Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ingles
Uploaded by
Brian ShawOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ingles
Uploaded by
Brian ShawCopyright:
Available Formats
Past Continuous
FORM [was/were + present participle] Examples: You were studying when she called. Were you studying when she called? You were not studying when she called. Complete List of Past Continuous Forms USE 1 Interrupted Action in the Past
Use the Past Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the past was interrupted. The interruption is usually a shorter action in the Simple Past. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time. Examples: I was watching TV when she called. When the phone rang, she was writing a letter. While we were having the picnic, it started to rain. What were you doing when the earthquake started? I was listening to my iPod, so I didn't hear the fire alarm. You were not listening to me when I told you to turn the oven off. While John was sleeping last night, someone stole his car. Sammy was waiting for us when we got off the plane. While I was writing the email, the computer suddenly went off. A: What were you doing when you broke your leg? B: I was snowboarding. USE 2 Specific Time as an Interruption
In USE 1, described above, the Past Continuous is interrupted by a shorter action in the Simple Past. However, you can also use a specific time as an interruption. Examples: Last night at 6 PM, I was eating dinner. At midnight, we were still driving through the desert. Yesterday at this time, I was sitting at my desk at work. IMPORTANT In the Simple Past, a specific time is used to show when an action began or finished. In the Past Continuous, a specific time only interrupts the action. Examples:
Last night at 6 PM, I ate dinner. I started eating at 6 PM. Last night at 6 PM, I was eating dinner. I started earlier; and at 6 PM, I was in the process of eating dinner. USE 3 Parallel Actions
When you use the Past Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions were happening at the same time. The actions are parallel. Examples: I was studying while he was making dinner. While Ellen was reading, Tim was watching television. Were you listening while he was talking? I wasn't paying attention while I was writing the letter, so I made several mistakes. What were you doing while you were waiting? Thomas wasn't working, and I wasn't working either. They were eating dinner, discussing their plans, and having a good time. USE 4 Atmosphere In English, we often use a series of parallel actions to describe the atmosphere at a particular time in the past. Example: When I walked into the office, several people were busily typing, some were talking on the phones, the boss was yelling directions, and customers were waiting to be helped. One customer was yelling at a secretary and waving his hands. Others were complaining to each other about the bad service. USE 5 Repetition and Irritation with "Always"
The Past Continuous with words such as "always" or "constantly" expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happened in the past. The concept is very similar to the expression "used to" but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words "always" or "constantly" between "be" and "verb+ing." Examples: She was always coming to class late. He was constantly talking. He annoyed everyone. I didn't like them because they were always complaining. While vs. When Clauses are groups of words which have meaning, but are often not complete sentences. Some clauses begin with the word "when" such as "when she called" or "when it bit me." Other clauses begin with "while" such as "while she was sleeping" and "while he was surfing." When you talk about things in the past, "when" is most often followed by the verb tense Simple Past, whereas "while" is usually followed by Past Continuous. "While" expresses the idea of "during that time." Study the examples below. They have similar meanings, but they emphasize different parts of the sentence. Examples: I was studying when she called.
While I was studying, she called. REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Past Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Past. Examples: Jane was being at my house when you arrived. Not Correct Jane was at my house when you arrived. Correct ADVERB PLACEMENT The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc. Examples: You were just studying when she called. Were you just studying when she called? ACTIVE / PASSIVE Examples: The salesman was helping the customer when the thief came into the store. Active The customer was being helped by the salesman when the thief came into the store. Passive The PAST PROGRESSIVE TENSE indicates continuing action, something that was happening, going on, at some point in the past. This tense is formed with the helping "to be" verb, in the past tense, plus the present participle of the verb (with an -ing ending): I was riding my bike all day yesterday. Joel was being a terrible role model for his younger brother.
The past progressive indicates a limited duration of time and is thus a convenient way to indicate that something took place (in the simple past) while something else was happening: Carlos lost his watch while he was running.
The past progressive can express incomplete action. I was sleeping on the couch when Bertie smashed through the door. (as opposed to the simple past, which suggests a completed action: I slept on the couch last night. The past progressive is also used to poke fun at or criticize an action that is sporadic but habitual in nature: Tashonda was always handing in late papers. My father was always lecturing my brother. Singular I was walking you were walking he/she/it was walking Plural we were walking you were walking they were walking
Singular I was sleeping you were sleeping he/she/it was sleeping
Plural we were sleeping you were sleeping they were sleeping
Singular I was being you were being he/she/it was being
Plural we were being you were being they were being
Present Progressive Notes: 1. 2. The written lesson is below. Links to quizzes, tests, etc. are to the left.
The present progressive is formed by combining the verb "to be" with the present participle. (The present participle is merely the "-ing" form of a verb.) I am studying. I am studying with Mara.
