Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sliding Friction
Uploaded by
Iqbal JafarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sliding Friction
Uploaded by
Iqbal JafarCopyright:
Available Formats
BFM 2821 Mechanics Laboratory
Title 3. Block moved quickly as static friction
was overcome.
To verify the sliding friction 4. Result recorded.
Test 3:
Theoretical Fundamental 1. Block turned into its narrow side.
2. Test 1 repeated and result recorded.
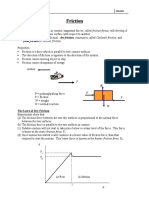
1. Friction is the force resisting the
relative motion of the solid surface, Test 4:
fluid layers and or material elements
sliding against each other. 1. Friction block is placed in its initial
2. When surfaces in contact move position as for test 1.
relative each other, the friction 2. Load 0.5,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0 (N) was added
between two surface converts kinetic on top of the block and the equivalent
energy into heat. One common forces to overcome was determined.
example for this situation happen 3. Result recorded.
when friction is use to start fire.
3. Different surfaces have different Test 5:
resistance. For example, it depends on
what type the two surface slides on, 1. Friction plate was placed on the plane
such as rubber has higher resistance between stops.
compare to shiny metal due to their 2. Friction block was turned upside
characteristics. down.
3. Test 4 repeated and result recorded.
Experimental set-up
Test 6:
1. Friction plate was turned over to
obtain the metal to rubber contact.
2. Load is placed on the hook to obtain
constant speed on the friction block.
3. Test 4 repeated and results recorded.
Result
Weight of friction block = 1.8 N
Weight of hook = 0.2 N
Experiments Procedures Total Weight 1 = Weight of hook + Weight
applied
Test 1:
Total Weight 2, R = Weight of block + Weight
1. Weight was placed on the hook. on the top block
2. The block was pushed, until it was
able to move due to the load applied.
3. Result recorded.
Test 2:
1. Test 1 was repeated without pushing
the block.
2. Weight was placed on the hook until
the block move.
Universiti Malaysia Pahang Page 1
BFM 2821 Mechanics Laboratory
Test 1: Test 4:
Weight Total Weight
Friction weight Weight added Total weight
applied Weight 1 Push placed on peg
movement on hook (N) 2, R (N)
(g) (N) (N)
5 0.25 Yes Not moving 0.5 0.6 2.3
10 0.30 Yes Not moving 1.0 0.8 2.8
20 0.40 Yes Not moving 2.0 0.8 3.8
Moving with 3.0 0.8 4.8
30 0.50 Yes
uniform speed 4.0 0.8 5.8
Moving with
40 0.60 Yes
fast
Moving with
50 0.70 No
faster
Test 2:
Friction
Weight Total weight 1
weight
applied (g) (N)
movement
5 0.25 Not moving
10 0.30 Not moving
20 0.40 Not moving
30 0.50 Not moving
40 0.60 Moving fast
50 0.70 Moving faster
Test 3:
Side 1 Side 2
Test 5:
Weight Total
applied Weight 1 Friction Friction Weight
(g) (N) weight weight Weight added Total weight
Push
movemen
Push
movem placed on peg
on hook (N) 2, R (N)
t ent (N)
Not Not 0.5 0.05 2.3
5 Yes Yes
moving moving
Not Not 1.0 0.05 2.8
10 Yes Yes
moving moving 2.0 0.05 3.8
Not Not
20 Yes
moving
Yes
moving 3.0 0.05 4.8
Moving
Moving 4.0 0.05 5.8
slow
slow with
25 Yes Yes with
uniform
uniform
speed
speed
Moving Moving
faster faster
30 No No
with with
speed speed
Moving Moving
fastest fastest
40 No No
with with
speed speed
Universiti Malaysia Pahang Page 2
BFM 2821 Mechanics Laboratory
Coefficient of friction is too small to calculate. Law 4:
Assume coefficient of friction, µ = 0
Wihtin rather large limits, kinetic friction is
independent if velocity.
Law 5:
Friction depends upon the nature of the surface
Test 6:
in contact.
