Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra 2 Notes
Uploaded by
Addison CollingsworthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra 2 Notes
Uploaded by
Addison CollingsworthCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultimate Algebra 2 Notes!
(1st Semester)
Chapter 1: Chapter 5: Chapter 6 cont.
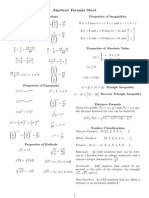
Properties of Adding and Multiplying Graphing a Quadratic function: The Rational Zero Theorem:
Property Addition Multiplication formula: y=ab^2+bx+c (this is a parabola) if ax^n......a(0)
Closure a+b is a real number ab is a real number The x coordinate of this graph is -b/2a ax^n represents the number with the highest power, in the
Commutative a+b = b+a ab=ab polynomial and a(0) represents the constant (only number
Associative (a+b) + c = a + (b+c) (ab)c=a(bc) Vertex and Intercepting Forms of Quadratic functions: with no power)
Identity a+0=a, 0+a=a a*1 =a, 1*a=a Form: Characteristics p = factor of constant term a(0)
Inverse a + (-a) =0 a*1/a =1, a doesn’t = 0 Vertex form: y= a(x-h)^2 + k The vertex is (h,k) q factor of leading coefficient a(n)
Distributive (involves both addition and multiplication) a(b+c) =ab +ac The axis of symmetry is x=h
Intercept form: y= a(x-p)(x-q) The x intercepts are p and q example: in the problem 3x^3 + 2x^2 +x +5, p = 3 and q=
Chapter 2: 5
Graphing Absolute Value Functions: Chapter 6:
formula: y=a |x-h| +k The vertex is (h,k) and is symmetric on on the Naming Polynomials Functions:
line x=h. The graph is V shaped. I opens up or down on x axis. Degree: Type: Standard form: Formulas and other things of use:
0 Constant f(x) = a(0) Area of circle: A=pie*r^2 (<-lol)
Chapter 4: 1 Linear f(x) = a(1)x +... Circumfrence of a Circle C=2pie*r (<-lol)
Properties of Matrix Operations: 2 Quadratic f(x) = a(2)x^2 +... slope: m= y(2)-y(1) = rise
*A and B stand for matrices* 3 Cubic f(x) = a(3)x^3 +... x(2)-x(1) run
Associative (add prop) (A+B) +C= A + (B+C) 4 Quartic f(x) = a(4)x^4 +... point slope form: y-y(1)=m(x-x(1))
Commutative (add prop) A+B = B+A
Distributive (add prop) c(A + B) =cA =cB Special Factoring Patterns: inequalities:
Distributive (subtract prop) c(A-B) = cA - cB Difference of Two Squares: a^2 - b^2= (a+b)(a-b) and = < (less than)
example: x^2 + 12x +36 = (x+6)^2 or = >(greater than)
Determinant of a Matrix: Perfect Square Trinomial: a^2 + 2ab + b^2 = (a+b)^2
For a 2x2 matrix, just criss cross and then do ad-bc a^2 - 2ab + b^2 = (a-b)^2 Standard Form:
for a 3x3, do the below. Add first 2 columns to end and do diagonals examples: x^2 + 12x + 36 = (x+6) ^2 ax-by = c
x^2 - 8x + 16 = (x-4)^2
Chapter 6: Absolute Value:
Special Product Patterns: y=|x| (leftmost) y=|x| + a(middle) y=|x-a| (right)
Sum and Difference: Examples:
(a+b)(a-b) = a^2 - b^2 (x+3)(x-3) = x^2 - 9 y= -|x| just opens down like ^ otherwise it follows
Square of a Binomial: the same rules.
