Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alimentacià N Desde 4.3V A 24V Partiendo de 5V
Uploaded by
GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alimentacià N Desde 4.3V A 24V Partiendo de 5V
Uploaded by
GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
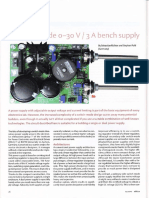
DESIGN TIPS
Avoltage booster using Arduino
By Clemens Valens (Elekior France Editorial)
lf your project needs a higher voltage rail than is already available
in the circuit, you can use an off-the-shelf step-up device. But when
you want a variable output voltage, it's less easy to find a ready-
made lC. However, it's not complicated to build such a circuit your-
self, especially if you have a microcontroller board that's as easy to
program as the Arduino. And this also lets you experiment with the
circuit so you can get a better understanding of how it works.
No surprises in the circuit- a largely conventional boost convertor. The
IVIOSFET is driven by a pulse width modulated (PWM) signalfrom the
pC, and the output voltage is measured by one of the pC's analogue
inputs. The driver adjusts the PWM signal according to the difference
between the output voltage measured and the voltage wanted.
We don't have enough space here to go into details about how this
circuitworl<s, but it's worth mentioning a few points of special inter-
est. The small capacitor across the diode improves the efficiency of
the circuit. The load is represented by R3. The components used
mal<e it possible to supply over 1 A (current limited by the MSSl 2607
683MLB inductor from Coilcraft), but maximum efficiency (89%) is grammed in assembler, allowing a maximum frequency of 62.5\<Hz
at around 95 mA (at an output voltage of 10 V). To avoid damaging (the pC runs at 16 MHz). To sample the output voltage, a frequency
the controller's analogue input (<5 V), the output voltage may not of 100 Hz is acceptable, which means we can use Arduino's standard
exceed 24Y. For higher voltages, the values of resistors R1 and R2 timers and analogue functions. The Arduino serial port is very handy
would need to be changed. - we can use it for sending the output voltage set point (5-24V)
The MOSFET is driven by the pC, which is nothing but a little Arduino and for collecting certain information about the operation.
board. The Arduino's default PWM signal frequency is around Thanl<s to the Arduino environment, it only tool< about half an hour
500 Hz - too low for this application, which needs a frequency at to program. You can download the software from 11l.
least 100 times higher. So we can't use the PWM functions offered (o9o894-l)
by Arduino. But that's no problem, as the Arduino can also be pro- [1 ] www.elel<tor.com/0g0gg4
UV light box
By Gert Baars (The Netherlands) is not nearly as difficult as most people assume.
The required items are a housing with a sheet of glass, UV fluo-
Fabricating printed circuit boards is not something that every elec- rescent tubes and perhaps a timer. The latter is not really neces-
tronics hobbyist does for themselves. lt is, however, not really that sary when a clock or watch is available. lt therefore comes down to
difficult. The most important necessities are a PCB layout, a printer obtaining the UV fluorescent tubes with starters and ballast and a
(or perhaps a copier), a light box, photo-sensitive PCB material, housing with a sheet of glass.
chemicals and an etching tray. lt is often the light box that presents There is a cheap solution for this. For the housing you can use a dis-
the most difficulties. carded sheet scanner with all the innards removed. The fluorescent
The PCB layout can be copied (using a copier) from an existing tubes could come from a face tanning machine, for example. ln the
design or you can design it yourself using a computer and suitable 'prototype' made by the author the frame complete with the fluo-
software. The layout needs to be printed onto a transparency (make rescent tubes was cut out. This could then be placed in its entirety
sure that the transparency is suitable for use in laser or inl<jet print- into the housing for the scanner. The accompanying starters and
ers). The necessary chemicals (sodium hydroxide for the develop- ballast fitted elsewhere in the old scanner housing and after con-
ing and iron(lll)-chloride or copper-chloride for the etching) are not necting allthe wires everything immediately worl<ed as it should.
