Professional Documents
Culture Documents
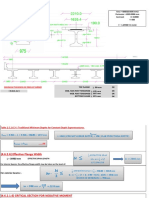
Interstiffener Collapse en 13445-3 - 8.6.3
Uploaded by
met-calc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views4 pagesInterstiffener Collapse en 13445-3
Original Title
Interstiffener Collapse en 13445-3_8.6.3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views4 pagesInterstiffener Collapse en 13445-3 - 8.6.3
Uploaded by
met-calcYou are on page 1of 4
8.6.
3 Interstiffener collapse
The minimum yield strength or 0,2% proof strength at
calculation temperature: Rp0,2T 345 [Mpa]
The nominal elastic limits for shell:
Ferritic material
𝜎 =𝑅 , /
Austenitic material
𝑅 , /
𝜎 =
1,25
Fer
σe 345 [Mpa]
The nominal thickness: en 35 [mm]
The corrosion allowance: c 2 [mm]
The absolute value of the possible negative tolerance
on the nominal thickness (EN 10029): quality C
de1 0 [mm]
Limit values of weld joint defects (EN ISO 5817): quality D
Linear offset between plates (EN 5817):
𝐵 → 𝛿 = 𝑚𝑖𝑛 0,2 + 0,1𝑒 ; 3
𝐶 → 𝛿 = 𝑚𝑖𝑛 0,2 + 0,15𝑒 ; 4
𝐷 → 𝛿 = 𝑚𝑖𝑛 0,2 + 0,25𝑒 ; 5
de2 5 [mm]
Defects of welds:
𝐵 → 𝛿 = 0,2𝑒 ∗ 0,04
𝐶 → 𝛿 = 0,3𝑒 ∗ 0,08
𝐷 → 𝛿 = 0,4𝑒 ∗ 0,16
de3 2,2 [mm]
The analysis thickness:
𝑒 =𝑒 −𝛿 −𝛿 −𝛿 −𝑐
ea 25,8 [mm]
The maximum radius of conical shell: Rmax 1000 [mm]
The mean radius of conical shell: Rn 567 [mm]
The semi angle of come at apex: α 30 [°]
The elastic modulus: E 210000 [MPa]
The unsupported length of the shell: L 1000 [mm]
The pressure at which mean circumferential stress in a
conical shell, reaches yield point:
𝑒 ∗ 𝜎 ∗ cos 𝛼
𝑃 =
𝑅
Py 7,7 [MPa]
L/2R=L/2Rncosα 1,0
ea/2R=ea/2Rncosα 0,026
The number of circumferential waves for an
unstiffened part of a conical shell: ncyl 3 []
Parameter:
𝜋 ∗ 𝑅 ∗ cos ∝
𝑍=
𝐿
Z 1,5 []
Poisson's ratio: ν 0,3 []
The mean elastic circumferential strain at collapse:
1 1 𝑒 ∗ cos ∝
𝜀= + 𝑛 −1+𝑍
𝑍 𝑛 12 𝑅 ∗ 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ∝ 1 − 𝜈
𝑛 −1+
2 +1
𝑍
ε 0,008 []
The theoretical elastic instability pressure for collapse
of a perfect conical shell:
𝐸 ∗ 𝑒 ∗ 𝜀 ∗ 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ∝
𝑃 =
𝑅
Pm 47,8 [MPa]
Pm/Py 6,2 [MPa]
Pr/Py 0,935 [MPa]
The calculated lower bound collapse pressure:
𝑃
𝑃 = ∗𝑃
𝑃
Pr 7,2 [MPa]
The calculation pressure: P 2,5 [Mpa]
The test pressure: Ptest 4 [Mpa]
𝑃 < 𝑃 /1,5 Pr/1,5 4,8 [Mpa]
𝑃 < 𝑃 /1,1 Pr/1,1 6,5 [Mpa]
You might also like
- Unstiffened Cylinders EN 13445-3 - 8.5.2 PDFDocument4 pagesUnstiffened Cylinders EN 13445-3 - 8.5.2 PDFfrlamontNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Design of Stairs Design of Stairs From Ground To Landing Material PropertiesDocument3 pagesDesign of Stairs Design of Stairs From Ground To Landing Material PropertiesJohn Paul Hilary EspejoNo ratings yet
- Principles of HydrotherapyDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Hydrotherapyvaishali jagtap100% (6)
- Figure 9.4-9 Cylindrical Shell With Isolated Opening, Increased Wall Thickness and Set-In Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-9Document4 pagesFigure 9.4-9 Cylindrical Shell With Isolated Opening, Increased Wall Thickness and Set-In Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-9met-calcNo ratings yet
- Overview of GRP PipesDocument14 pagesOverview of GRP PipesMD IBRARNo ratings yet
- Figure 9.5-1 Cylindrical Shell With Nozzle Oblique in The Longitudinal Cross Section en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-1Document5 pagesFigure 9.5-1 Cylindrical Shell With Nozzle Oblique in The Longitudinal Cross Section en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-1met-calcNo ratings yet
- Power ScrewsDocument4 pagesPower Screwsmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Circulatum MinusDocument2 pagesCirculatum MinusJoshua Arent100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Figure 9.5-2 Cylindrical Shell With Nozzle Oblique in The Transverse Cross Section en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-2Document5 pagesFigure 9.5-2 Cylindrical Shell With Nozzle Oblique in The Transverse Cross Section en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-2met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle ValveDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Nuts (11.4.3.2) EN 13445-3Document1 pageNuts (11.4.3.2) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Crochet Your Christmas Ornaments: 25 Christmas Decorations to MakeFrom EverandCrochet Your Christmas Ornaments: 25 Christmas Decorations to MakeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lattice Disc)Document18 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lattice Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Figure 9.4-13 Conical Shell With Isolated Opening. Combined Reinforcement From Shell and Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-13Document4 pagesFigure 9.4-13 Conical Shell With Isolated Opening. Combined Reinforcement From Shell and Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-13met-calcNo ratings yet
