Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Series for Single Displacement Reactions
Uploaded by
Yob BeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity Series for Single Displacement Reactions
Uploaded by
Yob BeeCopyright:
Available Formats
A.
Romero 2009
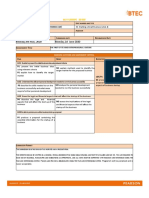
The Activity Series for Single Displacement Reactions
CHEM 30A
Activity Series:
Metals Non-metals
and H (Halogens)
Higher oxidation potential K F2 Higher reduction potential
(greater tendency to form cations) (greater tendency to form anions)
Ca Cl2
Na Br2
Mg I2
Al
Zn Increasing Activity
Fe
Ni
Sn
Pb
H
Cu
Ag
Hg
Au
A more active element (higher on the table above) will form an ion and displace the ion of like charge
from the compound. The displaced ion will become a neutral element (see diatomic elements below).
Al + PbCl2 ?
Al forms cations, and
Predict products: Al + PbCl2 AlCl3 + Pb is more active than Pb
Balance: 2 Al + 3 PbCl2 2 AlCl3 + 3 Pb
Cl2 + FeBr3 ?
Cl forms anions, and
Predict products: Cl2 + FeBr3 FeCl3 + Br2 is more active than Br
Balance: 3 Cl2 + 2 FeBr3 2 FeCl3 + 3 Br2
A less active element (lower on the table) cannot displace the ion from the compound, therefore, there
will be no reaction.
Pb + AlCl3 ?
Pb forms cations, but
Predict products: Pb + AlCl3 no reaction is less active than Al
Br2 + FeCl3 ?
Br forms anions, but
Predict products: Br2 + FeCl3 no reaction is less active than Cl
Diatomic elements:
There are seven elements that exist as diatomic (two atom) neutral molecules:
Br I N Cl H O F
These elements can have a subscript of one if they are an ion or part of a compound, but will pair up
(subscript of two) when alone and neutral.
Example: oxygen
O2– okay (ion)
H2 O okay (compound)
O not okay (alone and neutral)
write O2 instead
When a non-metal ion is being displaced, be sure to check whether or not the neutral element produced
is diatomic.
You might also like
- Exodus Post Apocalyptic PDF 10Document2 pagesExodus Post Apocalyptic PDF 10RushabhNo ratings yet
- QHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONDocument25 pagesQHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONherisb100% (1)
- Proposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Document6 pagesProposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Foster Boateng67% (3)
- 14 - Habeas Corpus PetitionDocument4 pages14 - Habeas Corpus PetitionJalaj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Element and CompoundsDocument14 pagesElement and CompoundsKehekeshan RizwanNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Topic 9 Oxidation & Reduction SL Past PaperDocument19 pagesIB Chemistry Topic 9 Oxidation & Reduction SL Past PaperNicholas Yeoh100% (7)
- Redox SL StudentsDocument18 pagesRedox SL StudentsMiaNo ratings yet
- Audience AnalysisDocument7 pagesAudience AnalysisSHAHKOT GRIDNo ratings yet
- Steps To Predicting The Products of Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesSteps To Predicting The Products of Chemical ReactionsAldi JonataNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Tools for Data Analysis and Quality EvaluationDocument45 pagesBasic Statistical Tools for Data Analysis and Quality EvaluationfarjanaNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesFrom EverandOrganometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesNo ratings yet
- Rhodes Solutions Ch4Document19 pagesRhodes Solutions Ch4Joson Chai100% (4)
- Chapter-8 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesChapter-8 ElectrolysisOhi AhmedNo ratings yet
- P Block ElementsDocument24 pagesP Block Elementssanjusenthil8No ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsHema lathaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations: Prepared By: Ariza D. Capucao, R.PH., MaedDocument27 pagesChemical Reactions and Chemical Equations: Prepared By: Ariza D. Capucao, R.PH., MaedJungkook JeonNo ratings yet
