Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Characteristics of The Earth by Ron Kurtus - Succeed in Understanding Astronomy - School For Champions PDF
Uploaded by
John Lloyd GildoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Characteristics of The Earth by Ron Kurtus - Succeed in Understanding Astronomy - School For Champions PDF
Uploaded by
John Lloyd GildoCopyright:
Available Formats
Custom Search Search Site
Lesson Mini-Quiz Feedback Q&A
SfC Home > Physical Science > Astronomy >
1.2K
Characteristics of the Earth
by Ron Kurtus (revised 19 June 2010)
Our planet Earth is a rotating sphere that orbits the Sun. The Earth's axis of rotation is at a
constant tilt with respect to its orbit around the Sun, resulting in the change of seasons.
The physical characteristics of the Earth include its size and composition. The Earth also has
gravity and magnetic force fields.
Questions you may have include: This site can’t
What is the Earth's relationship with the Sun?
What are the Earth's physical characteristics? Astronomy topics
What do the Earth's force fields do? Observations in Astronomy
This lesson will answer those questions.
Solar system
Solar System
Kepler's Laws of Orbital Motion
Characteristics of our Sun
This site can’t be reached Characteristics of the Earth
Motion of the Earth
Earth's relationship with Sun Characteristics of our Moon
Motion of the Moon
The Earth is the third planet from the Sun, with Mercury and Venus being closer. Its unique Phases of the Moon
position gives the Earth a temperate climate, allowing the chemical reactions necessary to sustain
life. But over the years, the climate has varied enough to melt the ice caps near the North and Planets
South poles, or to cause glaciers to move south in an Ice Age. Jupiter
Jupiter's 67 Moons
Revolves around the Sun in an orbit Jupiter's Galilean Moons
The Earth goes around the Sun in a counterclockwise orbit, taking a year or about 365 days to Universe
make one revolution. The orbit is an ellipse, so the Sun is slightly off-center.
Characteristics of the Universe
Astronomical Distances
Constellations
Galaxies
Black Holes
Big Bang Theory
Theory of Multiple Universes
The Earth orbits the Sun
Bigger Bang Theory
The average distance from the Sun is 149,597,890 kilometers (92,955,820 miles). This distance is
so great that it takes light about 8 minutes to reach the Earth from the Sun. Tools
Spectrometer Used in Astronomy
Spins on its axis
Graded test
The Earth spins or rotates on its axis in a counterclockwise motion, as viewed from above the Graded Astronomy Test
North Pole. It makes one revolution in 24 hours.
The spinning of the Earth on its axis is what causes the Sun to appear to move across the sky. The
effect the apparent movement of the Sun is similar to looking out the window of a moving car,
Also see
Weekly Feedback Blog
where things outside appear to be moving past you.
Astronomy Survey Results
Physical Science
Tilt affects seasons
Physics
The Earth's axis also tilts with respect to the Sun, causing the changes of the seasons. In summer, Chemistry
the Earth is tilted such that the Sun falls more directly, while in winter the Sun looks lower in the
horizon and the light comes at a glancing angle. The tilt of the Earth also causes the summer days
to be longer than the nights. In winter the days are shorter and there is less light to heat the Let's make the world a
ground.
better place
Be the best that you can be.
Use your knowledge and skills to help others
succeed.
Don't be wasteful; protect our environment.
You CAN influence the world.
The light from the Sun is more direct in summer than
in winter at the same latitude
The further north you go, the more the effect of the tilt of the Earth is apparent. Above the Arctic
Circle, daylight can be seen for a full 24 hours in the summer or night can be 24 hours in the
winter. That is why they call the area "the land of the midnight sun."
(See Motion of the Earth for more information.)
Moon This site can’t
The Earth has only one moon, while Mars has two moons and Jupiter has 9 moons.
Live Your Life as a
(See The Moon for more information.)
Champion:
Physical characteristics of Earth Take care of your health
Seek knowledge and gain skills
Physical characteristics include shape, size and composition.
Do excellent work
Spherical in shape Be valuable to others
Have utmost character
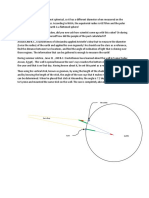
Just as the Sun and Moon appear as spheres, so too is the Earth spherical in shape. To people on
Earth, the planet appears to be generally flat (not counting for hills and valleys), but in reality the
Be a Champion!
surface of the Earth has a slight curve. This can be noticed when looking out on a large lake or the
ocean and seeing a ship come up along the horizon.