(a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2 (y+4)^2 = y^ + 8y + 16
(a-b)^2 + a^2 - 2ab + b^2 (3t^2-2) = 9t^4 -12t^2 - 8
Cube of a Binomial:
(a+b)^3 = a^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + b^3 Parabolas: y= x^2 + 1 (left) y= (x-1)^2 (right)
(x+1)^3=x^3 + 3x^2 + 3x + 1
(a-b)^3 = a^3 - 3a^2b + 3ab^2 - b^3
(p-2)^3 + p^3- 6p^2 + 12p -8
Special Factoring Patterns:
Sum of Two Cubes: Example:
a^3 + b^3= (a+b)(a^2 - ab + b^2) x^3 + 8 = (x+2)(x^2 -2x + 4)
Difference of Two Cubes:
a^3 - b^3= (a-b)(a^2 + ab + b^2) 8x^3 - 1 = (2x-2)(4x^2 -2x +
1)
You might also like
- Algebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKDocument6 pagesAlgebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKaditya_kumar_me80% (5)
- 021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFDocument136 pages021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFmekidmu tadesse100% (1)
- (Chapter 3) Quadratic FunctionDocument17 pages(Chapter 3) Quadratic Functiondenixng100% (3)
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetSophieSzhangNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dilution of Precision ComputationDocument25 pagesGeometric Dilution of Precision ComputationAntonius NiusNo ratings yet
- LES Integration PartialFractionsDocument25 pagesLES Integration PartialFractionsPeter John ManlapigNo ratings yet
- Middle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This ClassDocument9 pagesMiddle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This Class01. ZUENo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 - Functions, Notation, Domain, Range 2022Document8 pagesLesson 01 - Functions, Notation, Domain, Range 2022h6p4jbtpysNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae List Form 4Document16 pagesAdd Maths Formulae List Form 4Hasbull97No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Quadratic FunctionDocument20 pagesLesson 8 Quadratic FunctionNicole Daphnie LisNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Algebra FormulasDocument4 pagesMath Resources Algebra FormulasSanjiv GautamNo ratings yet
- M49 AQuadratic SkillsDocument2 pagesM49 AQuadratic SkillsMohamed Sufian DamanhuriNo ratings yet
- Politecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsDocument10 pagesPolitecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsJuan Luis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions PDFDocument36 pagesPartial Fractions PDFlakkaraju prasanna100% (1)
- WIMO Final Training Course S - AlgebraDocument29 pagesWIMO Final Training Course S - AlgebraMicin AnandiNo ratings yet
- 109 SummarydddDocument8 pages109 Summarydddstfirstfir stlastlaNo ratings yet
- A. Preparatory Activity: Review: Review About The Different Methods of Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument7 pagesA. Preparatory Activity: Review: Review About The Different Methods of Solving Quadratic EquationsMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationDocument3 pagesExs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationASYA HIZLINo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument17 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebradeenaNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)Document47 pagesSolving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)aaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Summary: Techniques of IntegrationDocument2 pagesSummary: Techniques of IntegrationStart 2 GamingNo ratings yet
- N Naf Yad: PrepaDocument7 pagesN Naf Yad: Prepanasru hajiNo ratings yet
- Finding the Equation of a Quadratic Function from its GraphDocument10 pagesFinding the Equation of a Quadratic Function from its GraphDwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsDocument16 pagesQuadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsGGy Joe YeeNo ratings yet
- Math Workshop by SlidesgoDocument35 pagesMath Workshop by SlidesgoAyesha Nayyer100% (1)
- Sec 2 Quadratic Graph 1Document5 pagesSec 2 Quadratic Graph 1altclips0No ratings yet
- F.4 Revision Exercises Form 4 Mathematics Revision ExercisesDocument4 pagesF.4 Revision Exercises Form 4 Mathematics Revision Exercisesanon_413394553No ratings yet
- TEST 5. Lines-Quadratics (SOLUTIONS)Document8 pagesTEST 5. Lines-Quadratics (SOLUTIONS)Zi StyleNo ratings yet
- D L A F G K R O: 6) 7) ? Is Quadratic EquationDocument7 pagesD L A F G K R O: 6) 7) ? Is Quadratic EquationMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Graphs Quadratic InequalitiesDocument5 pagesGraphs Quadratic InequalitiesEscudero, Mae FelizNo ratings yet
- Semis 12345Document6 pagesSemis 12345Mariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- CET Sail Mathematics, Algebra (2023)Document22 pagesCET Sail Mathematics, Algebra (2023)Dahlia OjalesNo ratings yet
- 2.1-Functions and GraphsDocument7 pages2.1-Functions and GraphsSophie L.No ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths: Using FormulaeDocument13 pagesSPM Add Maths: Using FormulaeMalaysiaBoleh100% (6)
- Integration by Partial FractionDocument23 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionMisa KurobaneNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 9Document12 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 9Zion Conrad FuentesNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2nd SemDocument81 pagesCalculus 2nd SemSaurabh BhutkarNo ratings yet
- Mat Tutorial 2Document2 pagesMat Tutorial 2Essel MichaelNo ratings yet
- Further Integration Worked Solutions Student EdDocument15 pagesFurther Integration Worked Solutions Student EdRD MACKNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - As Levels MathsDocument4 pagesEdexcel - As Levels MathsAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- FRM 2023Document4 pagesFRM 2023olemas1984No ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsmacgyverNo ratings yet
