Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Currency
Uploaded by
stega_megasaurusCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Currency
Uploaded by
stega_megasaurusCopyright:
Available Formats
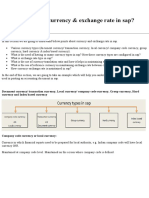
Currency and exchange rates play a fundamental and often over looked part of SAP financials.
For companies that do business abroad this is essential FI configuration. Invoices may come in from a vendor in the UK, and so a conversion from British pounds to U.S. dollars might need to happen. How do you convert so that the invoice posts and updates your accounts payable properly? SAP uses currency keys to represent each type of currency and most are pre-defined for you already. For example the most common one you'll deal with if you're in the U.S. is the USD currency key. GBP is the currency key for British pounds, EUR for euro, and so on. Maintaining the relationship between each currency key, or the exchange rate, will pose the majority of your customizing workload. If you've traveled abroad you'll have had experience with the concept of an exchange rate already. Most international airports will have a booth with a board displaying how much they will buy and sell a given currency. The buying/selling rate is based on values determined by currency markets and fluctuates constantly. In SAP the exchange rate between two currencies is identified by an exchange rate type and translation ratio. It sounds more complex than it really is a translation ratio is simply a ratio between the currencies. So the translation ratio between USD and GBP would be: USD/GBP = 1/1 Exchange rates fluctuate constantly and require updates that range from daily to real-time. SAP provides a few tools at your disposal to help automate this task: inversion, base currency, and exchange rate spreads. Each exhange rate type would use one of these tools, but exchange rate types can use different tools. Of these tools inversion is the oldest kind and is not really used often today. Base currency is assigned to an exchange rate type and makes life easier for you due to the fact that you only have to set up the exchange rate between the currency and the base currency. For example, let's say you select USD as your base currency. Therefore you only need to update the exchange rates between USD and all foreign currencies. USD to GBP USD to EUR If the system requires a conversion between two foreign currencies, like the pound and the euro, it would use USD for conversion. EUR to USD to GBP = EUR to GBP Exchange rate spreads work by creating an average spread between the rates banks buy and sell a given exchange rate for. These spreads typically remain fairly constant. A recommendation for efficiency from SAP is to use base currency and exchange rate spreads together. The average rate would use the base currency and the exchange rate spreads would be calculated by adding or subtracting the spread from or to the average rate. There are programs that can help maintain exchange rate type as well. If your company requires real-time updating, than program RFTBDF07 using RFC (remote function call like Y_CURRENCY_CONVERT), could be used. Another option is program RFTBFF00, which can be scheduled to periodically upload an input file sitting on a desktop or server. Currency values can be quoted directly or indirectly and SAP supports both methods. You will be
required to assign a standard notation to each exchange rate. To use direct quotation, which changes names based on where you read, price notation in SAP documentation and price currency via wikipedia, means to express a local currency (home currency) in terms of the foreign currency. Indirect quotation (or volume notation) is to express foreign currency in terms of local currency. Direct quotation example, where USD is local currency: 0.7000 EUR = 1 USD. Indirect quotation, where USD is local currency: 1 USD = 0.7000 EUR. Indirect quotation has risen in popularity due to requirements by the European Monetary Union (EMU) and the proliferation of the euro. You can maintain exchange rates in table TCURR via the IMG area General Settings => Currencies => Enter exchange rates for both direct and indirect quotations. Unless you specify otherwise when entering a value into an input field, like the amount field on an invoice, SAP will assume that you mean for direct quotation exchange rate. You can configure alpha prefixes so that you can specify indirect quotation at time of numeric input. If you do not, then entering a back-slash "\" is the default method to use indirect quotation. Of course you can configure the reverse or differently based on your business requirements. I recommend heading over to wiki.sdn.sap.com for further information identifying tcodes, configuration areas, and tables that touch upon currency configuration. Coupled with help.sap.com you'll be on your way to configuring currencies.
