Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamental of VoIP
Uploaded by
musharrafalamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamental of VoIP
Uploaded by
musharrafalamCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamental of VoIP
Muhammad Fayzan Siddiqui
Bahria university Karachi
Asad Ahmed Singani
Bahria university Karachi
Abstract
3. Types of Switching
Voice Over internet protocol is a technique in which
ordinary voice signals are converted to packets and There are two type of switching
send over IP networks. VoIP is very cheap way to
transfer voice over a long distance. In 1995 Vocal Tec 3.1. Circuit Switching:
Company of Israel started Internet telephone software
as “Internet Phone Since then in just four year it has In circuit switching there is a dedicated communication
grown very rapidly. In modern era the VOIP is being path between two stations. There are three phases call
used to rout the international calls. establishment, maintenance and termination. In circuit
switching there must have switching capacity and
Keywords: VOIP, Voice Over Internet Protocol, channel capacity to establish connection.
Packets, Switching, Gateways.
3.2. Packet Switching:
1. Introduction:
In packer switching, single node to node link can be
VoIP is sometimes referred to as Internet telephony; it shared by many packets over time. Packets are accepted
is a method of digitizing voice, into packets. Headers even when network is busy. Packets are handled in two
are added to the packets and transmitting those packets ways virtual circuit and datagram.
over a packet switched IP network. [2]
“Fig1.1 Rough Conceptualization of VoIP”
2. Internet Protocol:
IP itself is a connectionless protocol that resides at
Layer 3 (the network layer)
It is unreliable. Other protocols, such as TCP, can sit on
“Fig 1.2 Circuits vs. Packets”
top of IP (Layer 4, session) and can add flow control, Source: Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
sequencing, and other features. introduction”, OfCom
Protocols split transmitted data into packets, add
necessary addressing information to the packets and
transmit them and assemble again data in receiving end. 4. Overview of PSTN:
[3]
The telephone infrastructure starts with a simple pair of
copper wires running to the subscriber, known as a local
loop. The local loop physically connects subscriber • Call forwarding—Enables a subscriber to forward
telephone to the central office switch or exchange. incoming calls to a different destination.
The communication path between several central office
switches is known as a trunk. (e.g. E1, T1) • Three-way calling—Enables conference calling.
Switches are currently deployed in hierarchies. End
office switches (or central office switches) interconnect With the deployment of the SS7 network, advanced
through trunks to tandem switches (also referred to as features can now be carried end to end. A few of
Class 4 switches). Higher-layer tandem switches the CLASS features are mentioned in the following
connect local tandem switches. list:
Central office switches often directly connect to each
• Display—Displays the calling party's directory
other. Where the direct connections occur between
number, or Automatic Number Identification
central office switches depends to a great extent on call
(ANI).
patterns. If enough traffic occurs between two central
office switches, a dedicated circuit is placed between • Call blocking—Blocks specific incoming numbers
the two switches to offload those calls from the local so that callers are greeted with a message saying
tandem switches. Some portions of the PSTN use as the call is not accepted.
many as five levels of switching hierarchy. [1]
• Calling line ID blocking—Blocks the outgoing
directory number from being shown on someone
else's display. (This does not work when calling
800-numbers or certain other numbers.)
• Automatic callback—enables you to put a hold on
the last number dialed if a busy signal is received,
and then place the call after the line is free.
• Call return (*69)—Enables users to quickly reply
to missed calls. [1]
“Fig1.3. PSTN—Traditional VoIP” 7. Drawbacks to the PSTN:
Source: Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
introduction”, OfCom
Although the PSTN is effective and does a good job at
what it was built to do (that is, switch voice calls), many
5. PSTN Signaling: business drivers are striving to change it to a new
network, whereby voice is an application on top of a
Generally, two types of signaling methods run over data network. This is happening for several reasons:
various transmission media. The signaling methods are • Data has overtaken voice as the primary traffic
broken into the two groups: on many networks built for voice.
• User-to-network signaling— this is how an end user
• The PSTN cannot create and deploy features
communicates with the PSTN.
quickly enough.
