Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finding Medical Information Online: Pubmed, Medline Plus, or Google Scholar
Uploaded by
rsinn1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finding Medical Information Online: Pubmed, Medline Plus, or Google Scholar
Uploaded by
rsinn1Copyright:
Available Formats
Finding Medical
Information Online
Pubmed, Medline Plus, or Google
Scholar
Susan Payne, Virtual Services Librarian
susan.payne@jhu.edu
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
How Big is the Internet?
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
How Big is the Internet?
Estimated 1,650,000,000 users
(over a billion and a half) in
2010, up from 16 million in
1995
More than 1 in every 5 people
in the world use the Internet
Google has processed more
than 1 trillion unique URLs on
the web at once
Information from: Michelle McLean
http://librariesinteract.info/2008/07/26/si
ze-of-the-internet-2008/
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Comparing Web Resources
• 99% of practicing US
physicians use the Internet,
and 95% use search engines to
identify medical information
• Understanding the search
features of each resource will
help you find information
efficiently
• When Google pointed users to
eMedicine, fewer steps were
required to reach an answer
compared to PubMed or journal
sites
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Overview
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Medline Plus
• Brings together
authoritative
information from the
NLM, NIH, and other
government agencies
• Includes information
about drugs, an
illustrated medical
encyclopedia,
interactive patient
tutorials and health
news
• Go local – discover local
services by state for
health-related issues
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Medline Plus
Preformulated MEDLINE searches are included in
MEDLINEplus and give easy access to the medical research
literature. It also provides you with a database of full-text drug
information and an illustrated medical encyclopedia. Includes:
• Medical encyclopedia, dictionary.
• Prescription & non-prescription drugs.
• Over 800 diseases & conditions.
• Interactive tutorials.
• Health information in Spanish.
Daily
Topical
None
Finding authoritative health information from
the National Library of Medicine written for consumers and the
general public
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Medline Plus: goLocal
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
PubMed
Provides
free access to the
Medline NLM
database of over
citations from
6000 journals.
Core clinical
journals in dental,
nursing,
biomedicine,
medicine, history
of medicine,
bioethics, space,
life sciences.
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
PubMed
• Search only for articles with links to full-text
• Search for types of articles, such as clinical studies,
reviews, clinical trials
• Limit studies by age or gender, as well as human or
animal
Growing number of citations contain a
link to free full-text of the article archived in PubMed
Central or link to other sites where the article may be
available for requesting electronically or purchasing.
Comprehensive searching of biomedical
literature
Ranks the most recent and relevant articles at
the top. Can be sorted by author, publication, date, or
journal.
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
PubMed
Links
to related
articles, links
to full-text,
links to free
full text
articles for a
subset of
open access
journals.
Daily
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
My NCBI
◦ Save Searches ◦ Set up filters
◦ Save Collections ◦ Send e-mail updates
◦ Save Bibliographies ◦ Run saved searches
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Creating & Sharing Collections
• From the search
results page, check
the box next to the
item number to save
• Then select
Collections from
the Send to pull-
down menu and
choose Add to
Collections.
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Search Alerts
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Google Scholar
• Search across
many disciplines
and sources: peer-
reviews papers,
theses, books,
abstracts, articles,
preprint
repositories and
more.
• Advanced Search
allows to limit by
subject area, date,
author, and
publication.
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Google Scholar
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Google Scholar vs PubMed
• Google Scholar covers most scientific fields
• PubMed has medicine and biomedical sciences as its primary focus
• Google has a “cited by” link next to each paper. Clicking on this link
shows the citation analysis
• Pubmed does not have citation analysis
• Google links to PubMed, OCLC First Search
• Pubmed covers Medline, old Medline, PubMed Central, and links to other
specialized NLM databases such as OMIM & GENSTAT.
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
Google Scholar vs PubMed
• Google Scholar updates monthly
• PubMed updates daily
• Google links to full-text articles, free full-text articles, links to related
articles, and links to libraries
• PubMed links to related articles, links to full-text (5426 journals), links to
free full text articles for 827 open access journals
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
What would the best source be for…
Finding an interactive tutorial on breast cancer?
© 2009 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
What would the best source be for…
Finding an encyclopedia article about levels of lead in
blood?
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
What would the best source be for…
Finding out how many times an
article has been cited?
Why cite?
• To establish intellectual context
• To avoid plagiarizing
• To give credit where credit is due
• Provides evidence supporting your
point-of-view and lends credibility to
your work by showing you sought out
a variety of viewpoints
• Is standard practice for scholars and
students
• To lead us in further research
TIP: Use My Bibliography in PubMed to track
your own publications © 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
What would the best source be for…
Finding a review article about
H1N1?
