Ever MadeDocument3 pagesTimeOut Magz - 50 Sexiest Songs Ever MadeRahul VNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument6 pagesEssaylinhJNo ratings yet
- SodomiaDocument10 pagesSodomiaJason Camilo Hoyos ObandoNo ratings yet
- CLIFFORD PROCTOR'S NURSERIES LIMITED - Company Accounts From Level BusinessDocument7 pagesCLIFFORD PROCTOR'S NURSERIES LIMITED - Company Accounts From Level BusinessLevel BusinessNo ratings yet
- 1) Morales Vs Court of Appeals (d2017)Document2 pages1) Morales Vs Court of Appeals (d2017)Pau SaulNo ratings yet
- TEST 8th Grade (Had Better+needn't)Document2 pagesTEST 8th Grade (Had Better+needn't)anacincaNo ratings yet
- Essays On Hinduism-PDF 04Document54 pagesEssays On Hinduism-PDF 04YaaroNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument26 pagesPDFAjay Kumar GantiNo ratings yet
- Service Marketing Notes1 RejinpaulDocument47 pagesService Marketing Notes1 RejinpaulEr. THAMIZHMANI MNo ratings yet
- Wonder 6 Unit 7 ConsolidationDocument1 pageWonder 6 Unit 7 ConsolidationFer PineiroNo ratings yet
- Glory To GodDocument2 pagesGlory To GodMonica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal - Tanya BhatnagarDocument9 pagesProject Proposal - Tanya BhatnagarTanya BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Tripoli: International Airport DevelopmentDocument20 pagesTripoli: International Airport Developmentgoodwin.don5639No ratings yet
- Endole - Globe Services LTD - Comprehensive ReportDocument20 pagesEndole - Globe Services LTD - Comprehensive ReportMoamed EliasNo ratings yet
- EBO 2 - Worldwide Energy Scenario - FINALDocument15 pagesEBO 2 - Worldwide Energy Scenario - FINALmodesto66No ratings yet
- Endodontic Treatment During COVID-19 Pandemic - Economic Perception of Dental ProfessionalsDocument8 pagesEndodontic Treatment During COVID-19 Pandemic - Economic Perception of Dental Professionalsbobs_fisioNo ratings yet
- Cost-Effective Sustainable Design & ConstructionDocument6 pagesCost-Effective Sustainable Design & ConstructionKeith Parker100% (2)
- Drdtah: Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptDocument8 pagesDrdtah: Eticket Itinerary / ReceiptDoni HidayatNo ratings yet
- Europeanization of GreeceDocument20 pagesEuropeanization of GreecePhanes DanoukopoulosNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Federal ExpressDocument3 pagesCase Study On Federal ExpressDipanjan RoychoudharyNo ratings yet
- Epekto NG Kantutan Sa Mga KabataanDocument27 pagesEpekto NG Kantutan Sa Mga KabataanAngelo0% (1)