Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Velocity and Acceleration Analysis
Uploaded by
Prithvi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views6 pagesThe document is an assignment for a course on Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery. It contains 10 multi-part questions assessing students' ability to apply concepts related to determining velocity and acceleration in mechanisms (CO2). The questions involve calculations for mechanisms such as radial valve gears, four-bar linkages, engines, and more. Students are asked to use methods like Klein's construction to solve for velocities and accelerations at different positions in the mechanisms.
Original Description:
Problems related to velocity and acceleration analysis.
Original Title
Velocity and acceleration analysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is an assignment for a course on Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery. It contains 10 multi-part questions assessing students' ability to apply concepts related to determining velocity and acceleration in mechanisms (CO2). The questions involve calculations for mechanisms such as radial valve gears, four-bar linkages, engines, and more. Students are asked to use methods like Klein's construction to solve for velocities and accelerations at different positions in the mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views6 pagesVelocity and Acceleration Analysis
Uploaded by
PrithviThe document is an assignment for a course on Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery. It contains 10 multi-part questions assessing students' ability to apply concepts related to determining velocity and acceleration in mechanisms (CO2). The questions involve calculations for mechanisms such as radial valve gears, four-bar linkages, engines, and more. Students are asked to use methods like Klein's construction to solve for velocities and accelerations at different positions in the mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
THIAGARAJAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, MADURAI
(A Govt. Aided ISO 9001:2008 Certified Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Anna University)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
ASSIGNMENT – 5
Course Code 14ME620 Course Name Kinematics & Dynamics of Machinery
Degree B.E. Programme Mechanical Engineering Semester VI
Date 08.05.2019 Submission Date 15.05.2019 Max. Marks 100
Faculty-in-Charge Prof. B. Sankar
Assessment Pattern:
Remember Understand Apply Analyse Evaluate Create Total
20 20 60 - - - 100
Course Outcomes (COs) for Assessment in this test:
COs Course Outcome Bloom’s Category
CO2 Determine velocity and acceleration for simple mechanisms Apply
Answer all the Questions:
Part C (Apply) CO Marks
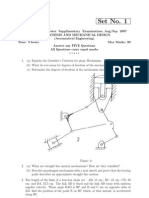
The following Figure shows the mechanism of a radial
valve gear. The crank OA turns uniformly at 150
revolutions per minute and is pinned at A to rod AB.
The point C in the rod is guided in the circular path
C1. with D as centre and DC as radius. The dimensions of CO2 (10)
various links are: OA = 150 mm; AB = 550 mm; AC
= 450 mm; DC = 500 mm; BE = 350 mm. Determine
velocity and acceleration of the ram E for the given
position of the mechanism.
In a Whitworth quick return motion, as shown in
Figure. OA is a crank rotating at 30 revolutions per
minute in a clockwise direction. The dimensions of
various links are: OA = 150 mm; OC = 10 mm; CD =
125 mm; and DR = 500 mm. Determine the
acceleration of the sliding block R and the angular
accelerating of the slotted lever CA.
C2. CO2 (10)
ABCD is a four-bar mechanism with the link AD
C3. fixed. The lengths of the links are: AB = 60 mm, BC CO2 (10)
= 175 mm, CD = 110 mm and DA = 200 mm.
The crank AB rotates at 100 rpm constant clockwise
and the angle BAD = 60°. At this instant.
(i) Draw the velocity diagram with suitable scale.
(ii) Find the velocity of the point C.
(iii) Find the magnitude and direction of the angular
velocity of the link
BC.
(iv)Draw the acceleration diagram with suitable scale.
(v) Find the acceleration of the point C.
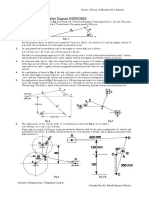
In a toggle mechanism, as shown in the figure, D is
constrained to move on a horizontal path. The
dimensions of the various links are: AB = 200 mm,
BC = 300 mm, OC = 150 mm and BD = 450 mm. The
crank OC is rotating in a counter clockwise direction
at a speed of 180 rpm, increasing at the rate of 50
rad/s2. Determine for given configuration,
(i) Velocity and acceleration of the slider D and
(ii) Angular velocity and angular acceleration of BD.
C4. CO2 (10)
A reciprocating engine mechanism shown in the
figure had crank 105 mm long rotates in clockwise
direction with an angular velocity of 175 rad/sec and CO2 (10)
C5.
an angular acceleration of 1600 rad/sec2. The
connecting rod is 300 mm long and its centre of
gravity (G) is 140 mm from the crank end. Determine
Velocity and acceleration of G and Angular velocity
and angular acceleration of Connecting rod.
