Professional Documents
Culture Documents
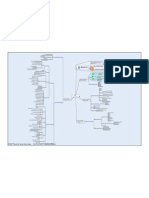
MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap
Uploaded by
jayarajanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap
Uploaded by
jayarajanCopyright:
Available Formats
Real time monitoring of
network activity
Traffic Detection
Incident Identification Listens to data and
Motivation and Study Techniques to help Cisco
helps with
Response you learn, remember, and pass your
CISSP
Logging technical exams!
CEH
Network Based More coming soon...
Systems
Host Based
Also known as Knowledge based IDS Visit us www.mindcert.com
Low False Positives
Advantages
Understandable alarms Signature Based
Resource intensive
Disadvantages
New attacks go unnoticed Provides security services at the IP layer
Methodologies
Detects based on user patterns
Can dynamically adapt to new attacks A framework of services
Advantages
Not as OS dependant Behavior Based
Intrusion Detection Adds security to the upper
layers in the OSI model By Implementing a new set of headers
High false positives Definition
Disadvantages
Can affect user activity One SA is required per direction
SNMP Utilizes Security Associations (SA) A router to router IPsec VPN
Logging will use two SA's One in each direction
Syslog
Launch and attack
Actions Access Control is the
Block
Issue an SMS or E-mail
heart of security
Trace the connection Fundamental for providing CIA
Configure Alarms Prevent modification by unauthorized users
Interferes with legitimate traffic Why Control Access? Prevent unintentional modification by
Three Goals
Have to check Systems using HIDS for unauthorized users
performance problems Concerns Preserve internal and external data consistency
NIDS may lose packets due to System and network latency
bandwidth limitations Avoid
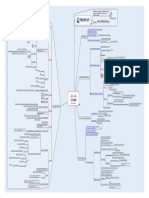
Preventative
As it states, Sign on Once Detective Identify
Users Love it
Deterrent Discourage
Novell NDS and Microsoft AD Controls may be
SSO Directory Services
Sign on once for access to all resources Fix or Repair
Corrective
Started as Project Athena
Recovery Restore
Currently in version 5
Introduced in Windows 2000 Policies
Uses Symmetric Key Cryptography
Procedures
Holds the Cryptographic Keys Administrative Controls
Key Distribution Centre (KDC) Training
Tickets Components Background checks
Ticket Granting Server (TGS) ACLs
Implementing Controls Logical/Technical Controls
Subject requests access to an object Encryption
Includes a session key derived from Gates
the users password Request goes via the KDC Guards
Kerberos Physical Controls
KDC Generates a ticket for the subject and object Fences
Kerberos Process
Subject validates the ticket came from the KDC Badges
Subject sends ticket to object "soft" policy procedures such as
Object validates the ticket Administrative background checks
Kerberized session is established Object grants access to subject
Encryption
Each piece of software must be Kerberized Single Sign on Preventative Technical Smart Cards
Requires synchronized time clocks Systems Biometrics
Relies on UDP Problems Examples
Badges
Weakness in v4 allowed password attacks Physical
Fences
KDC can be a SPOF Combinations
Job rotation
Secure European System for Applications in a Multivendor Environment
Control Types Administrative Supervision
Designed to extend Kerberos CISSP
Existing Violations
Uses Public Key and Symmetric Access Control
Cryptography IDS
Systems and Detective
Technical
Authenticates with a Privileged System Scanners
Attribute Certificate
Methodology
SESAME
One contains Authentication Motion Detectors
Uses two tickets Physical
One contains the access rights to the client CCTV
Only authenticates using the first All objects controlled at a central point
block of the message Very strict Access Control
Weaknesses
Initial exchange passed on password authentication Ease of Administration
IBM system like Kerberos Could be SPOF
Peer-to-Peer relationship between RADIUS
Client-Server KDC and parties KRYPTONIGHT Serves Dial In Users
Authentication through one way hash Incorporates an Authentication server
of users password stored on server Centralized Authentication and dynamic password
NETSP TACACS
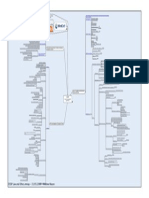
Centralized and Decen‐
Password tralized Access Control Types Static password
PIN What you Know
TACACS+
Passphrase
Weak Passwords
Type 1 Authentication Supports token authentication
Reused
Strong Passwords
Written Down Issues Remote Authentication
Default passwords Decision is closer to the objects
Decentralized
Password Age More Administration Overhead
Different User Rights around the network
Tokens
Tickets What you Have Hybrid Model A Mixture of centralized and decentralized
OTP
More Expensive than Type 1 Subject person or process
Controlling access by a
May have to be combined with Type 1 Type 2 Authentication subject to an object
Object file or resource