In English, present progressive can be used to describe what is happening now, or what will happen in the future. I am studying now. I am studying with Mara tonight.
In Spanish, the present progressive is only used to describe an action that is in the process of taking place. It is not used for future actions. I am studying now. (use present progressive) I am studying with Mara tonight. (do not use present progressive)
To form the present progressive in Spanish, combine a form of "estar" with the present participle. Estoy hablando. I am speaking. Juan est comiendo. John is eating. Mara est escribiendo una carta. Mary is writing a letter.
In order to form the present progressive, you must know how to conjugate the verb estar, and how to form the present participle. You already know how to conjugate the verb estar: estar estoy ests est estamos estis estn
To form the present participle of regular -ar verbs, add -ando to the stem of the verb. hablar: hablando (hablar - ar + ando) trabajar: trabajando (trabajar - ar + ando) estudiar: estudiando (estudiar - ar + ando)
To form the present participle of regular -er and -ir verbs, add -iendo to the stem of the verb. comer: comiendo (comer - er + iendo) hacer: haciendo (hacer - er + iendo) vivir: viviendo (vivir - ir + iendo) escribir: escribiendo (escribir - ir + iendo)
To form the present participle of -ir stem changing verbs, change e:i and o:u in the stem, and then add -iendo to the stem of the verb. servir: sirviendo pedir: pidiendo decir: diciendo dormir: durmiendo morir: muriendo poder: pudiendo
Sometimes when forming the present participle it is necessary to change the spelling of a word so that it agrees with the way it is pronounced. We call this an "orthographic" change. Here are some common examples: caer: cayendo creer: creyendo huir: huyendo ir: yendo influir: influyendo or: oyendo traer: trayendo leer: leyendo seguir: siguiendo
The following examples illustrate the rules for forming the present participle. hablar: hablando (-ar) comer: comiendo (-er) vivir: viviendo (-ir) decir: diciendo (e:i) dormir: durmiendo (o:u) leer: leyendo (orthographic) seguir: siguiendo (orthographic)
To form the present progressive, simply conjugate the verb estar to agree with the subject of the sentence, and follow it with the present participle. Juan est comiendo pan. John is eating bread. Mara y Carmen estn hablando con nosotros. Mary and Carmen are speaking with us.
Remember, only use the present progressive for actions that are "in progress." Compare the uses of the present indicative with the uses of the present progressive. Estudio espaol. (Present Indicative) I study Spanish. I am studying Spanish (these days). I do study Spanish. Estoy estudiando espaol. (Present Progressive) I am studying (right now, at this moment) Spanish. It is important to remember that you would never use the present progressive to say something like "We are going to Spain this summer." Use present progressive only for actions that are "in progress."
Let's add two more verb flashcards: one for present progressive and one for practice in forming the present participle: Verb Flashcards Complete List Present Progressive estar + present participle I am speaking (right now, at this moment) Never use present progressive for something that will occur in the future. Present Participle (-ando, -iendo, yendo) hablar - hablando (-ar) comer - comiendo (-er) vivir - viviendo (-ir) decir - diciendo (e:i) dormir - durmiendo (o:u) leer - leyendo (orthographic) seguir: siguiendo (orthographic) Present Continuous/Progressive Spelling Rules BE verb + ing verb 1. Add ing to the base form of most verbs start starting finish finishing wash washing 2. When the base form ends in ane, delete thee and add-ing live living care caring ride riding 3.
When the base the verb ends withee just add-ing agree agreeing see seeing 4. When the base verb ends inie, delete theie and addy then adding tie tying die dying 5. If the verb has one syllable and ends in a consonant + vowel + consonant (CVC), double the final consonant and adding. stop stopping rob robbing beg begging 6. Do not double finalw or x or y. sew sewing mix mixing play playing 7. If the verb has two syllables, and the final syllable is stressed, double the final consonant*. ad mit admitting oc cur occurring per mit permitting * in American English l is not doubled. 8. If the verb has two syllables, and the final syllable isnot stressed, donot double the final consonant. hap pen happening lis ten listening o pen opening Future Progressive Future progressive tense is used to indicate action which will be taking place at some time in the future. For example, I will be singing at Symphony Hall next month. We'll be leaving next Monday. When you arrive, I'll be cooking dinner. The future progressive tense is formed by adding will be to the ?ing form of the main verb. She will be coming around the mountain in a few minutes. She'll be riding a white horse into town. The future progressive tense is not as common as other tenses, and it can some-times be replaced by simple future, present progressive or even simple present. I'll be leaving in a few minutes. I'll leave in a few minutes.
I'm going to leave in a few minutes. I'm leaving in a few minutes. I leave in a few minutes.
