Professional Documents
Culture Documents
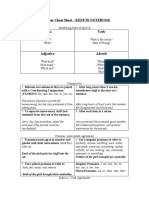
Subject Verb Rule
Uploaded by
Farhan HadjiSaidOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject Verb Rule
Uploaded by
Farhan HadjiSaidCopyright:
Available Formats
The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard English
1. Subjects and verbs must agree in number. This is the cornerstone rule that forms the background of the concept. The dog growls when he is angry. The dogs growl when they are angry. 2. Dont get confused by the words that come between the subject and verb; they do not affect agreement. The dog, who is chewing on my jeans, is usually very good. 3. Prepositional phrases between the subject and verb usually do not affect agreement. The colors of the rainbow are beautiful. 4. When sentences start with there or here, the subject will always be placed after the verb, so care needs to be taken to identify it correctly. There is a problem with the balance sheet.Here are the papers you requested. 5. Subjects don't always come before verbs in questions. Make sure you accurately identify the subject before deciding on the proper verb form to use. Does Lefty usually eat grass? Where are the pieces of this puzzle. 6. If two subjects are joined by and, they typically require a plural verb form. The cow and the pig are jumping over the moon. 7. The verb is singular if the two subjects separated by and refer to the same person or thing. Red beans and rice is my mom's favorite dish. 8. If one of the words each, every, or no comes before the subject, the verb is singular. No smoking or drinking is allowed.Every man and woman is required to check in. 9. If the subjects are both singular and are connected by the words or, nor, neither/nor, either/or, and not only/but also the verb is singular. Jessica or Christian is to blame for the accident. 10. The only time when the object of the preposition factors into the decision of plural or singular verb forms is when noun and pronoun subjects like some, half, none, more, all, etc. are followed by a prepositional phrase. In these sentences, theobject of the preposition determines the form of the verb. All of the chicken is gone.All of the chickens are gone.
11. The singular verb form is usually used for units of measurement. Four quarts of oil was required to get the car running. 12. If the subjects are both plural and are connected by the words or, nor, neither/nor, either/or, and not only/but also, the verb is plural.
Dogs and cats are both available at the pound. 13. If one subject is singular and one plural and the words are connected by the words or, nor, neither/nor, either/or, and not only/but also, you use the verb form of the subject that is nearest the verb. Either the bears or the lion has escaped from the zoo. Neither the lion nor thebears have escaped from the zoo. 14. Indefinite pronouns typically take singular verbs. Everybody wants to be loved. 15. * Except for the pronouns (few, many, several, both, all, some) that always take the plural form. Few were left alive after the flood. 16. If two infinitives are separated by and they take the plural form of the verb. To walk and to chew gum require great skill. 17. When gerunds are used as the subject of a sentence they take the singular verb form of the verb, but when they are linked by and they take the plural form. Standing in the water was a bad idea.Swimming in the ocean and playing drums are my hobbies. 18. Collective nouns like herd, senate, class, crowd, etc. usually take a singular verb form. The herd is stampeding. 19. Titles of books, movies, novels, etc. are treated as singular and take a singular verb. The Burbs is a movie starring Tom Hanks. 20. Final Rule Remember, only the subject affects the verb!