Sources TFIN10 Documentation Currency customizing at wiki.sdn.sap.com Exchange rate customizing at wiki.sdn.sap.com /wikipedia/en/wiki/Exchange_rate help.sap.com's Direct and Indirect Quotation Guide
You might also like
- Student Partners Program (SPP) ChecklistDocument4 pagesStudent Partners Program (SPP) ChecklistSoney ArjunNo ratings yet
- Forex Currency Correlation Table PDF and Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesForex Currency Correlation Table PDF and Cheat SheetHeritage Digital67% (3)
- Foreign Currency Valuation EXPLAINED With Example - TECH CONCEPT HUBDocument11 pagesForeign Currency Valuation EXPLAINED With Example - TECH CONCEPT HUBgirijadeviNo ratings yet
- Trump Saudi Nuclear Report July 2019Document50 pagesTrump Saudi Nuclear Report July 2019ABC News Politics83% (12)
- Exchange Rate CurrencyDocument9 pagesExchange Rate CurrencyAniruddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- iFOREX TutorialDocument20 pagesiFOREX TutorialAmjath ShariefNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale (Condo)Document5 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale (Condo)g printNo ratings yet
- Everything About Currency - Exchange Rate in SAPDocument11 pagesEverything About Currency - Exchange Rate in SAPrsivaramaNo ratings yet
- SAP Foreign Currency Valuation ExplainedDocument52 pagesSAP Foreign Currency Valuation ExplainedSuraj MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Tesda Perpetual and Periodic Inventory SystemsDocument6 pagesTesda Perpetual and Periodic Inventory Systemsnelia d. onteNo ratings yet
- SAP S - 4HANA Currency SetupDocument30 pagesSAP S - 4HANA Currency SetupRohit ShivankarNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions About Currencies in SAPDocument6 pagesFrequently Asked Questions About Currencies in SAPsandeepNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Exchange RatesDocument8 pagesMaintenance of Exchange RatesElena Puscu100% (1)
- SAP Currency ManagementDocument14 pagesSAP Currency ManagementHeamanth Kkumar Chiittibomma100% (1)
- Different Currency Type in SAPDocument9 pagesDifferent Currency Type in SAPUmakant MahapatraNo ratings yet
- IE Singapore MRA GrantDocument4 pagesIE Singapore MRA GrantAlfizanNo ratings yet
- Annual Review Pitch Deck by SlidesgoDocument7 pagesAnnual Review Pitch Deck by SlidesgoALJOHARA KHALID HAMAD ALSULIMANNo ratings yet
- SAP S4HANA - Currency SetupDocument15 pagesSAP S4HANA - Currency SetupMuhammed ASNo ratings yet
- Upload Exchange Rate From ECBDocument7 pagesUpload Exchange Rate From ECBpawans8110No ratings yet
- Forex Trading For Beginners: A Step by Step Guide to Making Money Trading Forex: Day Trading Strategies That Work, #1From EverandForex Trading For Beginners: A Step by Step Guide to Making Money Trading Forex: Day Trading Strategies That Work, #1No ratings yet
- LMD Multicurrency: Strategy DescriptionDocument8 pagesLMD Multicurrency: Strategy DescriptionCardoso PenhaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Supply Change ManagementDocument19 pages6 - Supply Change ManagementWall JohnNo ratings yet
- Entering Exchange Rate: Change in Company Code CurrencyDocument4 pagesEntering Exchange Rate: Change in Company Code CurrencyManohar G ShankarNo ratings yet
- CurrencyDocument5 pagesCurrencymonaNo ratings yet
- Preis Und MengennotierungDocument7 pagesPreis Und Mengennotierungdata_magicianNo ratings yet
- Currencies in Fixed Asset Accounting under 40 charsDocument4 pagesCurrencies in Fixed Asset Accounting under 40 charsPavan UlkNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Fields in Sales Order: Price vs FI PostingsDocument4 pagesExchange Rate Fields in Sales Order: Price vs FI PostingsSOUMEN DASNo ratings yet
