Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spelling Rules Summary
Uploaded by
Bhagya JayasingheOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spelling Rules Summary
Uploaded by
Bhagya JayasingheCopyright:
Available Formats
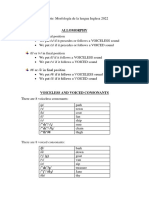
SPELLING RULES SPELLING PLURAL NOUNS 1.
Most words add s to the root forms without any change (barn - barns). 2. Words ending in sh, ch, ss, x, and z, usually add es to form the PLURAL (bush - bushes). 3. Words ending in a consonant and y change the y to i and add es (party - parties). 4. Some words ending in f change the f to v and add es (calf - calves). 5. Some singular words have different words for their plural form (man - men; mouse - mice; goose-geese). SUFFIXES 1. A letter or a syllable placed after a word to form a new word is called a suffix. Some suffixes are s, es, ed, ing, er, est, ly, ful, able, ible, ment, ive, ance, ence, ion, tion, ition, ation, sion, ous, ious, less, and al. Sometimes a word will have two suffixes. For example, respectfully has the two suffixes ful and ly added to the root word respect. 2. Many words are formed by adding ed and ing without any change (furnish - furnished furnishing). 3. Words ending in a silent e drop the e before adding ed and ing (move - moved - moving). 4. Words ending in a consonant and y change the y to i before adding ed, but do not make any change before adding ing (deny - denied - denying). 5. Words ending in a vowel and y add ed and ing without making any other change (delay - delayed - delaying). PREFIXES 1. A syllable placed before a word to change its meaning is called a prefix. Some prefixes are im, un, in, co, dis, inter. DOUBLING THE FINAL CONSONANT 1. Words of one syllable ending in a single consonant preceded by a single vowel double the final consonant before adding ed and ing (trim - trimmed - trimming). 2. Words of two or more syllables double the final consonant before adding ed and ing when these conditions are met: the last syllable ends in a single consonant preceded by a single vowel, and the accent is on the last syllable (refer - referred - referring). POSSESSIVE FORMS
1. Singular nouns form the possessive by adding an apostrophe and s (pilot - pilot's). 2. Plural nouns that end in s add only an apostrophe to form the possessive (aviators - aviators'). 3. Plural nouns that do not end in s add the apostrophe and s to form the possessive (men - men's). CONTRACTIONS 1. A word or phrase that has been shortened by leaving out some of the letters is called a contraction. 2. An apostrophe is used to show that the letters have been omitted (won't - will not), (o'clock - of the clock). CAPITALS 1. The beginning of a sentence is always capitalized (The day was bright and sunny.). 2. The names of holidays are capitalized (Christmas, Valentine's Day). 3. The names of the months of the year and the days of the week are capitalized (January, Monday). 4. The names of countries are capitalized (United States, Great Britain). 5. When you write the name of a particular avenue or street, capitalize the words avenue and street (Fifth Avenue, Oak Street). 6. The abbreviations Mr., Mrs. and Ms. are always capitalized and followed by a period (Mr. Callahan, Mrs. Perry, Ms. Smith). 7. The names of deities are capitalized (God, Allah, Buddha, Saviour). 8. The word republican is capitalized when it refers to the Republican party (The Republicans won the election.). 9. When words like senator and general are used as titles with a person's name, they are capitalized (General Herkes distinguished herself in battle.). 10. We capitalize the words capitol, senate, building, supreme and court when referring to the Capitol Building, the Senate, the Supreme Court of Canada. LETTERS AND SYLLABLES 1. The vowels are a, e, i, o, u, and sometimes y and w. The other letters are consonants. 2. Two vowels written together often have the sound of a single vowel. (In brain the ai has the sound of a. In eagle the ea has the sound of a long e, but in bread it has the sound of short e. This