Pronoun: Word that takes the place of a noun Antecedent: Noun to which the pronoun is referring (original noun)
Ex: Mary (A) is happy; she (P) just finished all of her homework. The pronoun must agree with its antecedent in three ways:
1. Person: First (I), Second (You), or Third person (He) Mistake: A person (A) must be careful about whom he (P) tells his secrets to. You (P) never want to put yourself (P) in a position of weakness. 2. Gender: Masculine (He; Him), Feminine (She; Her); Neuter (It) Who: Refers to people That/Which: Refers to things or ideas Mistake: The snake (A) moved down the path; he (P) was fast. Mistake: The man (A), that (P) was angry, left. 3. Number: Singular or Plural *Singular antecedents get singular pronouns; plural get plural Mistake: That driver (A) just cut me off; they (P) should get a ticket! Mistake: A person (A) who tells lies eventually gets caught. Then, they (P) have to deal with the consequences
Pronoun-Antecedent Number Agreement Rules:
1. Use a singular pronoun to refer to a singular indefinite antecedent: anybody, each, either, everybody, everyone, nobody, one, someone Each of the children got (his/her, their) things ready. Everyone is responsible for (themselves, him/herself). 2. Use a plural pronoun to refer to a plural indefinite antecedent: Few, several, many Few of the students forgot (their, his/her) homework. 3. The indefinite pronouns all, any, none, and some do not clearly express singular or plural. Agreement depends on meaning: All of the apples are rotten. Throw (it, them) away. All of the apple is good. Use (it, them) in the pie. 4. Two or more antecedents take a plural pronoun Joan and Chris picked up (his, their) kids after school. 5. Alternative antecedentsjoined by or, nor, either/or, not only/but alsorequire a pronoun that agrees with the nearer antecedent Neither the kids nor the guide brought (their, his) cameras. 6. When the antecedent is a collective noun, pronoun agreement depends on whether the antecedent is acting as a unit (singular) or individually (plural). The jury has reached (their, its) decision. 7. The words each and every before an antecedent make it singular. Each of the children brought (their, his/her) lunch. Every man and woman must get (themselves, him/herself) home.
A preposition links nouns, pronouns and phrases to other words in asentence. The word or phrase that the preposition introduces is called the object of the preposition.
Rule1: In situations, the prepositions might be required to be placed at the end of the sentence. In such scenarios, they can be used following ways a) When the relative pronoun is that Example: Here is the book that you have been searching for. b) When the preposition governs the relative pronoun. Example: He is the person whom we are searching for. This is the baby which we are looking after. Relative pronouns-whom and which c) When the relative pronoun is understood. Example: This is the boy you spoke to. Those are the goals we aim at. d) In the case the preposition governs the interrogative pronoun or interrogative verb. Example: What is she looking at? What is the name of the person on whom the whole responsibility is laid on? e) The preposition is used as infinitive and is placed at the end of the sentence. Example: Dont you have a pen to write down? Dont you have a chair to sit on? f) When the object governed by the preposition is place first in the sentence. Example: This I rely on. She is known all the country over. This is the point the professor on that day insisted on. Rule 2: A preposition can be used in the beginning of an interrogative sentence. Example: From which section are you? To whom should I submit this? In which country did this culture originate? Before how many days did you ever open this book? Rule 3: There are many words which can be used as both prepositions and adverbs. Some of them are above, about, along, across, before, below, behind, besides, by, down, in, near, off, over, past, round, through, under, up, etc. Example:
Preposition She was here before six. She was behind us. The station is just round the corner.
Adverb She has done this before. He is long way behind. Come round and meet me this evening.
Rule 4: There is a specific list of words with prepositions which require gerunds after them. Note: Gerund: a verb form which functions as a noun. It used as ing in a sentence. Would you mind me taking your book tonight? Today I spent more than 10 hours watching movies. Examples: Refrain from hunting Prevent from working Succeed in doing Disqualified from doing Abstain from drinking Help in doing Addicted to gambling Bent upon doing Averse to playing
You might also like
- Grammar Cheat Sheet To Use With BellworkDocument8 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet To Use With Bellworksaed ahmad100% (1)
- GMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsFrom EverandGMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- English Grammar Test 3Document7 pagesEnglish Grammar Test 3Norman SernaNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument5 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementJairus RubioNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementLiezel-jheng Apostol Lozada0% (1)