Future Progressive/Continuous Use 1) An action will be in progress at a certain time in the future. This action has begun before the certain time. 2) Something happens because it normally happens. Form will + be + infinitive + ing Examples 1) When I come to school, the other kids will be waiting for me. 2) We'll be going to the disco on Saturday. Complete Grammar Guide The Future Progressive Usage The future progressive is used to describe an action that will be "in progress" at a certain time in the future. "I will be waiting for you at the corner of Broadway and 42nd Street." It is often used with time expressions and a present tense verb to show the "time frame" in which a future action will happen: "I'll be working on the next chapter when we meet again." In this case we are showing the time relationship between the two actions. The speaker will start working on the chapter; he will meet the other person. At the time of their meeting, he won't have finished working on the chapter yet; it will be "in progress . So we use a progressive tense to show the action that is in progress at the time the other action occurs. Some verbs are never used in progressive tenses. These are called stative verbs because they describe states or conditions, not movement or action. Some stative verbs: think (when it means have an opinion-- "I thought the food was delicious.") believe / agree / understand / know / remember / forget /mean / d oubt / like/love/hate / imagine / want/wish / have (to possess) / say/tell/report / cost / seem/appear /weigh/measure "Speak more slowly and they will understand you better." (not "will be understanding") "When the holidays are over you will weigh 300 pounds." (not "will be weighing") "Believe me--when you see your hotel room you will want to go home immediately."
(not "will be wanting") "Just tell the truth; they will believe you." (not "will be believing") "When the house is finished we will have two guest rooms." (not "will be having") Structure The future progressive is formed with the future tense of the auxiliary verb be plus the -ing form of the main verb. There is no need for agreement between subject and verb; the verb form stays the same regardless of the subject: "He will be sleeping when you get home." "They will be sleeping when you get home." In negative sentences, the word not (or -n't) is placed immediately after the auxiliary verb will and before the verbbe. The negative will not can be contracted (shortened) towon't. "I will not be working at the lake this summer." "I won't be working at the lake this summer." To form questions, the auxiliary verb be and the subject are reversed: Question: "Will they be staying at your house?" Statement: "Yes, they will be staying at my house." Question: "Will your mother be going with you?" Statement: "Yes, she will." Question: "What will you be doing while your wife plays tennis?" Statement: "I will be sitting by the pool." For a question including a negative, -n't follows immediately after the auxiliary verb will and before the subject. "Won't you be working at that time?" If you use the uncontracted form, you must place the notafter the subject and before be. This structure is very formal. "Will you not be working for our firm?" Pasado Continuo FORMA [Fue / fueron + participio presente] Ejemplos: Se estaban estudiando cuando me llam. Estabas estudiando cuando llam? No estaban estudiando cuando llam. Lista completa de los anteriores formularios continuos USO una accin interrumpida en el pasado
Utilice el pasado continuo para indicar que una accin ya en el pasado fue interrumpido. La interrupcin es por lo general una accin ms corta en el pasado simple. Recuerde que esto puede ser una interrupcin real o slo una interrupcin en el tiempo. Ejemplos: Yo estaba viendo la tele cuando llam. Cuando son el telfono, que estaba escribiendo una carta. A pesar de que tenan el da de campo, empez a llover. Qu estabas haciendo cuando empez el terremoto? Estaba escuchando mi iPod, as que no oy la alarma de incendios. No se me escucha cuando le dije a apagar el horno. Mientras que John estaba durmiendo anoche, alguien le rob su automvil. Sammy estaba esperando por nosotros cuando nos bajamos del avin. Mientras estaba escribiendo el correo electrnico, el equipo de repente se apag. R: Qu estabas haciendo cuando te rompiste la pierna? B: Me snowboard. USO 2 tiempo especfico como una interrupcin
En USO 1, descrito anteriormente, el pasado continuo se ve interrumpida por una accin ms corta en el pasado simple. Sin embargo, tambin puede utilizar un tiempo determinado como una interrupcin. Ejemplos: Ayer por la noche a las 6 de la tarde, yo estaba comiendo la cena. A medianoche, todava estbamos conduciendo por el desierto. Ayer en este momento, yo estaba sentado en mi escritorio en el trabajo. IMPORTANTE En el pasado simple, un momento determinado se utiliza para mostrar el resultado de una accin cuando se haya comenzado o terminado. En el pasado continuo, un tiempo especfico slo se interrumpe la accin. Ejemplos: Ayer por la noche a las 6 de la tarde, me com la cena. Empec a comer a las 6 PM. Ayer por la noche a las 6 de la tarde, yo estaba comiendo la cena. Empec anterior, y a las 6 de la tarde, yo estaba en el proceso de comer la cena. USO tres acciones paralelas