• Network-to-network signaling— this is generally how
the switches in the PSTN intercommunicate. • Data/Voice/Video (D/V/V) cannot converge on
Network-to-network signaling also uses an out-of-band the PSTN as currently built.
signaling method known as Signaling System 7 (SS7)
(or C7 in European countries). [1] • The architecture built for voice is not flexible
enough to carry data. [1]
6. PSTN Services and Applications:
8. VoIP Technical Description:
The popular custom calling features commonly found in
the PSTN today:
• Call waiting—Notifies customers who already Figure 1.5 shows a simplified block diagram of VoIP
placed a call that they are receiving an incoming operation from an analog signal deriving from a
call. standard telephone, which is digitized and transmitted
over the Internet via a conversion device. Then, at the
distant end, it is converted back to analog telephony “Fig1.5. PC-to-PC VoIP”
using a similar device suitable for input to a standard Source: Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
telephone. The gateway is placed between the voice introduction”, OfCom
codec and the digital data transport circuit. An identical
device will also be found at the far end of the link. This 9.2. Phone-to-Phone:
equipment carries out the signaling role on a telephone
call among other functions. If the traditional telephone is use it will connect to an
Moving from left to right in Figure 1.5, we have the Analogue Telephone Adapter (ATA) or use an IP
spurty analog signal deriving from a standard telephone phone. The called party may be another VoIP user or,
set. The signal is then converted to a digital counterpart via a gateway, a traditional PSTN customer. [6]
using one of seven or so codecs [coder-decoder(s)] that
the VoIP system designer has to select from.
The binary output of the codec is then applied to a
conversion device (i.e., a “packetizer”) that loads these
binary 1s and 0s into an IP payload of from 20 to 40
octets in length.
The output of the converter consists of IP packets1 that
are transmitted on the web or other data circuit for
delivery to the distant end.
At the far end the IP packets or frames are input to a
converter (i.e., depacketizer) that strips off the IP
header, stores the payload, and then releases it in a “Fig1.6. Phone-to-Phone VoIP”
constant bit stream to a codec (i.e., a D–A converter). Source: Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
Of course this codec must be compatible with its near- introduction”, OfCom
end counterpart. The codec converts the digital bit
stream back to an analog signal that is then input to a 10. VoIP in PSTN:
standard telephone subset. [2]
Many traditional PSTN calls are carried as VoIP in part,
for efficiency reasons they may travel with other IP
traffic. These calls are different from other VoIP calls.
It is invisible to end customer. The private IP network is
used instead of internet cloud to control quality. [6]
“Fig1.4. Conceptualization of VoIP”
9. VoIP Calls:
Types of VoIP calls
9.1. PC-to-PC:
Software install on the machine (PC) allows voice “Fig1.7. VoIP in the PSTN”
“calls” from one PC to another. It enables voice to Source: Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
convert into IP packets at PC. [6] introduction”, OfCom
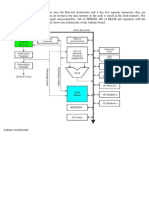
11. Function of Gateway:
Gateway
MGCP is an implementation of the Media Gateway
Control Protocols architecture for controlling Media
Internet Gateways on Internet protocols networks and the public
PSTN switched telephone network. MGCP is a signaling and
call control protocol used within VoIP systems that
typically interoperate with the public switched
telephone network. Media Gateway Control Protocol is
“Fig1.8. Concept of Gateway” used between elements of a decomposed multimedia
Source: Roger L. Freemen, “Fundamentals of gateway which consists of a Call Agent, which contains
Telecommunication, IEEE press, the call control "intelligence", and a media gateway
which contains the media functions, e.g., conversion
Gateway is a server; it may also be called a media from TDM voice to Voice over IP. [4]
gateway. It is the bridge of Internet and PSTN to
connect. For PSTN the Gateway has the interface 12.2. Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions:
of telephone net. (e.g. E1 (2048 kb/s)), and for
Internet side, Gateway has network interface (E.g.
MIME is a specification for enhancing the capabilities
Ethernet interface). Through the cooperation of
of standard Internet electronic mail. It offers a simple
hardware and software, realize between" Circuit
standardized way to represent and encode a wide variety
switch" and "Packet switch" voice coding form
of media types for transmission via Internet mail.
change mutually.
The MIME standard contains the following types of
Media gateways are part of the physical transport
messages:
layer. They are controlled by a call control function
• Text messages in US-ASCII
housed in a media gateway controller. It supports
• Character sets other than US-ASCII.
several types of access networks including media
• Multi-media: Image, Audio, and Video
such as copper, fiber, radio, and CATV cable. [2]
messages.