In the mechanism, as shown in Fig. 7.32, OA and OB
are two equal cranks at right angles rotating
about O at a speed of 40 r.p.m. anticlockwise. The
dimensions of the various links are as follows: OA =
OB = 50 mm; AC = BD = 175 mm; DE = CE = 75
mm; FG = 115 mm and EF = FC.
Draw velocity diagram for the given configuration of
the mechanism and find velocity of the slider G. CO2 (10)
C6.
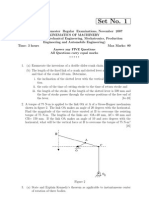
In a mechanism as shown in Figure, the crank OA is
100 mm long and rotates in a clockwise direction at a
speed of 100 r.p.m. The straight rod BCD rocks on a
C7.
fixed point at C. The links BC and CD are each 200 CO2 (10)
mm long and the link AB is 300 mm long. The slider
E, which is driven by the rod DE is 250 mm long. Find
the velocity and acceleration of E.
In the mechanism shown in Figure, find the
instantaneous centres of the links B, C and D. If the
link A rotates clockwise at 10 rad/s, find the angular
velocity of link E. The lengths of various links are as
follows:
Link A = 25 mm; Link B = Link C = 100 mm; Link D
= Link E = 50 mm. The link D is hinged to link B at
25 mm from the left-hand end of link B.
C8. CO2 (10)
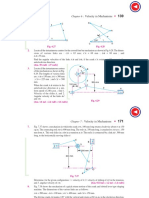
The Crank of a reciprocating engine is 225 mm long,
the connecting rod is 900 mm long and the speed of
rotation of the crank is 150 rpm. Find the velocity and
the acceleration of the piston and the angular velocity
and the angular acceleration of the connecting rod
when the angle which the crank makes with inner dead
centre is,
C9. Case: i). 300 CO2 (10)
Case: ii). 1200.
Case: iii). 00
Case: iv). 900
Use Klein’s Construction method. Take all the angles
CW from Inner dead centre
An IC Engine runs at 2000 rpm. The length of the
connecting rod is 270 mm and the crank radius is 60
mm. Determine using Klein’s Construction, the
i) Linear Velocity of the piston
ii) Linear Acceleration of the piston
iii) Angular Velocity of the connecting rod
iv) Angular Acceleration of the connecting rod
C10. CO2 (10)
Case: i). 600
Case: i). 450
Case: i). 1800
Case: i). 2700
Take all the angles CW from Inner dead centre.
You might also like
- Mechanisms and Mechanical DesignDocument9 pagesMechanisms and Mechanical DesignNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeHarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetAgare Tube0% (1)
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- 10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDocument5 pages10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Document11 pagesKinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration NumericalDocument2 pagesVelocity and Acceleration NumericalSpidyNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - U-Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisDocument2 pagesLab 4 - U-Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Question Bank KOMDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank KOMMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 KDMDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 KDMvishalNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument2 pagesTheory of MachineRıshabhBhawarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - KTM - 3131906Document11 pagesLab Manual - KTM - 3131906Jayal PatelNo ratings yet
- EMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Document4 pagesEMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Charles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Kom Assignment IDocument4 pagesKom Assignment IChadaram Jagadish JagadishNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Class Test Question Paper Kinematics of Machinery - 21-22 - FinalDocument3 pagesClass Test Question Paper Kinematics of Machinery - 21-22 - FinalRavi PatilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFSarvesh ArbattiNo ratings yet
- 18ME44 AssignmentDocument1 page18ME44 AssignmentbalajiNo ratings yet
- Relative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsDocument9 pagesRelative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsSanket KumbharNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Kamalesh DfcNo ratings yet
- Cms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsDocument17 pagesCms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsRajueswarNo ratings yet
- 10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pages10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartsatheeshNo ratings yet
- Tom 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTom 1 PDFSherry PetersonNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Theory of Machineries PDFDocument5 pagesMechanism and Theory of Machineries PDFJake AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument9 pagesKinematics of MachineryChinmay SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Acceleration AnalysisDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Acceleration Analysisameet_sata20000% (1)
- VelocitytutorialDocument4 pagesVelocitytutorialManoz Thapa KajiNo ratings yet
- Mechanism WorksheetDocument8 pagesMechanism Worksheetnatnaelzelalem03No ratings yet
- A.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesA.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- NR 220304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesNR 220304 Kinematics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KompsnasabariNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Velocity AnalysisDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Velocity Analysisdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Mech IV Sem Question BankDocument59 pagesMech IV Sem Question BankSivaNo ratings yet