difficult to obtain. lt is not necessary either to etch using a foam- Because the layout has to be in good contact with the PCB to pre-
etching box, but this does etch much quicker. Etching can simply vent shadowing, a sturdy piece of cardboard the same size as the
be done in a plastic tray, and etching with iron(lll)-chloride will be a glass was attached to the inside of the lid of the scanner. lt is neces-
little faster if the etchant is at about 40 "C. sary to apply some pressure on the lid during the exposure, but a
As already mentioned, exposing the PCB is often the most diffi- few books or fat catalogues on top ofthe lid is already sufficient. The
cult part. ln the past, the PCB with the layout in an exposing frame exposure time for the best results with this construction appears to
would sometimes be placed in the bright sun and it is also possible be about 2-3 minutes.
to expose the PCB using UV lamps. To mal<e a'real' light boxyourself (ogooBB)
elel<tor o4-2oio 75
You might also like
- THAN0060 Rev.1.50 EDocument12 pagesTHAN0060 Rev.1.50 EGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
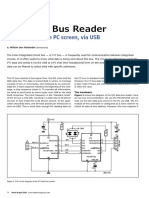
- Lector de Bus de Datos IÂ CDocument4 pagesLector de Bus de Datos IÂ CGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMiranda100% (1)
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentDocument23 pagesUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- SlideMembers FreeDesignTemplateAKoreanTileroofedHouse PS 2390Document6 pagesSlideMembers FreeDesignTemplateAKoreanTileroofedHouse PS 2390Layla LuluNo ratings yet
- MPX250S224J Suppression CapacitorDocument1 pageMPX250S224J Suppression CapacitorGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- Proteccià N DC para AltavocesDocument2 pagesProteccià N DC para AltavocesGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- SN75LVDS88PFD Texas InstrumentsDocument12 pagesSN75LVDS88PFD Texas InstrumentsGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- MSD3393LUDocument50 pagesMSD3393LUjose peresNo ratings yet
- T430QVN01 0-AuoDocument33 pagesT430QVN01 0-AuoGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- 5800-P24QB-WP20-C (Electric Diagram) 2012.9.13Document1 page5800-P24QB-WP20-C (Electric Diagram) 2012.9.13GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- 40 Mt56ee Mad2hgDocument11 pages40 Mt56ee Mad2hgcharly36100% (5)
- Ust8Lab: &" .RR, R T,.t,. S,/. !, L/, D-GR . T F F,"',4i18' - #+..Document5 pagesUst8Lab: &" .RR, R T,.t,. S,/. !, L/, D-GR . T F F,"',4i18' - #+..GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- American Wire Gauge Conductor Size TableDocument3 pagesAmerican Wire Gauge Conductor Size TablevahrmNo ratings yet
- China DVD Sphe8100 Fan8038 SCHDocument4 pagesChina DVD Sphe8100 Fan8038 SCHGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- 1200/1152/1080/960-Output TFT LCD Gate Driver: Fitipower Integrated Technology IncDocument26 pages1200/1152/1080/960-Output TFT LCD Gate Driver: Fitipower Integrated Technology IncGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- HX8218-A 960CH TFT LCD Source Driver With Built-In TCON: Preliminary Version 01 January 2005Document48 pagesHX8218-A 960CH TFT LCD Source Driver With Built-In TCON: Preliminary Version 01 January 2005GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- Infineon Application Motor Control Washing Machine TR v02 00 enDocument57 pagesInfineon Application Motor Control Washing Machine TR v02 00 enGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- FA Mainboard CV512H-B42Document53 pagesFA Mainboard CV512H-B42Salomon ChiquilloNo ratings yet
- FSFR1700Document19 pagesFSFR1700Alfredo Valencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Auto WasherDocument42 pagesService Manual: Auto WasherGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- Chasis KSCB N Cb5hDocument39 pagesChasis KSCB N Cb5hJimmyNo ratings yet
- N - Channel Enhancement Mode " Single Feature Size " Power MosfetDocument9 pagesN - Channel Enhancement Mode " Single Feature Size " Power MosfetGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- LG 32LB550B-SD Chassis LJ43B PDFDocument73 pagesLG 32LB550B-SD Chassis LJ43B PDFJesus Garcia Hernandez88% (16)
- SMPSRM DDocument73 pagesSMPSRM DtemplpaNo ratings yet
- Sunlord: Wire Wound SMD Power Inductors - SWPA SeriesDocument20 pagesSunlord: Wire Wound SMD Power Inductors - SWPA SeriesGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- FA1A60N/FA6B20N: Enhanced Efficiency With Dual ICDocument2 pagesFA1A60N/FA6B20N: Enhanced Efficiency With Dual ICGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- LG Led 32ln5400sa - 32ln540b CH - lj36bDocument77 pagesLG Led 32ln5400sa - 32ln540b CH - lj36bRobertoJavierANo ratings yet