- Working With Multi-Currency ApplicationsDocument9 pagesWorking With Multi-Currency ApplicationsJayaRam KothaNo ratings yet
- Javier Palomino - Journal or Subledger Level Reporting CurrenciesDocument85 pagesJavier Palomino - Journal or Subledger Level Reporting CurrenciesFco Jav RamNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Maintenance of Exchange RatesDocument3 pagesConcurrent Maintenance of Exchange RatesGaphur shaikNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates: Posting and ClearingDocument3 pagesExchange Rates: Posting and ClearingTeja SaiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Course On CurrenciesDocument24 pagesWelcome To The Course On CurrenciesHimanshu OswalNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic SettingDocument25 pages1 Basic SettingChirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Currency Exchange RatesDocument32 pages3 - Currency Exchange RatesAditya NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Foreign Currency ValuationDocument8 pagesForeign Currency ValuationSai Shravan MadarapuNo ratings yet
- Parallel Currency Activation & ConversionDocument7 pagesParallel Currency Activation & ConversionfcolaioriusNo ratings yet
- Multiple CurrenciesDocument12 pagesMultiple CurrenciesAaron KaleesNo ratings yet
- Manage transactions across currencies with NS multiple currency featureDocument2 pagesManage transactions across currencies with NS multiple currency featureRaymond MontonNo ratings yet
- SAP currencies guideDocument2 pagesSAP currencies guideTeja SaiNo ratings yet
- FWD-AVERAGE RATE FWD-UNIFORM RATE FWDDocument3 pagesFWD-AVERAGE RATE FWD-UNIFORM RATE FWDNarayan SetharamanNo ratings yet
- Economics Investment Chapter 9Document25 pagesEconomics Investment Chapter 9Anonymous A0jSvP1No ratings yet
- SAP S/4 HANA Finance Customizing For The SAP General LedgerDocument27 pagesSAP S/4 HANA Finance Customizing For The SAP General LedgerRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- PreviousNextForex FlashDocument19 pagesPreviousNextForex FlashMaham ShaikhNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2419243Document20 pagesSSRN Id2419243soumensahilNo ratings yet
- Forex For CAIIBDocument6 pagesForex For CAIIBkushalnadekarNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate SpreadDocument1 pageExchange Rate SpreadTeja SaiNo ratings yet
- Consolut - SAPF100 - Foreign Currency ValuationDocument7 pagesConsolut - SAPF100 - Foreign Currency ValuationRevathy SomaskandanNo ratings yet
- iFOREX TutorialDocument18 pagesiFOREX Tutorialvish.jaatNo ratings yet
- Entering Period Rates: WarningDocument2 pagesEntering Period Rates: WarningSuman_Beemisetty12No ratings yet
- Learnforexpips and PipettesDocument12 pagesLearnforexpips and Pipetteslewgraves33No ratings yet
- Cross Currency Receipts in ReceivablesDocument6 pagesCross Currency Receipts in Receivablessuresh mysNo ratings yet
- Equiy SwapsDocument6 pagesEquiy SwapsPenny Lyn CapsuyenNo ratings yet
- Ex RateDocument2 pagesEx Ratekasi_raghavNo ratings yet
- Kberry CurrencytranslationinhfmDocument54 pagesKberry Currencytranslationinhfmkonda83No ratings yet
- Manage Multiple Currencies: User Permissions NeededDocument5 pagesManage Multiple Currencies: User Permissions NeededtahamajidNo ratings yet
- Pricing IRSDocument13 pagesPricing IRSswapnil6121986No ratings yet
- Parallel Currencies in SAP Part IIDocument3 pagesParallel Currencies in SAP Part IIDeokMo Jung100% (1)
- NISM Currency Derivatives Study Material by WWW - MODELEXAM.INDocument18 pagesNISM Currency Derivatives Study Material by WWW - MODELEXAM.INSRINIVASANNo ratings yet
- Price Action Diver Power - Manual EngDocument5 pagesPrice Action Diver Power - Manual EngAdnan Wasim0% (1)
