Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SH Arm
Uploaded by
Shanne Shamsuddin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare inherited bleeding disorder caused by abnormal platelets. The platelets lack the ability to stick adequately to injured blood-vessel walls. This is a crucial aspect of the process of forming a blood clot.
Original Description:
Original Title
Sh Arm
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare inherited bleeding disorder caused by abnormal platelets. The platelets lack the ability to stick adequately to injured blood-vessel walls. This is a crucial aspect of the process of forming a blood clot.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSH Arm
Uploaded by
Shanne ShamsuddinBernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare inherited bleeding disorder caused by abnormal platelets. The platelets lack the ability to stick adequately to injured blood-vessel walls. This is a crucial aspect of the process of forming a blood clot.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
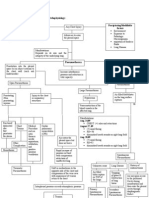
was originally described in 1948 What is the cause of Bernard- mapped to the short (p) arm of
Introduction to Bernard-Soulier by two physicians who were Soulier syndrome? chromosome 17
Syndrome treating a patient with a bleeding
problem. They discovered that this Bernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare How is Bernard-Soulier
IN 1948, BERNARD AND patient had a prolonged bleeding inherited disease and is transmitted syndrome diagnosed?
SOULIER described a young male time, fewer platelets, and larger in an autosomal recessive pattern.
patient with a severe bleeding platelets than the normal This means that both parents must Patients are often diagnosed with
disorder that was characterized by individual. Since then, the platelet carry a gene for the Bernard- B-SS after seeking medical
a prolonged bleeding time, abnormality has been described Soulier syndrome and transmit that attention following prolonged or
thrombocytopenia, and extremely and determined to be due to the gene to the child for the child to reoccurring bleeding episodes.
large platelets. They termed the platelets lacking the ability to stick have the disease. The prevalence is Some infants are diagnosed after
disorder “la dystrophie adequately to injured blood-vessel believed to be less than one in 1 excessive bleeding following
thrombocytaire-hémorragipare walls. This is a crucial aspect of million individuals. The molecular circumcision. Other children and
congénitale.” Since then, an the process of forming a blood clot, basis is now known and is due to a adults may be diagnosed after
identical or similar disorder has and as a result of this problem, defect in the platelet glycoprotein bleeding excessively following
been described in a large number there is abnormal bleeding. complex 1b-IX-V. This is referred trauma or tooth extraction. Very
of individuals, virtually always to as an adhesion complex and frequently there is a history of
transmitted in an autosomal What are the symptoms and forms a receptor that enables another family member with
recessive manner and often signs of Bernard-Soulier platelets to stick together to form a similar symptoms, and the
occurring in persons whose parents syndrome? clot. Normal platelets circulate in physician evaluating the patient
are close relatives. the blood and are the primary cells will often document a detailed
Bernard-Soulier syndrome usually responsible for initiating clotting. family history to assist in the
What is Bernard-Soulier presents in the newborn period, Without this receptor, platelets diagnosis. B-SS ultimately is a
syndrome? infancy, or early childhood with cannot stick together and clotting laboratory diagnosis and usually
bruises, nosebleeds (epistaxis), does not occur normally. The requires a specialized laboratory to
The Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (B- and/or gum (gingival) bleeding. parents of a child with B-SS will confirm the suspicion of the
SS) is a rare inherited bleeding Later problems can occur with have a decrease in the glycoprotein disease and involves platelet
disorder caused by abnormal anything that can induce bleeding but no impairment of platelet aggregation studies (testing for the
platelets and subsequent abnormal such as menstruation, trauma, function and no abnormal bleeding. "stickiness" of platelets) and flow
clotting. It is one of the giant surgery, or stomach ulcers. The Bernard-Soulier gene has been cytometry. It is important to
platelet syndromes. This syndrome distinguish this syndrome from
You might also like