Cuando se utiliza el Pasado Continuo con dos acciones en la misma frase, que expresa la idea de que ambas acciones fueron sucediendo al mismo tiempo. Las acciones son paralelas. Ejemplos:
Estaba estudiando cuando estaba preparando la cena. Mientras que Elena estaba leyendo, Tim estaba viendo la televisin. Le escucha mientras l estaba hablando? Yo no estaba prestando atencin, mientras yo estaba escribiendo la carta, as que hice varios errores. Qu hacas cuando estabas esperando? Toms no estaba trabajando, y yo no estaba funcionando bien. Estaban cenando, hablando de sus planes, y pasar un buen rato. USO 4 Ambiente En Ingls, que a menudo utilizan una serie de acciones paralelas para describir la atmsfera en un momento determinado en el pasado. Ejemplo: Cuando entr en la oficina, varias personas estaban muy ocupados escribiendo, algunos estaban hablando en los telfonos, el jefe le gritaba instrucciones, y los clientes estaban esperando para ser ayudados. Un cliente estaba gritando a un secretario y agitando las manos. Otros se quejaban el uno al otro sobre el mal servicio. USO 5 repeticin y la irritacin con "Siempre"
El pasado continuo con palabras como "siempre" o "constantemente" expresa la idea de que algo irritante o chocante a menudo ocurri en el pasado. El concepto es muy similar a la expresin " para ", pero con una emocin negativa. Recuerde que debe poner las palabras "siempre" o "constantemente" entre el "ser" y "verbo + ing". Ejemplos: Ella siempre fue llegar a clase tarde. Estaba constantemente hablando. Le molesta todo el mundo. No me gustan porque siempre estaban quejndose. Mientras vs Cuando Clusulas son grupos de palabras que tienen significado, pero a menudo no son oraciones completas. Algunas clusulas comenzar con la palabra "cuando", como "cuando llam a" o "cuando me mordi". Otras clusulas comienzan con "mientras que" tales como "mientras dorma" y "mientras l estaba navegando". Cuando se habla de las cosas en el pasado ", cuando" es ms a menudo seguido por el verbo en tiempo pasado simple , mientras que "mientras que" es generalmente seguido por Pasado Continuo. "Mientras que" expresa la idea de "durante ese tiempo." Estudio de los ejemplos a continuacin. Ellos tienen un significado similar, pero hacen hincapi en diferentes partes de la oracin. Ejemplos: Estaba estudiando cuando me llam. Mientras estudiaba, ella llam. RECUERDE verbos no continuos / Verbos mixto Es importante recordar que los verbos no-continua no se puede utilizar en cualquier tiempos continua. Adems, ciertos significados no continua de los verbos mixtos no pueden ser utilizados en tiempos continuos. En lugar de utilizar el pasado continuo con estos verbos, debe utilizar el pasado simple . Ejemplos: Jane estaba en mi casa cuando lleg. No es correcto Jane estaba en mi casa cuando lleg. Correcta
ADVERBIO COLOCACIN Los siguientes ejemplos muestran la colocacin de adverbios gramtica, tales como: siempre, slo, nunca, nunca, todava, justo, etc Ejemplos: Usted se acaba de estudiar cuando llam. Se acaba de estudiar cuando llam? ACTIVO / PASIVO Ejemplos: El vendedor estaba ayudando a los clientes cuando el ladrn entr en la tienda. Activo El cliente estaba siendo ayudado por el vendedor cuando el ladrn entr en la tienda. Pasivo El pasado progresivo TIEMPO indica prosecucin de la accin, algo que estaba pasando, pasando, en algn momento en el pasado. Este tiempo se forma con la ayuda "a ser" el verbo, en pasado, ms el participio presente del verbo (con una interminable ING): Yo estaba montando en bicicleta ayer todo el da. Joel estaba siendo un modelo a seguir terrible para su hermano menor.
El pasado progresiva indica una duracin de tiempo limitado y por lo tanto una forma conveniente para indicar que algo se llev a cabo (en el pasado simple), mientras que algo ms estaba ocurriendo: Carlos perdi su reloj mientras se encontraba en funcionamiento.
El pasado progresiva puede expresar accin incompleta. Yo estaba durmiendo en el sof cuando Bertie se estrell contra la puerta. (En comparacin con el pasado simple, lo que sugiere una accin terminada: Yo dorma en el sof la noche anterior. El pasado progresivo se utiliza tambin para burlarse o criticar una accin que es espordica, pero habitual en la naturaleza: Tashonda siempre fue la entrega de los documentos finales. Mi padre siempre estaba dando conferencias a mi hermano. Singular Estaba caminando que ests caminando l / ella / ello fue caminando Plural caminbamos que ests caminando caminaban
Singular Yo estaba durmiendo dormas l / ella / l estaba durmiendo
Plural dormamos dormas dorman
Singular Que estaba siendo que se estaban l / ella / ello se estaba
Presente Progresivo
Notas: 1. 2. La leccin est escrita a continuacin.
