Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan in Science 1
Uploaded by
Brigette Darren Baste Colita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views1 pageOriginal Title
lesson plan in science 1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views1 pageLesson Plan in Science 1
Uploaded by
Brigette Darren Baste ColitaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
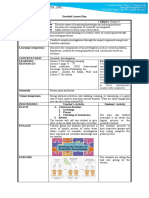
REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES
Department of Education
Region XII
Division of Sarangani
South Malungon District
Lesson Plan in Science 8
Date: Time:
I. Objectives: 1. Identify the forces acting on an object at rest.
2. Explain why objects stay at rest.
II. Subject Matter
a. Topic: Module I: FORCES AND MOTION Lesson 1: BALANCED AND UNBALANCED FORCES
b. References: Teacher’s Guide pp. 5-8; Learner’s Module pp. 3-6
c. Materials: visuals, pictures, ball, pen, string, book, scissor
III. Procedure
A. Preparatory Activities
a. Drill/Review: Present the following statement in class and ask the students if they agree or disagree with them.
Select two to three students per group to justify or explain their answer.
1. Force is needed to stop an object.
2. Force always results to motion.
3. Force can act even at a distance.
4. Objects have the tendency to remain at rest.
5. Objects have the tendency to resist change.
b. Motivation: Analyze the pictures.
What have you observed on the picture presented?
(The teacher will place a ball or any object on top of a table and ask :)
a) Will this object move by itself?
b) How can we make this object move?
c) While it is moving, how can we make the object speed up or slow down?
d) How can make it stop?
e) How can we make it change its direction?
B. Developmental Activities
a. Activity: Do Activity 1 Forces on Object at Rest in LM pp. 5- 6
b. Analysis: Presentation of the output per group/ Processing:
Situation 1
1. Is the pen at rest or in motion?
2. Are there forces acting on the pen? If yes, draw the forces. You may use arrows to represent these forces.
3. What happens to the pen? What could have caused the pen’s motion?
Situation 2
1. Is the book at rest or in motion?
2. Are there forces acting on the book? If yes, draw the forces acting on the book.
3. Did the book move? How will you make the book move?
C. Enhancement Activities
a. Abstraction: 1. What is force?
2. What are some other forces that can cause something to move?
3. How does gravity affect object on earth?
4. What is a force that can cause an object to slow down or have little movement?
5. In your own words define friction.
b. Application: Present the statement in the class “You may be bigger but I am faster”.
a. How does this line illustrate Newton’s Second Law of Motion?
b. How is the statement related to mass and acceleration?
IV. Evaluation
Multiple Choice: Read each statement carefully and write only the letter of the correct answer.
1. A book is at rest on top of a table. Which of the following is correct?
A. There is no force acting on the book. C. There is no force acting on the table.
B. The book has no inertia. *D. The book is in equilibrium.
2. Which of the following situations involves friction?
A. A bicycle rolling down a hill C. A diver falling through the air to a pool
B. A baseball player sliding into 2nd base *D. All of the above experience some friction.
3. What is gravity?
A. Newton’s first law *C The downward pull on the Earth
B. The force that objects exert on each other because of their masses D. The friction that an object has put on it
4. Which is the best example of gravity?
A. A car hits a tree, and its motion stops C. A book is pushed, and it moves across the table
B. A breeze blows, and a sailboat moves *D. A person drops a ball, and it falls to the ground
5. How does Earth‘s gravity affect objects near Earth?
A. It pushes them away. *B. It pulls them in C. It makes them larger. D. It makes them move faster
V. Enrichment Activity/Assignment
Ask the students to write situation/ examples where the presence of other forces is beneficial.
