Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coax-to-Waveguide Adapters Meet Needs of Communications Equipment
Uploaded by
João RodriguesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coax-to-Waveguide Adapters Meet Needs of Communications Equipment
Uploaded by
João RodriguesCopyright:
Available Formats
Coax-to-Waveguide Adapters Meet
Needs of Communications Equipment
By Richard M. Kurzrok, PE
RMK Consultants
oax to waveguide adapters without tuning
C screws were originally developed for full
waveguide bandwidths with maximum
VSWR specifications of 1.25. Subsequently,
adapters with factory-adjusted tuning screws pro-
vided full waveguide band coverage with lower
VSWR. For some satellite and terrestrial commu-
nications equipment, the need for coax-to-wave-
guide adapters involves smaller usable band-
widths of 500 to 800 MHz with a maximum
VSWR of about 1.10. This is usually achievable
via the factory-tuned configuration. This article
presents approximate information for the devel-
opment of coax to waveguide adapters suitable for
many applications. Note that different approach-
es will be needed for high-power applications.
Coax-to-waveguide adapter configuration
The coax-to-waveguide adapters have several
significant parts:
• Housing using rectangular waveguide tubing
• Standard waveguide flange
• Metallic end plate
• Coaxial probe assembly with modified coaxial
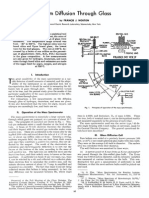
adapter, probe and hardware ▲ Figure 1. Coax-to-waveguide adapter design details.
• Tuning screws with hardware (except for set
screws)
sizes and recommended coaxial connectors are shown in
The coax-to-waveguide adapter design details are Table 2. For the larger size waveguides, bulkhead
shown in Figure 1. The coaxial probe assembly for SMA feedthrough coaxial adapters are needed to increase the
connectors is also used in waveguide bandpass filters adjustment ranges. These preliminary dimensions
with coaxial interfaces [1]. Applicable details will not be might require modifications when design objectives
repeated here. New probes must be designed when using include optimization.
SSMA connectors. The top broad wall of the waveguide
housing is tapped for a modified female to female coaxi- Coax-to-waveguide adapter alignment
al adapter. The bottom broad wall of the waveguide con- Coax-to-waveguide adapter alignment uses a stan-
tains four tapped holes for metallic tuning screws. For dard coaxial reflectometer of adequate directivity. The
small quantity fabrication, most metallic parts are of swept frequency input is applied to the coaxial port. The
copper alloys. Stainless steel hardware is preferred for waveguide port should be terminated in a load with a
durability. VSWR that is less than 1.02. Different size probes and
different probe insertion depths provide a cut and try
Coax-to-waveguide adapter mechanical dimensions situation when used with the tuning screw array.
Typical mechanical dimensions for various rectangu- Typical probe depths are near one half the waveguide
lar waveguide sizes are shown in Table 1. Tuning screw height while typical tuning screw penetrations are about
98 · APPLIED MICROWAVE & WIRELESS
one quarter waveguide WG Size A B C D E F G
height. Sometimes, one or WR-229 0.625 0.812 1.000 1.312 2.500 0.438 0.312
more of the tuning screws are
WR-137 0.375 0.500 0.625 0.812 2.000 0.281 0.187
not used. After alignment is
WR-112 0.312 0.406 0.500 0.656 1.500 0.219 0.156
completed, the coaxial probe
assembly and the tuning WR-90 0.250 0.340 0.475 0.610 1.250 0.187 0.125
screws can be staked to the WR-75 0.250 0.312 0.375 0.500 1.125 0.187 0.125
housing with epoxy. WR-62 0.187 0.250 0.312 0.437 1.000 0.187 0.125
WR-51 0.156 0.219 0.281 0.406 1.000 0.156 0.093
Conclusions WR-42 0.125 0.187 0.250 0.375 1.000 0.125 0.093
Coax-to-waveguide adap- Note: For E, tolerances are plus or minus 0.005. All other tolerances are plus or minus 0.002.
ters for low power communi-
cations applications can be ▲ Table 1: Coax to waveguide adapter mechanical dimensions.
developed readily using these
recommended dimensions as
a starting point. There are useful technological Waveguide Tuning Coaxial
overlaps with some waveguide bandpass filters. Size Screws Connectors
For manufacturing in substantial quantities, WR-229 #10-32 SMA Bulkhead Feedthrough
other fabrication methods, such as dip brazed WR-137 #8-32 SMA Bulkhead Feedthrough
aluminum, aluminum casting, or electroforming WR-112 #6-32 SMA
can be used. ■ WR-90 #4-40 SMA
WR-75 #2-56 SMA
Acknowledgements
WR-62 #2-56 SMA
The type of coax-to-waveguide adapter dis-
cussed in this article has been developed inde- WR-51 #1-72 SSMA
pendently by other microwave engineers. It has WR-42 #0-80 SSMA
also been integrated into various waveguide sub-
Note: SMA adapters have 0.250 to 36 UNS-2A threads, and SSMA
assemblies. adapters have 0.190 to 36 UNS-2A threads.