rule will help you with the ei and ie words: i comes before e except after c or when sounded like a, as in neighbor and weigh. 3. A syllable is a word or part of a word which has one vowel sound and is spoken as a unit. (boy is a one-syllable word; chil dren is a two-syllable word; or na ment is a three syllable word. In every word of two or more syllables one syllable is given more emphasis than the other. This extra emphasis is called accent, and is shown in the dictionary by an accent mark ( ' ) 4. (In meet' ing the first syllable is accented.) Most words have only one accented syllable, but some have more than one (in' for ma' tion). The accent that is the heavier is called the primary accent. The other accent is called the secondary accent. 5. In your dictionary each word is re-spelled according to its pronunciation. The vowels are marked according to their sounds, and the accented syllables are shown. The marks for the vowel sounds are called diacritical marks. These marks vary from dictionary to dictionary. Please consult the beginning of your own dictionary for the explanation of diacritical marks used in that particular publication. 6. The two words at the top of each dictionary page are called guide words. The guide words are the first and last words on that particular page. SPECIAL WORDS 1. Compound Words are made by writing two small words together to make one larger word. (newspaper, somebody) 2. A root word is the root, or beginning word, from which another word is made. Play is the root word of plays, played and playing. 3. Derived words are words that come from other words. Suitable is derived from suit; advertisement from advertise. Sometimes the spelling of the root word is slightly changed in the derived word. 4. A synonym is a word having almost the same meaning as another word. (replied - answered; accurate - exact) 5. An antonym is a word that is opposite in meaning to another word. (private -public; good - bad) 6. Homonyms are words that are pronounced alike but which are spelled in different ways and have different meanings (knew - new; steel - steal; deer - dear)
You might also like
- Tarifit DictionaryDocument9 pagesTarifit DictionaryAbdu Amenukal50% (4)
- English Grammar 101: All You Need to KnowDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammar 101: All You Need to KnowDharmarao BalagaNo ratings yet
- Word Stress Patterns in EnglishDocument10 pagesWord Stress Patterns in EnglishAbeebNo ratings yet
- Grammar2011 A3Document45 pagesGrammar2011 A3tauseefali@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Introducing To Morphology Syntax BAB 3 - 7Document10 pagesRangkuman Introducing To Morphology Syntax BAB 3 - 7YesiRatna100% (1)
- Phonetics and Phonology Session 2 (Autoguardado)Document26 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Session 2 (Autoguardado)sandokanbedikabirNo ratings yet
- A Word and Its Form InflectionDocument17 pagesA Word and Its Form InflectionErvin EXorcistNo ratings yet
- Summary of Words and Its Forms: InflectionalDocument4 pagesSummary of Words and Its Forms: Inflectionalhapsari mutyaNo ratings yet
- Tema Pe Acasa LexicologieDocument5 pagesTema Pe Acasa LexicologieLele DoNo ratings yet
- HS-001A L 6 Stress PatternDocument42 pagesHS-001A L 6 Stress PatternS KohliNo ratings yet
- Improve your English communication skills with this comprehensive guideDocument16 pagesImprove your English communication skills with this comprehensive guideAarohi JagtapNo ratings yet
- Lexicos Of/for Words'. Thus, The Focus of Lexicology Is On The Idea of Word'. Here Are SomeDocument4 pagesLexicos Of/for Words'. Thus, The Focus of Lexicology Is On The Idea of Word'. Here Are SomeIoanaGanscaNo ratings yet
- Word Morphology and Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesWord Morphology and Parts of SpeechAjeng YupikaNo ratings yet
- Ingles Espacialidad - TEMA 9-13-14Document21 pagesIngles Espacialidad - TEMA 9-13-14David VilcaNo ratings yet
- Word Structure and Word FormationDocument49 pagesWord Structure and Word FormationMalika MalikaNo ratings yet