- System LandscapeDocument73 pagesSystem LandscapeRaju BothraNo ratings yet
- NISM Currency Notes Dec 2012Document18 pagesNISM Currency Notes Dec 2012ajatgdNo ratings yet
- Blackwell Global EducationDocument3 pagesBlackwell Global EducationSureshkumar SekarNo ratings yet
- Working With Multi-Currency Applications: Oravision Oracle Online Training/Consultancy SolutionDocument9 pagesWorking With Multi-Currency Applications: Oravision Oracle Online Training/Consultancy SolutionAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Calculation Types Spot ForwardDocument6 pagesExchange Rate Calculation Types Spot ForwardRohit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates For Everyone EbookDocument10 pagesExchange Rates For Everyone EbookmovizepNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange ManagementDocument2 pagesForeign Exchange ManagementobreroeldojohnNo ratings yet
- Dgcis Report Kolkata PDFDocument12 pagesDgcis Report Kolkata PDFABCDNo ratings yet
- Position Description WWF Serbia Operations ManagerDocument3 pagesPosition Description WWF Serbia Operations ManagerMilica Lalovic-BozicNo ratings yet
- Pro Forma Invoice for Visa Processing FeesDocument1 pagePro Forma Invoice for Visa Processing FeesShakeel AbbasiNo ratings yet
- 790 Pi SpeedxDocument1 page790 Pi SpeedxtaniyaNo ratings yet
- Indigo by Louis FischerDocument6 pagesIndigo by Louis Fischermitasha_saini100% (5)
- PPDA User Guide for Procurement and Disposal PlanningDocument21 pagesPPDA User Guide for Procurement and Disposal PlanningThoboloMaunNo ratings yet
- International-Organisation List NotesDocument62 pagesInternational-Organisation List NotesVINOD KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Rapid Population Growth On Economic Development in Ethiopia - 045539Document51 pagesThe Impact of Rapid Population Growth On Economic Development in Ethiopia - 045539ABAYNEGETAHUN getahunNo ratings yet
- Product Data Mtu Kinetic PowerPackDocument9 pagesProduct Data Mtu Kinetic PowerPackEhab AllazyNo ratings yet
- Recasting FSDocument1 pageRecasting FSCapung SolehNo ratings yet
- Informative FinalDocument7 pagesInformative FinalJefry GhazalehNo ratings yet
- Inventory Cost MethodsDocument8 pagesInventory Cost MethodswijayaNo ratings yet
- Formulación Matemática Del Sistema RicardianoDocument22 pagesFormulación Matemática Del Sistema RicardianoPili BarrosNo ratings yet
- Product Highlight Sheet-Retire SmartDocument3 pagesProduct Highlight Sheet-Retire SmartLU HERRERANo ratings yet
- Role of Agriculture in Economic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesRole of Agriculture in Economic DevelopmentFrank Macharia100% (1)
- PRQNP 11 FBND 275 HXDocument2 pagesPRQNP 11 FBND 275 HXjeevan gowdaNo ratings yet
- Local Educator Begins New Career With Launch of Spaulding Decon Franchise in FriscoDocument2 pagesLocal Educator Begins New Career With Launch of Spaulding Decon Franchise in FriscoPR.comNo ratings yet
- History and Types of Insurance in IndiaDocument72 pagesHistory and Types of Insurance in India6338250% (4)
- National Mineral Policy Guide for Sustainable GrowthDocument18 pagesNational Mineral Policy Guide for Sustainable GrowthIas PrelimsNo ratings yet
- Sample MC QuestionsDocument6 pagesSample MC QuestionsJoshua OhNo ratings yet
- Accounting equation problems and solutionsDocument2 pagesAccounting equation problems and solutionsSenthil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Income Measurement and Reporting Numerical Questions SolvedDocument2 pagesIncome Measurement and Reporting Numerical Questions SolvedKBA AMIR100% (2)
- Foreign Investment Act SummaryDocument3 pagesForeign Investment Act SummaryPrisiclla C CarfelNo ratings yet