Plural que se estaban que se estaban que estaban siendo
Enlaces a cuestionarios, exmenes, etc estn a la izquierda.
El presente progresivo se forma al combinar el verbo "estar" con el participio presente. (El participio presente es ms que el "-ing" forma de un verbo.) Estoy estudiando. Estoy estudiando con Mara.
En Ingls, progresiva se puede utilizar para describir lo que est sucediendo ahora, o lo que suceder en el futuro. Estoy estudiando ahora. Estoy estudiando en esta noche Mara.
En espaol, el presente progresivo es utilizado para describir una accin que est en el proceso de tomar su lugar. No se utiliza para acciones futuras. Estoy estudiando ahora. (Uso actual progresiva) Estoy estudiando en esta noche Mara. (No utilice presente progresivo)
Para formar el presente progresivo en espaol, combina una forma de "estar" con el participio presente. Estoy Hablando. Estoy hablando. Juan est comiendo. Juan est comiendo. Mara est Escribiendo Una carta. Mara est escribiendo una carta.
Para formar el presente progresivo, se debe saber cmo conjugar el verbo estar, y cmo formar el participio presente.Usted ya sabe cmo conjugar el verbo estar: ESTAR
Estoy ESTAS est ESTAMOS Estais estan
Para formar el participio presente de los verbos regulares-ar, ando complemento a la raz del verbo. Hablando: Hablar (Hablar - ar + ando) Trabajar: Trabajando (Trabajar - ar + ando) Estudiar: estudiando (Estudiar - ar + ando)
Para formar el participio presente del regulares-er y-ir verbos, iendo complemento a la raz del verbo. esquina: comiendo (Esquina - er + iendo) HACER: Haciendo (HACER - er + iendo) Vivir: Viviendo (Vivir - ir + iendo) Escribir: Escribiendo (Escribir - ir + iendo)
Para formar el participio presente de la madre-ir cambiando los verbos, el cambio e: i y o: u en el tronco, y luego agregar-iendo a la raz del verbo. SERVIR: sirviendo Pedir: Pidiendo Decir: diciendo Dormir: durmiendo morir: Muriendo Poder: pudiendo
A veces, cuando se forma el participio presente que es necesario cambiar la ortografa de una palabra lo que est de acuerdo con la forma en que se pronuncia. A esto le llamamos una "ortogrfica" cambio. stos son algunos ejemplos comunes: Caer: Cayendo CREER: creyendo huir: huyendo IR: Yendo influir: influyendo Or: oyendo Traer: trayendo
leer: leyendo Seguir: siguiendo
Los siguientes ejemplos ilustran las reglas para formar el participio presente. Hablar: Hablando (-ar) esquina: comiendo (-er) Vivir: Viviendo (-ir) Decir: diciendo (e: i) Dormir: durmiendo (o: u) leer: leyendo (ortogrfica) Seguir: siguiendo (ortogrfica)
Para formar el presente progresivo, slo tiene que conjugar el verbo estar de acuerdo con el sujeto de la oracin, y seguir con el participio presente. Juan est comiendo pan. Juan es comer pan. Mara y Carmen Hablando Con Nosotros estan. Mara y Carmen estn hablando con nosotros.
Recuerde, slo se utiliza el presente progresivo de las acciones que estn "en progreso". Comparacin de los usos del presente de indicativo con los usos del presente progresivo. Estudio espaol. (Presente Indicativo) Yo estudio espaol. Estoy estudiando espaol (en estos das). Yo estudio espaol. Estoy estudiando espaol. (Presente Progresivo) Estoy estudiando (ahora, en este momento) en espaol. Es importante recordar que usted nunca utiliza el presente progresivo para decir algo as como "Vamos a Espaa este verano." Utilice presente progresivo slo para las acciones que estn "en progreso".
Vamos a aadir dos ms flashcards verbo: uno para la presente progresivo y otro para la prctica en la formacin del participio presente:
Verbo Flashcards
Lista completa Presente Progresivo estar + participio presente Estoy hablando (en este momento, en este momento) Nunca use presente progresivo para algo que ocurrir en el futuro. Presente Participio (-ando,-iendo, Yendo) Hablar - Hablando (-ar) esquina - comiendo (-er) Vivir - Viviendo (-ir) Decir - diciendo (e: i) Dormir - durmiendo (o: u)
leer - leyendo (ortogrfica) Seguir: siguiendo (ortogrfica)
Presente Progresivo / Continuo - versin breve
Presente Progresivo / continua Resumen Utilice Palabras de advertencia Formulario de, negativos senences afirmativa y preguntas Ortografa verbos especiales Diagrama Larga formas y formas cortas Presente Progresivo - Complejo Prueba 1 Prueba 2 Complejo Ejercicios - Presente Progresivo
Presente Progresivo - Uso
1) Las acciones sucediendo en el momento de hablar Pedro se lee un libro ING ahora.
