Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Compressor Power
Uploaded by
muhd.qasimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Compressor Power
Uploaded by
muhd.qasimCopyright:
Available Formats
5-126
5-152 An air compressor consumes 4.5 kW of power to compress a specified rate of air. The flow work
required by the compressor is to be compared to the power used to increase the pressure of the air.
Assumptions 1 Flow through the compressor is steady. 2 Air is an ideal gas.
Properties The gas constant of air is 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K (Table A-1).
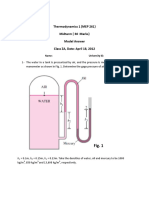
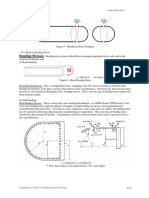
1 MPa
Analysis The specific volume of the air at the inlet is 300°C
RT1 (0.287 kPa ⋅ m 3 /kg ⋅ K )(20 + 273 K )
v1 = = = 0.7008 m 3 /kg Compressor
P1 120 kPa
The mass flow rate of the air is
120 kPa
V 0.010 m 3 /s 20°C
m& = 1 = = 0.01427 kg/s
v 1 0.7008 m 3 /kg
Combining the flow work expression with the ideal gas equation of state gives the flow work as
wflow = P2v 2 − P1v 1 = R(T2 − T1 ) = (0.287 kJ/kg ⋅ K)(300 − 20)K = 80.36 kJ/kg
The flow power is
W& flow = m& wflow = (0.01427 kg/s)(80.36 kJ/kg) = 1.147 kW
The remainder of compressor power input is used to increase the pressure of the air:
W& = W& total,in − W& flow = 4.5 − 1.147 = 3.353 kW
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and
educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
You might also like
- ES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument5 pagesES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat Transferyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document7 pagesUntitled 1Jesica QuentNo ratings yet
- Tme 213 Classwork SolutionsDocument15 pagesTme 213 Classwork SolutionsEnenamahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Answer's SchemeDocument27 pagesAssignment 1 Answer's Schemedangoy raulNo ratings yet
- 2W04 Assignment 5 - 2023 Solutions PDFDocument4 pages2W04 Assignment 5 - 2023 Solutions PDFas asNo ratings yet
- Solutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007Document7 pagesSolutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007clearcastingNo ratings yet
- Boundary Work CalculationsDocument8 pagesBoundary Work Calculationsyeng botzNo ratings yet
- 3Document10 pages3Ariel Carlos De LeonNo ratings yet
- BENGUET STATE UNIVERSITY PROBLEM SOLVINGDocument7 pagesBENGUET STATE UNIVERSITY PROBLEM SOLVINGyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Valdez, Shenny RoseDocument3 pagesValdez, Shenny Roseyeng botzNo ratings yet
- TutorialsDocument11 pagesTutorialsAditya MallickNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeDocument13 pages2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeSergey ShkapovNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P061Document22 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P061IENCSNo ratings yet
- Gage Atm O: PG 500 KpaDocument3 pagesGage Atm O: PG 500 Kpayeng botzNo ratings yet
- Lunes, Herzon S.Document7 pagesLunes, Herzon S.yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Iron block dropped in insulated water tank entropy changeDocument5 pagesIron block dropped in insulated water tank entropy changeMUHAMMAD ALIFF HAIKAL BIN SHOLAHUDIN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- BUGNAY, Jula ClaireDocument6 pagesBUGNAY, Jula Claireyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Es 31: Laboratoty Activity Bugnay, Jula Claire E. Bsaeng'G 4ADocument6 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Es 31: Laboratoty Activity Bugnay, Jula Claire E. Bsaeng'G 4Ayeng botzNo ratings yet
- BALLESTA, Karen Antoinnete A.Document3 pagesBALLESTA, Karen Antoinnete A.yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PDFMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4nick thompsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PDFSusana PérezNo ratings yet
- Ke PeDocument11 pagesKe PeAriel Carlos De LeonNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 Solutions Water and Air Thermodynamic Process TableDocument4 pagesHomework 6 Solutions Water and Air Thermodynamic Process TableCatherineNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Laboratory ExerciseDocument6 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Laboratory Exerciseyeng botzNo ratings yet
- hw#3 SolutionsDocument7 pageshw#3 SolutionsZumaflyNo ratings yet
- Mallare, Cindy Gayle MDocument3 pagesMallare, Cindy Gayle Myeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Tut-3 - Problems - AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Tut-3 - Problems - AnswersArchishman SinghNo ratings yet
- Chattom, Tim S.Document7 pagesChattom, Tim S.yeng botzNo ratings yet
- 2300 HW 11 Sol PDFDocument4 pages2300 HW 11 Sol PDFJose Luis Huaman AlbornozNo ratings yet
- KJ/KG 1 - 2988 C 0 35 Mpa 8 ¿ QDocument5 pagesKJ/KG 1 - 2988 C 0 35 Mpa 8 ¿ QKimi HakimiNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350Document1 pageSupplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350physics a2No ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P061Document22 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P061Darly DanielaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation ReportDocument8 pagesPresentation ReportJackson ChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Examples&SolutionDocument42 pagesChapter 9 Examples&SolutionSami ullahNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionDocument10 pagesThermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionEarl Maxie Lagdamin ErederaNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P102Document20 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P102Marilyn EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesThermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualRhondaFisherjity100% (54)
- Thermodyancs chapter 9 solution manuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs chapter 9 solution manuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet
- PAC ES, MishaelDocument7 pagesPAC ES, Mishaelyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasDocument7 pagesEngineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasazzraNo ratings yet
