Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Robo Viva
Uploaded by
RAMAKANT RANA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
886 views3 pagesDegeneracy occurs when the robot looses a degree of freedom and thus cannot perform as desired. It occurs under two condition: I. When the robot's joints reach their physical limits, and as result, cannot move any further. Dexterity is the ability to position and orientate a six-degree-of-freedom robot at any desired location within its work envelope.
Original Description:
Original Title
robo viva
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDegeneracy occurs when the robot looses a degree of freedom and thus cannot perform as desired. It occurs under two condition: I. When the robot's joints reach their physical limits, and as result, cannot move any further. Dexterity is the ability to position and orientate a six-degree-of-freedom robot at any desired location within its work envelope.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
886 views3 pagesRobo Viva
Uploaded by
RAMAKANT RANADegeneracy occurs when the robot looses a degree of freedom and thus cannot perform as desired. It occurs under two condition: I. When the robot's joints reach their physical limits, and as result, cannot move any further. Dexterity is the ability to position and orientate a six-degree-of-freedom robot at any desired location within its work envelope.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
VIVA VOCE QUESTION for ROBOTICS MAIT
1. What are ROBOT`s component?
ANS.1. Manipulator
ANS.2. End Effector
ANS.3. Actuators
ANS.4. Sensors
ANS.5. Controller
ANS.6. Processor
ANS.7. Software
2. What are the types of robot joints?
ANS.1. (P) Prismatic: are the linear i.e. no revolution involved
ANS.2. (R) Revolute: are the rotary.
3. What are ROBOT coordinates?
ANS.1. Cartesian/Rectangular (3P)
ANS.2. Cylindrical (R2P)
ANS.3. Spherical (2RP)
ANS.4. Articulated / Anthropomorphic (3R)
4. What are the ROBOT reference frames?
ANS.1. World reference frame: is a universal coordinate frame defined by x, y , z-axes.
ANS.2. Joint reference frame: is used to specify movements of each individual joint of
the robot.
ANS.3. Tool reference frame:
5. What is pure translation?
ANS.1. If a frame moves in space without any change in its orientation, the
Transformation is known as pure translation.
6. Define PITCH.
ANS.1. Rotation about Y-axis.
7. Define ROLL.
ANS.1. Rotation about Z-axis
8. Define YAW.
ANS.1. Rotation about X-axis
9. Define DEGENERACY.
ANS.1. It occurs when the robot looses a degree of freedom and thus cannot perform
as desired.
10. What causes DEGENERACY?
ANS.1. This occurs under two condition:
i. When the robot`s joints reach their physical limits, and as result, cannot move any
further, and
ii. A robot may become degenerate in middle of its workspace if the z-axis of two similar
joints becomes collinear. This, means that at this instant, whichever joint moves, the
same motion will result.
11. Define DEXTERITY.
ANS.1. One is supposed to be able to position and orientate a six-degree-of-freedom
Robot at any desired location within its work envelope by specifying the position and
the orientation of the hand. However, as the robot gets increasingly closer to the limits
of its workspace, it will get to appoint where although it is possible to locate it at a
By: RAMAKANT RANA ramakantrana.blogspot.com Page 1
VIVA VOCE QUESTION for ROBOTICS MAIT
desired point, it will be impossible to orientate it at desired orientation. The volume of
points where one can position the robot as desired, but not orientate it is called
nondexterous volume.
12. What are the actuators?
ANS.1. are the muscles of the ROBOT as if links and joints are the skeleton of the robot.
13. What are the types of actuators?
ANS.1. Following are the types of actuators:
i. Electric motors
a. Servo motors
b. Stepper motors
c. Direct-drive electric motors
ii. Hydraulic actuators
iii. Pneumatic actuators
iv. Magnetostrictive actuators
v. Shape memory metal actuators
14. Characteristics of actuating systems?
ANS.1. Following are the Characteristics of actuating systems:
i. Power-to-weight Ratio,
ii. Operating pressure
iii. Stiffness vs Compliance
iv. Use of reduction Gears
15. Compare Hydraulic actuators, Electric actuators and Pneumatic actuators.
ANS.1. Comparisons:
Hydraulic actuators Electric actuators Pneumatic actuators
1. Good for large robots 1. Good for all sizes 1. No leaks or sparks
2. Good for heavy payloads 2. Reliable 2. Inexpensive and Simple
3. High Accuracy 3. Low Maintenance 3. Good for on-off
application,
4. Better Response 4. Better Control 4. Good for pick and place
5. Not fit for clean room 5. Does not leak, so good for 5. Noisy Systems
application, as may leak. clean room.
