Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SUGAR and Health
Uploaded by
Ranganath Ethiraj KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SUGAR and Health
Uploaded by
Ranganath Ethiraj KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
SUGAR & HEALTH
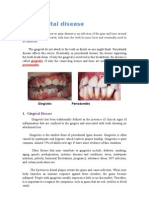
Of-late, sustained publicity campaign is being made by the producers of chemical sweeteners against sugar consumption by attributing to it various health problems. This has no scientific basis at all. Sugar is a perfectly healthy product as would be evident from the following: MYTHS CAUSES DENTAL CARIES:
FACTS
It is an infectious disease caused by the interaction of bacteria which reside in plague on the surface of the teeth with retained food particles especially carbohydrates. Good oral hygiene is essential which include reducing the frequency of intake of carbohydrates and drinks as well as regular dental check-ups and using fluoridated toothpaste when brushing teeth. Scientific studies show that people who are over weight often eat less sugar than thin people and there is plenty of evidence to show that carbohydrate rich diets can help suppress appetite Diabetes is a disorder of the body's metabolism. Many scientific studies show that the risk of diabetes is inversely related to carbohydrates and sugar consumption. In other words, people who develop diabetes have been found to eat less sugar than healthy people. The researchers indicate that sugar is not a cause of coronary heart disease. As there is no consistent and independent relationship between intake of sucrose or other carbohydrates and incidence of coronary heart disease. Empty calorie myth is really an empty complaint. Sugar is consumed as an essential or enhancing ingredient in wide variety of nutritious foods. Also, there is no reason for any concern as sugar consumption does not contribute to any nutritious deficiencies in population.
SUGAR CAUSE OBESITY: EATING SUGAR CAUSE DIABETES:
SUGAR CAUSE CORONOARY HEART DISEASE (CHD): EMPTY NUTRITION:
WHAT IS SUGAR Sugars are a major form of carbohydrates and are found probably in all green plants they occur in significant amounts in most fruits and vegetables there are three main simple sugars sucrose, fructose, glucose, sucrose is in fact a combination of fructose and glucose and the body quickly breaks down into these separate substances THE NEED FOR ENERGY All energy stored in food is derived originally from the sun and it is made by green plant life. The sun's energy acts upon the green chemical "chlorophyll" in the leaves of plants to produce sugars and Starches from the carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere and the water from the roots by a process known as Photosynthesis .These carbohydrates (starches and sugar) acts as a plants food and energy supply. .The Energy need of human body is largely dependent on the carbohydrates that are derived from plants. A BALANCE DIET A balanced diet can (and should) come from a variety of different foods ,calculated to give the desired
levels of carbohydrates ,proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals .Nutritional scientists advocate that carbohydrates should provide at least 50% of over energy requirements . SUGARS ROLE Starches provide the large part of our carbohydrate needs .The sugar which nature provides alongside the starches in our food supply have also a very special role to play in human metabolism for primitive man the sweet taste probably acted as a signal that the food was safe to eat .For modern man sugar is used to improve the palatability of many foods and can thereby encourage a more varied diet. THE USE OF SUGAR IN FOODS Sucrose is a natural and economical sweetener .It is the most versatile of all the sweeteners , performing many useful functions in a range of foods - As a sweetener. - Acting as a preservative. - Enhancing flavour in foods . - Providing bulk and texture in ice cream, custard, baked goods and confectionary . Acting as a food for yeast in baking and brewing beer and cider. - Contributing to crust colour , and flavour and delaying staleness in cakes and biscuits. SUGAR HAS MEDICAL VALUE Apart from sugar being a cheapest instant source of energy ,It has several medical & therapentical Values some of them are as elaborated below 1.SUGAR FOR ORAL REHYDERATION Sugar is extremely valuable in treatment of serve infantile diarrhea, a serious problem that kills around 3.5 million children in a year in underdeveloped countries .Oral re-hydration treatment (restoring of liquids by mouth) is used for infants with diarrhea due to cholera or re-hydrating viruses . It is simpler and easier to mix sugar with salt to treat de-hydration children even in The most remote areas .Further studies prove that oral sucrose was an effective as intravenous Treatment in retaining re-hydration 2. SUGAR HEALS WOUNDS Sugar has tremendous healing power .Sugar helps in wiping out infections in all types of wounds And speed up the healing time as well .For sugar fills up open wounds and it dissolves in tissue Where micro organism cannot survive 3. SUGAR IS BEST CARRIER OF VITAMINE A AND MINERALS Vitamin A deficiency in South American population is being combated successfully with the use of fortified sugar .Encouraged by the results ,fortification of sugar with vitamin A is being attempted to combat vitamin A as well as mineral (iron ) deficiencies a major area of concern In some of the developing countries MYTH ON SUGAR CONSUMPTION Food caused health impairment scares are always and will always be a legitimate matter of concern to consumers There is a difference between the food scare which effects one in two consumers and another which effects one. In a million. It is important to put information in proper perspective to assess the risk and to report accordingly .It is equally important that the information is based on scientific evidence .Keeping this in view we are giving hereunder. The scientific findings on various concerns expressed over sugar consumption. 