Ship coming up over the horizon
The shape of the Earth has been proven by ships circling the Earth, as well as from pictures of the
Earth taken from the space vehicles.
View of Earth from space
Its shape is actually slightly flattened at the poles.
Size
The diameter of the Earth at the equator is 12,756 km (7,926 miles), and its circumference or
distance around the Earth at the equator is 40,075 km (24,901 miles).
Composition
The composition of the Earth consists of the solid and liquid portion and the atmosphere or
gaseous portion.
Solid and liquid
The percentage composition of the Earth's solid and liquid materials (by mass) is:
Element Percentage
Iron 34.6%
Oxygen 29.5%
Silicon 15.2%
Magnesium 12.7%
Nickel 2.4%
Sulfur 1.9%
Titanium 0.05%
Oxygen is chemically combined with many substances to produce liquid and solid compounds.
Although water (H2O) is a dominant compound on Earth, Hydrogen is not listed above because of
its small mass.
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) is sand, and that compound makes up a large portion of the Earth's mass.
Much of the Iron is in the Earth's core and is responsible for the Earth's magnetic field.
Atmosphere
Although most people think air is mainly Oxygen, the atmosphere of the Earth actually consists of
79% Nitrogen (N2), 20% Oxygen (O2) and 1% of other gases such as Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
Force fields
The Earth has two major force fields: gravity and magnetism.
Gravity
Gravity is the force at a distance that attracts objects of mass toward each other. The force of
gravity from the Earth holds down our atmosphere, oceans and everything else.
Lost atmosphere
Some planets and moons that have less gravity than Earth have lost their atmosphere because it
wasn't sufficient to hold the gas close to the surface.
Escape velocity
When you throw a ball or shoot a bullet upward, it will slow down due to the Earth's gravity, until it
finally falls back to the ground. You would have to shoot the object at 40,248 km/hr (25,009 mph)
for it to escape the Earth's gravity and fly out into space. This is called the Earth's Escape Velocity.
(See the lesson on Gravity for more information.)
Magnetic field
The Earth is like a giant magnet with a magnetic pole near the North Pole and the opposite near
the South Pole. The north pole of a magnet seeks the North Magnetic Pole. Through the ages,
indications are that the poles switched directions. No one is sure why this happened.
The rotation of the Earth and the fact that the core of the Earth is made of iron are major factors in
creating the magnetic field.
One thing the magnetic field does is to attract charged particles that have been emitted from the
Sun. The focusing of these particles at the poles may help to prevent us from being harmed by the
high energy particles.
These particles cause the air in the upper atmosphere to glow. This is called the northern lights
(aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis).
(See the lesson on Magnetism for more information.)
Summary
The Earth is a rotating sphere that orbits the Sun. The axis of rotation of the Earth is at a constant
tilt with respect to its orbit around the Sun, thus resulting in the change of seasons. Iron and
oxygen make up 65% of the Earth's mass. The Earth also has gravity and magnetic force fields.
This is the only Earth we have. Keep it a good place to live.
Resources and references
Ron Kurtus' Credentials
Websites
Earth Facts and Figures - From NASA
The Earth - Details from Nine-Planets website
Earth's Atmosphere - From the University of Tennessee Department of Physics
Space Weather - News about Earth-Sun environment
Earth's Magnetic Field Is Fading by John Roach for National Geographic News September 9,
2004
Astronomy Resources
Books on the Earth
Top-rated books on Earth Astronomy
Gravity and Gravitation
My physics book covers an important subject with easy-to-
understand explanations. It is great for science buffs and
students.
You can purchase the hardcopy book through
Amazon.com or Barnes & Noble for $19.95.
Purchase the Kindle or Nook / EPUB e-book for $3.50.
Like us on Facebook | Follow on Twitter
Questions and comments
Do you have any questions, comments, or opinions on this subject? If so, send an email with your
feedback. I will try to get back to you as soon as possible.
Share this page
Click on a button to bookmark or share this page through Twitter, Facebook, email, or other
services:
1.2K
Students and researchers
The Web address of this page is:
www.school-for-champions.com/astronomy/
earth.htm
Please include it as a link on your website or as a reference in your report, document, or thesis.