- Kimia Dasar Bahan Kuliah 7Document21 pagesKimia Dasar Bahan Kuliah 7Alifa ZahiraNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND BALANCING EQUATIONSDocument36 pagesCHEMICAL REACTIONS AND BALANCING EQUATIONSChelsia Venice MorilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Periodic TableDocument27 pagesChapter 13 Periodic TableMatthew John RashadMehanyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical SeriesDocument8 pagesTutorial on Reactivity Series vs Electrochemical SeriesoscarbecNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - IDocument46 pagesS-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - Iविशाल जायसवालNo ratings yet
- Orgmol Lec Prelims Trans 1Document13 pagesOrgmol Lec Prelims Trans 1Aya Xiara HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- The HalogensDocument9 pagesThe HalogensAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsvfdfdNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Document20 pagesUnit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Thilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Oxidation State Size: Making It InertDocument12 pagesOxidation State Size: Making It InertsdnishacNo ratings yet
- Oxidising Power of Halogens Oxidising Power of Halogens: No Organic Solvent UsedDocument2 pagesOxidising Power of Halogens Oxidising Power of Halogens: No Organic Solvent Usedcharlesma123No ratings yet
- Graduation of properties in the Modern periodic tableDocument2 pagesGraduation of properties in the Modern periodic tablemido titoNo ratings yet
- 72bd0be0-7231-11ee-a64d-dba66c595fb0Document29 pages72bd0be0-7231-11ee-a64d-dba66c595fb0carla.habib7579No ratings yet
- S-Block Lecture NotesDocument43 pagesS-Block Lecture NotesIchhpilani KabirNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis and Electroplating ExplainedDocument24 pagesElectrolysis and Electroplating ExplainedRosmaini MohamadNo ratings yet
- S Block-1Document46 pagesS Block-1Jeevan KumarNo ratings yet
- S Block (Landscape)Document8 pagesS Block (Landscape)Drastic Pranksters Inc.No ratings yet
- Chapmann Oxidation-Reduction Activity SeriesDocument6 pagesChapmann Oxidation-Reduction Activity SeriesDanyNo ratings yet
- Activity Series Lab (Akey)Document4 pagesActivity Series Lab (Akey)jcastill77No ratings yet
- Topic 9 QDocument19 pagesTopic 9 QIndraneel BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- STPM 2013 SEM 2Document5 pagesSTPM 2013 SEM 2m-4306022No ratings yet
- Day+-+1Document6 pagesDay+-+1tnsqnrw000No ratings yet
- Groupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaDocument6 pagesGroupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaGlad YsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 C-C C-X Bods Formation With Organometallics 2021 22Document71 pagesChapter 7 C-C C-X Bods Formation With Organometallics 2021 22hectormunozroNo ratings yet
- Learn ionic formulas and naming compoundsDocument11 pagesLearn ionic formulas and naming compoundsAdi ChhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PharChemDocument6 pagesChapter 1 PharChemno nameNo ratings yet
- Group I & II MetalsDocument60 pagesGroup I & II MetalsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Atomic Structure - AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Atomic Structure - Answerscom 2501No ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Periodic Table Valency and FormulaDocument7 pagesSilo - Tips Periodic Table Valency and Formulamainakdas73No ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Workbook Revised 1ADocument15 pagesOxidation and Reduction Workbook Revised 1AMarisa St. LouisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Writing Formula and Chemical EquationsDocument18 pagesChemistry - Writing Formula and Chemical EquationsexperiorNo ratings yet
- 509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Document9 pages509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Rakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes OLDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes OLHooria AminNo ratings yet
- T3 - Redox I SLOP BookletDocument13 pagesT3 - Redox I SLOP BookletJakeNo ratings yet
- Activity Series of MetalsDocument48 pagesActivity Series of MetalsUzma shaheenNo ratings yet
- 1.4 BI CompleteDocument9 pages1.4 BI CompleteRawid GoshanNo ratings yet
- OL Chemistry Notes - Periodic Table (1)Document2 pagesOL Chemistry Notes - Periodic Table (1)manoirfan987No ratings yet