1. EMPTY NUTRITION MYTH The complaint about sugar is that it contributes only calories but no nutrients to the diet . "Empty calorie"
myth is really an empty complaint. Sugar is never eaten alone It is almost always consumed as an essential Or enhancing ingredient in a wide varieties of other nutritious foods .Sugar is a 100% utilizable carbohydrate Another way to look at this issue is to ask whether there is any reason for Concern that sugar actually contributes to any nutrient deficiencies in population .The answer is no , A recent study concluded .There is no evidence that continuing to eat the present level of sugar will result in inadequate micro-nutrient nutrition 2. SUGAR AND DIABETES Diabetes "mellitus" is a disorder of the body's metabolism .The carbohydrates which a normal person eats are converted into glucose which is absorbed into the blood stream and is used by the body for energy .The diabetic person cannot utilize carbohydrates efficiently .as a result blood has higher than normal amount of glucose and it is often present in urine Though all the causes of diabetes are not known ,genetic factors play a major part in the development of this disease The question of whether sugar consumption is related to diabetes has been exclusively examined through epidemiologic surveys and experimental data The consensus of the scientific community is that sugar consumption is not Related to onset of diabetes . Many studies shows that the risk of diabetes is inversely related to carbohydrates and sugar consumption .That is people who develop diabetes have found to eat less sugar than healthy people .These people found to eat more fat and consume more total calories than healthy people increasing there likelihood of becoming obese and risk of developing diabetes . Once a person develops diabetes the intake of sugar and other simple carbohydrates is usually restricted .However there is little actual evidence to support this practice research now indicates that not all starches and sugars are alike in there effect on blood sugar .For example carrots can produce a higher blood sugar then a candy bar and honey has a greater effect than sucrose .Eating modest amounts of sucrose as a part of regular meals does not leads to higher amount of blood sugar as has been commonly supposed .The dietary recommendations of the American dietary association (ADA) Are in most respect the same as nondiabetic person and are based on sound principal of nutrition . Eating a modest amount of sugar is acceptable says (ADA) council of nutrition as long as metabolic control is maintained . 3. SUGAR AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE (CHD) The researches say that sugar is not a cause of coronary heart disease .The issue has been thoroughly studied in recent years because of one scientist's widely publicized theory of the 1960 that heart disease is linked to excessive sugar intake .The medical community has resoundingly rejected this theory . The prevailing view point is reflected in one scientist's conclusion after reviewing the literature that the evidence available does not support the view that the sugar in the level present in diabetes afflicted persons is a causative factor in the development of (CHD) The American society of clinical nutrition in (1979) stated there is no consistent and independent relationship between intake of sucrose or other carbohydrates and incidence of prevalence of (CHD) In an attempt to pin down the various risk factors involved in (CHD )many studies of the lifestyle and diets of different population have been conducted .A recent review of three major studies -the Framingham study the Honolulu heart study the Puertorico heart health program found no association between sugar consumption and ( CHD) risk the (UK) panel on diet and cardio-vascular disease could find no evidence that sugar was specifically related to ( CHD )despite a barrage of prepublication by food activists that sugar was a major contributory factor It is generally agreed that the primary diet factors involved in ( CHD) are nature and amount of fat in the diet .That is why dietary guidelines frequently called for a decrease in intake to be accompanied by an increase in carbohydrates consumption .Although these guidelines often recommended that the increased carbohydrate intake should take the form of complex carbohydrates .It can include sugar . 4. SUGAR AND OBESITY Eating too much of anything makes you fat specially if calories are consumed if more than calories used up. Scientific studies show that people who are over weight often eat less sugar then thin people and there is now plenty of evidence to show that carbohydrates rich diet can help suppress appetite .One explanation for this is that lean people have more active lifestyle which not only keep them trim but also