- Lembrete SintaxeDocument5 pagesLembrete SintaxeMarcelo VicenteNo ratings yet
- 6 Lesson-6-MechanicsDocument64 pages6 Lesson-6-Mechanicsreveriehale1210No ratings yet
- SyllableDocument3 pagesSyllableMangku BumiNo ratings yet
- Anglais CoursDocument6 pagesAnglais CoursMalek ZailabNo ratings yet
- Lektsia 21 11 23Document2 pagesLektsia 21 11 23adolfovicgeorgijNo ratings yet
- COMPOUND NOUN-dikonversiDocument7 pagesCOMPOUND NOUN-dikonversiFizra TrillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of SyllableDocument9 pagesAssignment of SyllableAcademic ReadingNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Word Structure and Formation: 1.1 The MorphemeDocument12 pagesChapter I: Word Structure and Formation: 1.1 The Morphemengọc diệpNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Syntax: Moh. Firmansyah, S.PD., M.PDDocument12 pagesIntroduction of Syntax: Moh. Firmansyah, S.PD., M.PDChindy KatiandaghoNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 3-1 PDFDocument46 pages11 - Chapter 3-1 PDFPhamngoc TuanNo ratings yet
- Word BuildingDocument7 pagesWord BuildingNatia LashqareishviliNo ratings yet
- Essentials of CommunicationDocument71 pagesEssentials of CommunicationAparajita RoyNo ratings yet
- Na'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A NutshellDocument33 pagesNa'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A Nutshell Na'vi in A NutshellAna Karina D'AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Rules For Accentual PatternsDocument5 pagesRules For Accentual PatternsPearl100% (1)
- Sentence StructureHandoutDocument42 pagesSentence StructureHandoutCNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PhonologyDocument9 pagesUnit 3 PhonologyDilan AdithyaNo ratings yet
- Building Words (Morphology)Document7 pagesBuilding Words (Morphology)Jorace Martini Ballovar DayritNo ratings yet
- Grammar 101Document14 pagesGrammar 101Reza Ayah MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Grammar 101: All You NeedDocument10 pagesGrammar 101: All You NeedTalibovic TalibovNo ratings yet
- Реферат Adjectives Прилагательные (Копия)Document15 pagesРеферат Adjectives Прилагательные (Копия)Catherine ElizarovaNo ratings yet
- What Is PhonologyDocument7 pagesWhat Is PhonologyMartin HopeNo ratings yet
- The difference between prescriptive and descriptive grammarDocument47 pagesThe difference between prescriptive and descriptive grammarIgor DudzikNo ratings yet
- Gramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Document64 pagesGramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Adam DmochowskiNo ratings yet
- Lexis & Morphology: Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesLexis & Morphology: Key ConceptsqamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4vimincryNo ratings yet
- Renewable Rewritable Re + New + Able Re + Writ (E) + AbleDocument10 pagesRenewable Rewritable Re + New + Able Re + Writ (E) + AbleJennifer Hipolito OraniNo ratings yet
- 4 Word MeaningDocument27 pages4 Word MeaningAudyNo ratings yet
- Gei002 NotesDocument10 pagesGei002 NotesAdrianne Mae Almalvez RodrigoNo ratings yet
- STRESSDocument4 pagesSTRESSbessoNo ratings yet
- 语言学4Document55 pages语言学4mochen439No ratings yet
- Vowel Phonemes: Phoneme ExamplesDocument6 pagesVowel Phonemes: Phoneme ExamplesAnna Rhea BurerosNo ratings yet
- лексикология 4Document4 pagesлексикология 4Sevara AbdumalikovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter V CL AT THE LEVEL OF PHONOLOGYDocument45 pagesChapter V CL AT THE LEVEL OF PHONOLOGYcuthithanh1033No ratings yet
- Week 5 Morphology and SyntaxDocument26 pagesWeek 5 Morphology and Syntaxzelfi okti fianefaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01Document10 pagesLesson 01criscruzado01No ratings yet
- Teorías Preguntas Llamados F2Document4 pagesTeorías Preguntas Llamados F2Rocío RosalesNo ratings yet
- Phonology LecturesDocument8 pagesPhonology LecturesMoahmmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- English Communication Skills - 40-45Document6 pagesEnglish Communication Skills - 40-45nagaraja1685No ratings yet