- Figure 9.5-3 Spherical Shell With A Non Radial Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-3Document5 pagesFigure 9.5-3 Spherical Shell With A Non Radial Nozzle en 13445-3 - Figure 9.5-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Conical Shells (7.6.4) EN 13445-3Document3 pagesConical Shells (7.6.4) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)Document18 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Allowable Stress: R Mpa C SDocument1 pageAllowable Stress: R Mpa C Smet-calcNo ratings yet
- Spherical Shells (7.4.3) EN 13445-3Document3 pagesSpherical Shells (7.4.3) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Contact Stress of The Cylinder in The Cylindrical SocketDocument3 pagesContact Stress of The Cylinder in The Cylindrical Socketmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Contact Stress of Cylinder On Flat SurfaceDocument3 pagesContact Stress of Cylinder On Flat Surfacemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Threaded Holes (11.4.3.3) EN 13445-3Document1 pageThreaded Holes (11.4.3.3) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Unstiffened Cylinders en 13445-3 - 8.5.2Document4 pagesUnstiffened Cylinders en 13445-3 - 8.5.2met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Bunger ValveDocument34 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Bunger Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lenticular Disc)Document28 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lenticular Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The PistonDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The Pistonmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve For Pump Operation (Lattice Disc)Document24 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve For Pump Operation (Lattice Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Spherical Shells en 13445-3 - 7.4.3Document3 pagesSpherical Shells en 13445-3 - 7.4.3met-calc100% (1)
- Rolled Shells (7.4.2) According To Standards EN 13445-3: Values For CalculationDocument3 pagesRolled Shells (7.4.2) According To Standards EN 13445-3: Values For Calculationmet-calcNo ratings yet
- U-Shaped Unreinforced Bellows (Austenitic Steel)Document9 pagesU-Shaped Unreinforced Bellows (Austenitic Steel)met-calc100% (1)
- Full Face Flange With Metal To Metal Contact (11.10) EN 13445-3Document5 pagesFull Face Flange With Metal To Metal Contact (11.10) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
- The Flow Characteristic On The Position of The DriveDocument7 pagesThe Flow Characteristic On The Position of The Drivemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lattice Disc)Document31 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Lattice Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- BucklingDocument2 pagesBucklingmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through Conduit)Document14 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through Conduit)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)Document31 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through-Conduit)Document23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through-Conduit)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve For Pump Operation (Lattice Disc)Document19 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve For Pump Operation (Lattice Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Articulated Trunnion in The RodDocument5 pagesArticulated Trunnion in The Rodmet-calc100% (1)
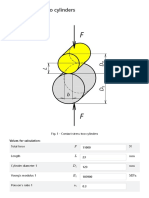
- Contact Stress Two CylindersDocument3 pagesContact Stress Two Cylindersmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Spherical ValveDocument40 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Spherical Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Flange With Hole With Continuous Sealing Surface With Metal To Metal Contact (11.10.0) EN 13445-3Document4 pagesFlange With Hole With Continuous Sealing Surface With Metal To Metal Contact (11.10.0) EN 13445-3met-calcNo ratings yet
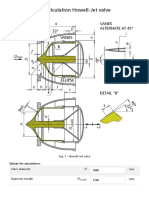
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Jet ValveDocument17 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Jet Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Multi-Stage ValveDocument2 pagesMulti-Stage Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Ellipsoidal Ends en 13445-3 - 8.8.3Document2 pagesEllipsoidal Ends en 13445-3 - 8.8.3met-calcNo ratings yet
- Junction Between The Large End of A Cone and A Cylinder With A Knuckle en 13445-3 - 7.6.7Document4 pagesJunction Between The Large End of A Cone and A Cylinder With A Knuckle en 13445-3 - 7.6.7met-calcNo ratings yet
- Junction Between The Large End of A Cone and A Cylinder Without A Knuckle en 13445-3 - 7.6.6Document3 pagesJunction Between The Large End of A Cone and A Cylinder Without A Knuckle en 13445-3 - 7.6.6met-calcNo ratings yet