allow them to eat more of the foods they like and less of fats .Which contributes more than twice as many calories as sugar ,and alcohol also almost twice as many . 5. SUGAR AND HYPOGLYCEMIA Medical community believes that this is a rare condition that has been over diagnosed in recent years .Misinformation and the natural desire to find a physical cause for poorly defined symptoms such as fatigue irritability and nervousness have led to the popularization of hypoglycemia as a diagnosis even though similar symptoms may also arise due to stress in our lives . Understanding hypoglycemia is complicated by the fact that there is no standard medical definition as to where a normal blood sugar levels ends and low blood sugar begins .In fact there is a vide range of blood sugar levels that can be considered normal. Recent investigations into how the body responds to various carbohydrates indicate no reason to suspect the sugar poses a special metabolic problem .Sugar has been found to have only a moderate effect on blood sugar levels .Various carbohydrates sources such as carrots and potato has been found to effect the body blood sugar more markedly than sucrose In a recent symposium sponsored by the national alliance for research on schizophrenia and depression a national organization based on (GREAT NECK) . N.Y a study on the relationship between sugar and stress and the brain mechanism that control weight and appetite was presented according to this a pathway called the hypothalamopituitary-adrenal axis has been identified as the main regulator of the body stress response .It was observed that intake of more sugar reduced the level of corticosteroid responsible for stress by almost half. 6. SUGAR AND HYPERACTIVITY IN CHILDREN This statement is not supported by any medical evidence according to the American medical association hyperactivity is a complex behavioural syndrome the American council on science and health have questioned whether or not it can be related to diet at all .The 1989 (UK) committee on medical aspect on food policy ("COMA") concluded that sugar has no significant specific effect on behaviour or psychological functions Research shoes that the perceived effect of sugar on children behaviour has more to do with the influence of people around them then with any sugar containing food they are eating . 7. SUGAR AND DENTAL CARIES Dental caries is an infectious disease by the interaction of bacteria which reside in plague on the surface of the teeth with retained food particles especially carbohydrate. This acid produced erode tooth enamel leading to the formation of cavities .For caries to develop three factors are required -a susceptible tooth bacteria and a carbohydrate food stuff .A susceptible tooth surface which is not already decayed but prone to develop caries .Secondly micro organisms present in the mouth which used micro organism food to grow on the tooth surface .The ability of these micro organism to grow depends upon the frequency of food consumption and the length of time it remained in the teeth .Many tooth which contain little or no sucrose (but contain other fermentable carbohydrates )are capable of performing tooth decay . A primary consideration in dietary control of dental caries must be that of frequency and form of intake . Food which adhere to or between tooth surface may be particularly harmful Use of fluoride in drinking water is the most efficient way to reduce incidence of caries in America .The reduction in the dental caries has been 50% to70% as a result of water fluoridation .In Ireland apart from fluoridated water usage of fluoride tooth paste resulted in dramatic fall in tooth decay .Good oral hygiene is obviously essential . The etilogy of dental caries is multifactorial with oral microbial flora host factors and dietary factors being the three major factors involved in the development of the disease . 8. CHEMICAL SWEETENERS From time to time a number of chemical sweeteners were produced and used by the public. With passage of time and further research, some of these had to be banned as being harmful to health. It took quite some time before such conclusions could be reached. In the meanwhile, gullible public were
induced into consumption of such harmful chemical sweeteners. A few such instances are as follows: Likewise some of the recently introduced chemical sweeteners may subsequently prove to be a health hazard since scientific research is a continuous process. Consumption of such products may thus be beset with unknown risk which may become known later at a stage when damage may have been caused due to their consumption over a period of time. On the other hand, sugar, whether expressed in terms of sucrose or fructose is a natural product and is a wonderful gift of nature to the mankind. It has many virtues and cannot cause health hazard unless misused. Therefore, the risk evaluation between sugar consumption and that of chemical sweeteners must take this important factor into account. 