6. Requires pump, reservoir, 6. Motor needs braking 6. Require air pressure, filter,
motor, etc. device when not powered. etc.
7. Can be expensive 7. Deform under load
constantly.
8. Can be noisy 8. Inaccurate Response
9. Requires maintenance 9. Lowest power to weight
ratio.
10. High Torque
11. High Pressure
16. What are the Characteristics of sensors?
ANS.1. Following are the Characteristics of sensors:
i. Cost
ii. Size
iii. Weight
iv. Type of output (analog or digital)
By: RAMAKANT RANA ramakantrana.blogspot.com Page 2
VIVA VOCE QUESTION for ROBOTICS MAIT
v. Interfacing
vi. Resolution
vii. Sensitivity
viii. Linearity
ix. Range
x. Response Time
xi. Frequency Response
xii. Reliability
xiii. Accuracy
xiv. Repeatability
17. What are the types of sensors?
ANS.1. Following are the types of sensors:
i. Position Sensors
ii. Velocity Sensors
iii. Acceleration Sensors
iv. Force and Pressure Sensors
v. Torque Sensors
vi. Microswitches
vii. Light and Infrared Sensors
viii. Touch and Tactile Sensors
ix. Proximity Sensors
x. Range Finders
xi. Vision Systems
xii. Voice-Recognition Devices
18. What are the types of position sensors?
ANS.1. Following are the types of position sensors:
i. Potentiometers
ii. Encoders
iii. Linear Variable Differential transformers (LVDT)
iv. Resolvers
v. Magneto Reflective Displacement Sensors
19. What are the types of Velocity sensors?
ANS.1. Following are the types of Velocity sensors:
i. Encoders
ii. Tachometers
20. What are the types of Force and Pressure Sensors?
ANS.1. Following are the types of Force and Pressure Sensors:
i. Piezoelectric
ii. Force-Sensing Resistor
iii. Strain Gauges
21. What can we do with this software?
22. Why do we use following commands
ANS.1. Open
ANS.2. Insert
ANS.3. Import
By: RAMAKANT RANA ramakantrana.blogspot.com Page 3
You might also like
- Unit 1: 6 HRS: Introduction: Basic Concepts, Laws of Robotics, RobotDocument69 pagesUnit 1: 6 HRS: Introduction: Basic Concepts, Laws of Robotics, Robotvithal100% (1)
- ROBOTICS TITLEDocument10 pagesROBOTICS TITLEmaverickhydronNo ratings yet
- Robotics ProperDocument182 pagesRobotics PropermacxNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQprabhaNo ratings yet
- 5th ModuleDocument23 pages5th ModuleJayasmita DasNo ratings yet
- Important Questions and Answers - Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors PDFDocument5 pagesImportant Questions and Answers - Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors PDFvicky tNo ratings yet
- Robotics PPT 1Document16 pagesRobotics PPT 1Himanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process Automation Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument7 pagesManufacturing Process Automation Questions and Answers - SanfoundryKumar Ravindra100% (1)
- Building Automation Sample PapersDocument4 pagesBuilding Automation Sample Papersrashmi patilNo ratings yet
- Robotics Practical FileDocument131 pagesRobotics Practical FileRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- CS8691-Artificial Intelligence NOTES 1Document220 pagesCS8691-Artificial Intelligence NOTES 1SANDEEP R NNo ratings yet
- Types of ManagersDocument4 pagesTypes of ManagersCarrie PetersonNo ratings yet
- RMD Sinhagad School of Engineering: Unit: 01 ES Overview (MCQ)Document4 pagesRMD Sinhagad School of Engineering: Unit: 01 ES Overview (MCQ)Spiderspider2021No ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Robotics de Es Zg561: Lecture - 2Document49 pagesMechanisms and Robotics de Es Zg561: Lecture - 2AnkithNo ratings yet
- Digital Lab VIVA QuestionsDocument4 pagesDigital Lab VIVA QuestionsAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM Unit - 3 PPT-ilovepdf-compressedDocument66 pagesCAD CAM Unit - 3 PPT-ilovepdf-compressedTaha SakriwalaNo ratings yet
- DSP Ec1302 Parta & Part B Questions and Answers11Document33 pagesDSP Ec1302 Parta & Part B Questions and Answers11ohmshankar100% (2)
- Robot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsDocument25 pagesRobot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsANONYMOUS PDFSNo ratings yet