- The Parts of SpeechDocument13 pagesThe Parts of SpeechJoykson HaronisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document19 pagesUnit 1mnisa6701No ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument19 pagesChapter IiNurhasanah SasmaliaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar SumDocument24 pagesEnglish Grammar SumDiane LeytorNo ratings yet
- Homonymy Synonymy AntonymyDocument27 pagesHomonymy Synonymy Antonymykienphu111003No ratings yet
- Understanding SyllablesDocument7 pagesUnderstanding SyllablesMhmmd AbdNo ratings yet
- A 44Jkk64Jkkdkk44Jjjjkkkkjj A44Jkk64Jkkkk44Jjjjjkkjj Akk64Jkdkkkkkjkk44Jkkjzkjj Akk64Jkdkkkjjkk44JkkijjDocument8 pagesA 44Jkk64Jkkdkk44Jjjjkkkkjj A44Jkk64Jkkkk44Jjjjjkkjj Akk64Jkdkkkkkjkk44Jkkjzkjj Akk64Jkdkkkjjkk44JkkijjluisguiquijanorNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument8 pagesThesisShahid AliNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL NOTES FOR SPANISH TRANSCRIPTSDocument241 pagesESSENTIAL NOTES FOR SPANISH TRANSCRIPTSp50% (2)
- Trucos para TranscribirDocument3 pagesTrucos para TranscribirOmaima ArraisNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Quarter 1 Lessons 1 Through 9 (IPlan)Document12 pages6th Grade Quarter 1 Lessons 1 Through 9 (IPlan)Islam TahaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Test Poetry in EltDocument3 pagesMid Term Test Poetry in EltSilva Noridha SitompulNo ratings yet
- ENG501 - Finals Solved - by Maha MalikDocument21 pagesENG501 - Finals Solved - by Maha MalikUmer MUHAMMAD100% (3)
- New Spelling BookDocument128 pagesNew Spelling Booka singhNo ratings yet
- Goals and Expectations - Pronunciation and ListeningDocument35 pagesGoals and Expectations - Pronunciation and Listeningmelikekk_818780830No ratings yet
- HaikuDocument3 pagesHaikuFaisal MehmoodNo ratings yet
- English & Literature Syllabus for Santiago Trillana AcademyDocument25 pagesEnglish & Literature Syllabus for Santiago Trillana AcademyMa Elena Umali50% (2)
- FonologiaDocument115 pagesFonologiaIlmaNo ratings yet
- Nova Organi Armonia Ad Graduale Part 7Document253 pagesNova Organi Armonia Ad Graduale Part 7getrozoidNo ratings yet
- An Error Analysis in Pronunciation of English Vowels of The First Semester Students of EnglishDocument128 pagesAn Error Analysis in Pronunciation of English Vowels of The First Semester Students of EnglishNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Poetry SoundsDocument9 pagesPoetry SoundsdoradaramaNo ratings yet
- TN 3 Unit 03Document23 pagesTN 3 Unit 03Daniel BenitezNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication For Non-Native Speakers of English: October 2020Document52 pagesOral Communication For Non-Native Speakers of English: October 2020YurielNo ratings yet
- Assessing Speaking Part1Document10 pagesAssessing Speaking Part1dilia100% (1)
- Fonética y Fonología II: Prominence and Degrees of Word StressDocument16 pagesFonética y Fonología II: Prominence and Degrees of Word Stress10enero88No ratings yet
- Norwegian Grammar and Reader - Julius OlsonDocument350 pagesNorwegian Grammar and Reader - Julius OlsonMateo Jiménez Giraldo100% (2)
- Books and activitiesDocument304 pagesBooks and activitieshoangthubaNo ratings yet
- Little Greek 101Document6 pagesLittle Greek 101stan4dddNo ratings yet
- The Accentual Structure of English WordsDocument31 pagesThe Accentual Structure of English WordsBagzhanNo ratings yet
- Spelling Strategies Single Consonants That Have More Than One SoundDocument16 pagesSpelling Strategies Single Consonants That Have More Than One SoundМаксим ВолынецNo ratings yet
- Coursebook ELT2 VLVHDocument161 pagesCoursebook ELT2 VLVHDao Quoc NamNo ratings yet
- 24 EvidenceBasedSpeechDisorders. LofDocument33 pages24 EvidenceBasedSpeechDisorders. LofMateoNo ratings yet
- ED012914 Bengali BookDocument150 pagesED012914 Bengali BookSoupramanien KathirvelouNo ratings yet
- Englishhawaiian DictionaryDocument268 pagesEnglishhawaiian Dictionarymarinafalaga100% (1)