9. CYCLAMATE Cyclamate, a cyclohexylsuphamic acid (related in its chemical structure to saccharin), 30-40 times sweeter than sucrose, was discovered in 1944 and became popular in the mid-sixties when it was used primarily in soft drinks along with saccharin. Cyclamate was banned in 1970 in the UK and the USA following some adverse toxicity results, which indicated that it is carcinogenic in animals and causes testicular atrophy. However, despite its ban in the UK and USA, it is still permitted in some European countries, Australia and New Zealand. 10. SACCHARIN Saccharin, sodium salt of ortho-sulphobenzoic acid, 300 times sweeter than sucrose, was the first artificial sweetener to be discovered in 1879. Consumption rates increased significantly during the war time (both 1 and II) when sugar was rationed. Use of saccharin continued to increase in the sixties and seventies due to the rising popularity of low calorie food and drink and its low cost. Unlike sugar, saccharin has a lingering bitter metallic after taste. There were fears about its safety when studies suggested that saccharin caused bladder cancer in laboratory rats. Its use was banned in Canada in 1977. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considered banning it in 1977 based on this animal research. However, Congress placed a moratorium on the ban to allow for more research on saccharin's safety. This moratorium has been extended seven times due to continued consumer demand. The FDA withdrew the ban in 1991, but the moratorium is still in effect until the year 2002. The use of saccharine is permitted in the USA but the products have to contain warning statement, "Use of this product may be hazardous to your health. This product contains saccharin which ahs been determined to cause cancer in laboratory animals". 11. OVER-CONSUMPTION OF SUGARS AND FAT BALANCE: Dietary carbohydrates are either immediately oxidised to provide energy, stored as glycogen (an energy reserve) or converted to fat in the liver by a process known as do novo lipogenesis. This is an energetically expensive so carbohydrates do not contribute significantly to the fat store. There are some concerns that as the proportion of refined carbohydrates increases in the diet, de novo lipogenesis may contribute more than once thought to the body's fat stores. This was investigated in a group of lean and obese people who were over fed sucrose and fructose. The study showed that although de novo lipogenesis was increased (by 2-3 times), it did not contribute significantly to the body's overall fat balance confirming our original hypothesis, that carbohydrates do not contribute greatly to the body's fat stores. 12. HIGH CARBOHYDRATES INTAKE ASSOCIATED WITH LOWER MEASURES OF BODY WEIGHT:
A study of dietary intake in 3000 men and women with type 1 diabetes found that those who had higher intakes of carbohydrates, including sugars and starches, had lower body mass index and waist circumference (WC). Intake or saturated fats, those found in meat and dairy products, was associated with higher measures of body weight. These findings are constantly reproduced in studies. 13. NUTRITION GUIDELINES AND EDUCATION OF THE PUBLIC The abstract discusses the purpose of dietary guidelines and the factors that influence their effectiveness. It considers that holistic approaches that are targeted to reduction in risks of dietary deficiencies, foodborne illnesses and multiple chronic degenerative diseases are probably the most useful for the nutrition education of the public. Guidelines also need to be updated periodically and communicated effectively. 14. IS WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE (WC) A USEFUL PREDICTOR OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE RISK ? Measuring WC is a simple and useful tool with which to measure abdominal obesity. As abdominal obesity is known to increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease, WC is considered, along with other measures, to be a good means of predicting risk of coronary heart disease. A study was carried out to investigate this but found it only to be true in the case of younger subjects. In older subjects, once body mass index was known, WC did not add to the prediction of risk of heart disease.
WORLD SUGAR MARKET REVIEW
The second revision of the world sugar balance in the 2010/11 (October/September) crop cycle by ISO puts world production at a record 168.045 mln tonnes, raw value, up 4.66% from the last season. Although ISO still expect a record high world sugar production, it has been revised downwards by 0.910 mln tonnes from their previous assessment in November, 2010. In contrast to output,world consumption has been revised marginally upwards and now is put at 167.849 mln tonnes. Consumption is expected to grow at 2.01%, slower than the 10-year average of 2.6%, due to historically high prices in both the world and domestic markets. After two seasons of large deficits, the stocks/consumption ratio had reduced to the lowest level for more than 20 years since 1989/90. The ratio is expected to decrease further to 35.04% in 2010/11 from 35.73% in the previous season of a large deficit. Despite the downward revision of world production, export availability still covers projected import demand. The absence of a physical trade deficit may act to cap prices for the rest of 2010/11 season. The world export availability is put at 50.496 mln tonnes exceeding import demand estimated at 50.309 mln tonnes. A summary of the third assessment of the world sugar balance in 2010/11 is given in the table below.