- HalogenosDocument12 pagesHalogenosAlexander PavonNo ratings yet
- Jee S BlockDocument129 pagesJee S BlockAmirtha RajNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction: Chem 16 Lab Second Long ExamDocument4 pagesRedox Reaction: Chem 16 Lab Second Long ExamAmethyst GomezNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument61 pagesChemical ReactionsTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument39 pagesAlkaline Earth MetalsAigerim TurlanovaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument13 pagesChemical ReactionSujit LawareNo ratings yet
- Chemical Substances and Processes Chapter SummaryDocument50 pagesChemical Substances and Processes Chapter SummaryTechnical Section- Sr.DEE/G/ASNNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 4Document34 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 4Akiyo WeiNo ratings yet
- bondingDocument8 pagesbondingb52352986No ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument51 pagesThe S-Block ElementsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- S - 10-HO 1.3 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument4 pagesS - 10-HO 1.3 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsSaatvik RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 KSSM: 8 February 2021Document24 pagesChemistry Form 5 KSSM: 8 February 2021NurNo ratings yet
- DU - BSC (H) CS BookletDocument121 pagesDU - BSC (H) CS BookletNagendra DuhanNo ratings yet
- GNED 500 Social AnalysisDocument2 pagesGNED 500 Social AnalysisEshita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)Document3 pagesChapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)JayjayNo ratings yet
- Assignment Brief Starting A Small BusinessDocument3 pagesAssignment Brief Starting A Small BusinessFaraz0% (1)
- Leibniz Integral Rule - WikipediaDocument70 pagesLeibniz Integral Rule - WikipediaMannu Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Awareness Training On Filipino Sign Language (FSL) PDFDocument3 pagesAwareness Training On Filipino Sign Language (FSL) PDFEmerito PerezNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Consumer BehaviourDocument16 pagesDeterminants of Consumer BehaviouritistysondogNo ratings yet
- John R. Van Wazer's concise overview of phosphorus compound nomenclatureDocument7 pagesJohn R. Van Wazer's concise overview of phosphorus compound nomenclatureFernanda Stuani PereiraNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Analytics Training at MAJUDocument1 pageSAP HANA Analytics Training at MAJUXINo ratings yet
- Overview of Isopanisad, Text, Anvaya and TranslationDocument7 pagesOverview of Isopanisad, Text, Anvaya and TranslationVidvan Gauranga DasaNo ratings yet
- Jaimini Astrology - Calculation of Mandook Dasha With A Case StudyDocument6 pagesJaimini Astrology - Calculation of Mandook Dasha With A Case StudyANTHONY WRITER100% (3)
- Challengue 2 Simpe P.P TenseDocument7 pagesChallengue 2 Simpe P.P TenseAngel AngelNo ratings yet
- Understanding EndogeneityDocument25 pagesUnderstanding EndogeneityagustinusNo ratings yet
- Jobgpt 9d48h0joDocument6 pagesJobgpt 9d48h0jomaijel CancinesNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Corporate GovernanceDocument21 pagesRangkuman Corporate GovernanceAlissa JanssensNo ratings yet
- A Study of Outdoor Interactional Spaces in High-Rise HousingDocument13 pagesA Study of Outdoor Interactional Spaces in High-Rise HousingRekha TanpureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Nhi Nguyễn Ngọc PhươngNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced ResearchDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced Researchsoumya mahantiNo ratings yet
- New GK PDFDocument3 pagesNew GK PDFkbkwebsNo ratings yet
- The Great Idea of Brook TaylorDocument7 pagesThe Great Idea of Brook TaylorGeorge Mpantes mathematics teacherNo ratings yet
- CvSU Vision and MissionDocument2 pagesCvSU Vision and MissionJoshua LagonoyNo ratings yet
- Power of Positive Thinking EssayDocument7 pagesPower of Positive Thinking Essayafiboeolrhismk100% (2)
- Portal ScienceDocument5 pagesPortal ScienceiuhalsdjvauhNo ratings yet