Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FUROSEMIDE
Uploaded by
a_lavina02Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FUROSEMIDE
Uploaded by
a_lavina02Copyright:
Available Formats
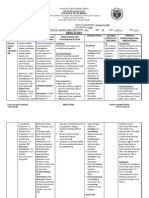
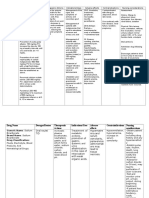
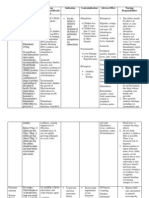
Drug name
Mechanis m of action Classificati on: Loop diuretics Mode of action:
Furosemide is a potent diuretic (water pill) that is used to eliminate water and salt from the body. In the kidneys, salt (composed of sodium and chloride), water, and other small molecules normally are filtered out of the blood and into the tubules of the kidney. The filtered fluid ultimately becomes urine. Most of the sodium, chloride and water that is filtered out of the blood is reabsorbed into the blood before the filtered fluid becomes urine and is eliminated from the body. Furosemide works by blocking the absorption of sodium, chloride, and water from the
Administrat ion
Indicatio n
Contraindicat ion
Adverse Effects
Nursing responsibilities
Generic Name:
Dosage and route:
Edema Adult: PO 2080 mg in 1 or more divided doses up to 600 mg/d if needed
furosemide
Brand Name:
Lasix
IV/IM 2040 mg in 1 or more divided doses up to 600 mg/d Child: PO 2 mg/kg, may be increased by 1 2 mg/kg q68h (max: 6 mg/kg/dose)
Treatment of edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome. May be used for management of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, and for treatment of hypercalcemia. Has been used concomitantly with mannitol for treatment of severe cerebral edema, particularly in meningitis.
History of hypersensitivity to furosemide or sulfonamides; increasing oliguria, anuria, fluid and electrolyte depletion states; hepatic coma; pregnancy (category C), lactation. Furosemide should be used with caution in patients with preexisting electrolyte or water balance abnormalities, impaired hepatic function (may precipitate hepatic coma) and diabetes mellitus. Patients with conditions that may lead to electrolyte or water balance abnormalities (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea, etc.) should be monitored carefully. Patients hypersensitive to sulfonamides may also be hypersensitive to furosemide (not documented in veterinary species).
IV/IM 1 mg/kg, may be increased by 1 mg/kg q2h if needed (max: mg/kg/dose) Neonate: PO 1 4 mg/kg q12 24h IV/IM 12 mg/kg q1224h Hypertension Adult: PO 1040 mg b.i.d. (max: 480 mg/d)
CV: Postural hypotension, dizziness with excessive diuresis, acute hypotensive episodes, circulatory collapse. Metabolic: Hypovolemia, dehydration, hyponatremia hypokalemia, hypochloremia metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia (tetany), hyperglycemia, glycosuria, elevated BUN, hyperuricemia. GI: Nausea, vomiting, oral and gastric burning, anorexia, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal cramping, acute pancreatitis, jaundice. Urogenital: Allergic interstitial nephritis, irreversible renal failure, urinary frequency. Hematologic: Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura; aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis (rare). Special Senses: Tinnitus, vertigo, feeling of fullness in ears, hearing loss (rarely permanent), blurred vision.
Assessment & Drug Effects: Observe patients receiving parenteral drug carefully; closely monitor BP and vital signs. Sudden death from cardiac arrest has been reported.
Monit or BP during periods of diuresis and through period of dosage adjustment. Obse rve older adults closely during period of brisk diuresis. Sudden alteration in fluid and electrolyte balance may precipitate significant adverse reactions. Report symptoms to physician. Lab tests: Obtain frequent blood count, serum and urine electrolytes, CO2, BUN, blood sugar, and uric acid values during first few months of therapy and periodically thereafter.
Frequency:
Q 12 hours
filtered fluid in the kidney tubules, causing a profound increase in the output of urine (diuresis).
Skin: Pruritus, urticaria, exfoliative dermatitis, purpura, photosensitivity, porphyria cutanea tarde, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis). Body as a Whole: Increased perspiration; paresthesias; activation of SLE, muscle spasms, weakness; thrombophlebitis, pain at IM injection site.