2) el plan fija en un futuro prximo Ella es ir de ING en Basilea, el sbado.
3) acciones de carcter temporal Su padre es el trabajo de ING en Roma este mes.
4) acciones pasando en el momento de hablar (ya las acciones) Mi amigo es el Ing. prepa para sus exmenes.
5) las tendencias Ms y ms gente se nos ING sus computadoras para escuchar msica.
6) acciones repetidas que son irritantes para el altavoz (con siempre, siempre, siempre) Andrew es siempre com ING tarde.
Palabras de advertencia
ahora, en este momento, Mira! Escucha!
Forma
que (por la maana, son, es) + infinitivo +-cin
Ejemplos
oraciones afirmativas:
Estoy jugando al ftbol. Estoy jugando al ftbol.
Usted est jugando al ftbol. Ests jugando al ftbol.
Oraciones negativas:
No estoy jugando al ftbol. No voy a jugar al ftbol.
No estn jugando al ftbol. No ests jugando al ftbol.
No estn jugando al ftbol.
Preguntas:
Estoy jugando al ftbol?
Si es usted jugar al ftbol?
Futuro Progresista Tiempo Haga clic para Audio
Futuro tiempo progresivo se utiliza para indicar la accin que se llevar a cabo en algn momento en el futuro. Por ejemplo, Voy a estar cantando en el Symphony Hall el prximo mes. Vamos a dejar el prximo lunes. Cuando llegue, voy a ser la cena de cocina. El futuro de tiempo progresivo se forma aadiendo ser el ING forma? Del verbo principal. Ella va a estar llegando alrededor de la montaa en pocos minutos. Ella ll ser montado en un caballo blanco a la ciudad. El futuro de tiempo progresivo no es tan comn como otros tiempos, y puede a veces se sustituye por el futuro simple, progresivo, incluso presente simple o presente. Me ir en unos minutos. Voy a salir en unos minutos. Voy a salir en unos minutos. Me voy en unos minutos. Me voy en unos minutos. Ver Futuro continuo (de tambin: Englishpage.com)
Si usted tiene preguntas o comentarios sobre esta pgina, por favor contacte con nosotros . Asegrese de incluir el ttulo de esta pgina en la lnea de asunto de su e-mail.
Gramtica Completa Gua del Futuro Progresista
Uso
El futuro progresivo se utiliza para describir una accin que ser "en curso" en un momento determinado en el futuro. "Yo estar esperando en la esquina de Broadway y la calle 42." A menudo se utiliza con expresiones temporales y un verbo en tiempo presente para mostrar el "marco de tiempo" en el que una accin futura que ocurrir: "Voy a estar trabajando en el captulo siguiente, cuando nos encontremos de nuevo." En este caso se muestra la relacin de tiempo entre las dos acciones. El orador se comenzar a trabajar en el captulo, se reunir con la otra persona. En el momento de su reunin, no se han terminado de trabajar en el captulo sin embargo, ser "en progreso Por lo tanto, utilizar un tiempo progresivo para mostrar la accin que est en curso en el momento de la otra accin se produce.. Algunos verbos no se utilizan nunca en los tiempos progresivos. Estos se llaman verbos estticos porque describen estados o condiciones, no movimiento o accin. Algunos verbos estativos: creo que (cuando significa tener una opinin - "Yo pensaba que la comida estaba deliciosa. ") Creemos / acuerdo / entender / saber / recordar / olvidar /media / dudas / como / de amor / odio / imagino / quiero / deseo / ha (poseer) / decir / contar / informe / coste /parece / aparece / peso / medida "Habla ms lentamente y que se entienda mejor." (No "ser la comprensin")
"Cuando las vacaciones son ms que tendr un peso de 300 libras." ("No ser un peso") "Cranme - cuando vea a su habitacin de hoteltendr que ir a casa inmediatamente." (No "se quiere") "Slo digo la verdad: que se cree." (No "se cree") "Cuando la casa est terminada vamos a tener dos habitaciones." (No "va a tener")
Estructura
El futuro progresivo se forma con el tiempo futuro del verbo auxiliar ser ms-cin de la forma del verbo principal. No hay necesidad de un acuerdo entre el sujeto y el verbo, el verbo es el mismo independientemente de la materia: "l va a estar durmiendo cuando llegue a casa." "Van a estar durmiendo cuando llegue a casa." En las oraciones negativas, la palabra no (-n 't o) se coloca inmediatamente despus del verbo auxiliar y antes del verbo ser. La negativa no puede ser contratado (abreviado) a no. "No voy a estar trabajando en el lago durante el verano." "No voy a estar trabajando en el lago durante el verano." Para formar preguntas, el verbo auxiliar ser y el tema se invierten: Pregunta: "Van a quedarse en su casa?" Declaracin: "S, va a permanecer en mi casa." Pregunta: "Tu madre se va con ustedes?" Declaracin: "S, lo har." Pregunta: "Qu vas a hacer, mientras que su esposa juega al tenis?" Declaracin: "Voy a estar sentado junto a la piscina." Por una cuestin, que incluya un negativo, - n't sigue inmediatamente despus del verbo auxiliar y antes el tema. "No vas a estar trabajando en ese momento?" Si utiliza el formulario no existe contrato, debe colocar el nodespus de que el sujeto y ante s. Esta estructura es muy formal. "No se va a trabajar para nuestra empresa?"