You might also like
- Lwsson Plan Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDocument17 pagesLwsson Plan Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesJeiril DivinoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Motion and DistanceDocument5 pagesMeasuring Motion and DistanceFloramae SeradorNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q1 Mod6 Colors of Light Version 3Document27 pagesSci8 Q1 Mod6 Colors of Light Version 3Paker LeeNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument11 pagesDepartment of EducationKim GenandaNo ratings yet
- S7 - Q2 - Week 5 - LAADocument6 pagesS7 - Q2 - Week 5 - LAALenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2Kathy Mae Morales Forcadilla - DaclanNo ratings yet
- 7e's Lesson PlanDocument3 pages7e's Lesson PlanKathleen Alcantara RomaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 8 I. ObjectivesAngelique BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Wednesday Observation-1st QuarterDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For Wednesday Observation-1st QuarterRia Biong TaripeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document2 pagesLesson 1Marissa FontanilNo ratings yet
- Forms of Potential EnergyDocument10 pagesForms of Potential EnergyRinmie Jalandoon RagudoNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument4 pagesLiving Things and Their EnvironmentSamlall RabindranauthNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanMaeflor Adolfo100% (1)
- Science 7 Lesson Exemplar Biological Organization Q2Document16 pagesScience 7 Lesson Exemplar Biological Organization Q2Marian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Particles Model of The States of MatterDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - Particles Model of The States of MatterRezelyn AnnNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science EarthquakeDocument2 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Earthquakeirene ilustrisimoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanKC EspinaNo ratings yet
- Quarter: THIRD Chapter1: Motion: Lesson 1Document3 pagesQuarter: THIRD Chapter1: Motion: Lesson 1Braddock Mcgrath DyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Scientifc Investigation Science7Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Scientifc Investigation Science7marcNo ratings yet
- Science Week 6 Day 1 Enumerating Precautionary Measures Before A TyphoonDocument20 pagesScience Week 6 Day 1 Enumerating Precautionary Measures Before A TyphoonPrecious IdiosoloNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ModulesDocument7 pagesGrade 8 ModulesnoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan inDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan inJay Jay0% (1)
- Unit 1 Ecology Performance Task CerDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Ecology Performance Task Cerapi-534779290100% (1)
- Active Fault WorksheetDocument3 pagesActive Fault WorksheetKatherine AudienciaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Weeks 1 - 2Document22 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Weeks 1 - 2Maljan CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDivine Grace ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in PhysicsDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in PhysicsFerlin Paru Rapal100% (1)
- Summative Test No. 1 Grade 8Document2 pagesSummative Test No. 1 Grade 8LENETTE ALAGONNo ratings yet
- 3 Pinoy Superstitions about Comets, MeteorsDocument1 page3 Pinoy Superstitions about Comets, MeteorsTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Department of Education Region IIIDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Department of Education Region IIIMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- OmnibusCertification SHSDocument1 pageOmnibusCertification SHSAngelica Rumbaua Guillermo100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Layers of The AtmosphereDocument1 pageSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Layers of The AtmosphereBik Bok100% (1)
- Investigating Inertia: Grade Level Quarter/Domain Week & Day No. LC Code S8FE-Ia-17Document32 pagesInvestigating Inertia: Grade Level Quarter/Domain Week & Day No. LC Code S8FE-Ia-17caveNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy LessonDocument4 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy LessonDominique Louise Solis100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan About CellDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan About CellRichard ServoNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformations in Simple ActivitiesDocument2 pagesEnergy Transformations in Simple ActivitiesChristianNo ratings yet
- Atomic Models Through TimeDocument4 pagesAtomic Models Through TimeJanice PranadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Philippine Area of ResponsibilityDocument5 pagesLesson 1: The Philippine Area of ResponsibilityMaria Cristina DelmoNo ratings yet
