Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerobic Respiration
Uploaded by
Patrick AlavaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerobic Respiration
Uploaded by
Patrick AlavaCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerobic respiration is the release of energy from glucose or another organic substrate in the presence of Oxygen.
Strictly speaking aerobic means in air, but it is the Oxygen in the air which is necessary for aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is in the absence of air. Here is a molecular model of a glucose molecule. You do not need to memorize the diagram for you GCSE exam, but it should help you to understand that a molecule of glucose contains six atoms of Carbon (shown in blue), twelve atoms of Hydrogen (shown in green), and six atoms of Oxygen (shown in red).
In our tissues glucose can be broken down to release energy. The energy is used to make a substance called Adenosine Tri-Phosphate or ATP as it is usually called. ATP can provide energy for other processes such as muscle contractions. Here is a balanced chemical equation for the process of aerobic respiration. You only need to memorise this for the Higher Tier GCSE paper, however I am sure that you really want a grade "A" so why not memorise it.
You should be able to see six carbon atoms on each side of the equation; One molecule of glucose contains six atoms of Carbon and six molecules of Carbon Dioxide each contain one atom of Carbon.
You should also be able to see that the Hydrogen is balanced. One molecule of Glucose contains twelve atoms of Hydrogen and six molecules of water each contain two atoms of Oxygen. Now look at the Oxygen. To make six molecules of Carbon Dioxide we need twelve atoms of Oxygen and to make six molecules of water we need another six atoms of Oxygen. That makes a total of eighteen atoms of Oxygen. The glucose already contains six atoms of Oxygen so the cell will need a further six molecules of Oxygen from the air. The basic minimum knowledge for GCSE biology is the word equation given below. Even if you don't understand it you can memorise it like a parrot. Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy Aerobic respiration takes place in almost all living things. It is easy to get rid of the Carbon Dioxide and excess water; this is excretion (the removal of the toxic waste products of metabolism), and maximum energy is released from the glucose. Some organisms can respire in the absence of air: this is anaerobic respiration. This does not release so much energy and it produces much more toxic waste products. However, if Oxygen is not available, anaerobic respiration is better than nothing. When this happens in our muscles we produce lactic acid which gives you cramp. The bacteria in milk produce the same chemical when they turn it sour. "Lactic" means "of milk". So lactic acid is the acid in sour milk. Yeasts produce alcohol which is also toxic. Eventually there will be so much alcohol that the yeast cannot survive. _____________________________________________________________ The model for aerobic respiration is the oxidation of the glucose molecule: (1) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O + 38 ADP +38 P 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + 38 ATP + 420 Kcal This equation has an oxidation component, (2) C6H12O6 6 CO2 And a reduction component: (3) 6 O2 6 H2O Aerobic respiration has four stages
1. 2.
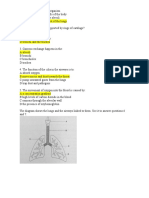
Glycolysis Process occurs in the cytoplasm; A six-carbon glucose molecule is converted to two, 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate This process occurs in the cytoplasm. In order to initiate the process, 2 molecules of ATP are consumed. Four molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADH are produced; Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Process involves shuttling pyruvate molecules into mitochondrion Each pyruvate molecules is oxidized to carbon dioxide and a 2carbon acetyl group. The carbon dioxide is released as a waste product, and the 2carbon acetyl group is bound to coenzyme A and brought into the mitochondrion; The citric acid cycle Each of the 2-carbon acetyl groups produced from the original glucose molecule is bonded to a pre-existing molecule of oxaloacetate to form citrate (i.e. citric acid). These two citric acid molecules are gradually oxidized, and the hydrogen ions are bound to NAD to form NADH and to FAD to form FADH2. Oxaloacetate is produced when the last carbon atom is released in the form of carbon dioxide; Two ATP molecules are synthesized for each glucose molecule entering the cell. Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis The electrons removed from the molecules in glycolysis and citric acid follow a series of cytochromes on the mitochondrial membrane, Hydrogen ions (protons) are pumped across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
3.
4.
These protons flow through ATP synthase enzyme molecules, and thereby release energy which drives the formation of 34 ATP molecules.