World Sugar Balance
2010/11 2009/10 Change in mln t in % (mln tonne, raw value)
Production Consumption Surplus / Deficit Import demand Export availability End Stocks Stocks/Consumption ratio in%
168.045 167.849 0.196 50.309 50.496 58.808 35.04
160.569 164.549 -3.980 53.393 53.023 58.799 35.73
7.476 3.300
4.66 2.01
-3.084 -2.527 0.009
-5.78 -4.77 0.02
Source: ISO Quarterly Market Outlook, February 2011 SUGAR ABROAD AUSTRALIA'S SUGAR CROP FACES CYCLONE THREAT A massive cyclone threat to the crop in Australia adds further pressure to global prices for the sweetener that are hovering around 30 year highs around 33 cents per lb. Australia typically commands around 11% of the global raw sugar trade with most of its production shipped into growing Asian market such as Indonesia. The Queensland Sugar Ltd expects the country to ship around 2.4 million tonnes of raw sugar in 2010/11, down from the previous season's 3.2 million tonnes. In December, 2010 the QSL said it might have to buy sugar from other countries such as Brazil to honour contracts. Australia harvested 27.4 million tonnes of cane in 2010/11, well below expectations of at least a 33 million tonnes crop as rain disrupted harvesting. BRAZIL 10/11 SUGAR OUTPUT SEEN SLIGHTLY UP Brazil's sugar output in the 2010/11 season was revised slightly upward after exceptionally dry weather in 2010 raised sugar concentration in cane. Sugar production was estimated at 38.7 million tonnes, up from the 38.15 million tonnes forecast in September. Because of the dryness, cane crushing in Brazil was projected at 625 million tonnes, still a record high but down from the 651.5 million tonnes forecast in September, according to Conab's third and final estimate for the season. Brazil's 2010/11 average yields were estimated at 77.8 tonnes per hectare, down 4.6% from the 2009/10 season. Sugar content in cane stood at an average of 140.9 kg per tonne. Ethanol production was estimated at 27.7 billion liters, down from 28.4 billion liters in September's forecast. Mills directed more cane to sugar production rather than to ethanol production due to higher returns. Brazilian sugar exports in 2010/11 were estimated at 28 million tonnes, up 14.6% from the previous season. CHINA SUGAR PRODUCTION MAY FALL Sugar output in China may decline by as much as 300,000 tonnes after snow and frost this year damaged crops. China's output is expected to be 11 million to 11.5 million tonnes, down from the initial forecast, said Parin Amatyakul, vice president of Mitr Phol
Sugar Corp. The China Sugar Association on Nov. 10 estimated Guangxi output in the crushing season that began in Nov. 1 to be 7.6 million tonnes, about 63% of China's total of 12 million tonnes. EU EYES SUGAR SALES, IMPORTS TO CURB SHORTAGE EU would approve extra sugar imports and the sale of out-of-quota sugar on the EU market to address an expected supply shortage and to curb rising prices. The European Commission said it would open an autonomous import quota for sugar from any non-EU country, but there were no details on the total volume of the quota or any tariffs that may apply. The Commission's plans to approve the sale of EU out-of-quota sugar on the domestic market appeared to confirm the reversal of its decision to export 350,000 tonnes, which it announced in November but subsequently delayed. Out-of-quota sugar refers to excess sugar produced above EU national quotas, which is often sold on world markets as, unlike quota sugar, it does not benefit from a guaranteed EU minimum sale price. INDONESIA PERMITS TO IMPORT 2.43 MLN T RAW SUGAR Indonesia has issued permits to import 2.43 million tonnes of raw sugar for 2011, an increase of 5% from 2010. The raw sugar, which could come from Thailand, India and Australia, will be processed into refined sugar and sold to Indonesia's food and beverage industry. JAPAN RAISES 2010/11 SUGAR IMPORT ESTIMATE Japan has revised up its sugar import estimate for the year to September 2011 from three months ago as local sugar beet output fell more than expected. Japan now estimates sugar imports for the current sugar year at 1.372 million tonnes on a refined basis, up 10.3% from a year earlier. In September, sugar imports in 2010/2011 were estimated at 1.265 million tonnes. If annual imports were at 1.372 million tonnes, that would be the highest level since 2007/2008. Major foreign sugar suppliers to Japan are Thailand, Australia and South Africa. RUSSIA MAY CUT RAW SUGAR IMPORT TARIFF FROM MARCH The customs union of Russia, Kazakhstan and Belarus may cut import tariffs for raw cane sugar to $50 per tonne from March following a drop in domestic beet sugar production due to a drought. Currently, the tariff is $140 per tonne, unchanged from October 2010. Brazil, Cuba and Thailand are the main raw sugar suppliers. Russia, the world's third-largest sugar buyer, imported 1.94 million tonnes of raw sugar in JanuaryOctober last year, up 59.7% year-on-year. THAILAND SUGAR ESTIMATE SEEN RISING BY 100,000 TONNES