- Sounds ExemplarDocument6 pagesSounds ExemplarCharolyn Centeno MenesesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document7 pagesLesson Plan 3trexia autidaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 10 Science I. Lesson ObjectivesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Grade 10 Science I. Lesson ObjectivesRobelyn CamerosNo ratings yet
- PROTISTADocument13 pagesPROTISTARichard Tañada RosalesNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Q3 Module3Document23 pagesSci7 Q3 Module3Marion Sofia Ganancial50% (2)
- 4a's LESSON PLAN ScienceDocument4 pages4a's LESSON PLAN ScienceVenancio Franz A.No ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 10 Intensity and MagnitudeDocument9 pagesScience 8 Module 10 Intensity and Magnituderegail copy centerNo ratings yet
- INSET 2019 Powerpoint Tabgon SCIENCEDocument15 pagesINSET 2019 Powerpoint Tabgon SCIENCEDennis O. GadosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 (Energy) 2Document7 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6 (Energy) 2Kel FrancisNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development StagesDocument4 pagesEmbryonic Development StagesDotecho Jzo Ey100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningChona M. RosalitaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 8Document5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 8Justine Montemayor100% (1)
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument20 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsrodalynjoydizonNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion DLP 062019Document5 pagesCircular Motion DLP 062019IRISNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 9 ScienceJeffrey FloresNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in 1st QuarterArzjohn Niel BritanicoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in ScienceDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log in ScienceJosephine Valdez ManaloNo ratings yet
- Forces and motion in scienceDocument4 pagesForces and motion in scienceJuvi Mae Burgos ObenzaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 DLLDocument331 pagesGrade 8 DLLanon_29890413250% (2)
- Grading Test Eng7Document4 pagesGrading Test Eng7Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines8Document2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines8Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- CACNHS Reading ReportDocument7 pagesCACNHS Reading ReportBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Clas1Document6 pagesGood Morning Clas1Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines7Document1 pageRepublic of The Philippines7Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Demonstration Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Demonstration Lesson PlanBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam in English 10Document2 pagesSecond Quarter Exam in English 10Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Examination in English 9: Lawa National High School - Nueva Villa ExtensionDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Examination in English 9: Lawa National High School - Nueva Villa ExtensionBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines8Document2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines8Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Office of The Punong Barangay: Certification To TravelDocument1 pageOffice of The Punong Barangay: Certification To TravelBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Region Xi Schools Division of Davao OccidentalDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Region Xi Schools Division of Davao OccidentalBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan English Grade IX I. ObjectiveDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan English Grade IX I. ObjectiveBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Using Appropriate Body LanguageDocument7 pagesUsing Appropriate Body LanguageBrigette Darren Baste Colita0% (1)
- After Two Classroom Visits: Journal Entry No. 2Document2 pagesAfter Two Classroom Visits: Journal Entry No. 2Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- After The Final Visit: Journal Entry No. 4Document2 pagesAfter The Final Visit: Journal Entry No. 4Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills: Journal Entry No.3Document2 pagesCommunication Skills: Journal Entry No.3Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan English Grade IX I. ObjectiveDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan English Grade IX I. ObjectiveBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Journal Entry No.1Document2 pagesJournal Entry No.1Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Biography To BeDocument3 pagesBiography To BeBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- DLL 10 Feb Week 1Document5 pagesDLL 10 Feb Week 1Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Matrix (June 1-5, 2020) Making of Learning Modules Based On MELCDocument2 pagesWeekly Matrix (June 1-5, 2020) Making of Learning Modules Based On MELCBrigette Darren Baste Colita100% (1)