- Me1252 Kinematics of MachineryDocument3 pagesMe1252 Kinematics of MachineryManikandan SelvamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery May2004 Rr222105 Nr220304Document9 pagesKinematics of Machinery May2004 Rr222105 Nr220304Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- KoM-LQs Units3, 4&5Document7 pagesKoM-LQs Units3, 4&5puneethNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Illustrate Your Answers With Neat Sketches Wherever NecessaryDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Illustrate Your Answers With Neat Sketches Wherever NecessaryKumaran RNo ratings yet
- R05 Set No. 2Document12 pagesR05 Set No. 2Rajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pages9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 NewDocument2 pagesTutorial-2 NewAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- r05310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument10 pagesr05310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- HW 4Document4 pagesHW 4earn owinoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery QPDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinery QPshiekziaNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajNo ratings yet
- ME6401-Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesME6401-Kinematics of Machineryappuanandh7811No ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument3 pagesAssignment IJET JETNo ratings yet
- 16 Mark QuestionDocument6 pages16 Mark QuestionMECH HODNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument7 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankpanneerthambiNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Mechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsFrom EverandMechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualFrom EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Week 7..Document3 pagesWeek 7..Lance Cj S. CapistranoNo ratings yet
- UT - Questions and AnswersDocument238 pagesUT - Questions and AnswersDeepak_Gurjar100% (7)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 - EM-WAVESDocument12 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 - EM-WAVESCyril Cauilan100% (2)
- Communication Cables-Specification For Test MethodsDocument54 pagesCommunication Cables-Specification For Test MethodsquycoctuNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Remco Van Der Plaats PDFDocument82 pagesMSC Thesis Remco Van Der Plaats PDFKaide Johar BohraNo ratings yet
- 1756 Pa75 PDFDocument24 pages1756 Pa75 PDFDiogo FiaesNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerMilorad RadenovicNo ratings yet
- EMT Quiz - 1 Type A Answers UnderlinedDocument3 pagesEMT Quiz - 1 Type A Answers UnderlinedAbhishekKumarNo ratings yet
- Battery TenderDocument2 pagesBattery TenderEduardo VicoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation CFDDocument4 pagesDissertation CFDPaperHelpCanada100% (1)
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument7 pagesBrushless DC MotorsRonald LugwireNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis of 8-Bus Power System Using ETAPDocument11 pagesLoad Flow Analysis of 8-Bus Power System Using ETAPsaadiaNo ratings yet
- Brushless Excitation SystemDocument27 pagesBrushless Excitation SystemSam100% (2)
- Electric Power Systems ResearchDocument10 pagesElectric Power Systems ResearchEmad GameilNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument14 pagesCircular MotionTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Verification of Thevenin's Theorem.Document3 pagesVerification of Thevenin's Theorem.Sharmin83% (6)
- Electricity Tariff Rates of Nepal Electricity Authority: Category A: Domestic ConsumersDocument3 pagesElectricity Tariff Rates of Nepal Electricity Authority: Category A: Domestic Consumersmarab12No ratings yet
- Samsung k15d Chassis Ct21v10mnfxrclDocument40 pagesSamsung k15d Chassis Ct21v10mnfxrclVictor Javelosa Azuelo Jr.No ratings yet
- Cotactors Relays MCCBDocument3 pagesCotactors Relays MCCBchamara kumarasingheNo ratings yet
- Advances in Pulsed Power Technology 1-Opening Switches PDFDocument321 pagesAdvances in Pulsed Power Technology 1-Opening Switches PDFtheodorakis017781100% (1)
- 1 Motor Protection Single SessionDocument27 pages1 Motor Protection Single Sessionmubarakkirko100% (1)
- Course Title: Electrical Drives Dated: 01-12-2014 Course Code: EEE 3422 Course Structure: 3-1-0-4 Course ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCourse Title: Electrical Drives Dated: 01-12-2014 Course Code: EEE 3422 Course Structure: 3-1-0-4 Course ObjectivesAR-TNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics NotesDocument115 pagesClass 12 Physics NotesAiden Pearce100% (1)
- Power Calculation Summary and ExamplesDocument12 pagesPower Calculation Summary and ExamplesHernán RodarteNo ratings yet
- Performance Testing of Different Grounding SystemsDocument8 pagesPerformance Testing of Different Grounding SystemsFernandoCrespoMonNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of TransformersDocument3 pagesParallel Operation of TransformersHARIHARANNo ratings yet
- A Sensitive Vibrating Sample MagnetometerDocument3 pagesA Sensitive Vibrating Sample Magnetometersoumendra ghoraiNo ratings yet
- LED Floodlight: Mounting InstructionsDocument3 pagesLED Floodlight: Mounting InstructionsRomly 710No ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument5 pagesWork Energy and PowerjunquelalaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticDocument10 pagesModule 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticPermanente Health Plan Corporation PHPNo ratings yet