• Multiple objects in a single message.
12. VoIP Protocols: • Multi-font messages.
• Messages of unlimited length.
Protocols are set of rules determining the format • Binary files. [4]
and transmission of data, so protocols will
determine that what will be the format of the data 12.3. Remote VoIP:
and how will be data transmitted. [4]
The most common VoIP protocols used are: Remote Voice Protocol (RVP) is MCK (McKesson
1. Megaco H.248 Corporation) Communications' protocol for transporting
2. MGCP digital telephony sessions over packet or circuit based
3. Media Gateway Control Protocol data networks. The protocol is used primarily in Mack’s
4. MIME Extender product family, which extends PBX services
5. RVP over IP over Wide Area Networks (WANs).
6. Remote Voice Protocol Over IP Specification RVP/IP uses TCP to transport signaling and control
7. SAPv2 data, and UDP to transport voice data. Control and
8. Session Announcement Protocol signaling packets carried over TCP are encapsulated
9. SDP using the following format; a header followed by
10. Session Description Protocol signaling or control messages: [4]
11. SGCP
12. Simple Gateway Control Protocol
13. SIP
14. Session Initiation Protocol
15. Skinny
16. Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP)
17. Gateway Control Protocol
12.1. Media Gateway Control Protocol:
“Fig1.9. RVP over IP packet structure”
• Benefits of Voice over IP (VoIP), including
12.4. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): cost savings, single infrastructure savings, and
new applications
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application layer • Using a packet telephony call center versus a
control simple signaling protocol for VoIP circuit-switched call center
implementations using the Redirect Mode. SIP is a
textual client-server base protocol and provides the • Service provider prepaid calling card
necessary protocol mechanisms so that the end user applications
systems and proxy servers can provide different • Service provider enhanced services (such as
services. Internet call waiting and click to talk) [2]
Call forwarding in several scenarios: no answer, busy,
unconditional, address manipulations (as 700, 800, and
900- type calls). 14. VoIP in Pakistan:
Called and calling number identification
Personal mobility, caller and called authentication,
Voice over IP is nothing new in Pakistan from - VOIP
invitations to multicast conference, basic Automatic
has played an important role for people to stay close to
Call Distribution (ACD).
those who are far away from them. In the current times
SIP supports five distinct features of establishing and
when life is becoming more mobile, keeping oneself
terminating multimedia communications: User location,
attached to PC, is very cumbersome and the increasing
User capabilities, User availability, and Call setup, Call
power crises in the country makes it more difficult to
handling. [4]
use it.
Here comes VOIP on mobile, supported by SKYPE and
12.5. T.38 Fring. FRING is free software which supports to use
SKYPE with ease, just register once and you can talk
The T.38 IP-based fax service maps the T.30 fax away any where you are - all you need is a supporting
protocol onto an IP network. Both fax and voiced data cell phone and data cable connection.
are managed through a single gateway. T.38 uses 2 Fring is versatile, it’s not limited only to high end
protocols, one for UDP packets and one for TCP phones, from Nokia 1680 to Nokia N97, from Symbian
packets. Data is encoded using ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax to UIQ to Windows Mobile and iPhone, and it works on
Notation One) to ensure a standard technique every kind of cell phones effortlessly. There are a lot of
It allows users to transfer facsimile documents between advantages of VOIP, as international phone calls from
2 standard fax terminals over the Internet or other Pakistan is almost free but here is a need to pay charges
network using IP protocols. [4] for calling to Pakistan. With Mobile VOIP, a
businessman can have his worldwide associates call him
12.6 The Real-time Transport: over on his SKYPE id whether he is in office or
lounging at home, a family can talk away via speaker
phone with their loved ones abroad even if the lights are
The Real-time Transport (RTP) Protocol provides end-
out, those concerned with security can sleep easy, it’s
to-end network transport functions suitable for
rumored that only NASA has the technology to listen
applications transmitting real-time data such as audio,
over SKYPE and that too will take much of their
video or simulation data, over multicast (the delivery of
precious super computer time to hack into the
information to a group of destinations simultaneously)
conversation. [5]
or unicast (the sending of information packets to a
single network destination.) network services.