Copyright © Restrictions
Where are you now?
School for Champions
Astronomy topics
Characteristics of the Earth
The School for Champions helps you become the type of person who can be called a Champion.
You might also like
- Module P7 L1Document13 pagesModule P7 L1geth jonesNo ratings yet
- Locating Planets in Sky Using Manual CalculationsDocument8 pagesLocating Planets in Sky Using Manual Calculationsmuratanil70No ratings yet
- Astronomy: Concept MapDocument29 pagesAstronomy: Concept MapDaoud KhanNo ratings yet
- Space L5 Orbits PowerPointDocument15 pagesSpace L5 Orbits PowerPointkenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29Document32 pagesChapter 29Hazel Grace SalmonNo ratings yet
- The Sun, The Closest Star: Background For Next Week's LabDocument22 pagesThe Sun, The Closest Star: Background For Next Week's LabSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Topic 1Document4 pagesAstronomy Topic 1Dinesh JisangkarNo ratings yet
- Exploring Astronomy ConceptsDocument7 pagesExploring Astronomy ConceptsJoseph ManaseNo ratings yet
- STARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSEFrom EverandSTARMAP: AN INTRODUCTORY PICTORIAL TOUR OF THE UNIVERSENo ratings yet
- Astronomical Phenomena and ObjectsDocument51 pagesAstronomical Phenomena and ObjectsAndrei BarelaNo ratings yet
- Solar System: PlanetsDocument2 pagesSolar System: PlanetsChad HooNo ratings yet
- Solar Eclipse Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSolar Eclipse Lesson PlanShaira Jane Villareal AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Easy Space Definitions Astronomy Picture Book for Kids | Astronomy & Space ScienceFrom EverandEasy Space Definitions Astronomy Picture Book for Kids | Astronomy & Space ScienceNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4Emmarie LlantinoNo ratings yet
- The Great Chain of Origins: Early Hypotheses of Planetary FormationDocument20 pagesThe Great Chain of Origins: Early Hypotheses of Planetary FormationMarshaley MalubayNo ratings yet
- 1 Motion in The UniverseDocument38 pages1 Motion in The UniverseJohan SwartzNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System 220913 004914Document50 pagesEarth and The Solar System 220913 004914Bobfian WidjajaNo ratings yet
- Planetary Motions: GoalsDocument10 pagesPlanetary Motions: Goalsari sudrajatNo ratings yet
- Navigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Document526 pagesNavigation 3 Nautical Astronomy and Celestial Navigation (PART 1)Cyver Kent DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Celestial BodiesDocument14 pagesCelestial Bodieslokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- Universe & Solar System - Study NotesDocument22 pagesUniverse & Solar System - Study Notessuthish kumarNo ratings yet
- Space Physics 1Document15 pagesSpace Physics 1WafleNo ratings yet
- 63eef0f6feeba2001883ff48 - ## - 1) Space and Earth (Physical Geography)Document13 pages63eef0f6feeba2001883ff48 - ## - 1) Space and Earth (Physical Geography)shriram photoNo ratings yet
- Celestial Motion and MechanicsDocument48 pagesCelestial Motion and MechanicsSay KhoNo ratings yet
- On Food and Setting Yourself FreeDocument55 pagesOn Food and Setting Yourself FreeIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument23 pagesScienceJanice RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 01Document82 pagesChapter 06 01ِDark DarknessNo ratings yet
- AGU Space Physics and Aeronomy SectionDocument37 pagesAGU Space Physics and Aeronomy Sectionbagus wicaksonoNo ratings yet
- The Sun and StarDocument16 pagesThe Sun and StarB. Tiara Shafa ZahirahNo ratings yet
- SFM TheoryDocument4 pagesSFM TheoryAniket DhoneNo ratings yet
- Earth and the Solar System ExplainedDocument13 pagesEarth and the Solar System ExplainedManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in EarthSci Module 1-4 (Magramo, Dawn Eriel)Document7 pagesAnswer Sheet in EarthSci Module 1-4 (Magramo, Dawn Eriel)Eriel MagramoNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics SummaryDocument10 pagesAstrophysics SummaryHafsah PirzadaNo ratings yet
- How Small is Mercury? Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandHow Small is Mercury? Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet
- 1 The Night Sky - AVEDocument57 pages1 The Night Sky - AVEAndrea VettorinoNo ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About Dwarf Planets: A 15-Minute BookFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About Dwarf Planets: A 15-Minute BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanDan Dan Dan100% (1)
- Geography - Universe & Solar System Old - English - 1608316685Document22 pagesGeography - Universe & Solar System Old - English - 1608316685ribasefNo ratings yet
- Geography: Chapter - IDocument25 pagesGeography: Chapter - IDiveshNo ratings yet
- Astronomy for Beginners: Ideal guide for beginners on astronomy, the Universe, planets and cosmologyFrom EverandAstronomy for Beginners: Ideal guide for beginners on astronomy, the Universe, planets and cosmologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument103 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemJoan S. LanuzgaNo ratings yet
- The Moon: Key To The Universe, Explorations in Space and TimeDocument48 pagesThe Moon: Key To The Universe, Explorations in Space and TimeIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- OnlyIAS Physical GeographyDocument193 pagesOnlyIAS Physical Geographyaayuish100% (1)
- 18.origins IDocument12 pages18.origins IMinetteStellaDecoyNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument34 pagesSolar Systemtupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Astrodynamics: ASD4: Orbital PerturbationsDocument9 pagesAstrodynamics: ASD4: Orbital PerturbationsMagno JuniorNo ratings yet
- Our Place in SpaceDocument11 pagesOur Place in Spaceapi-409345099No ratings yet
- How Do Scientists Discover New Planets? Astronomy Book 2nd Grade | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksFrom EverandHow Do Scientists Discover New Planets? Astronomy Book 2nd Grade | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University presents "The Moon and MercuryDocument10 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University presents "The Moon and MercuryJim CordovaNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Without A TelescopeDocument4 pagesAstronomy Without A Telescopebitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Bello-Pasteur Physics q2 m3Document8 pagesBello-Pasteur Physics q2 m3Ronald CuencaNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton and Orbital Motion: Principia in 1687 Placed Science On A FirmDocument6 pagesIsaac Newton and Orbital Motion: Principia in 1687 Placed Science On A FirmKyle Angela IlanNo ratings yet
- Solar System Formation and PropertiesDocument13 pagesSolar System Formation and PropertiesGweneth WajeNo ratings yet
- C16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsDocument62 pagesC16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Week # 3 MR Chapter 3: - Tutorial #3Document46 pagesWeek # 3 MR Chapter 3: - Tutorial #3John Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Banana Industry Roadmap 2019 2022Document52 pagesPhilippine Banana Industry Roadmap 2019 2022Noel Marial PiencenavesNo ratings yet
- Junior Chapter Mindanao Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Implementing Rules and Regulations Quiz BowlDocument5 pagesJunior Chapter Mindanao Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Implementing Rules and Regulations Quiz BowlJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Transition WordsDocument1 pageTransition WordsJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Experimental Results For The Settling Behaviour of Particle-Fiber MixturesDocument6 pagesResearch Article: Experimental Results For The Settling Behaviour of Particle-Fiber MixturesJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Marginalization Through Land Disposition PDFDocument16 pagesMarginalization Through Land Disposition PDFJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- 21 Indispensable Qualities of A Leader - John Maxwell (Presentation)Document23 pages21 Indispensable Qualities of A Leader - John Maxwell (Presentation)Le Po100% (1)
- Commonwealth Act No. 141 Amends Laws on Public Land DispositionsDocument1 pageCommonwealth Act No. 141 Amends Laws on Public Land DispositionsJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- In Vessel Composting As Related LiteratureDocument8 pagesIn Vessel Composting As Related LiteratureJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- How To Measure The Size of The EarthDocument2 pagesHow To Measure The Size of The EarthJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Animal Phyla - HandoutDocument4 pagesAnimal Phyla - HandoutJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation ActivityDocument12 pagesSedimentation ActivityJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- AAG Philippine Solid Wastes Nov2017Document4 pagesAAG Philippine Solid Wastes Nov2017Gherald EdañoNo ratings yet
- WACS of Mina IloiloDocument75 pagesWACS of Mina IloiloJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Sieving The Class Teaching Particle Size DistributionDocument25 pagesSieving The Class Teaching Particle Size DistributionJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potential PowerpointDocument55 pagesMembrane Potential PowerpointJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc Waste Recycling - A Simple IntroductionDocument1 pagePlasma Arc Waste Recycling - A Simple IntroductionJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Che 153Document3 pagesSyllabus Che 153John Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Debate On Rizal As National HeroDocument1 pageDebate On Rizal As National HeroJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Magic SquareDocument1 pageMagic SquarequantumtensorsNo ratings yet
- Болцманова расподела - извођењеDocument6 pagesБолцманова расподела - извођењеОгњен ГркинићNo ratings yet
- Assignment in BiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment in BiologyJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- PLanetsDocument13 pagesPLanetsJaena Mark GuavezNo ratings yet
- Q1 Earth Life Science SHS Module 1Document24 pagesQ1 Earth Life Science SHS Module 1KAREN BIANCA TIGULLONo ratings yet
- Relics WarframeDocument4 pagesRelics WarframeMatei BenescuNo ratings yet
- Antrian Online BPJSDocument55 pagesAntrian Online BPJSadie82kuNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Weight and Mass: Vocabulary: Balance, Force, Gravity, Mass, Newton, Spring Scale, WeightDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Weight and Mass: Vocabulary: Balance, Force, Gravity, Mass, Newton, Spring Scale, WeightAdamNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 1Q ExamDocument2 pagesEarth and Life 1Q ExamImmanuel GranadaNo ratings yet
- French Cinema - The New Wave by SlidesgoDocument49 pagesFrench Cinema - The New Wave by Slidesgosaumya gaurNo ratings yet
- GK BookDocument115 pagesGK BookPriyanka Jain0% (1)
- Solar Eclipses PDFDocument1 pageSolar Eclipses PDFplfs1974No ratings yet
- Task 2-Orbital-Motion-PPQDocument8 pagesTask 2-Orbital-Motion-PPQᴛᴀsɴᴇᴇᴍNo ratings yet
- ELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetDocument25 pagesELS Q1 M1 2 3 Activity SheetLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- The Sthir Karakas: Functions of The Char Karkas AtmakarakDocument2 pagesThe Sthir Karakas: Functions of The Char Karkas AtmakarakDipyaman SahaNo ratings yet
- 10march - Grade 6 - Test PDFDocument27 pages10march - Grade 6 - Test PDFEron Roi Centina-gacutanNo ratings yet
- Flowery Gradient by SlidesgoDocument47 pagesFlowery Gradient by Slidesgorandy kurniaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: The Study of Earth for ConstructionDocument87 pagesEngineering Geology: The Study of Earth for ConstructionHadh HaraamNo ratings yet
- Science VI - Solar SystemDocument5 pagesScience VI - Solar SystemRuby Flor Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- I. Preliminaries: Lesson: Universe and Solar SystemDocument17 pagesI. Preliminaries: Lesson: Universe and Solar SystemCecilia ReyesNo ratings yet
- GPS Course Overview and ObjectivesDocument42 pagesGPS Course Overview and Objectivessham2258No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Maria Ybonne Gandeza100% (1)
- The Future of Space Exploration (Students' Worksheet)Document3 pagesThe Future of Space Exploration (Students' Worksheet)Nastya BevzNo ratings yet
- Silver Pitch Deck by SlidesgoDocument52 pagesSilver Pitch Deck by SlidesgoCESÉ Samaniego ChNo ratings yet
- 04 Moon Landing - Weird and Wacky Training Techniques - KidsNewsDocument2 pages04 Moon Landing - Weird and Wacky Training Techniques - KidsNewsSIQIAN LIUNo ratings yet
- The Origin & Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesThe Origin & Structure of The EarthJasmine LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument2 pagesBig Bang TheoryNene FortalejoNo ratings yet
- Kepler 186fDocument9 pagesKepler 186fnorma6742No ratings yet
- Extreme PlanetsDocument1 pageExtreme PlanetsHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- The Planets: Lesson 36Document38 pagesThe Planets: Lesson 36eha_9213423No ratings yet
- Clinical Case in Neurology: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument46 pagesClinical Case in Neurology: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsMaribelNo ratings yet
- Earth's Unique Characteristics that Support LifeDocument4 pagesEarth's Unique Characteristics that Support Lifemaverick arquilloNo ratings yet
- Science - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesScience - Plate Tectonicspogi si mark leeNo ratings yet