- Catalogue Vulcanic English 2015Document155 pagesCatalogue Vulcanic English 2015raja raniNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide: Microwave Ovens With InvertersDocument46 pagesTechnical Guide: Microwave Ovens With InvertersKybernetikum100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 10 - Starting and ReversingDocument4 pages10 - Starting and ReversingAisha Zaheer100% (3)
- Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: Review of FundamentalsDocument38 pagesMonoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: Review of FundamentalsmakroniNo ratings yet
- 8 The Future Value of Money and The Present Value of MoneyDocument26 pages8 The Future Value of Money and The Present Value of Moneyrommel legaspi62% (13)
- ANFISDocument19 pagesANFISShimaa Barakat100% (1)
- Lista Ejercicios 3 PPEDocument25 pagesLista Ejercicios 3 PPEKarla HermorNo ratings yet
- Luke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesLuke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismseablueNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: Heat & Mass Transfer Unit - I Conduction Part - ADocument3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: Heat & Mass Transfer Unit - I Conduction Part - AkarthikNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument71 pagesDigital Image ProcessingPratibha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument10 pagesCorrelational ResearchSari100% (1)
- Mechanism Analysis of Gas Solid Flow Non-Uniformity Problem of 330 MW CFB BoilerDocument10 pagesMechanism Analysis of Gas Solid Flow Non-Uniformity Problem of 330 MW CFB BoilerTan Nguyen HuuNo ratings yet
- Fourier's Law and The Heat Equation: Chapter TwoDocument16 pagesFourier's Law and The Heat Equation: Chapter TwoZAVEN TORTIANNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practice QueestionsDocument2 pagesDBMS Practice QueestionsAbhibhava Bhatt VIII [E] 4No ratings yet
- Atlatl Dart TuningDocument3 pagesAtlatl Dart TuningGuillermo BustosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Maps Data Entry Part 1Document80 pagesLecture 4 Maps Data Entry Part 1arifNo ratings yet
- Air Dan BiomolekulDocument61 pagesAir Dan BiomolekulgabbymonicaputriNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Heat Treatment PDFDocument6 pagesIsothermal Heat Treatment PDFsmani170No ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootDocument56 pagesBeckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootChrisNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- LuK Tractor Diagnosis LQDocument20 pagesLuK Tractor Diagnosis LQZam BiloiuNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Vessels Gas LiquidsDocument9 pagesStorage Tanks Vessels Gas Liquidswei wangNo ratings yet
- Asmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemDocument4 pagesAsmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemManuel FreireNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus SHS General Physics 1 (Stem, MELC) SY 2021-2022Document14 pagesCourse Syllabus SHS General Physics 1 (Stem, MELC) SY 2021-2022Eushane Chiya SyNo ratings yet
- Dawood University of Engineering & Technology Karachi Department of Basic Sciences & HumanitiesDocument4 pagesDawood University of Engineering & Technology Karachi Department of Basic Sciences & HumanitiessamadNo ratings yet
- For Bookbind Final April 2019 PDFDocument151 pagesFor Bookbind Final April 2019 PDFNeo VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas Law Lab Report HJM ResearchDocument5 pagesCombined Gas Law Lab Report HJM ResearchHelen100% (4)
- Experiment 3: Department of Civil Engineering, IIT DelhiDocument2 pagesExperiment 3: Department of Civil Engineering, IIT DelhiSRNo ratings yet
- Cennamo - Intransitivity, Object Marking and Event StructureDocument16 pagesCennamo - Intransitivity, Object Marking and Event StructureAugusto PérezNo ratings yet
- Fund. Acerinox Horno ArcoDocument8 pagesFund. Acerinox Horno ArcoJavier Mauricio Neira CastrillonNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 4th SemesterDocument16 pagesQuestion Bank 4th SemesterJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- File: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6Document18 pagesFile: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6mendofriulNo ratings yet