More Complex
Issues
Can lock the user out if they lose token Involves Rule Creation
Can be copied or forged Assigns classification levels to objects
Again, total strength is in the PIN Subject must have equal or higher
Security Labels
security than the object
Physical Characteristics
Identification and May be assigned per user, or per group
Iris/Retina Scans
Authentication Mandatory Set of Rules
Fingerprinting
Biometrics Rule based Access Control
Voice Recognition
What you Are Data Owners have less freedom than DAC
Signature Mandatory Access
Access Granted on Rules or Security Labels
DNA, Blood Control (MAC)
More Secure (Government)
Cannot be lent or borrowed Control Models
Every Resource has a label, every user has a clearance
Lasts forever
Used by the military
Wrong rejections
False Rejection Rate (FRR) Embodies the concept of need to know
Turn down the sensitivity Type 3 Authentication Identity Based Access Control
VERY BAD
Discretionary Access Owner specifies access levels
Wrong acceptions Control (DAC)
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) Like UNIX and Windows
Turn Up the Sensitivity
Most common Access Control
False Rejection Rate (FRR) Issues
Access based on Job Description
The FRR and FAR combined gives you Role based Access Control
Lower CER is Always Better the Crossover Error Rate (CER) Good for high staff turnover
Non discretionary
Lattice based ACL Access based on the job role and the task
Expensive
Immature market
Bad user acceptance
You might also like
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Real time network monitoring and incident detectionDocument1 pageReal time network monitoring and incident detectionZeeshan RanaNo ratings yet
- CISSP Mind Maps by Matheus PDF 1638358395Document10 pagesCISSP Mind Maps by Matheus PDF 1638358395Rodrigo Juan100% (1)
- Security Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesFrom EverandSecurity Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- MindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapcpawan_69No ratings yet
- Mindcert Cissp BCP MindmapDocument1 pageMindcert Cissp BCP MindmapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapbesmart2000100% (1)
- CISSP CryptographyDocument1 pageCISSP CryptographyonlysubasNo ratings yet
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 6Document11 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 6babyNo ratings yet
- CISSP Study NotesDocument11 pagesCISSP Study NotesCISSPInspired100% (1)
- Network Security FundamentalsDocument41 pagesNetwork Security FundamentalsMarco Lopez ReinosoNo ratings yet
- CISSP exam questions on physical securityDocument58 pagesCISSP exam questions on physical securityIvan MartinezNo ratings yet
- MindCert Wireshark MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Wireshark MindMapacehussainNo ratings yet
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8Document30 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 8baby100% (1)
- Operationalizing Information Security: Putting the Top 10 SIEM Best Practices to WorkFrom EverandOperationalizing Information Security: Putting the Top 10 SIEM Best Practices to WorkNo ratings yet
- CISSP Quiz QuestionsDocument7 pagesCISSP Quiz Questionsthejoker2055100% (1)
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFzinzinNo ratings yet
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 7Document40 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 7babyNo ratings yet
- CISSP Skillset OverviewDocument66 pagesCISSP Skillset OverviewicvNo ratings yet
- Cissp Domain 2 Asset SecurityDocument8 pagesCissp Domain 2 Asset Securitysrivatsan_ece0% (1)
- Intrusion Detection Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandIntrusion Detection Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- CISSP ExqsDocument20 pagesCISSP Exqssentoubudo1647No ratings yet
- CISSP Certified - OutlineDocument76 pagesCISSP Certified - OutlineDominica McCoy100% (2)
- Abhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b8Document1 pageAbhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b8madhu jhaNo ratings yet
- Ec-Council Testinises 312-50v11 Exam Question 2021-Jun-26 by Bartholomew 131q VceDocument18 pagesEc-Council Testinises 312-50v11 Exam Question 2021-Jun-26 by Bartholomew 131q VceYazid BenjamaâNo ratings yet
- CCSP Certification Exam OutlineDocument14 pagesCCSP Certification Exam OutlineironmanNo ratings yet
- Top 15 Indicators of CompromiseDocument7 pagesTop 15 Indicators of CompromisenandaanujNo ratings yet
- Cyber Information Security Analyst in Seattle WA Resume Robin GarrettDocument3 pagesCyber Information Security Analyst in Seattle WA Resume Robin GarrettRobinGarrettNo ratings yet
- EC-Council Certified Security Analyst Standard RequirementsFrom EverandEC-Council Certified Security Analyst Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Security Certifications RoadmapDocument2 pagesSecurity Certifications Roadmapnoisi80No ratings yet