Weight
Weight added Total weight (2)
placed on peg
on hook (N) 2, R (N)
(N) Friction is affected by the area of the
0.5 0.9 2.3 contact between two surfaces because
1.0 0.9 2.8 of the normal forces available on the
2.0 0.9 3.8 object and the roughness of those
3.0 0.9 4.8 surfaces.
4.0 0.1 5.8
(3)
For low surface pressure the friction is
directly proportional to the pressure
between the surfaces. As the pressure
rises the friction factor rises slightly. A
very high pressure the friction factor
then quickly increases to seizing.
2. When two bodies in contact move with
respect with each other, rubbing the
surfaces in contact the friction between
them is called kinetic friction. The
direction of frictional forces such that
is opposes the relative motion. Friction
forces can also act between two bodies
Discussion which are in contact but not moving or
sliding with respect to each other. The
1. friction in such case is static friction.
(1)
3. The advantages of friction are that may
Law 1: help in walking and braking system.
The drawback of friction is it may
When object is moving, the friction is make movement more difficult if it is
proportional and perpendicular to the normal too high and may waste energy.
force.
Law 2: Conclusion
Friction is dependent of the area of contact so The higher the friction, more force is needed to
long as there is an area of contact. move an object. Pressure is one of the factors
that affect the friction.
Law 3:
The coefficient of static friction is slightly
greater than the coefficient of kinetic friction.
Universiti Malaysia Pahang Page 3
You might also like
- Physics Friction LabDocument3 pagesPhysics Friction LabDave Darrin0% (1)
- FrictionDocument14 pagesFrictionReincarnation Anukriti Nandan50% (6)
- Static and Kinetic Friction: ComputerDocument6 pagesStatic and Kinetic Friction: ComputerbobpleaseNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum Lab Report-2Document10 pagesConservation of Momentum Lab Report-2api-35896745350% (2)
- Physics 1301w Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesPhysics 1301w Laboratory Reportmt9260No ratings yet
- Worksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Document9 pagesWorksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Joshua DellosaNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 Experiment (Question and Answer)Document64 pagesPhysics Paper 3 Experiment (Question and Answer)Azman SelamatNo ratings yet
- Co-Efficient of Static FrictionDocument9 pagesCo-Efficient of Static Frictionatul_gangwar0% (1)
- FrictionDocument8 pagesFrictiontoxicjjNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument92 pagesFrictionstallone21No ratings yet
- Forces and Friction Investigation LabDocument11 pagesForces and Friction Investigation LabMichael Mohamed75% (4)
- Exp. 6, Theory Rigid Body EquilibriumDocument4 pagesExp. 6, Theory Rigid Body Equilibriumdayangmyra100% (2)
- Intro to Lab Safety TrainingDocument20 pagesIntro to Lab Safety TrainingAkhil AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Friction Lab ReportDocument10 pagesFriction Lab ReportMohammed Islam100% (3)
- Chapter2 PlasticityDocument34 pagesChapter2 PlasticityGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- PHY10L - Resolution of ForcesDocument14 pagesPHY10L - Resolution of Forcesdenzel94No ratings yet
- 5 4 Friction Lab Write-UpDocument9 pages5 4 Friction Lab Write-Upapi-385003483No ratings yet
- Static vs Kinetic FrictionDocument15 pagesStatic vs Kinetic FrictionWirote DewilaiNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Verification ExperimentDocument19 pagesHooke's Law Verification ExperimentWan Afiff100% (1)
- Engg - Mech Lab Manual 2017 18Document28 pagesEngg - Mech Lab Manual 2017 18Girish ShindeNo ratings yet
- Project Fluid MechanicsDocument8 pagesProject Fluid MechanicsSyed Izzat Hussain AlHussainiNo ratings yet
- Som 2013 - 001 PDFDocument431 pagesSom 2013 - 001 PDFKumar SamreshNo ratings yet
- Unit and Measurements Physics LabDocument12 pagesUnit and Measurements Physics LabiganNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering 8Document48 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering 8Fish ShuangNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab:Coefficient of Linear ExpansionNatalie Sherwood100% (1)
- Matriculation Physics (Alternating Current)Document93 pagesMatriculation Physics (Alternating Current)ridwan100% (2)