References ▲ Table 2: Coax to waveguide adapter tuning screws and
1. R.M. Kurzrok, “Waveguide Bandpass Filter coaxial connectors.
with Coaxial Interfaces Reduces Equipment
Costs,” Applied Microwave & Wireless, (June
1999): 100–102.
through microwave frequencies. He can be reached at
Author Information RMK Consultants, 82-34 210th St., Queens Village, NY,
Richard M. Kurzrok, PE, is an independent consul- 11427-1310; Tel: 718-776-6343; Fax: 718-776-6087; and
tant specializing in filters and equalizers from baseband E-mail: rmkconsulting@aol.com.
Every engineer has developed practical circuit design or fabrication approaches that save time or simplify the
design process. We invite you to share your favorite engineering notes with other Applied Microwave &
Wireless readers in our Design Ideas column! To get started, just send a brief description of your idea to:
Design Ideas
Applied Microwave & Wireless
630 Pinnacle Court
Norcross, GA 30071
Fax: 770-448-2839
E-mail: amw@amwireless.com
100 · APPLIED MICROWAVE & WIRELESS
You might also like
- NTC ThermistorsDocument17 pagesNTC ThermistorssumivrindavanNo ratings yet
- Diamond Chemical Vapor Deposition: Nucleation and Early Growth StagesFrom EverandDiamond Chemical Vapor Deposition: Nucleation and Early Growth StagesNo ratings yet
- THE Working of Steel: Page V Preface To Second EditionDocument207 pagesTHE Working of Steel: Page V Preface To Second EditionGutenberg.org100% (2)
- Analytical Fleet Maintenance Management: 3rd EditionDocument1 pageAnalytical Fleet Maintenance Management: 3rd EditionAnas R. Abu KashefNo ratings yet
- Utility of PETCT in Diagnosis, Staging, Assessment of Resectability and Metabolic Response of Pancreatic CancerDocument11 pagesUtility of PETCT in Diagnosis, Staging, Assessment of Resectability and Metabolic Response of Pancreatic CancerVictor Alfonso Martinez DiazNo ratings yet
- Copper in Electrical ContactsDocument22 pagesCopper in Electrical ContactsSanj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Porous Anodic Metal OxidesDocument20 pagesPorous Anodic Metal Oxidescargetoianu2357No ratings yet
- Research On Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of Stainless PDFDocument7 pagesResearch On Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of Stainless PDFMuhammad LukmanNo ratings yet
- MCM AllDocument7 pagesMCM AllPalanisamy RajaNo ratings yet
- Electroplating Handbook GuideDocument13 pagesElectroplating Handbook GuideAbeerNo ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- Loading Tax Withholding Information For The US Using HCM Data LoaderDocument67 pagesLoading Tax Withholding Information For The US Using HCM Data LoadersivasubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- Etchant Composition Conc. Conditions Comments Kalling's No. 1Document1 pageEtchant Composition Conc. Conditions Comments Kalling's No. 1Nick LaveryNo ratings yet
- Acct GenDocument8 pagesAcct GenguravareddymNo ratings yet
- Srs For Online Movie Ticket BookingDocument9 pagesSrs For Online Movie Ticket BookingKaran Kadakia71% (7)
- Alnico Magnets: Types Features Applications Manufacturing Process Magnetizing Graphical Representation PropertiesDocument18 pagesAlnico Magnets: Types Features Applications Manufacturing Process Magnetizing Graphical Representation PropertiesparthpatelparthNo ratings yet
- Siemens Sentron BuswayDocument2 pagesSiemens Sentron Buswayduyan1987No ratings yet
- Astm B344-01Document3 pagesAstm B344-01Srinivasan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Aluminum 2024-T6 PropertiesDocument4 pagesAluminum 2024-T6 PropertiesThiru Kumaran0% (1)
- Cobham WaveguideDocument98 pagesCobham Waveguidehenryaaron_10100% (1)
- Mil DTL 24211CDocument8 pagesMil DTL 24211CmurphygtNo ratings yet