- 2015 MC Ques Ans FDocument11 pages2015 MC Ques Ans Fs9dijdjiNo ratings yet
- MSCBSE0005Document28 pagesMSCBSE0005milapdhruvcomputerworkNo ratings yet
- Topic 2A. Theory of FunctionsDocument72 pagesTopic 2A. Theory of FunctionsZEEL PATELNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision in P1, P2, P3Document26 pagesQuick Revision in P1, P2, P3surendrakumar.adhikari2023No ratings yet
- Partial Fractions IntegrationDocument4 pagesPartial Fractions IntegrationErgie PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - Derivatives Solutions September 28, 2009Document4 pagesWorksheet 2 - Derivatives Solutions September 28, 2009Majd Abu KhalafNo ratings yet
- Factorization of Polynomials Pre-RMO Worksheet - 5Document9 pagesFactorization of Polynomials Pre-RMO Worksheet - 5Anirudha SharmaNo ratings yet
- III. Procedure: Daily Routine: Greetings: Exercise: Checking Of: A. Preparatory ActivityDocument7 pagesIII. Procedure: Daily Routine: Greetings: Exercise: Checking Of: A. Preparatory ActivityMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean When You Have More, You See Less?: D L A F G K R ODocument7 pagesWhat Does It Mean When You Have More, You See Less?: D L A F G K R OMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Proportion Exam 1to4Document2 pagesProportion Exam 1to4saad sheikhNo ratings yet
- Exercise: (A) Determine Its DomainDocument5 pagesExercise: (A) Determine Its DomainWowow BehNo ratings yet
- MAT2691 Assingment 03 2023 S1Document9 pagesMAT2691 Assingment 03 2023 S1Carole-ann de BeerNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument12 pagesQuadratic Functionsjulian MNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Number Systems PDFDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Number Systems PDFDivya MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument6 pagesChapter 3 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- Hey Math FinalDocument1 pageHey Math FinalPatrick YeboahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionFrom EverandCambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Types of Sensor and Their ApplicationDocument6 pagesTypes of Sensor and Their Applicationpogisimpatiko0% (1)
- Verification of First Law V-SonometerDocument3 pagesVerification of First Law V-SonometerRick astley's microphoneNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 q3 Mod4 Typesofmajoraccounts FinalDocument25 pagesFabm1 q3 Mod4 Typesofmajoraccounts FinalClifford FloresNo ratings yet
- Wargames Illustrated #115Document64 pagesWargames Illustrated #115Анатолий Золотухин100% (1)
- 14 - Hydraulic Design of Urban Drainage Systems PDFDocument45 pages14 - Hydraulic Design of Urban Drainage Systems PDFDeprizon SyamsunurNo ratings yet
- IS 2848 - Specition For PRT SensorDocument25 pagesIS 2848 - Specition For PRT SensorDiptee PatingeNo ratings yet
- Carbapenamses in Antibiotic ResistanceDocument53 pagesCarbapenamses in Antibiotic Resistancetummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Contract To Sell LansanganDocument2 pagesContract To Sell LansanganTet BuanNo ratings yet
- Ericsson 3G Chapter 5 (Service Integrity) - WCDMA RAN OptDocument61 pagesEricsson 3G Chapter 5 (Service Integrity) - WCDMA RAN OptMehmet Can KahramanNo ratings yet
- Programming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduDocument34 pagesProgramming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduNaruto DragneelNo ratings yet
- Purp Com Lesson 1.2Document2 pagesPurp Com Lesson 1.2bualjuldeeangelNo ratings yet
- Efficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsDocument7 pagesEfficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsMary AndersonNo ratings yet
- Löwenstein Medical: Intensive Care VentilationDocument16 pagesLöwenstein Medical: Intensive Care VentilationAlina Pedraza100% (1)
- Expected OutcomesDocument4 pagesExpected OutcomesPankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- Marriage Gift PolicyDocument4 pagesMarriage Gift PolicyGanesh Gaikwad100% (3)
- Lignan & NeolignanDocument12 pagesLignan & NeolignanUle UleNo ratings yet
- Capex Vs RescoDocument1 pageCapex Vs Rescosingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- Digestive System Song by MR ParrDocument2 pagesDigestive System Song by MR ParrRanulfo MayolNo ratings yet
- Gavrila Eduard 2Document6 pagesGavrila Eduard 2Eduard Gabriel GavrilăNo ratings yet
- Project Final Report: Crop BreedingDocument16 pagesProject Final Report: Crop BreedingAniket PatilNo ratings yet
- Government of The Punjab Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentDocument3 pagesGovernment of The Punjab Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentYasir GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Relation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesDocument4 pagesRelation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesPranjaliBawaneNo ratings yet
- Liu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain ClimbersDocument2 pagesLiu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain Climberssanti.miranda.parrillaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering by S C Goyal U A Bakshi PDFDocument3 pagesControl Systems Engineering by S C Goyal U A Bakshi PDFShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- WCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Document211 pagesWCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Antonio VargasNo ratings yet
- Yardi Commercial SuiteDocument52 pagesYardi Commercial SuiteSpicyNo ratings yet
- Farm mechanization subsidy applications invitedDocument2 pagesFarm mechanization subsidy applications inviteddraqbhattiNo ratings yet
- Thinking and Acting Outside The BoxDocument36 pagesThinking and Acting Outside The BoxMariecris GatlabayanNo ratings yet