- ME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionDocument3 pagesME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionallyhawNo ratings yet
- DUGAYON, Anice DDocument4 pagesDUGAYON, Anice Dyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Work ProblemsDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Work ProblemsSaroj BaralNo ratings yet
- Assumptions 1 This Is A Steady-Flow Process and Thus The Mass Flow Rate of Dry Air Remains Constant During The EntireDocument1 pageAssumptions 1 This Is A Steady-Flow Process and Thus The Mass Flow Rate of Dry Air Remains Constant During The EntireOsbaldoSolorzanoHerreraNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P102Document20 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P102IENCSNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheets For Thermodynamics 02Document3 pagesTutorial Sheets For Thermodynamics 02Aditya raj sachdevNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MED205Document4 pagesTutorial MED205Anonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- 8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkDocument8 pages8-39E Oxygen Gas Is Compressed From A Specified Initial State To A Final Specified State. The Reversible WorkAnonymous 5OI0ClBZNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Engineers Si Edition 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesThermodynamics For Engineers Si Edition 1st Edition Kroos Solutions ManualBrianDaviswxfd100% (27)
- 2300 HW 9 SolDocument4 pages2300 HW 9 SolMonishaNo ratings yet
- Given: Req'd:: 1. The Pressure Gage On A 2.5-mDocument5 pagesGiven: Req'd:: 1. The Pressure Gage On A 2.5-myeng botzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1daejung1025No ratings yet
- ME3100 Solution Tut-2Document8 pagesME3100 Solution Tut-2B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- Westermann Table 7Document1 pageWestermann Table 7muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Seismic Zones of PakistanDocument1 pageSeismic Zones of Pakistanmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Westermann Tables: Steels For Hardening and TemperingDocument1 pageWestermann Tables: Steels For Hardening and Temperingmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Westermann Table 8Document1 pageWestermann Table 8muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Scope of This ManualDocument1 page1.0 Scope of This Manualmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Rate of Heat Lost From TurbineDocument1 pageRate of Heat Lost From Turbinemuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Westermann Tables: Specific Weights, Melting Points, Coefficients of Thermal Expansion and ShrinkageDocument1 pageWestermann Tables: Specific Weights, Melting Points, Coefficients of Thermal Expansion and Shrinkagemuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Westermann Table 7Document1 pageWestermann Table 7muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Westermann Tables: IS:1762-1961 IS:4843-1968Document1 pageWestermann Tables: IS:1762-1961 IS:4843-1968muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Flow Power of ExchangerDocument1 pageFlow Power of Exchangermuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Existing Bottom Plate Existing Bottom Plate: NotesDocument1 pageExisting Bottom Plate Existing Bottom Plate: Notesmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- CalibrationDocument1 pageCalibrationmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Materials classification and properties tableDocument1 pageMaterials classification and properties tablemuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Tray of ColumnDocument1 pageTray of Columnmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Tehsil Seismic Zone Tehsil Seismic Zone Tehsil Seismic Zone: BCP SP-2007 CH-02Document1 pageTehsil Seismic Zone Tehsil Seismic Zone Tehsil Seismic Zone: BCP SP-2007 CH-02muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Seismic Zones of Pakistan Part 2Document1 pageSeismic Zones of Pakistan Part 2muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Bending Stresses.: ... Two Kinds of Bending StressDocument1 pageBending Stresses.: ... Two Kinds of Bending Stressmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- PF For Heat ExchangerDocument1 pagePF For Heat Exchangermuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Nozzle/Pro Load Cases and Combinations: NozzleproDocument1 pageNozzle/Pro Load Cases and Combinations: Nozzlepromuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Bending Stresses.: ... Two Kinds of Bending StressDocument1 pageBending Stresses.: ... Two Kinds of Bending Stressmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Table 4-1 Maximum Allowable Shell Stresses: (Not For Use For Reconstructed Tanks, See Note 6)Document1 pageTable 4-1 Maximum Allowable Shell Stresses: (Not For Use For Reconstructed Tanks, See Note 6)muhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- 160 Principles of HVAC, 8th Edition: Table 5-11 Relative Thermal Resistances of Building MaterialDocument1 page160 Principles of HVAC, 8th Edition: Table 5-11 Relative Thermal Resistances of Building Materialmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Occasional LoadDocument1 pageOccasional Loadmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Common Load Types and Categories Common Load Types and Categories Primary Loads Primary LoadsDocument1 pageCommon Load Types and Categories Common Load Types and Categories Primary Loads Primary Loadsmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- SQ Honeycomb SketchDocument1 pageSQ Honeycomb Sketchmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- PEB Structure SampleDocument1 pagePEB Structure Samplemuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Index 7thedDocument4 pagesIndex 7thedmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Fabric Pad Sliding BearingsDocument1 pageFabric Pad Sliding Bearingsmuhd.qasimNo ratings yet
- Heating Load Calculation ExampleDocument1 pageHeating Load Calculation Examplemuhd.qasimNo ratings yet