- AWG Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesAWG Characteristics and ApplicationsMukunda Saiteja AnnamNo ratings yet
- Electrode Converted Into TextDocument14 pagesElectrode Converted Into TextNeha NimbarkNo ratings yet
- BRAINWARE UNIVERSITY REPORT ON SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDINGDocument7 pagesBRAINWARE UNIVERSITY REPORT ON SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDINGsrijaNo ratings yet
- Mil DTL 3922cDocument7 pagesMil DTL 3922cshravan_3393No ratings yet
- Term Paper-Sheet Metal WeldingDocument6 pagesTerm Paper-Sheet Metal Welding11gargdinesh7No ratings yet
- Copper-Clad Aluminum Bar For Electrical Purposes (Bus Bar)Document5 pagesCopper-Clad Aluminum Bar For Electrical Purposes (Bus Bar)Tuanbk NguyenNo ratings yet
- Waveguide FlangesDocument7 pagesWaveguide FlangesV'nod Rathode BNo ratings yet
- ESAB Consumable PDFDocument165 pagesESAB Consumable PDFbond8031No ratings yet
- Spacecraft Electrical Harness DesignDocument3 pagesSpacecraft Electrical Harness Designe1094739No ratings yet
- Aluminizing Nickel Foam by A Slurry Coating ProcessDocument3 pagesAluminizing Nickel Foam by A Slurry Coating ProcessFatih BozkurtNo ratings yet
- Stud Welding Capacitive Discharge WeldingDocument30 pagesStud Welding Capacitive Discharge WeldingwenigmaNo ratings yet
- Arcelor High Yield IfDocument4 pagesArcelor High Yield IfJayDadrassNo ratings yet
- Helium Diffusion Through GlassDocument7 pagesHelium Diffusion Through GlassElenaNo ratings yet
- Advance Materials and Materials Processing SessionDocument55 pagesAdvance Materials and Materials Processing SessionShubham Indoria100% (1)
- Atmosphere Reentry of A Hydrazine TankDocument11 pagesAtmosphere Reentry of A Hydrazine TankdroberNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Carburizing Using Acetylene GasDocument6 pagesVacuum Carburizing Using Acetylene GasRamesh JakkanagoudarNo ratings yet
- A867-03 (2013) Standard Specification For Iron-Silicon Relay SteelsDocument4 pagesA867-03 (2013) Standard Specification For Iron-Silicon Relay SteelsdcardonasterNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc WeldingDocument13 pagesGas Tungsten Arc WeldingEmad A.AhmadNo ratings yet
- GMAW of Creep Resistant SteelsDocument5 pagesGMAW of Creep Resistant SteelsJustin Morse100% (1)
- Atmospheric Corrosion of Copper and The Colour Structure and Composition of Natural Patinas On Copper 2006 Corrosion ScienceDocument30 pagesAtmospheric Corrosion of Copper and The Colour Structure and Composition of Natural Patinas On Copper 2006 Corrosion ScienceEmanuela Leite FragosoNo ratings yet
- Alloy 625 Supplier GuideDocument1 pageAlloy 625 Supplier Guidevickyflyer1No ratings yet
- Aluminium Alloys GuideDocument74 pagesAluminium Alloys GuideAladdin AdelNo ratings yet
- Joining KovarDocument11 pagesJoining Kovarharan2000No ratings yet
- Aluminium 2014 t6 2014 t651Document3 pagesAluminium 2014 t6 2014 t651Agung Sapto AjiNo ratings yet
- Physics of Welding Better VersionDocument3 pagesPhysics of Welding Better VersionKhurram RehmanNo ratings yet
- Diamond Like Carbon DLCDocument5 pagesDiamond Like Carbon DLCjbertralNo ratings yet
- Alloys DensityDocument4 pagesAlloys DensityArnold Melissa CollettNo ratings yet
- Dual Phase SteelsDocument22 pagesDual Phase SteelsAngele IvanovskiNo ratings yet
- Welding Term PaperDocument26 pagesWelding Term PaperBiswajit SenNo ratings yet
- A Review of Mathematical ModellingDocument15 pagesA Review of Mathematical ModellingParamita HaldarNo ratings yet
- 55 Aluminum-Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Technical Bulletin 6 - Cut Edge Protection v20153Document2 pages55 Aluminum-Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Technical Bulletin 6 - Cut Edge Protection v20153Syed Raja AdeelNo ratings yet