- Table of SpecificationDocument1 pageTable of SpecificationBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- DLL 9 Feb Week 1Document5 pagesDLL 9 Feb Week 1Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument3 pagesLetterBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Solit LetterDocument1 pageSolit LetterBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- DLL 9 Feb Week 2Document5 pagesDLL 9 Feb Week 2Brigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument3 pagesLetterBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Mps ENGLISH AND FILIPINODocument2 pagesMps ENGLISH AND FILIPINOBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Solit LetterDocument1 pageSolit LetterBrigette Darren Baste ColitaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Design: A SeriesDocument3 pagesMechanism Design: A Seriesamirmasood kholojiniNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pad Geometry and Material On Performance of Evaporative CoolerDocument11 pagesEffect of Pad Geometry and Material On Performance of Evaporative CoolerNavsumeet Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Bolted Connections PDFDocument56 pagesBolted Connections PDFÃvēđÆñ ŤhåķųřNo ratings yet
- TUDelft MBD LectureDocument8 pagesTUDelft MBD Lecturestarling1001408No ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetics Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesEngineering Electromagnetics Solutions Manualaamirjaved40No ratings yet
- (Environmental Science and Engineering) Jaime Klapp, Leonardo Di G. Sigalotti, Abraham Medina, Abel López, Gerardo Ruiz-Chavarría (Eds.)-Recent Advances in Fluid Dynamics With Environmental ApplicatioDocument509 pages(Environmental Science and Engineering) Jaime Klapp, Leonardo Di G. Sigalotti, Abraham Medina, Abel López, Gerardo Ruiz-Chavarría (Eds.)-Recent Advances in Fluid Dynamics With Environmental ApplicatioKyler GreenwayNo ratings yet
- Euler-Bernoulli Beam Theory - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesEuler-Bernoulli Beam Theory - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCordy Jourvel Itoua-TseleNo ratings yet
- Astrological Concepts and Applications DiscussedDocument2 pagesAstrological Concepts and Applications Discusseddevesh parwaniNo ratings yet
- True Stress-True Strain CurveDocument3 pagesTrue Stress-True Strain CurvePunith MlNo ratings yet
- Steel Jacket Retrofitting 1 PDFDocument12 pagesSteel Jacket Retrofitting 1 PDFzakaria200811060No ratings yet
- Dis7 PDFDocument3 pagesDis7 PDFRajasree RajiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers ExplainedDocument2 pagesQuantum Numbers ExplainedSelva ManiNo ratings yet
- L4 - Application of Momentum Integral Theorem and Boundary Layer SeparationDocument25 pagesL4 - Application of Momentum Integral Theorem and Boundary Layer SeparationKar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Microscale Heat Transfer - Fundamentals and Applications PDFDocument516 pagesMicroscale Heat Transfer - Fundamentals and Applications PDFAndréRocha100% (1)
- Roger Malina On Jim Campbell Art Series "Illuminated Averages"Document2 pagesRoger Malina On Jim Campbell Art Series "Illuminated Averages"roger malinaNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Buried Pipelines in Dense Sand For Oblique Movement in Vertical - Lateral PlaneDocument12 pagesModeling of Buried Pipelines in Dense Sand For Oblique Movement in Vertical - Lateral PlaneMD Anan MorshedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism and Magnetism ReviewDocument3 pagesElectromagnetism and Magnetism ReviewEncey Enerva GacasanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - VOL 1 UNIT 1 KEY CONCEPTSDocument135 pagesPHYSICS - VOL 1 UNIT 1 KEY CONCEPTSUma Maheswari100% (1)
- Quantum Physics, Depth Psychology, and BeyondDocument16 pagesQuantum Physics, Depth Psychology, and BeyondquantumrealmNo ratings yet
- Exchange InteractionDocument3 pagesExchange InteractionCharudatta GalandeNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Thermodynamic Data: (HJ) (HJ)Document18 pagesAppendix A Thermodynamic Data: (HJ) (HJ)jhNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept: By:-Harjit Singh MEC106Document12 pagesBasic Concept: By:-Harjit Singh MEC106nirobNo ratings yet
- Analysis of continuous prestressed concrete beamsDocument14 pagesAnalysis of continuous prestressed concrete beamsChinnu JacobNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument6 pagesStepper MotorAsith Savinda100% (1)
- SeminarDocument20 pagesSeminarGaurav UmarNo ratings yet
- A Study On Piled Raft FoundationDocument7 pagesA Study On Piled Raft FoundationCostas SachpazisNo ratings yet
- Elder 1967Document15 pagesElder 1967ALEJANDRO GANCEDO TORALNo ratings yet
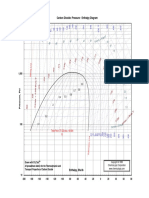
- CO2 Mollier Chart PDFDocument1 pageCO2 Mollier Chart PDFmarko quirozNo ratings yet
- Physics - ANSWERS - David Homer and Michael Bowen-Jones - Oxford 2014Document39 pagesPhysics - ANSWERS - David Homer and Michael Bowen-Jones - Oxford 2014Proleteriat Dictatorship of Koperia100% (1)
- Plate Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesPlate Heat Exchanger조기현No ratings yet