Information about asthma and
H1N1?
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
What to use?
© 2010 The Sheridan Libraries of
The Johns Hopkins University
You might also like
- Unit 2. Sources of LiteratureDocument21 pagesUnit 2. Sources of Literaturerajatsharma.sdsNo ratings yet
- Can'T Find The Item You Need?: Double Check Yorsearch Try Google Scholar Access Nhs ResourcesDocument1 pageCan'T Find The Item You Need?: Double Check Yorsearch Try Google Scholar Access Nhs ResourcesUniversity of York InformationNo ratings yet
- Literature Search & Referencing Style 21102022Document48 pagesLiterature Search & Referencing Style 21102022Jauharah Az ZahraNo ratings yet
- Research Guide Library Handout Aug2nd2016Document2 pagesResearch Guide Library Handout Aug2nd2016David WheelerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11. Computer Application That Supports Nursing ResearchDocument6 pagesLesson 11. Computer Application That Supports Nursing ResearchGroup 8 BSN 33No ratings yet
- Evidence Based Dentistry UAB School of Dentistry Fall 2010Document49 pagesEvidence Based Dentistry UAB School of Dentistry Fall 2010lorbeer7046No ratings yet
- Jennifer Lyon, MS, MLIS, AHIP - Supporting Clinical ResearchDocument22 pagesJennifer Lyon, MS, MLIS, AHIP - Supporting Clinical ResearchAMIANo ratings yet
- Nursing ResourcesDocument2 pagesNursing Resourcesdeltaspirit767No ratings yet
- Molla S. Donaldson, Editor The National Roundtable On Health Care Quality, Institute of MedicineDocument43 pagesMolla S. Donaldson, Editor The National Roundtable On Health Care Quality, Institute of MedicineZul Fahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Types of Drug Information Resources - EditedDocument122 pagesTypes of Drug Information Resources - EditedGammachuu Leejjiisa Mul'ataa SabbooqaaNo ratings yet
- Tools For Nursing Research & EBPDocument4 pagesTools For Nursing Research & EBPJbl2328No ratings yet
- Bioinformatics AssignmentDocument10 pagesBioinformatics AssignmentPriyanka KasturiaNo ratings yet
- Helbingcvjul 20 RedactedDocument14 pagesHelbingcvjul 20 Redactedapi-519866270No ratings yet
- University of Wisconsin Thesis LibraryDocument4 pagesUniversity of Wisconsin Thesis LibraryHeather Strinden100% (2)
- Biblographic DatabaseDocument14 pagesBiblographic DatabaseNandni JhaNo ratings yet
- drug resorce فكك منهDocument39 pagesdrug resorce فكك منهMohamed HussienNo ratings yet
- Cina HL: Kristy Padron, MlisDocument31 pagesCina HL: Kristy Padron, MlisPaul EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Sources Drug InfoDocument16 pagesSources Drug InfoAhmed ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Ijstd 35 85Document7 pagesIjstd 35 85Incubateur UmabNo ratings yet
- L5 Indexing Databases in ResearchDocument15 pagesL5 Indexing Databases in Researchrahulyadav.hbtiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Human Nutrition by Jim Mann, Stewart TruswellDocument716 pagesEssentials of Human Nutrition by Jim Mann, Stewart TruswellKFNo ratings yet
- PHIN211 Topic 3Document84 pagesPHIN211 Topic 3sherilleNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument17 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsJane Roxanne DichosaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Sciences An International Open-Access PDocument4 pagesBehavioral Sciences An International Open-Access Pkarin dhamaraniNo ratings yet
- Search StrategyDocument2 pagesSearch StrategySteven A'Baqr EgiliNo ratings yet
- K17 - (DR. Dr. Legiran, M.Kes) Pengembanga Iptekdok Melalui Studi Pustaka Dan PenelitianDocument37 pagesK17 - (DR. Dr. Legiran, M.Kes) Pengembanga Iptekdok Melalui Studi Pustaka Dan PenelitianAkbar SandyNo ratings yet
- 5.1-Types of Drug Information ResourcesDocument115 pages5.1-Types of Drug Information Resourcesaklilu YebuzeyeNo ratings yet
- PubMedFinal_revised_2Document2 pagesPubMedFinal_revised_2The Penitent OneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Reseach LectureDocument19 pagesNursing Reseach LectureAyanne ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Information Literacy and Research Methods For The OMM Case ReportDocument14 pagesInformation Literacy and Research Methods For The OMM Case ReportSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Students Guide to Internet ResourcesDocument8 pagesNursing Students Guide to Internet ResourcesANGELICA MACASONo ratings yet