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument22 pagesSubject Verb AgreementAljenneth MicallerNo ratings yet
- Prepositional Phrases: AdjectivesDocument5 pagesPrepositional Phrases: AdjectivesSuzanne LauNo ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement Reviewer 1Document5 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement Reviewer 1Mark Allan Conde Dacara100% (2)
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument2 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishRomuel Pioquinto100% (1)
- Esperanto PrimerDocument36 pagesEsperanto Primershellington92100% (1)
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument2 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishArinez DanteNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement: Basic RuleDocument9 pagesSubject Verb Agreement: Basic RuleTassinda De Souza100% (1)
- IELTS Grammar ExerciseDocument5 pagesIELTS Grammar ExerciseХиба Ю100% (1)
- Grammar & Syntax - TheoryDocument24 pagesGrammar & Syntax - Theorycosme.fulanitaNo ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument29 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishAriel Aguinaldo100% (5)
- Oxford Preparation Practice A2 Key Schools Answer KeyDocument19 pagesOxford Preparation Practice A2 Key Schools Answer KeyTim CherryNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit LessonDocument66 pagesSanskrit LessonLang HepingNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT VERB AGREEMENT RulesDocument6 pagesSUBJECT VERB AGREEMENT RulesFuad Hasan100% (1)
- Latin Prose Composition With Exercises From Caesar Cicero LivyDocument388 pagesLatin Prose Composition With Exercises From Caesar Cicero LivyCarl D'Souza100% (2)
- BK 2 Unit 29 To 32 Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument16 pagesBK 2 Unit 29 To 32 Gerunds and InfinitivesLaura CamilaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Grammar RulesDocument21 pagesCompilation of Grammar RulesVersoza NelNo ratings yet
- Correct The MistakesDocument6 pagesCorrect The Mistakesjanebennet3000No ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementJohn Walter TorreNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument5 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementHap Ppii Lagasca LayamNo ratings yet
- Rules of SVADocument24 pagesRules of SVAAzlan PspNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceFrom EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument14 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishcarolNo ratings yet
- Red Beans and Rice Is My Mom's Favorite DishDocument2 pagesRed Beans and Rice Is My Mom's Favorite DishRochelle Alava CercadoNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT and VERB AGREEMENTDocument4 pagesSUBJECT and VERB AGREEMENTPerrie Lyn Sta RosaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1663226958732 6976079485918400199Document2 pagesOrca Share Media1663226958732 6976079485918400199maria lily h manticahonNo ratings yet
- Buku LauraDocument2 pagesBuku LauraKiki DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement RulesDocument3 pagesSubject Verb Agreement RulespereenaNo ratings yet
- What Are The RulesDocument1 pageWhat Are The RulesLouise Veronica JoseNo ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument2 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishusunomNo ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument2 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard Englishjm logdatNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument27 pagesSubject Verb AgreementBeverly BuhayNo ratings yet
- Rule 1. Number Agreement: Rules of Subject-Verb AgreementDocument5 pagesRule 1. Number Agreement: Rules of Subject-Verb AgreementChristine ParrenoNo ratings yet
- Sub Verb Agrrement RulesDocument2 pagesSub Verb Agrrement Rulesmithu11No ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument2 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard Englishpauline_jwNo ratings yet
- Subject and Verb AgreementDocument5 pagesSubject and Verb AgreementEdgar Custodio FerrerNo ratings yet
- What Are The Rules - ConcordDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Rules - ConcordKarthik ACNo ratings yet
- Rules On Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesRules On Subject Verb AgreementTasyo LCruz Jr.No ratings yet
- Basic Rule.: Subject/Verb AgreementDocument13 pagesBasic Rule.: Subject/Verb AgreementRenu SyamNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument5 pagesSubject Verb AgreementRahul RaoNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement: What Are The Rules?Document6 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement: What Are The Rules?Parimalar RathinasamyNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pages20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementThucNguyenNgocNo ratings yet