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?zvegaNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousILy SofiaNo ratings yet
- 04.past ContinuousDocument4 pages04.past ContinuousAdinaNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument25 pagesContinuousLula KotulovaNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesThe Past Continuous TenseYeerina DebnathNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousCamelia PleșaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Philip KingNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Andreea Lascu100% (1)
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?SenaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document3 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Peter LuvisNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast ContinuousJair MolinaNo ratings yet
- Grammar TensesDocument27 pagesGrammar Tenseswendy nguNo ratings yet
- Dosier AlvaroDocument22 pagesDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Blog InglesDocument10 pagesBlog InglesLuis CoboNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Tense NewDocument3 pagesPast Continuous Tense NewHamidiNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Document7 pagesPresent Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Marija MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianDocument37 pagesSimple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianAbirami SanmugumNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast ContinuousRené RamosNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Past Continuous FormsDocument2 pagesComplete List of Past Continuous FormsCristiana LapusanNo ratings yet
- Verb Perfect and ProgressiveDocument12 pagesVerb Perfect and ProgressiveJoanne JoanneNo ratings yet
- Tense TheoryDocument33 pagesTense TheoryAnamaria Blajan-LazaNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document24 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Noelia Nancy PonceNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses TESTDocument13 pagesVerb Tenses TESTEniahl Nuñez PescanteNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses - Group 3Document48 pagesVerb Tenses - Group 3Luz RijoNo ratings yet
- Verbs TensesDocument32 pagesVerbs TensesLucas Padrão100% (1)
- Past TenseDocument14 pagesPast Tensepandu MNo ratings yet
- Present ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent ProgressiveFauzan 'AzimNo ratings yet
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Document25 pagesUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: EnglezaDocument21 pagesSimple Past: EnglezaLarissa TodeaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument9 pagesTensesSadiyah KaniNo ratings yet
- Verbs: 1. History of VerbDocument11 pagesVerbs: 1. History of VerbBwin NetNo ratings yet
- Verbs: 1. History of VerbDocument11 pagesVerbs: 1. History of VerbBwin NetNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses For Spanish Speakers 2016Document11 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses For Spanish Speakers 2016Ricardo100% (2)
- Tenses Oft He Verb QWDocument9 pagesTenses Oft He Verb QWvincentc84No ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses For Spanish Speakers 2016Document13 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses For Spanish Speakers 2016Ricardo100% (1)
- Simple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDocument28 pagesSimple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDiamun FikriNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past ContinuousDocument13 pagesPast Simple Past ContinuousbiffinNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous InformationDocument7 pagesPast Continuous InformationHoskar Mendoza StanfordNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent ContinuousAndreea BalabanNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast ContinuousAdina BadeaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Summary 1-11Document17 pagesTugas Summary 1-11sherinaNo ratings yet
- Tugas BHS - InggrisDocument21 pagesTugas BHS - InggrisYuni kartiniNo ratings yet
- Verbs TypesDocument24 pagesVerbs TypesSairamTirumalaiGovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousFelipe R CruzNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument46 pagesPast ContinuousmiaNo ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument26 pagesEnglish Tense SystemJordan CruzNo ratings yet
- Unidad 13Document40 pagesUnidad 13Juan HermidaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and ContinousDocument6 pagesSimple Present and ContinousVanja GrujicNo ratings yet
- Direct Object Pronouns: Part I: BallDocument5 pagesDirect Object Pronouns: Part I: Ballamn628No ratings yet
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument16 pagesSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohNo ratings yet
- Units Report: Unit 1Document12 pagesUnits Report: Unit 1Lhy HernándezNo ratings yet