The Cane & Sugar Board may revise its output forecast for the crop year ending Sept. 30 to around 7 million tonnes from an earlier estimate of 6.9 million tonnes. Cool weather is aiding harvesting and the crop quality also looks good. Area under cane plantation also increased to 1.1 million hectares this year from about 1 million hectares in 2009/10. Sugarcane yields are as high as 110 kilograms a tonne, up 10%. Sugar crushing in Thailand, the largest exporter after Brazil, began in end-November and will likely continue until May.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Minor Oral Surgical Procedures in Children ClassDocument65 pagesMinor Oral Surgical Procedures in Children ClassReenaChauhanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriDocument585 pagesOral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriKrish NatbhanjanNo ratings yet
- Oral PathologyDocument59 pagesOral PathologyJohn Brewster100% (5)
- Crown and Bridge: An IntroductionDocument5 pagesCrown and Bridge: An IntroductionRihan RihanNo ratings yet
- Pickard's Manual-Tooth Wear (Dragged)Document8 pagesPickard's Manual-Tooth Wear (Dragged)Adit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Tumors and Syndromes of the Oral CavityDocument23 pagesTumors and Syndromes of the Oral CavityAsma Sam100% (3)
- Color Atlas of Common Oral Diseases-0812112490Document142 pagesColor Atlas of Common Oral Diseases-0812112490Casandra Costin86% (7)
- Periodontal DiseaseDocument2 pagesPeriodontal Diseasekiki119100% (1)
- The Plaque Control RecordDocument3 pagesThe Plaque Control RecordEhab Kardouh100% (2)
- Esthetic Rehabilitation of A Severely Worn Dentition With MIPPDocument22 pagesEsthetic Rehabilitation of A Severely Worn Dentition With MIPPKarla Margine PérezNo ratings yet
- Dentistry 09 00107 v2Document9 pagesDentistry 09 00107 v2khalisha salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Saude Coletiva 2009Document77 pagesSaude Coletiva 2009Geovania AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary of English For NursingDocument37 pagesVocabulary of English For Nursingkelvin BinhNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4 LoDocument4 pagesScenario 4 LoFahrur RoziNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliDocument27 pagesRadiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliMugahed Abdo Al-gahdariNo ratings yet
- The State of Fixed Prosthodontic Impressions: Room For ImprovementDocument4 pagesThe State of Fixed Prosthodontic Impressions: Room For ImprovementErika MuñozNo ratings yet
- Minor Oral Surgery ComplicationsDocument53 pagesMinor Oral Surgery ComplicationsDrNagendra Dutt Sharma100% (1)
- Oral Health Risk Assessment ToolDocument3 pagesOral Health Risk Assessment ToolGSENo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument3 pagesSummative Assessmentapi-509225720No ratings yet
- Dentalcaries 130111084153 Phpapp01Document79 pagesDentalcaries 130111084153 Phpapp01Krishma ShakyaNo ratings yet
- WHO Oral Health Surveys Basic Methods 5th Edition 2013Document137 pagesWHO Oral Health Surveys Basic Methods 5th Edition 2013Hello GitapNo ratings yet
- Absorption of FoodDocument8 pagesAbsorption of FoodMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- History of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesHistory of Dental CariesHarish Chowdary100% (1)
- Oral Biology AssignmentDocument5 pagesOral Biology AssignmentShaza Khalid0% (1)
- Dental Caries - SravanDocument18 pagesDental Caries - Sravan12C29 SRAVAN VSNo ratings yet
- Zachrisson2004 Management of Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth With Emphasis On AutotransplantationDocument5 pagesZachrisson2004 Management of Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth With Emphasis On AutotransplantationplsssssNo ratings yet
- Eoj Max Can RevwDocument8 pagesEoj Max Can RevwJoji IsacNo ratings yet
- Provisional Splinting 2013Document87 pagesProvisional Splinting 2013felicedaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal ExodontiaDocument5 pagesPeriodontal ExodontiaDARKS_EDSNo ratings yet
- DR.Orange - Key Findings from SDLE 2019Document46 pagesDR.Orange - Key Findings from SDLE 2019خالد الحربي100% (1)