RTP does not address resource reservation and does not 15. REFRENCES
guarantee quality-of-service for real-time services. The
data transport is augmented by a control protocol “Real [1] Jonathan Davidson, James peter “Voice over IP
Time Transport Control Protocol” to allow monitoring Fundamentals”, Cisco press release, USA, 2000
[2] Roger L. Freemen, “Fundamentals of Telecommunication,
of the data delivery. [4]
IEEE press, Canada, 2005
[3] www.wikepedia.com
13. Voice over IP Benefits and Applications: [4] www.protocols.com
[5] www.propakistan.com
[6] Peter Ingram, “Voice over Internet Protocol- An
introduction”, OfCom, 18th January 2005
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Arduino ArchitectureDocument3 pagesArduino Architecturejisskuruvilla100% (1)
- Oracle Data IntegratorDocument4 pagesOracle Data IntegratorGert WuytsNo ratings yet
- 2PAA103676 H en Compact Control Builder Course T530 - ConfigurationDocument2 pages2PAA103676 H en Compact Control Builder Course T530 - ConfigurationAkoKhalediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Ethernet: CCNA Exploration 4.0Document90 pagesChapter 9 - Ethernet: CCNA Exploration 4.0kiennaNo ratings yet
- ISP Busniess PlanDocument65 pagesISP Busniess PlanRaheel ZararNo ratings yet
- BMC Mobile Device Management: Flexible DeliveryDocument4 pagesBMC Mobile Device Management: Flexible DeliveryTHAN HANNo ratings yet
- Software - Back Office - DocuPRODocument2 pagesSoftware - Back Office - DocuPROMatias Nicolas ParraNo ratings yet
- Blue Prism User Guide - Web ServicesDocument2 pagesBlue Prism User Guide - Web Servicesreddy_vemula_praveenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Free SoftwareDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Free Softwaretomsds5310No ratings yet
- LTE Frequency Planning V2.0Document25 pagesLTE Frequency Planning V2.0pepilve100% (2)
- OBIEE 11G Logs and Configuration Files - ReferenceDocument7 pagesOBIEE 11G Logs and Configuration Files - Referencejoselara19No ratings yet
- CCNA Guide To Networking - Ch1 - Quiz SolutionsDocument5 pagesCCNA Guide To Networking - Ch1 - Quiz SolutionsNickHenryNo ratings yet
- MsfpayloadDocument14 pagesMsfpayloadfrogman1001No ratings yet
- Test Strategy: For Home Page Hotincontri - ItDocument6 pagesTest Strategy: For Home Page Hotincontri - ItAleksandar BrandicNo ratings yet
- Beep Code Manual PDFDocument4 pagesBeep Code Manual PDFDelte XUndeadNo ratings yet
- Sergiu-Adrian Dumitrescu: Mobile Phone: EmailDocument3 pagesSergiu-Adrian Dumitrescu: Mobile Phone: EmailSergiu DecauronNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial PDFDocument9 pagesCadence Tutorial PDFerdvkNo ratings yet
- IP770 Mau enDocument47 pagesIP770 Mau enpuregold916No ratings yet
- RoheDocument2 pagesRoheDebajyoti DattaNo ratings yet
- Itu-T Q.1912.5 P020100707552040138128Document114 pagesItu-T Q.1912.5 P020100707552040138128oneronerdNo ratings yet
- SpeakingDocument420 pagesSpeakinganon_254355400No ratings yet
- Net2-2-Network ភាសាខ្មែរDocument155 pagesNet2-2-Network ភាសាខ្មែរSambath MuchNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument15 pagesTable of ContentNarinderjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Konsep Kanal Fisik Dan Logik Pada GSMDocument34 pagesKonsep Kanal Fisik Dan Logik Pada GSMNahlaDewiSNo ratings yet
- BT0068 IndexDocument5 pagesBT0068 IndexJitendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Smart Door Lock SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Door Lock SystemRahul RajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- ALOHADocument26 pagesALOHApranay639No ratings yet
- DIGITUS ds-43300 - HDMI Video Splıter User - ManualDocument6 pagesDIGITUS ds-43300 - HDMI Video Splıter User - ManualEjder İNCENo ratings yet
- 3000E Operating ManualDocument550 pages3000E Operating ManualBrian Ferree100% (5)
- MalwareDocument23 pagesMalwareasddsaqweNo ratings yet