- Being Able To Find The Right Subject and Verb Will Help You Correct Errors of Subject-Verb AgreementDocument7 pagesBeing Able To Find The Right Subject and Verb Will Help You Correct Errors of Subject-Verb AgreementSalem Nissi MayorNo ratings yet
- The 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement inDocument21 pagesThe 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement inulises quixanoNo ratings yet
- Answer key-SVADocument13 pagesAnswer key-SVAsapnaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument7 pagesSubject-Verb Agreementchichi marie buaNo ratings yet
- July 2021 ModuleDocument5 pagesJuly 2021 ModuleJayzell MonroyNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement (Rules)Document9 pagesSubject Verb Agreement (Rules)Johnree A. Evangelista0% (1)
- FALLSEMFY2023-24 BSTS201P SS CH2023241700237 Reference Material I 25-10-2023 L24 - Subject-Verb AgreementDocument33 pagesFALLSEMFY2023-24 BSTS201P SS CH2023241700237 Reference Material I 25-10-2023 L24 - Subject-Verb AgreementFawaz AhamedNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement ExercisesDocument6 pagesSubject Verb Agreement ExercisesaiNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument22 pagesSubject Verb AgreementEdward Almazan JrNo ratings yet
- Rules For Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesRules For Subject Verb AgreementBryan JanierNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument11 pagesSubject Verb AgreementSaud KhanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Rules of Subject-Verb Agreement?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Rules of Subject-Verb Agreement?pauNo ratings yet
- The Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesThe Rules of Subject Verb AgreementBryan CasidoNo ratings yet
- Finding Subjects and Verbs: ExampleDocument5 pagesFinding Subjects and Verbs: ExampleDinesh SugumaranNo ratings yet
- English10 Q4 M5Document15 pagesEnglish10 Q4 M5Sky MontalvoNo ratings yet
- English 101 PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish 101 PDFKorong KapampanganNo ratings yet
- Basic Rule.: ExampleDocument41 pagesBasic Rule.: ExampleCaren Yap MacadoNo ratings yet
- SUMSEM-2021-22 ENG2000 LO VL2021220700597 Reference Material I 26-05-2022 ConcordDocument18 pagesSUMSEM-2021-22 ENG2000 LO VL2021220700597 Reference Material I 26-05-2022 ConcordDeadshotNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument11 pagesSubject Verb AgreementMark Anthony PadillaNo ratings yet
- 02 CC S-V Agreement PDFDocument12 pages02 CC S-V Agreement PDFBerna Calugtong de LeonNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument9 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementYash JainNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesSubject Verb AgreementJay-MarNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement-1 - 1st Year Basic - ShamiliDocument25 pagesSubject Verb Agreement-1 - 1st Year Basic - Shamilimikku ninaviNo ratings yet
- PI BOOK Full (1)Document202 pagesPI BOOK Full (1)Sushant AryallNo ratings yet
- Le Discours IndirectDocument17 pagesLe Discours IndirectsezinevivianeNo ratings yet
- Inglés I Mg. Nancy León Pereyra Showing Possession: Possessive Adjectives and PronounsDocument5 pagesInglés I Mg. Nancy León Pereyra Showing Possession: Possessive Adjectives and PronounsJARA AREVALO JOSE LUISNo ratings yet
- Word Classes g7Document12 pagesWord Classes g7WaLkiEs TaLkIeSNo ratings yet
- Zestawienie Czasow ItpDocument15 pagesZestawienie Czasow ItpKrolewskaNo ratings yet
- DAILY-LESSON-LOG-revised SampleDocument3 pagesDAILY-LESSON-LOG-revised SampleHeart SophieNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Transformation of The Sentence, The Person or Thing That Is The Centre of The Action Is Placed As SubjectDocument2 pagesPassive Voice Transformation of The Sentence, The Person or Thing That Is The Centre of The Action Is Placed As Subjectbea_x50% (2)
- Uso Del Verbo "To Be"Document6 pagesUso Del Verbo "To Be"DiegoNo ratings yet
- Comparative Adjectives WorksheetDocument1 pageComparative Adjectives WorksheetMARIA VALENTINA MATEUS LAGUNANo ratings yet
- At, On and in (Time) - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument7 pagesAt, On and in (Time) - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryKo JiroNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisPe30arlNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans Worldview 2a & 2b Parte 2Document133 pagesLesson Plans Worldview 2a & 2b Parte 2Servicios Tecnicos100% (1)
- English 5 WWP First Quarter LeoDocument4 pagesEnglish 5 WWP First Quarter LeoLEONARDO JR ENRIQUEZNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: DialogueDocument10 pagesUnit 6: Dialoguecchello100% (1)
- Conditonal Sentences: (Definition, Types, Example)Document12 pagesConditonal Sentences: (Definition, Types, Example)salwa kanahayaNo ratings yet
- Sentence Pattern Lesson 2Document15 pagesSentence Pattern Lesson 2DinnarNo ratings yet
- ClusivityDocument27 pagesClusivitypraveenNo ratings yet
- Yes, I Can PDFDocument38 pagesYes, I Can PDFATNo ratings yet
- Abstract NounsDocument2 pagesAbstract NounsDeea Paris-Popa0% (1)