- CISSP NotesDocument2 pagesCISSP NotesafeeshNo ratings yet
- Information Security Architecture Framework and Policy StatementsDocument12 pagesInformation Security Architecture Framework and Policy StatementsKumar0% (1)
- Exabeam SecurityDocument32 pagesExabeam SecurityAbie Widyatmojo100% (1)
- CISSP Mem AidDocument4 pagesCISSP Mem Aidsandra072353100% (2)
- CompTIA Security Test 1Document7 pagesCompTIA Security Test 1annNo ratings yet
- Cissp2.2 - Glossary Good 2015Document44 pagesCissp2.2 - Glossary Good 2015Alex DcostaNo ratings yet
- Domain 4 Communication and Network SecurityDocument9 pagesDomain 4 Communication and Network Securitysrivatsan_eceNo ratings yet
- 008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document24 pages008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)LinuxPower100% (1)
- CISSP Study PlanDocument1 pageCISSP Study PlanAnonymous RA353CNo ratings yet
- 01a - General Security ConceptsDocument61 pages01a - General Security ConceptsMa Hoàng Hải KhôiNo ratings yet
- Network Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandNetwork Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Training Career Pathways - Final v1.0 Rev 10062020Document2 pagesCybersecurity Training Career Pathways - Final v1.0 Rev 10062020HafizPradanaGemilangNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Vulnerability Management: by Umesh Chavan, CISSPDocument3 pagesAn Approach To Vulnerability Management: by Umesh Chavan, CISSPRaju PatleNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Prevention Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandIntrusion Prevention Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- My Cissp Success Journey: (Lalit Kumar, CISSP, CISA, ISO 27001 LA, CEH, ITIL, DBA, System Admin)Document2 pagesMy Cissp Success Journey: (Lalit Kumar, CISSP, CISA, ISO 27001 LA, CEH, ITIL, DBA, System Admin)Abdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Ebook - CISSP - Domain - 03 - Security Architecture and EngineeringDocument279 pagesEbook - CISSP - Domain - 03 - Security Architecture and EngineeringNOAH ABALONDENo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips for Passing the CISSP ExamDocument6 pagesTop 10 Tips for Passing the CISSP Examgriffin_ilinkNo ratings yet
- CISSP MindMapDocument66 pagesCISSP MindMapJuan Carlos Angarita C.100% (7)
- NIST CSF Practitioner Chapter 8 - Security Operations Center (SOC)Document70 pagesNIST CSF Practitioner Chapter 8 - Security Operations Center (SOC)Arjun100% (1)
- Asset Attack Vectors: Building Effective Vulnerability Management Strategies to Protect OrganizationsFrom EverandAsset Attack Vectors: Building Effective Vulnerability Management Strategies to Protect OrganizationsNo ratings yet
- Domain 6 - Security Assessment and TestingDocument35 pagesDomain 6 - Security Assessment and TestingNgoc Do100% (1)
- What Is Identity and Access Management - Guide To IAMDocument8 pagesWhat Is Identity and Access Management - Guide To IAMharshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Prepare RPADocument12 pagesLesson 4 - Prepare RPAichaz22No ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Platform ComponentsDocument2 pagesUiPath Licensing - Platform ComponentsjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - The RPA Journey and The BA's RoleDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - The RPA Journey and The BA's RolejayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The RPA Business Analyst - Role, Skills and ChallengesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - The RPA Business Analyst - Role, Skills and ChallengesjayarajanNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Recommended Setup and License DistributionDocument3 pagesUiPath Licensing - Recommended Setup and License DistributionjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Comic Book - Calvin and Hobbes - Yukon Ho 1987-1988 PDFDocument293 pagesComic Book - Calvin and Hobbes - Yukon Ho 1987-1988 PDFamrinderNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveJhady BolivarNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Standalone LicensesDocument2 pagesUiPath Licensing - Standalone LicensesjayarajanNo ratings yet
- ESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingDocument8 pagesESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingjayarajanNo ratings yet
- UiPath Licensing - Licensing ModelsDocument3 pagesUiPath Licensing - Licensing ModelsjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Calvin and Hobbes CollectionDocument541 pagesCalvin and Hobbes Collectiondevesh_200367% (3)
- Lesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - What Is A Process. The RPA PerspectiveJhady BolivarNo ratings yet