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Nora Guides Gonzales CVDocument3 pagesNora Guides Gonzales CVShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument2 pagesLeprosyShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Fetal GrowthDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Human Fetal GrowthShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Calmette-Guérin: (Not MMR)Document2 pagesBacillus Calmette-Guérin: (Not MMR)Shanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- GradesDocument1 pageGradesShanne ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Zhu Scalp From South AmericaDocument16 pagesZhu Scalp From South AmericaG Bhagirathee83% (6)
- Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses: PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPigmented Purpuric Dermatoses: PathophysiologyrohitNo ratings yet
- Androgenetic Alopecia and Current Methods of TreatmentDocument4 pagesAndrogenetic Alopecia and Current Methods of TreatmentPamela TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Implementing Evidence-Based Decisions in Clinical Practice: Elliot AbtDocument7 pagesImplementing Evidence-Based Decisions in Clinical Practice: Elliot AbtSri Hari100% (1)
- MPS Therapy Flyer April 10 2018Document8 pagesMPS Therapy Flyer April 10 2018Neptune ShellNo ratings yet
- MDI Major Depression Inventory - English PDFDocument3 pagesMDI Major Depression Inventory - English PDFcmenikarachchiNo ratings yet
- Circulation Case Study Week 4Document10 pagesCirculation Case Study Week 4Caroline GamboneNo ratings yet
- Nursing notes sample for body malaise and fracture painDocument6 pagesNursing notes sample for body malaise and fracture painLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- CPM 2nd Ed Allergic RhinitisDocument6 pagesCPM 2nd Ed Allergic RhinitisSuresh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Mucopyocele of The Maxillary Sinus A Case StudyDocument3 pagesMucopyocele of The Maxillary Sinus A Case StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- E. Legal Aspects of PharmacologyDocument29 pagesE. Legal Aspects of PharmacologyTricia Mae BayubayNo ratings yet
- TIVA Pocket Reference 3rd Edition (Sept 2015)Document42 pagesTIVA Pocket Reference 3rd Edition (Sept 2015)Jabraan J100% (1)
- Medical - Surgical Nursing 3 & 4: Final ExaminationsDocument6 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing 3 & 4: Final ExaminationsBRYAN JOSEPH TIONGSON100% (1)
- Services Marketing "Shouldice Hospital Limited" - Case SubmissionDocument6 pagesServices Marketing "Shouldice Hospital Limited" - Case SubmissionVenkata Sai Pavan JeerlaNo ratings yet
- Pg36 37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument2 pagesPg36 37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyCharles Dean Ugalde100% (2)
- Disaster Management and ResponseDocument37 pagesDisaster Management and ResponseFroi Ann CabasagNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure GuideDocument9 pagesLaparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure GuideMay Ann Magdaraog ArdamilNo ratings yet
- 2020 AGEAGEING Deprescribing in Older People Approaching en of Life Development and Validation of STOPPFrail Version 2Document7 pages2020 AGEAGEING Deprescribing in Older People Approaching en of Life Development and Validation of STOPPFrail Version 2erika avelina rodriguez jaureguiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaReza Ridho PahleviNo ratings yet
- Free TOEFL Practice Questions About The TOEFLDocument39 pagesFree TOEFL Practice Questions About The TOEFLDieu-Donné NoukounwouiNo ratings yet
- Apixaban in Patients With Atrial FibrillationDocument12 pagesApixaban in Patients With Atrial FibrillationthedancingseaNo ratings yet
- Predictors of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Commercial Minibus Drivers in Accra Metropolis, GhanaDocument13 pagesPredictors of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Commercial Minibus Drivers in Accra Metropolis, GhanaLivia Meidy UbayidNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Data Sheet TableDocument3 pagesNephrology Data Sheet TableAnisulHaqueNo ratings yet
- ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDINGDocument4 pagesABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDINGMohamad Nur M. AliNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021Document5 pagesCardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021olawandeilo123No ratings yet
- PRC Room Assignment For June 2013 Nursing Board Exam (Pagadian)Document31 pagesPRC Room Assignment For June 2013 Nursing Board Exam (Pagadian)PhilippineNursingDirectory.comNo ratings yet
- TOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY NURSING REVIEWDocument9 pagesTOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY NURSING REVIEWRalph Pampola100% (2)
- Biomedical Equipment ValueDocument10 pagesBiomedical Equipment ValueRQAU SALEM QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAMNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Eye LidsDocument33 pagesDisorders of The Eye Lidsc/risaaq yuusuf ColoowNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainjrilleraNo ratings yet