Monit or for S&S of hypokalemia . Monit or I&O ratio and pattern. Report decrease or unusual increase in output. Excessive diuresis can result in dehydration and hypovolemi a, circulatory collapse, and hypotension . Weigh patient daily under standard conditions. Monit or urine and blood glucose & HbA1C closely in diabetics and patients with decompensa ted hepatic cirrhosis. Drug may cause hyperglyce mia.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 282-Essentials of Pain Management-Nalini Vadivelu Richard D. Urman Roberta L. Hines-0387875786-Sp PDFDocument859 pages282-Essentials of Pain Management-Nalini Vadivelu Richard D. Urman Roberta L. Hines-0387875786-Sp PDFarief-024100% (2)
- The Progressive Muscle RelaxationDocument4 pagesThe Progressive Muscle Relaxationmaier_gabriela943980% (5)
- Interoception-201 March-2019Document38 pagesInteroception-201 March-2019api-526165635No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hyperparathyroidism, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hyperparathyroidism, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 3 ReviewDocument6 pagesPharmacology Test 3 ReviewNatalia BortellNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Potassium ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Potassium ChlorideBalloonsRus PHNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument4 pagesFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- How to Dilute Blood and Count White Blood CellsDocument2 pagesHow to Dilute Blood and Count White Blood CellsAlfred ChowNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization Power Point and ActivityDocument8 pagesLevels of Organization Power Point and ActivityJudy RianoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Solutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifeFrom EverandSolutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifeNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology HL Biological LOADocument11 pagesIB Psychology HL Biological LOAgfore3No ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug Guide for Nursing CareDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug Guide for Nursing CareIan Kenneth Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Loop Diuretics and Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesLoop Diuretics and Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoana Marie GuanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideIzza DeloriaNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideBorlong100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsDocument5 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemidezimmerstyle09No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Furosemide (LASIX)Document1 pageFurosemide (LASIX)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNo ratings yet
- AldactoneDocument2 pagesAldactoneianecunarNo ratings yet
- Fusid®: TabletsDocument8 pagesFusid®: Tabletsddandan_2No ratings yet
- Unit VI Drugs used on urinary systemDocument46 pagesUnit VI Drugs used on urinary systemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocument6 pagesDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Online AudioDocument4 pagesFurosemide: Online AudioDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- PLASIL antiemetics classificationDocument5 pagesPLASIL antiemetics classificationAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument5 pagesAcetazolamideIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Ify Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesIfy Drug StudiesifyNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideFeliza Therese A. DeloriaNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Loop Diuretic LasixDocument4 pagesLoop Diuretic LasixSabita PaudelNo ratings yet
- Drug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyDocument57 pagesDrug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyMichelle Davis-JacksonNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationDocument4 pagesFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkNo ratings yet
- Pritor PlusDocument4 pagesPritor Plusianecunar100% (2)
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Medication CardDocument2 pagesFurosemide Medication CardAnja de VriesNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- CTG Interpretation of CTG and CFHM During Antepartum and Intrapartum Periods Ho Lai FongDocument33 pagesCTG Interpretation of CTG and CFHM During Antepartum and Intrapartum Periods Ho Lai FongSabrina AzizNo ratings yet
- Auditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015Document24 pagesAuditory Pathways: Anatomy and Physiology: Handbook of Clinical Neurology March 2015florensiaNo ratings yet
- Subject Enrichment Activity For Term 2Document5 pagesSubject Enrichment Activity For Term 2AADITRYA JAINNo ratings yet
- PNTD 0005534 s001Document22 pagesPNTD 0005534 s001Paolo VidalNo ratings yet
- Master List of Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument37 pagesMaster List of Common Medical AbbreviationshealerharishNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiographyDocument21 pagesElectrocardiographyTol Man ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nexgen Complete Knee Solution Epicondylar Instrumentation Surgical Technique For Legacy Posterior Stabalized Knees Surgical TechniqueDocument32 pagesNexgen Complete Knee Solution Epicondylar Instrumentation Surgical Technique For Legacy Posterior Stabalized Knees Surgical TechniqueTudor MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Entrance Test For M.Phil/Ph.D. (Biotechnology) (Sample Paper)Document19 pagesEntrance Test For M.Phil/Ph.D. (Biotechnology) (Sample Paper)Rehaan FayazNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnatomy Practice Questionsfrank davidNo ratings yet
- CCDocument4 pagesCCJaymih Santos AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Supervisor ICDS Kerala PSC Exam Question Paper 2013Document14 pagesSupervisor ICDS Kerala PSC Exam Question Paper 2013lakshmyNo ratings yet
- Russel Body - Cause of Cancer and DeathDocument12 pagesRussel Body - Cause of Cancer and DeathAndré AmorimNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & EnzymesDocument102 pagesMolecules of Life: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & Enzymeskavya nandhiNo ratings yet
- KIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesDocument16 pagesKIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesVlado VladNo ratings yet
- Reflex Testing Methods For Evaluating C.N.S. Development - Anna's ArchiveDocument78 pagesReflex Testing Methods For Evaluating C.N.S. Development - Anna's ArchiveBrain AngNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration: Chemiosmosis and Electron Transport ChainDocument17 pagesAerobic Respiration: Chemiosmosis and Electron Transport ChainAihk kenneth BaronaNo ratings yet
- Cormie2011 PDFDocument22 pagesCormie2011 PDFGust AvoNo ratings yet
- Pathomorphology Final ExamDocument262 pagesPathomorphology Final ExamMann SarwanNo ratings yet
- CH 11 AnswersDocument23 pagesCH 11 AnswersJennifer Bash100% (4)
- Glikogenesis Dan GlikogenolisisDocument23 pagesGlikogenesis Dan GlikogenolisisKinarNo ratings yet
- Conduction SystemDocument2 pagesConduction SystemMalik Asif HussainNo ratings yet
- Veta 3 - Datasheet - ENG - 20210315Document2 pagesVeta 3 - Datasheet - ENG - 20210315JuanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersbillNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive Training HandballDocument23 pagesProprioceptive Training HandballRoginicD100% (1)