- EC2029-R08Mayjun 13 PDFDocument3 pagesEC2029-R08Mayjun 13 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08 AprilMay 15Document3 pagesEC2029 R08 AprilMay 15jayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08NovDec 13 PDFDocument2 pagesEC2029 R08NovDec 13 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029 R08 MayJune 14 PDFDocument2 pagesEC2029 R08 MayJune 14 PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- WidgetDocument8 pagesWidgetjayarajanNo ratings yet
- EC2029-DIP Important Question PDFDocument7 pagesEC2029-DIP Important Question PDFjayarajanNo ratings yet
- ARM Processor Embedded Systems DesignDocument6 pagesARM Processor Embedded Systems Designjayarajan0% (1)
- CS2204 Adc V+ QBDocument4 pagesCS2204 Adc V+ QBjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 1768Document84 pagesLab Manual 1768jayarajanNo ratings yet
- Group Discussion With AnswersDocument4 pagesGroup Discussion With AnswersjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Robo Pica E30Document88 pagesRobo Pica E30montri_lpk1728100% (1)
- Arduino ManualDocument40 pagesArduino ManualDaniela Cardenas LuboNo ratings yet
- Arthashastra of Chanakya - EnglishDocument614 pagesArthashastra of Chanakya - EnglishHari Chandana K83% (6)
- Israel and The 1948 WarDocument3 pagesIsrael and The 1948 WarjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Class 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsDocument17 pagesClass 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsRakesh SinghNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Law MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Law MindMap PDFprog_man_0101No ratings yet
- Mindcert Cissp BCP MindmapDocument1 pageMindcert Cissp BCP MindmapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- L00161 1121Document29 pagesL00161 1121aboofazilNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Implementation of A BPSK Modulator On FPGADocument14 pagesSimulation and Implementation of A BPSK Modulator On FPGAAnonymous 01LLHnZTSNo ratings yet
- ZXR10 5900E Configuration Guide (Basic Configuration)Document174 pagesZXR10 5900E Configuration Guide (Basic Configuration)HectorNo ratings yet
- Smartphones - A great invention? Or a dependency trapDocument1 pageSmartphones - A great invention? Or a dependency trapMabel SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal Examjohn francisNo ratings yet
- HPE - A00104922en - Us - ClearPass Policy Manager Scaling and Ordering GuideDocument17 pagesHPE - A00104922en - Us - ClearPass Policy Manager Scaling and Ordering Guide陳建和No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document34 pagesLecture 8Anonymous rcmeSfj5No ratings yet
- PS-474 Induction Heat Tube Extraction PDFDocument4 pagesPS-474 Induction Heat Tube Extraction PDFحمودي معزNo ratings yet
- SUP-01-Document ControlDocument2 pagesSUP-01-Document ControlSALAH HELLARANo ratings yet
- WSO2 Product AdministrationDocument17 pagesWSO2 Product AdministrationVivek R KoushikNo ratings yet
- SB286 Update For EMV Book C 5Document4 pagesSB286 Update For EMV Book C 5Raven 83No ratings yet
- Manager Director CTO Telecommunications in Denver CO Resume Bruce RotvoldDocument4 pagesManager Director CTO Telecommunications in Denver CO Resume Bruce RotvoldBruceRotvoldNo ratings yet
- 95 8657 2.3 FlexSonic AcousticDocument37 pages95 8657 2.3 FlexSonic Acousticsudipta_kolNo ratings yet
- 05 DistanceProt-7SA8 Principles V02 PDFDocument23 pages05 DistanceProt-7SA8 Principles V02 PDFOliver RisteskiNo ratings yet
- Liquid MFCDocument4 pagesLiquid MFCAhmad Syihan AuzaniNo ratings yet
- Computers: What Is A Computer Program?Document11 pagesComputers: What Is A Computer Program?fabiobonadiaNo ratings yet
- Mercruiser 860168051Document102 pagesMercruiser 860168051JorjNo ratings yet
- Avionics - QBDocument5 pagesAvionics - QBVeeramani ShankarNo ratings yet
- RTI Information HandbookDocument179 pagesRTI Information Handbookcol.asyadavNo ratings yet
- Flat-Eight Engine: Design Use in Automobiles Use in Aircraft Use in Marine Vessels See Also ReferencesDocument5 pagesFlat-Eight Engine: Design Use in Automobiles Use in Aircraft Use in Marine Vessels See Also ReferencesAve FenixNo ratings yet
- Tor and Deep Web Secrets PDFDocument127 pagesTor and Deep Web Secrets PDFOssas One100% (8)
- Francis turbines optimizedDocument5 pagesFrancis turbines optimizedmamok supraptoNo ratings yet
- Applied ElectricityDocument5 pagesApplied ElectricityTitiloyeNo ratings yet
- Page 1Document6 pagesPage 1langbotNo ratings yet
- Ds04108bf Data Sheet (Nm4-108b)Document2 pagesDs04108bf Data Sheet (Nm4-108b)johnnygabrielNo ratings yet
- Metashape ComparisonDocument5 pagesMetashape ComparisonRyo Lordan GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Vol.1 (CH 00 - CH 31)Document605 pagesVol.1 (CH 00 - CH 31)versineNo ratings yet
- Activating X Entry XDOS OPEN SHELL 9.2020Document12 pagesActivating X Entry XDOS OPEN SHELL 9.2020OBD bytesNo ratings yet
- SEVO Systems Pocket BrochureDocument8 pagesSEVO Systems Pocket BrochureNikhil RajanNo ratings yet