- Crystals 12 00978Document9 pagesCrystals 12 00978irmaNo ratings yet
- Fcaw Welding Guide PDFDocument2 pagesFcaw Welding Guide PDFElizabethNo ratings yet
- Welding AluminumDocument4 pagesWelding AluminumHeryanda OnDaudNo ratings yet
- Modern Electroplating Fourth Edition Edited by M SDocument2 pagesModern Electroplating Fourth Edition Edited by M Smiguelin91690% (1)
- Electrolytic Nickel Phosphorus PlatingDocument34 pagesElectrolytic Nickel Phosphorus PlatingKhoa Vũ100% (1)
- Manual Book XK3190-A28EDocument15 pagesManual Book XK3190-A28ETakaSenseiNo ratings yet
- Index of Gold Technology journal articles 1990-2002Document7 pagesIndex of Gold Technology journal articles 1990-2002mv_jewellers0% (1)
- Literature ReviewDocument23 pagesLiterature ReviewRISHAVNo ratings yet
- Astm A192 Asme Sa192 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm A192 Asme Sa192 PDFWil Vasquez C100% (1)
- The Physical Metallurgy of Fracture: Fourth International Conference on Fracture, June 1977, University of Waterloo, CanadaFrom EverandThe Physical Metallurgy of Fracture: Fourth International Conference on Fracture, June 1977, University of Waterloo, CanadaD M R TaplinNo ratings yet
- Cad StandardsDocument21 pagesCad Standardsarch_ankitNo ratings yet
- Cs304 Quiz 2 2022Document29 pagesCs304 Quiz 2 2022UmerNo ratings yet
- Rony Das CV New E-MailDocument3 pagesRony Das CV New E-Mailrony_27No ratings yet
- FJHJ Volume 85 Issue 1 Pages 320-357Document38 pagesFJHJ Volume 85 Issue 1 Pages 320-357DaliNo ratings yet
- Riaz Ahmad: Advisory Software Engineer (Oracle EBS) at Systems LimitedDocument9 pagesRiaz Ahmad: Advisory Software Engineer (Oracle EBS) at Systems Limitedriazahmad82No ratings yet
- Toyota Aisin Fire & IBM FinalDocument5 pagesToyota Aisin Fire & IBM Finalkhem_singhNo ratings yet
- 521.105.03.2 Quick Start P1F - English 1.0Document20 pages521.105.03.2 Quick Start P1F - English 1.0LucasNo ratings yet
- AGLiS DMS For TNS - Customer Upload Template - TXTDocument2 pagesAGLiS DMS For TNS - Customer Upload Template - TXTfajar wahyudiNo ratings yet
- FC 822 PCB PDFDocument1 pageFC 822 PCB PDFKellyNo ratings yet
- Hacking Module 11Document53 pagesHacking Module 11Chye HengNo ratings yet
- Michael Nasol (April)Document10 pagesMichael Nasol (April)Anonymous CuIeVjHNo ratings yet
- Cross Launch Jabber IOS ClientsDocument6 pagesCross Launch Jabber IOS ClientserlifieNo ratings yet
- Andromax Product Defect RatesDocument12 pagesAndromax Product Defect Ratesanat17No ratings yet
- Haivision Calypso Administration Guide v2.1Document142 pagesHaivision Calypso Administration Guide v2.1The Narcotic Dragon CafeNo ratings yet
- CFD LectureDocument19 pagesCFD LectureRobi Afrizal100% (1)
- ECC 602 Computer Communication Network exam modulesDocument2 pagesECC 602 Computer Communication Network exam modulesRatnakar YadavNo ratings yet
- Subhadip CVDocument3 pagesSubhadip CVToufik HossainNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligent Application To Power System ProtectionDocument7 pagesArtificial Intelligent Application To Power System Protectionjijo123408No ratings yet
- Bta BTB PDFDocument5 pagesBta BTB PDFAnonymous wYU9h0No ratings yet
- Interface Trip StopDocument3 pagesInterface Trip StopRamesh Garikapati100% (1)
- Defining a Risk Appetite That WorksDocument38 pagesDefining a Risk Appetite That WorksPRASAD6219No ratings yet
- Attendance Management System Using Face-RecognitioDocument6 pagesAttendance Management System Using Face-Recognitioabid qureshiNo ratings yet
- HGI Catalog PDFDocument33 pagesHGI Catalog PDFYaqien ChusnoelNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 2 PDFDocument2 pagesExercise Sheet 2 PDFMariem BoussaadiaNo ratings yet
- IEC and ISO Standards: How To Best UseDocument12 pagesIEC and ISO Standards: How To Best UseNamiJen LobatoNo ratings yet