- Full Report Solid MechDocument19 pagesFull Report Solid MechMUHAMMAD ARIFF DYAMIMNo ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyDocument7 pagesPROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyEmily Watts100% (3)
- Electromagnetism Experiment Simulates DC & AC CircuitsDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism Experiment Simulates DC & AC Circuitsizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Machine Friction (Inclined Plane)Document4 pagesMechanic Machine Friction (Inclined Plane)limakupang_mat100% (1)
- Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesTamilManiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Elasticity and OscillationDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Elasticity and OscillationKenny Jay LabianoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy (2011)Document65 pagesNuclear Energy (2011)SonNguyenNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities Matriculation STPMDocument58 pagesPhysical Quantities Matriculation STPMJue Saadiah75% (4)
- Iction PDFDocument5 pagesIction PDFMd ImranNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Analysing Impulse & Impulsive ForceDocument12 pages2.6 Analysing Impulse & Impulsive ForceAisha Chunsha CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Lab Measuring Spring ConstantDocument6 pagesHooke's Law Lab Measuring Spring ConstantngwaNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' PrincipleDocument7 pagesArchimedes' PrincipleSharania Udhaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Newtons 2ndDocument3 pagesLab Newtons 2ndUgur ASİT50% (2)
- Lecture 5 Equillibrium of ForcesDocument41 pagesLecture 5 Equillibrium of ForcesAwais Ahmed MirzaNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument6 pagesArchimedes PrincipleRakshit Gupta100% (2)
- Lab - Coefficient of Static and Kinetic FrictionDocument1 pageLab - Coefficient of Static and Kinetic Frictionascd_msvu100% (1)
- EXPERIMENTAL BEAMSDocument10 pagesEXPERIMENTAL BEAMSNurul NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Formal Lab Report - Work and EnergyDocument4 pagesFormal Lab Report - Work and Energyapi-270086937No ratings yet
- Module BDA27301 StaticsDocument39 pagesModule BDA27301 StaticsZarul IkramNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On FrictionDocument10 pagesLab Report On FrictionUnnati VinayakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesHeather LaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocument62 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsAzrul NizarNo ratings yet
- Momentum QPDocument6 pagesMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Friction Experiment Finds Surface Material Affects CoefficientDocument8 pagesKinetic Friction Experiment Finds Surface Material Affects Coefficientkate anne del castroNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Young ModulusDocument9 pagesExp 1 Young ModulusNgYuMeiNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Centre of GravityDocument10 pagesLab1 Centre of GravityJoko MrNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Gas Law: Bicol University College of Science Legazpi CityDocument4 pagesThe Ideal Gas Law: Bicol University College of Science Legazpi Citylemor arevanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Linear Momentum - Lecturer-1Document11 pagesChapter 6 Linear Momentum - Lecturer-1Wahizah WahidNo ratings yet
- CH 5-2 Free-Body DiagramsDocument7 pagesCH 5-2 Free-Body DiagramssunliasNo ratings yet
- (LAB 9) FrictionDocument9 pages(LAB 9) FrictionMuhammad ShadzrinNo ratings yet
- Lovino B9 Report1 PHYS101LDocument8 pagesLovino B9 Report1 PHYS101LJulia LovinoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 (A) : Moment of Force Experiment 1 (B) : Study of EquilibriumDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 (A) : Moment of Force Experiment 1 (B) : Study of EquilibriumMohd Khobir Yahya AzmiNo ratings yet
- E104 Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument5 pagesE104 Newton's Second Law of MotionKenneth Llantos100% (3)
- Does Mass Affect Gravitational ForceDocument2 pagesDoes Mass Affect Gravitational ForceuihuihNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Drive SystemDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Drive SystemIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- W6ZGXSDocument6 pagesW6ZGXSIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Pumps and ValvesDocument28 pagesHydraulic Pumps and ValvesIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- ActuatorsDocument22 pagesActuatorsIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- Cuti 2Document4 pagesCuti 2Iqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document2 pagesLab 3Iqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document2 pagesLab 2Iqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- BFM2821 Mechanics Laboratory ReportDocument6 pagesBFM2821 Mechanics Laboratory ReportIqbal Jafar75% (4)