- Review of Literature SourcesDocument35 pagesReview of Literature SourcesSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Reviewing The Literature: Choosing A Review Design: Evidence-Based Nursing March 2018Document8 pagesReviewing The Literature: Choosing A Review Design: Evidence-Based Nursing March 2018waldemar russellNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust PDFDocument291 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust PDFpierdevaloisNo ratings yet
- The Intersection: Where Evidence Based Nursing and Information Literacy MeetFrom EverandThe Intersection: Where Evidence Based Nursing and Information Literacy MeetSue PhelpsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Productivity in Medical Education Research: An Examination of Countries of OriginDocument10 pagesProductivity in Medical Education Research: An Examination of Countries of OriginNikole Stefania Vasquez RamirezNo ratings yet
- ContraceptiveDocument535 pagesContraceptiveamyrleaxxNo ratings yet
- Strategic Collaborations in Health Sciences LibrariesFrom EverandStrategic Collaborations in Health Sciences LibrariesJean P. ShipmanNo ratings yet
- Journals & Databases - Pharmacology and Toxicology - LibGuides at University of OtagoDocument1 pageJournals & Databases - Pharmacology and Toxicology - LibGuides at University of OtagoSuryakantaRoulTuntunNo ratings yet
- Redesigning The Clinical Effectiveness ResearchDocument443 pagesRedesigning The Clinical Effectiveness ResearchbabyetchelNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Reliable Search Engines and Databases That Is Applicable in Nursing Research? Explain Comprehensively The ComponentsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Reliable Search Engines and Databases That Is Applicable in Nursing Research? Explain Comprehensively The ComponentsMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Health LiteracyDocument367 pagesHealth LiteracyRizma Adlia100% (1)
- Download ebook Cohens Pathways Of The Pulp Expert Consult Pdf full chapter pdfDocument55 pagesDownload ebook Cohens Pathways Of The Pulp Expert Consult Pdf full chapter pdfchristopher.jenkins207100% (18)
- Welcome To Evansdale Library!: Noël Kopriva Agriculture, Natural Resources, & Design Librarian 304.293.9747Document8 pagesWelcome To Evansdale Library!: Noël Kopriva Agriculture, Natural Resources, & Design Librarian 304.293.9747nokoprivaNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Cohens Pathways Of The Pulp 12Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Cohens Pathways Of The Pulp 12Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfchristopher.jenkins207100% (24)
- E-Resources in Health Sciences: by Sukhdev SinghDocument95 pagesE-Resources in Health Sciences: by Sukhdev Singhade_liaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Websites For Education and ResearchDocument4 pagesTop 10 Websites For Education and ResearchManimala ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Drug Informatics Lecture 3: Effective Searching, Retrieving and Critically Evaluating Literature PHR3100Document23 pagesDrug Informatics Lecture 3: Effective Searching, Retrieving and Critically Evaluating Literature PHR3100Ahmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Rol 2Document32 pagesRol 2Stephina ImmaculateNo ratings yet
- (Oxford Library of Psychology) Jonathan S. Comer, Philip C. Kendall-The Oxford Handbook of Research Strategies For Clinical Psychology-Oxford University Press (2013) PDFDocument476 pages(Oxford Library of Psychology) Jonathan S. Comer, Philip C. Kendall-The Oxford Handbook of Research Strategies For Clinical Psychology-Oxford University Press (2013) PDFAna Rita Serra100% (3)
- Making PubMed Searching SimpleDocument11 pagesMaking PubMed Searching SimpleGinna Paola Saavedra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Target Validity and The Hierarchy of Study Designs American Journal of Epidemiology Oxford AcademicDocument10 pagesTarget Validity and The Hierarchy of Study Designs American Journal of Epidemiology Oxford AcademicJorge BalbinNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Practice Fact SheetDocument3 pagesEvidence-Based Practice Fact Sheetmohamedwhatever100% (2)
- Thesis Titles For Veterinary MedicineDocument7 pagesThesis Titles For Veterinary MedicineHelpMeWriteMyEssayCambridge100% (2)
- IT 7 - InformationSources - MBADocument28 pagesIT 7 - InformationSources - MBADavi DzikirianNo ratings yet
- Sources of Information Used in Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesSources of Information Used in Literature Reviewaflsrxfoe100% (1)
- Order #844 - NursingKnowledgeDocument4 pagesOrder #844 - NursingKnowledgeVenus Marie Real-CatubayNo ratings yet