- Introduction to UML: Modeling Language for Software SystemsDocument208 pagesIntroduction to UML: Modeling Language for Software SystemsRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Intro2robotics PPT SMRDocument48 pagesIntro2robotics PPT SMRapi-115728880No ratings yet
- 05 OS90525EN15GLA0 Connecting The Radio NetworkDocument60 pages05 OS90525EN15GLA0 Connecting The Radio NetworkElego13thNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and pneumatic systems examDocument2 pagesHydraulic and pneumatic systems examAravinthNo ratings yet
- Intro Robot Kinematics 5Document25 pagesIntro Robot Kinematics 5Gnanesh PendliNo ratings yet
- Getting StartedDocument46 pagesGetting StartedThenappan SNo ratings yet
- MechatronicsDocument32 pagesMechatronicskr_abhijeet72356587No ratings yet
- Review of Control Systems in RoboticsDocument10 pagesReview of Control Systems in Roboticsroyson316No ratings yet
- 2 Marks Question & AnswerDocument9 pages2 Marks Question & AnswerShanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- ADP I Lab Manual FinalDocument52 pagesADP I Lab Manual Finalसंकेत कलगुटकरNo ratings yet
- ROBOTS IeDocument21 pagesROBOTS IeSachin ShindeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Drone Technology SlidesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Drone Technology SlidesLeadingEdge FTNo ratings yet
- Robot Drive Systems & End EffectorsDocument71 pagesRobot Drive Systems & End EffectorsbabuNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Signal ProcessingDocument24 pagesAdaptive Signal Processinganilshaw27No ratings yet
- rOBOTICS Unit-2,3Document2 pagesrOBOTICS Unit-2,3dsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Robot Programming TechniquesDocument32 pagesRobot Programming TechniquesDjuraTheHarpYNo ratings yet
- Robot Components: The Robots Can Be Made Out of The Below MentionedDocument7 pagesRobot Components: The Robots Can Be Made Out of The Below MentionedNani KumarNo ratings yet
- Robotics NotesDocument22 pagesRobotics NotesUpendra020% (1)
- Automation in Manufacturing 10ME757: Department of Mechanical Engineering, SIRMVIT (Ramesh C G & Hanamantraygouda M B)Document193 pagesAutomation in Manufacturing 10ME757: Department of Mechanical Engineering, SIRMVIT (Ramesh C G & Hanamantraygouda M B)Wtf rajuNo ratings yet
- Robotics Programming and ApplicationsDocument38 pagesRobotics Programming and ApplicationsShanti Lal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Robotics Unit1 SlidesDocument65 pagesRobotics Unit1 SlidesJanarthanan BalakrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- 08 Robotics F16MTE Path and Trajectory PlanningDocument21 pages08 Robotics F16MTE Path and Trajectory PlanningasadNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Embedded OSDocument34 pagesReal-Time Embedded OSFandik ArmansyahNo ratings yet
- Robot Motion Planning: Approaches and Research IssuesDocument26 pagesRobot Motion Planning: Approaches and Research IssuesRahul KalaNo ratings yet
- CS461 Real Time SystemsDocument69 pagesCS461 Real Time Systemsprabakaran.rNo ratings yet
- Robotics Vision Lecture1Document258 pagesRobotics Vision Lecture1Nayan GuptaNo ratings yet
- CIM-2 MarksDocument18 pagesCIM-2 MarksHod MechNo ratings yet
- EcCST ManualDocument62 pagesEcCST Manualmatius.qNo ratings yet
- MCQ Robotics Fundamentals TestDocument5 pagesMCQ Robotics Fundamentals TestNel Sweetie0% (1)
- Question Bank SensorsDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank SensorsJasmine Kaur ButtarNo ratings yet
- DMS QB 2015 RDocument8 pagesDMS QB 2015 RKeerthe VaasanNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesDigital Signal Processing Question and AnswersShikharTyagiNo ratings yet
- Robotics, Laboratory ManualDocument26 pagesRobotics, Laboratory ManualManu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Robotics 2markDocument14 pagesRobotics 2markisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Design of Mechatronics SystemsDocument2 pagesDesign of Mechatronics Systemsmundu mustafa100% (1)
- New IC PaperDocument150 pagesNew IC PaperRaja Ramesh DNo ratings yet
- Development of Robotic Arm Using Arduino Uno: Priyambada Mishra, Riki Patel, Trushit Upadhyaya, Arpan DesaiDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Robotic Arm Using Arduino Uno: Priyambada Mishra, Riki Patel, Trushit Upadhyaya, Arpan Desaihussien amareNo ratings yet
- Robotics - 2 MarksDocument10 pagesRobotics - 2 MarksVijayNo ratings yet
- Robotics - 2Document65 pagesRobotics - 2chandansonics06No ratings yet
- IV Year 2 Marks 16 Marks MechDocument108 pagesIV Year 2 Marks 16 Marks Mechjagadeeshwar vasudevanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FundamentalsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - FundamentalsHayleysus ShmelashNo ratings yet
- Part A Ans Key 1,2,4Document3 pagesPart A Ans Key 1,2,4VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- SOME Write UPDocument3 pagesSOME Write UPRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering RAME-2016 (Proceedings)Document768 pagesRecent Advances in Mechanical Engineering RAME-2016 (Proceedings)RAMAKANT RANA100% (4)
- Engg Graphics 2 Edition PrefaceDocument16 pagesEngg Graphics 2 Edition PrefaceRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining ECMDocument11 pagesElectrochemical Machining ECMRAMAKANT RANA100% (1)
- Introduction To Advanced AMethods of MachiningDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Advanced AMethods of MachiningRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process SyllabusDocument4 pagesManufacturing Process SyllabusRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Lab ManualDocument32 pagesMechatronics Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Robotics Practical FileDocument131 pagesRobotics Practical FileRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM)Document11 pagesElectrochemical Machining (ECM)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Course 17Document4 pagesCourse 17getprize4surveyNo ratings yet
- CupolaDocument3 pagesCupolaRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Machining (Usm)Document12 pagesUltrasonic Machining (Usm)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Presentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirDocument72 pagesPresentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirRAMAKANT RANA100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Lab ManualDocument52 pagesEngineering Drawing Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANA93% (15)
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Document10 pagesLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Viva QuestionsDocument1 pageEngineering Graphics Viva QuestionsRAMAKANT RANA75% (4)
- Electrical Discharge MachiningDocument13 pagesElectrical Discharge MachiningRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Assignment Instrumentation V Sem EveningDocument5 pagesAssignment Instrumentation V Sem EveningRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
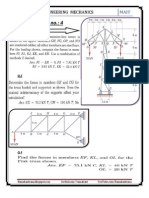
- Tutorial No. 4Document2 pagesTutorial No. 4RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Lab ManualDocument51 pagesEngineering Graphics Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANA63% (8)
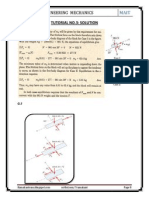
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 4) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Document3 pagesSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 4) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- EMM Lecture Unit VIDocument7 pagesEMM Lecture Unit VIRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
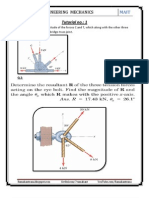
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 3) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Document5 pagesSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 3) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Tutorial No 1Document3 pagesTutorial No 1RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Solutions To The Tutorial (No. 2) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !Document4 pagesSolutions To The Tutorial (No. 2) of Engineering Mechanics (First Semester) !RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics by RAMAKANT RANADocument1 pageEngineering Graphics by RAMAKANT RANARAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 5Document1 pageTutorial No. 5RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Mechanical SwitchesDocument1 pageMechanical SwitchesRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- 2nd Sessional SyllabusDocument2 pages2nd Sessional SyllabusRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Mecha Syllabus Point WiseDocument2 pagesMecha Syllabus Point WiseRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Monitoring & Control SystemDocument6 pagesBluetooth Based Monitoring & Control SystemTowsifNo ratings yet