- MultivibratorDocument1 pageMultivibratorIqbal JafarNo ratings yet
- Triangle of ForcesDocument4 pagesTriangle of ForcesIqbal Jafar67% (6)
- Calender HijriDocument13 pagesCalender HijriIqbal Jafar100% (1)
- Conventions Applicable To Electrochemical Measurements in Corrosion TestingDocument9 pagesConventions Applicable To Electrochemical Measurements in Corrosion TestingالGINIRAL FREE FIRENo ratings yet
- Intro To ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesIntro To ThermodynamicsOmer IqbalNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2Yi-Chun LingNo ratings yet
- Omron E5 JDocument69 pagesOmron E5 JVoneisisoNo ratings yet
- Developing an Electromagnetic Energy Regenerative Suspension Test RigDocument25 pagesDeveloping an Electromagnetic Energy Regenerative Suspension Test RigPoonam MankarNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalação Samsung FJM Duto SlimDocument16 pagesManual de Instalação Samsung FJM Duto SlimRobson FreitasNo ratings yet
- Experiment#6 DC Circuit Analysis: Electrical Circuits Lab 0905212Document13 pagesExperiment#6 DC Circuit Analysis: Electrical Circuits Lab 0905212aliyahNo ratings yet
- System Converts High Frequency EMF to Electrical EnergyDocument15 pagesSystem Converts High Frequency EMF to Electrical EnergyFabrice BresilNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Gravitation SS2Document6 pagesNewtons Law of Gravitation SS2Nwoye ChinenyeNo ratings yet
- MATERIALSandMECHANICSmanual CycleiDocument28 pagesMATERIALSandMECHANICSmanual CycleiSrichandNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Module 2Document20 pagesGenPhysics2 Module 2I can see your pixels 2No ratings yet
- Wakata Mock UCE Phy 2Document4 pagesWakata Mock UCE Phy 2Alex BukenyaNo ratings yet
- Technical Particular and Guarantee: Pt. Prima Indah LestariDocument2 pagesTechnical Particular and Guarantee: Pt. Prima Indah Lestaritees220510No ratings yet
- NRS 097-2-1Document37 pagesNRS 097-2-1Ivor KrugerNo ratings yet
- Steam Cycle and Power Plant Thermal EfficiencyDocument20 pagesSteam Cycle and Power Plant Thermal EfficiencyMark Joseph Nambio NievaNo ratings yet
- Resistor Techniques Worksheet - Ahaguru Date 12.0819Document3 pagesResistor Techniques Worksheet - Ahaguru Date 12.0819AyurvaidyaNo ratings yet
- CAPE® Physics Past Papers Unit 1Document11 pagesCAPE® Physics Past Papers Unit 1AlexNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 633 6375Document262 pages10 1 1 633 6375Roberto GRNo ratings yet
- New BQ Proposal - 20230625Document13 pagesNew BQ Proposal - 20230625Ranu BayaNo ratings yet
- Boeing 757 Electrics - Battery - Standby Power SystemDocument4 pagesBoeing 757 Electrics - Battery - Standby Power SystemAnonymous mfgFBX9X100% (1)
- Radiation Coloring Page and Crossword With Key W8cmjeDocument4 pagesRadiation Coloring Page and Crossword With Key W8cmjerenneNo ratings yet
- Solving Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument4 pagesSolving Series and Parallel CircuitsLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test-3 CBSEDocument2 pagesMock Test-3 CBSEAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Radiation Fog With Tall VegetationDocument14 pagesInteraction of Radiation Fog With Tall VegetationMuhammad SyamNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Material and Their Magnetic Properties and Its ApplicationsDocument16 pagesCeramic Material and Their Magnetic Properties and Its Applicationsarindham chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- EMI Important Questions-1Document13 pagesEMI Important Questions-1SBU eduNo ratings yet
- Field Installation and IP 16-13-1 Testing of Electrical EquipmentDocument8 pagesField Installation and IP 16-13-1 Testing of Electrical EquipmentOrlando E Cabrera RojasNo ratings yet
- AN5004Document5 pagesAN5004rdc02271No ratings yet
- EN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForcesDocument6 pagesEN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForceskarthikaNo ratings yet
- RV Al - U-1000 AR2V Eng - Rev5 PDFDocument4 pagesRV Al - U-1000 AR2V Eng - Rev5 PDFjarias-solarpackNo ratings yet