_____________________________________________________________ Aerobic respiration is the cellular processing of energy-rich molecules, primarily glucose, are converted into carbon dioxide and water through oxidation, and the released energy is subsequently used to support life processes in the form of ATP. Unlike the oxidation of a fire or other nonorganic processes, aerobic respiration is a carefully-controlled process that works in gradated steps. Aerobic respiration in almost every organic cell involves first the breakdown of complex sugars and carbohydrates into glucose, the simplest sugar. In mitochondria, glucose reacts with oxygen to create water, carbon dioxide, and energy. In the Krebs cycle, the energy is captured in the easily-broken, high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Once ATP is carried to appropriate spots in the cell, it is hydrolyzed. The addition of water breaks the bonds and releases energy, which enables cellular processes to go on. Waste products from aerobic respiration include carbon dioxide and water, which are released in exhaled air, sweat, and urine in animals, and are exhaled into the air through the many surfaces of plants. Overall, aerobic respiration is more efficient than most forms of anaerobic metabolism, such as fermentation. All prokaryotic cells use aerobic respiration to fuel their critical functions. _____________________________________________________________
You might also like
- Igcse Biology Chapter 9 RespirationDocument34 pagesIgcse Biology Chapter 9 RespirationEric ChewNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Year 9 Science Exam Revision Notes - Sets 1-5 PDFDocument11 pagesYear 9 Science Exam Revision Notes - Sets 1-5 PDFdayahn100% (1)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Breathing - and - Gas Exchange Igcse BiologyDocument88 pagesBreathing - and - Gas Exchange Igcse BiologyEllie HousenNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration .Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesTypes of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration .Anaerobic RespirationHahsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Respiration and Gas Exchange29seolaiscooltbhNo ratings yet
- Spot The Mistake - RespirationDocument2 pagesSpot The Mistake - Respirationakshyta gantanNo ratings yet
- B2.14d RespirationDocument2 pagesB2.14d Respirationboredok0% (1)
- General BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCDocument10 pagesGeneral BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCAldrin James DafunNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration: AbstractDocument2 pagesCell Respiration: AbstractStuckInSchoolNo ratings yet
- Worksheet RespiratoryDocument1 pageWorksheet RespiratoryANDREA PAOLA DIAZ ANDRADENo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 pagesSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Respiration Worksheet - AnswersDocument5 pagesRespiration Worksheet - AnswersSophia NgNo ratings yet
- What Is RespirationDocument22 pagesWhat Is RespirationToscanini MarkNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasessuryababaNo ratings yet
- Connecting Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesConnecting Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesislucy.mcallister510No ratings yet
- 10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2Document86 pages10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2kaziamna62No ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- 1670490268lesson No10 NotesDocument6 pages1670490268lesson No10 NotesVijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiNo ratings yet
- Researchpaper NataliemillerDocument2 pagesResearchpaper Nataliemillerapi-319936915No ratings yet
- Biology AutumnDocument4 pagesBiology AutumnlucylubuNo ratings yet
- Biology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesBiology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod ActivityDocument8 pagesDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activityapi-264479456No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument27 pagesRespirationZemetu Gimjaw AlemuNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 Chap 7Document15 pagesBio Form 4 Chap 7Lim Hong ShengNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument34 pagesAnaerobic RespirationArmero, Mariah Sophia V.No ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Respiratory System)Document11 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Respiratory System)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- 1 OxygenDocument17 pages1 OxygenX-ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument9 pagesRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557No ratings yet
- Respiratory System ArticleDocument4 pagesRespiratory System ArticleSumayah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Ans Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceDocument2 pagesAns Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceAishwarya DattaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyMae Ann Tomimbang MaglinteNo ratings yet
- 01 1-LifeProcessDocument5 pages01 1-LifeProcessRama RaoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument17 pagesRespiration in OrganismsSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesUnit 5. Respiratory SystemRaquelNo ratings yet
- What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?Document1 pageWhat Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?AqilahNo ratings yet
- 12 Do LabDocument3 pages12 Do LabRick MoraNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- Grade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismDocument6 pagesGrade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Oct 16 - QuizzDocument5 pagesOct 16 - Quizzsusan nobregaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (3 Class) : Chapter Two Carbohydrates DR: Zeyan A. AliDocument37 pagesBiochemistry (3 Class) : Chapter Two Carbohydrates DR: Zeyan A. AlizeyanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationMohamad Syafie Bin SamsirNo ratings yet
- Notes CELLULAR RESPDocument6 pagesNotes CELLULAR RESPela ravenaNo ratings yet
- STEM 5.9D 2.0 Explain STEMscopedia Eng PDFDocument5 pagesSTEM 5.9D 2.0 Explain STEMscopedia Eng PDFspaghett 1No ratings yet