- Present Progressive: NotesDocument4 pagesPresent Progressive: NotesRojasJosuesNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDocument7 pagesSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastYsa YesoNo ratings yet
- University of Panama Vicepresidency of Research and Graduate Studies College of Humanities English DepartmentDocument28 pagesUniversity of Panama Vicepresidency of Research and Graduate Studies College of Humanities English DepartmentlingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple or Continuous Review Clasa A 6Document6 pagesPresent Simple or Continuous Review Clasa A 6Liliana GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Simple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectDocument14 pagesSimple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectRe'ka Miha'lyNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousPaula DiazNo ratings yet
- English Compendium 2Document16 pagesEnglish Compendium 2Erick Mendiola TorresNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Simple Past TenseDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses: Simple Past TenseHasnaoui DiaNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Volumetric Analysis PDFDocument24 pages9.2 Volumetric Analysis PDFJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Match The Animal With Its NameDocument4 pagesMatch The Animal With Its Namekawa kawka kawuniaNo ratings yet
- Oleracea Contain 13.2% Dry Matter, 15.7% Crude Protein, 5.4% Ether ExtractionDocument47 pagesOleracea Contain 13.2% Dry Matter, 15.7% Crude Protein, 5.4% Ether ExtractionJakin Aia TapanganNo ratings yet
- Clinimetrics Single Assessment Numeric EvaluationDocument1 pageClinimetrics Single Assessment Numeric EvaluationNicol SandovalNo ratings yet
- International Human Rights LawDocument21 pagesInternational Human Rights LawRea Nica GeronaNo ratings yet
- Vrushalirhatwal (14 0)Document5 pagesVrushalirhatwal (14 0)GuruRakshithNo ratings yet
- Lesson I. Background InformationDocument21 pagesLesson I. Background InformationsuidivoNo ratings yet
- Openfire XXMPP Server On Windows Server 2012 R2Document9 pagesOpenfire XXMPP Server On Windows Server 2012 R2crobertoNo ratings yet
- Bossa Nova Book PDFDocument5 pagesBossa Nova Book PDFschmimiNo ratings yet
- A Global StudyDocument57 pagesA Global StudyRoynal PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Isc The Tempest Workbook Answers Act 1 Scene 2: Home Science Commerce Mathematics Language LiteratureDocument31 pagesIsc The Tempest Workbook Answers Act 1 Scene 2: Home Science Commerce Mathematics Language LiteratureHarsh Ahirwar100% (1)
- Chapter Three: Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesChapter Three: Research MethodologyEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- 76 ECL GuideDocument45 pages76 ECL GuideOana SavulescuNo ratings yet
- Soal Midtest + Kunci JawabanDocument28 pagesSoal Midtest + Kunci JawabanYuyun RasulongNo ratings yet
- Congental Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument38 pagesCongental Abdominal Wall DefectsAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 9 - First QuarterDocument9 pagesMathematics - Grade 9 - First QuarterSanty Enril Belardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Eugène Burnouf: Legends of Indian Buddhism (1911)Document136 pagesEugène Burnouf: Legends of Indian Buddhism (1911)Levente Bakos100% (1)
- AmplifierDocument20 pagesAmplifierValerie StraussNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorDocument22 pagesIntroduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorSayyid Al ArizieNo ratings yet
- Oracle QuestDocument521 pagesOracle Questprasanna ghareNo ratings yet
- RFP On Internal AuditDocument33 pagesRFP On Internal AuditCan dien tu Thai Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- Gothic Revival ArchitectureDocument19 pagesGothic Revival ArchitectureAlexandra Maria NeaguNo ratings yet
- A Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFDocument9 pagesA Tool For The Assessment of Project Com PDFgskodikara2000No ratings yet
- India Marine Insurance Act 1963Document21 pagesIndia Marine Insurance Act 1963Aman GroverNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Investors in Indian Equity Markets: Submitted byDocument26 pagesBehaviour of Investors in Indian Equity Markets: Submitted byDibyanshu AmanNo ratings yet
- 1929 Davos DisputationDocument20 pages1929 Davos DisputationEstevao Cruz100% (1)
- WWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideDocument122 pagesWWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideHendrikEspinozaLoyola100% (2)
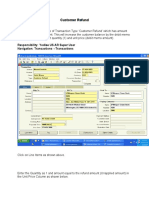
- Customer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsDocument12 pagesCustomer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsAziz KhanNo ratings yet
- Filipino HousesDocument4 pagesFilipino HousesjackNo ratings yet
- Chemiphase Oilfield Demulsifier Testing ProcedureDocument4 pagesChemiphase Oilfield Demulsifier Testing ProcedureBen Wiggins100% (1)