- 2535ar01 Bma eDocument1 page2535ar01 Bma eAyoo PcpNo ratings yet
- PYD 1388 7083 Dual Element Pyrodetector DatasheetDocument11 pagesPYD 1388 7083 Dual Element Pyrodetector DatasheetrenoNo ratings yet
- 64662GB - SWG200-1 Biogas - User - Manual PDFDocument89 pages64662GB - SWG200-1 Biogas - User - Manual PDFStuart KilgourNo ratings yet
- System Renishaw For Machine ToolDocument56 pagesSystem Renishaw For Machine ToolIlija SisoskiNo ratings yet
- FIRE FIGHTING INSTALLATIONS & EQUIPMENTSDocument35 pagesFIRE FIGHTING INSTALLATIONS & EQUIPMENTSFrancis BascosNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Sampling System: Domino Uss BenefitsDocument4 pagesUltimate Sampling System: Domino Uss BenefitsDavid PeredoNo ratings yet
- Smart Dust Core ArchitectureDocument14 pagesSmart Dust Core ArchitectureBaldev RamNo ratings yet
- Analogue Sensors On The Raspberry Pi Using An MCP3008Document9 pagesAnalogue Sensors On The Raspberry Pi Using An MCP3008Tatenda BizureNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Disaster ManagementDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Disaster ManagementMashrufa HussainNo ratings yet
- Mode06 SIEMENS655 d27LDocument15 pagesMode06 SIEMENS655 d27LAngel CastNo ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin With GSM and Arduino ModuleDocument2 pagesSmart Dustbin With GSM and Arduino ModuleirfanNo ratings yet
- Paper481774 1776 PDFDocument4 pagesPaper481774 1776 PDFPavan Murali ManoharaNo ratings yet
- Hexoskin Patent PDFDocument34 pagesHexoskin Patent PDFSayantan RahaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Leak DetectionDocument4 pagesFuel Leak Detectionocduran42004No ratings yet
- C&I - TSI System For Steam TurbineDocument42 pagesC&I - TSI System For Steam TurbineThanh Son100% (2)
- AQUA24A3D ReginDocument2 pagesAQUA24A3D ReginLeed ENNo ratings yet
- CDG 6000Document31 pagesCDG 6000Alex AlexNo ratings yet
- CondutivimetroDocument108 pagesCondutivimetroTalles CursoNo ratings yet
- DHB - 99904-01-02 LICCON2 PDFDocument75 pagesDHB - 99904-01-02 LICCON2 PDFMgc Elektronik100% (2)
- Simodrive Sensor User Manual Absolute Value Encoder With ProDocument62 pagesSimodrive Sensor User Manual Absolute Value Encoder With ProtamanogNo ratings yet
- FlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoPod DL14 DL24 DL34 ManualDocument29 pagesFlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoPod DL14 DL24 DL34 ManualPromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Arduino and Iot Based Solar Irrigation SystemDocument27 pagesArduino and Iot Based Solar Irrigation SystemrudraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - For - Load - Cell - Weight - Sensor 50KG PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial - For - Load - Cell - Weight - Sensor 50KG PDFanon_509738968No ratings yet
- Automatic Rain-Sensing Wiper System For 4-Wheeler Vehicles: December 2015Document6 pagesAutomatic Rain-Sensing Wiper System For 4-Wheeler Vehicles: December 2015Sameer KumthekarNo ratings yet
- Nice BuildingDocument43 pagesNice Buildinghak2310No ratings yet
- Ds F SimulatorDocument4 pagesDs F SimulatorLuiza OcheanaNo ratings yet
- Atmos Wave AWAS-6: 3 Channel, High-Speed, High-Resolution, Pressure Data Acquisition UnitDocument4 pagesAtmos Wave AWAS-6: 3 Channel, High-Speed, High-Resolution, Pressure Data Acquisition Unitait.koufiNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Emiliano Schena, Giulia Lupi, Stefano Cecchini, Sergio SilvestriDocument8 pagesMeasurement: Emiliano Schena, Giulia Lupi, Stefano Cecchini, Sergio SilvestrizertNo ratings yet
- Andritz Krauss-Maffei HZ Peeler CentrifugeDocument16 pagesAndritz Krauss-Maffei HZ Peeler Centrifugetarek555No ratings yet