- EBM - Apply Evidence-Based Medicine To Search Article and MedicalDocument56 pagesEBM - Apply Evidence-Based Medicine To Search Article and MedicalkrisnadewirahadiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesDocument5 pagesComparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesMostafa AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Literature SearchingDocument19 pagesLiterature SearchingMuhammad Adzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- PIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsDocument3 pagesPIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsBob AdleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan The Child or Adolescent Hospitalized With DepressionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan The Child or Adolescent Hospitalized With DepressionVette Angelikka Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Health and Social Care in ContextDocument25 pagesHealth and Social Care in ContextJoshtine AngoluanNo ratings yet
- DWATCHDocument92 pagesDWATCHFawaz SayedNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Guidelines For Free Standing FP Clinic DOHDocument15 pagesGuidelines For Free Standing FP Clinic DOHAnthony Napalit TaneoNo ratings yet
- Public Health DirectoryDocument7 pagesPublic Health DirectoryAyobami OdewoleNo ratings yet
- CindyDocument4 pagesCindyUsama QayyumNo ratings yet
- All Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)Document3 pagesAll Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)matentenNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy and Seizure DisordersDocument38 pagesEpilepsy and Seizure DisordersMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Employee AbsenteeismDocument13 pagesEmployee AbsenteeismManuel KevogoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Neuropathic Pain: DR Tay Kwang Hui Dept of Anaesthesia, NUHS 8 Jan 2011Document37 pagesOverview of Neuropathic Pain: DR Tay Kwang Hui Dept of Anaesthesia, NUHS 8 Jan 2011CaioSelaimenNo ratings yet
- McIlwaine Et Al-2015-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument74 pagesMcIlwaine Et Al-2015-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviewsangelica barrazaNo ratings yet
- Meal Plan MenDocument35 pagesMeal Plan Menoddo_mneNo ratings yet
- Ethico-Legal Considerations in Conducting Health EducationDocument45 pagesEthico-Legal Considerations in Conducting Health EducationSherwyn Uy Hatab100% (1)
- Bentonite MSDSDocument3 pagesBentonite MSDSMohammed Ahmed NasherNo ratings yet
- IFFCO-TOKIO General Insurance claim formDocument4 pagesIFFCO-TOKIO General Insurance claim formRaju.PalNo ratings yet
- Rare Sigmoid Abdominal Wall Fistula After Appendectomy: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesRare Sigmoid Abdominal Wall Fistula After Appendectomy: A Case Reportjlcano1210No ratings yet
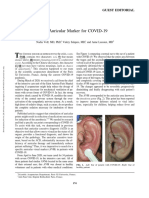
- An Auricular Marker For Covid-19: Nadia Volf, MD, PHD, Valery Salques, MD, and Anne Lassaux, MDDocument2 pagesAn Auricular Marker For Covid-19: Nadia Volf, MD, PHD, Valery Salques, MD, and Anne Lassaux, MDyan92120No ratings yet
- Project:: Community Initiated Fish Pond Harvesting in Kunike Chiefdom - Tonkolili DistrictDocument10 pagesProject:: Community Initiated Fish Pond Harvesting in Kunike Chiefdom - Tonkolili DistrictSimon DaudaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Mortality and MorbidityDocument8 pagesCauses of Mortality and MorbiditypurletpunkNo ratings yet
- Valid and Ethical Use of Psych AssessmentDocument2 pagesValid and Ethical Use of Psych AssessmentEJNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors in Dental ErosionDocument6 pagesRisk Factors in Dental ErosionMuftihat IsrarNo ratings yet
- When A Child Dies LeafletDocument2 pagesWhen A Child Dies LeafletCruseBexleyNo ratings yet
- Labour Room LayoutDocument1 pageLabour Room LayoutRana Vandana100% (2)
- PEDIATRIC AUDIOLOGY WEEKLY TOPICSDocument3 pagesPEDIATRIC AUDIOLOGY WEEKLY TOPICSAhiawortor KplorlaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Public RelationsDocument3 pagesMethods of Public RelationsAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Daftar Isi Bridwell SpineDocument38 pagesDaftar Isi Bridwell Spineronny0% (1)
- Registration Requirments of Animal Derived Non Medicated ProductsDocument2 pagesRegistration Requirments of Animal Derived Non Medicated ProductsValeria DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- February Health Programs CalendarDocument29 pagesFebruary Health Programs CalendarTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet