Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Soalan 1
Uploaded by
Radziah MohamedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Soalan 1
Uploaded by
Radziah MohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
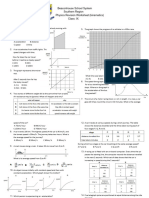
1: Analysing Linear Motion
1. A cow walked along a curved path from P to Q 5. A trolley pulled a ticker tape through a ticker timer
which is 70 m away from P. Q the distance while moving down an inclined plane. Figure below
travelled by the cow is 240 m and the time taken is shows the ticker tape produce.
160 s.
Determine the average velocity (purata halaju) of
the trolley.
Calculate from P to Q the
a. Average speed / Purata laju,
6. Figure below shows ticker tapes produced from the
b. Average velocity / Purata halaju motion of a trolley.
2. The diagram below shows the path travelled by a
car from P to S.
Describe the type of motion of the trolley for each
ticker tape.
What is the magnitude of the displacement / a.
sesaran of the car?
b.
3. A van accelerates uniformly from a velocity of 10 c.
ms-1 to 20 ms-1 in 2.5 s. what is the acceleration
(pecutan) of the van?
7. A train travelling in a straight line at 30 ms-1
accelerates uniformly to 54 ms-1 in 3.0 seconds.
Calculate the distance travelled by the train during
4. A car travelling at 24 ms-1 slow down when the that time.
traffic light turned red. After undergoing
deceleration for 4 s, it stopped in front of the traffic
light. Calculate the acceleration (pecutan) of the
car.
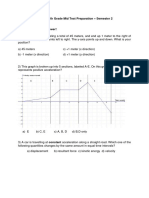
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
8. A trolley travelled down an inclined plane pulling 10. A car is travelling with a uniform velocity (halaju
along a ticker tape. Figure below shows a chart Seragam) of 80 kmh-1 northward from Johor
formed by cutting and arranging the ticker tape into Bahru. What is the displacement (sesaran) after
strips of ten ticks each. 15 minutes?
11. Figure below shows a chart representing the
movement of a trolley with uniform acceleration.
Determine the acceleration (pecutan) of the trolley.
Determine its acceleration (pecutan).
9. A long jumper was running at a velocity 5 m s -1
towards the long jump pit. He needed to achieve a
velocity 10 ms-1 after covering a distance of 4.5 m
before lifting himself off the ground from the
jumping board.
12. A school bus accelerates with an acceleration of
4.0 ms-2 after picking up some students at a bus
stop.
Calculate the
a. Velocity (halaju) of the bus after 5 s.
a. Calculate the required acceleration (pecutan)
for him to do so. b. Distance travelled by the bus after 5 s.
b. Calculate the time taken for him to cover the 13. Figure below shows a strip of ticker tape depicting
horizontal distance (jarak mendatar) 4.5 m. the motion of a toy car with uniform acceleration.
Determine the acceleration (pecutan) of the toy
car.
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
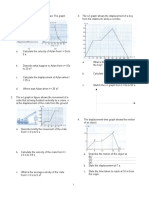
14. Diagram below show tha path travelled by Linda 18. The figure below shows two tapes depicting the
from J to M. motion of two trolleys, A and B.
What is her displacement (sesaran)?
Determine which trolley is faster.
15. The figure below shows the path travelled by
Mansor from point A to C. He took 2 hours to
travel from point A to point B and 3 hours from
point B to point C.
Find
a. The velocity from A to B. 19. The figure below shows two tapes for the motion
of two trolleys, P and Q.
b. The velocity from B to C
c. The average velocity of the whole journey.
16. A car is moving with constant velocity of 50 ms-1
increases its velocity to 80 ms-1 in 2 s. Find the acceleration of
a. Trolley P
What is the acceleration of the car?
b. Trolley Q
17. A car starts off at 5 ms-1 and accelerates at 4 ms-2
for 10 s. What is its final velocity?
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
20. The ticker tape below shows the motion of a 23. The figure below shows a car slowing down from
trolley travelling from one point to another. 60 ms-1 in 9 s.
Calculate the acceleration of the trolley.
What is the deceleration of the car?
21. The figure below shows the chart of the motion of
a trolley.
24. Diagram 1 shows a chart of ticker tape obtained
from a trolley moving on a plane. Each strip ticker
tape contains 10 ticks. The frequency of the ticker
tape is 50 Hz.
What is the aceleration of the trolley?
a. Describe the motion of the trolley.
b. What is the time take for the whole 6 strips of
10 ticks on the ticker tape?
c. What is the initial velocity of the trolley?
d. What is the final velocity of the trolley?
e. What is the average velocity for the whole
22. A car travelling at 20 ms-1 stops after a distance of motion of the trolley?
30 m. what is its deceleration?
f. Calculate the acceleration of the trolley.
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
25. During class activity, Hasim walks 20 m to the b.
east. He reverse his direction and walks 12 m.
after that he reverses his direction again to walk
another 10 m. if the total time taken is 30 s,
calculate
a. His speed
b. His velocity
26. A speedboat moves due north for 12 km before
turning to the east for 8 km. later, the speedboat
moves to the south for another 6 km. c.
a. What is the displacement of the speedboat
from its original position?
b. Find its average velocity if the time taken is
30 minutes.
27. Find the acceleration or deceleration for the tape
charts below. The ticker tape in use vibrates at
frequency 50 Hz.
a.
d.
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
28.
32. Daniel is driving his car at a constant velocity of
20 ms-1. He steps on his brakes to reduce the
velocity to 10 ms-1 after travelling 30 m. Calculate
the deceleration and the distance travelled before
the car stops.
If the frequency used is 50 Hz and the
acceleration is 30 cms-2, calculate the length of
the sixth strip.
29. A sport car accelerates from rest and covers a
33.
distance of 90 m in 6 s. what is its acceleration?
If the plane can accelerate at 3 ms-1, calculate the
minimum length of the run away.
30. A cyclist starts from rest and reaches a velocity of
20 ms-1 in 8 s. Calculates his acceleration.
31. A dart leaves the barrel of a blow pipe of length
1.2 m at a speed of 15 ms-1. Find the time taken
for the dart to travel in the barrel.
2.1: Analysing Linear Motion
34.
Find the acceleration before the baseball is
released.
You might also like
- Analysis of MotionDocument5 pagesAnalysis of MotionDong Chooi YingNo ratings yet
- 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 B E D C: Generated From Saranextgen AppDocument8 pages60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 B E D C: Generated From Saranextgen Appచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- USTH-B1 Exercise Chapter1 01Document6 pagesUSTH-B1 Exercise Chapter1 01Long Phan DuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Velocity and Acceleration: Method 1 in The Fi RST 3 Minutes The Average Velocity IsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Velocity and Acceleration: Method 1 in The Fi RST 3 Minutes The Average Velocity IsAnuj PaudelNo ratings yet
- WS-13 - KN - 1-D Motion - SubDocument2 pagesWS-13 - KN - 1-D Motion - SubSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document1 pageAssignment 01Mohamed SharafNo ratings yet
- A1 Revision Quesions For MY 2078Document6 pagesA1 Revision Quesions For MY 2078Anuj PaudelNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Mcqs RevisionDocument3 pagesKinematics Mcqs Revisionwajeehmohsin96No ratings yet
- Revision On Motion: SI UnitsDocument6 pagesRevision On Motion: SI UnitsYoussef SalemNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics-Motion and Rest Test Paper PDFDocument3 pages9th Physics-Motion and Rest Test Paper PDFHardik singhNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics-Motion and Rest Test PaperDocument3 pages9th Physics-Motion and Rest Test PaperAYUSH JAINNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4435889675498454681Document1 pageInbound 4435889675498454681keepersilent2No ratings yet
- Ye S AkuDocument19 pagesYe S Akudebs icapsNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionDocument8 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionCó Tên KhôngNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 9702 Questions - 3Document1 pageKinematics 9702 Questions - 3Zeeshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Https:Noida - Cambridgeschool.edu - In:wp Content:Uploads:Sites:4:2019:06:Class 9 MOTION ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesHttps:Noida - Cambridgeschool.edu - In:wp Content:Uploads:Sites:4:2019:06:Class 9 MOTION ASSIGNMENTPriti GuptaNo ratings yet
- 9TH Physics HHWDocument4 pages9TH Physics HHWrachna chhabraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Motion Basic Level-1Document3 pagesWorksheet On Motion Basic Level-1Yahya AhsanNo ratings yet
- Exam I Redo 2010Document1 pageExam I Redo 2010Benjamin FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Physics (23 Sept) PDFDocument8 pagesPhysics (23 Sept) PDFMega Brother GamingNo ratings yet
- Costant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Document11 pagesCostant Acceleation - Horizontal Motion Exam Questions 2Dominic SavioNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinematics-1Document3 pages3 Kinematics-1arunpatel32No ratings yet
- Class 9 Phy: Chapter Motion Sample QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass 9 Phy: Chapter Motion Sample QuestionsXâlmañ KháñNo ratings yet
- GR XI Motion in A Straight Line Chapter TestDocument3 pagesGR XI Motion in A Straight Line Chapter TestKevin AgeraNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Worksheet 1Document4 pagesKinematics Worksheet 1CesarNo ratings yet
- Class 9 MOTION WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 9 MOTION WorksheetChetan AnandNo ratings yet
- 1d Class QuestionDocument2 pages1d Class QuestionDibyajoti SahooNo ratings yet
- Ex 1Document1 pageEx 1Ioanna BoumpoutsiNo ratings yet
- Kinematicsschool 2009Document7 pagesKinematicsschool 2009EzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- Numericals Class IX TMHDocument80 pagesNumericals Class IX TMHMr. JocularNo ratings yet
- Soalan AkuDocument19 pagesSoalan Akudebs icapsNo ratings yet
- Assignments Physics 1Document6 pagesAssignments Physics 1Sifat MongaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Motion Assignment 1Document4 pagesClass 9 Motion Assignment 1Alok RanjanNo ratings yet
- 2 Kinematics OrigDocument118 pages2 Kinematics Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Ws 1 Kinema Tics 2223Document1 pageWs 1 Kinema Tics 2223Yanshen PangestuNo ratings yet
- Physics Motion Numerical WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Motion Numerical WorksheetvikashNo ratings yet
- MILLENNIUM PUBL Class 11 QP-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesMILLENNIUM PUBL Class 11 QP-WPS OfficeShiv VathsNo ratings yet
- Mech PsetDocument7 pagesMech PsetJomel JazminNo ratings yet
- Physiscs Form 4 Chp2 Obj QuestionsDocument5 pagesPhysiscs Form 4 Chp2 Obj QuestionsLemathaNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line Class 11 WorksheetDocument4 pagesMotion in A Straight Line Class 11 Worksheetmn m,n m, bm43% (7)
- Mid Test Practice Physics 7th Grade 2nd SemesterDocument7 pagesMid Test Practice Physics 7th Grade 2nd SemesterWilliam RyandinataNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1 - Displacement & Average VelocityDocument3 pagesKinematics 1 - Displacement & Average VelocityFelixNo ratings yet
- Motion NcertDocument3 pagesMotion NcertpillapandurangapatruduNo ratings yet
- Numericals Class - IX TMHDocument80 pagesNumericals Class - IX TMHSohan Yadav65% (26)
- Physics Motion Numerical Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Motion Numerical Worksheet PDFDeepakNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1Document3 pagesKinematics 1Harish RaghavendarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Physics - Motion in A Straight LineDocument23 pagesClass 11 - Physics - Motion in A Straight LineM KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - MotionDocument11 pages1.2 - Motionsamikshakumar2009No ratings yet
- Kinematics ReviewDocument2 pagesKinematics Reviewapi-237070241No ratings yet
- Work Sheet Tow 9thDocument3 pagesWork Sheet Tow 9thFiraol TegenuNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Practice Question Class9sDocument3 pagesAcceleration Practice Question Class9sSanjay NayakNo ratings yet
- Tutorial KinematicsDocument3 pagesTutorial KinematicsAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Solution: A.: Kinematics Physics Questions (1-37)Document35 pagesSolution: A.: Kinematics Physics Questions (1-37)teklil tigani100% (1)
- MISDocument3 pagesMISAshmith MonteiroNo ratings yet
- 11physics - Motion in A Straight Line-AssignmentDocument1 page11physics - Motion in A Straight Line-AssignmentDETECTIVE UNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02 Class Ix MotionDocument2 pagesAssignment 02 Class Ix MotionRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 S3Document6 pagesUnit 1 S3cyumadripNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 KinematicsDocument14 pagesTOPIC 2 KinematicsMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- 2.2-Analysing Linear GraphDocument6 pages2.2-Analysing Linear GraphtheebighaaNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Blueberry Recipe 1Document2 pagesBlueberry Recipe 1api-529255365No ratings yet
- ALDI Growth Announcment FINAL 2.8Document2 pagesALDI Growth Announcment FINAL 2.8Shengulovski IvanNo ratings yet
- Freezer Bag Recipes PDFDocument38 pagesFreezer Bag Recipes PDFchieflittlehorse100% (1)
- Steps in Bituminous Road ConstructionDocument3 pagesSteps in Bituminous Road Constructionlance lancelottiNo ratings yet
- Warner Records IncDocument5 pagesWarner Records IncMi PhanNo ratings yet
- Writing Unit Plan: Fractured Fairy TalesDocument16 pagesWriting Unit Plan: Fractured Fairy TaleslinneaannetteNo ratings yet
- Atg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFDocument2 pagesAtg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFbunhuot100% (2)
- Aragorn EssayDocument7 pagesAragorn EssayAdam SuddarthNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - English ViDocument20 pagesSession 2 - English ViMANUEL FELIPE HUERTAS PINGONo ratings yet
- ERLPhase USB Driver InstructionsDocument9 pagesERLPhase USB Driver InstructionscacobecoNo ratings yet
- Blackout - ScriptDocument9 pagesBlackout - Scriptapi-295129288No ratings yet
- Hangman Report1Document10 pagesHangman Report1RenjithNo ratings yet
- Accessories: ADP45-MSTP-x: Quick Connect MS/TP AdaptersDocument2 pagesAccessories: ADP45-MSTP-x: Quick Connect MS/TP AdaptersBMSNo ratings yet
- Peking Opera - WikipediaDocument20 pagesPeking Opera - WikipedialindianNo ratings yet
- Orthodox Theatre in ByzantiumDocument3 pagesOrthodox Theatre in ByzantiumASRNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08-Sep-2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 08-Sep-2023Diptiranjan SahuNo ratings yet
- Fire Shut Up in My Bones Programme Metropolitan OperaDocument24 pagesFire Shut Up in My Bones Programme Metropolitan OperaIvory PlatypusNo ratings yet
- Up PeriscopeDocument145 pagesUp Periscoperemow100% (4)
- Unicast, Broadcast, and MulticastDocument2 pagesUnicast, Broadcast, and MulticastVictor BragaNo ratings yet
- Khawas Ji Ki HaveliDocument2 pagesKhawas Ji Ki HaveliAayushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- 一指禅规则 v2.9.80Document11 pages一指禅规则 v2.9.80fox jinNo ratings yet
- Project 1 Magazine BiographiesDocument3 pagesProject 1 Magazine Biographiesdeki20No ratings yet
- Kbeatbox KSNet450 User GuideDocument12 pagesKbeatbox KSNet450 User GuideRin DragonNo ratings yet
- Final Project Basket BallDocument40 pagesFinal Project Basket BallUlrike Regina0% (1)
- Chapter 5Document28 pagesChapter 5Nada ElDeebNo ratings yet
- Apax EnglishDocument4 pagesApax EnglishJayzNo ratings yet
- Manual Analizador Pirogenio Ellab Man - Py - SW - 20090626 - 3.0 PDFDocument122 pagesManual Analizador Pirogenio Ellab Man - Py - SW - 20090626 - 3.0 PDFAlam AlvesNo ratings yet
- Lesson A: Lifestyle Trends: DecreasedDocument3 pagesLesson A: Lifestyle Trends: DecreasedJean Pierre Sulluchuco ValentinNo ratings yet
- 3 The Swimming DeclineDocument29 pages3 The Swimming DeclinejkgfgNo ratings yet
- 92-96 4ws SystemDocument49 pages92-96 4ws Systemsean1121100% (3)