- Light Stiffeners EN 13445-3 - 8.6.4.1.2Document10 pagesLight Stiffeners EN 13445-3 - 8.6.4.1.2met-calcNo ratings yet
- U-Shaped Reinforced Bellows (Austenitic Steel)Document10 pagesU-Shaped Reinforced Bellows (Austenitic Steel)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Figure 9.4-5 Cylindrical Shell With Isolated Opening and Reinforcing Ring, With External Blind Flange B en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-5Document4 pagesFigure 9.4-5 Cylindrical Shell With Isolated Opening and Reinforcing Ring, With External Blind Flange B en 13445-3 - Figure 9.4-5met-calcNo ratings yet
- Nozzles Which Encroach Into The Knuckle Region (Kloepper) en 13445-3 - 7.7Document6 pagesNozzles Which Encroach Into The Knuckle Region (Kloepper) en 13445-3 - 7.7met-calcNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Pin For Shaft-Hub ConnectionDocument6 pagesLongitudinal Pin For Shaft-Hub Connectionmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Component DesignDocument32 pagesComponent Designdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- 08 Practical Application Press FitDocument6 pages08 Practical Application Press Fitenrico.michelatoNo ratings yet
- Example 2 To Start ExplainationDocument8 pagesExample 2 To Start ExplainationsamehNo ratings yet
- BEARING STRESS CALCULATIONDocument21 pagesBEARING STRESS CALCULATIONDenver NieverasNo ratings yet
- Beams: (Frame 2)Document54 pagesBeams: (Frame 2)John Rafael R. CanoosNo ratings yet
- Coupling and Its TypesDocument22 pagesCoupling and Its TypesAnantha BhatNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Slab Design AnalysisDocument12 pagesTwo-Way Slab Design AnalysisMin Min IINo ratings yet
- Design Test 1 - (With Memo)Document5 pagesDesign Test 1 - (With Memo)Tukisho MacheteNo ratings yet
- 06 Practical Application Bolted Cylindrical VesselDocument12 pages06 Practical Application Bolted Cylindrical Vesselenrico.michelatoNo ratings yet
- Composite AssDocument13 pagesComposite AssBelay BayuNo ratings yet
- Barrier Connector CalculationDocument2 pagesBarrier Connector CalculationSaifan RizaldyNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Design Book PDFDocument19 pagesIC Engines Design Book PDFRohith FernandoNo ratings yet
- Double Action Lifting Jack Design CalculationsDocument26 pagesDouble Action Lifting Jack Design CalculationsGabriel AkNo ratings yet
- Sample SolutionsDocument10 pagesSample SolutionsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- CE199-2L Deesuyn-MergedDocument67 pagesCE199-2L Deesuyn-MergedMark Kenneth BaldoqueNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Allowable Hertz PressureDocument1 pageAllowable Hertz Pressuremet-calcNo ratings yet
- Multi-Hole CageDocument7 pagesMulti-Hole Cagemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Fat Digestion and Metabolism in RuminantsDocument23 pagesFat Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminantsshahbaz zafarNo ratings yet
- Weld Design-GrDocument58 pagesWeld Design-Grvenky100% (1)
- Scope and Sequence - ChemistryDocument2 pagesScope and Sequence - Chemistryapi-232424041No ratings yet
- Abrasive-A ReviewDocument43 pagesAbrasive-A ReviewA.YusoffNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology v1.0Document43 pagesNanotechnology v1.0Faizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physico-chemical Water Treatment Processes AssignmentDocument6 pagesPhysico-chemical Water Treatment Processes AssignmentAbir HasanNo ratings yet
- Folder ILF Upstream Facilities enDocument4 pagesFolder ILF Upstream Facilities enSterling GordianNo ratings yet
- 12.co Ordination CompoundsExerciseDocument34 pages12.co Ordination CompoundsExerciseMaster Of HakingNo ratings yet
- Ts 1 5 Specific Feed Safety LimitsDocument87 pagesTs 1 5 Specific Feed Safety Limitsraed abujoudehNo ratings yet
- M.E.Forge Tech: Customer:M/s L & T Valves LimitedDocument1 pageM.E.Forge Tech: Customer:M/s L & T Valves LimitedK.s. Raghavendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Notice IchloreDocument228 pagesNotice IchloreHervé MunozNo ratings yet
- Study of Gas-Condensate Well Productivity in Santa Barbara Field, Venezuela, by Well Test AnalysisDocument9 pagesStudy of Gas-Condensate Well Productivity in Santa Barbara Field, Venezuela, by Well Test AnalysisWaleed Barakat MariaNo ratings yet
- Newton HydroSeal 107F Elastic 2K TDS 4.0Document8 pagesNewton HydroSeal 107F Elastic 2K TDS 4.0Дмитрий СаламатовNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Volume 28 Issue 10 1956 (Doi 10.1021/ac60118a012) Pflaum, R. T. Howick, L. C. - Spectrophotometric Determination of Potassium With Sodium TetraphenylborateDocument3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Volume 28 Issue 10 1956 (Doi 10.1021/ac60118a012) Pflaum, R. T. Howick, L. C. - Spectrophotometric Determination of Potassium With Sodium TetraphenylboratekhqqxyzNo ratings yet
- Allelopathic Potential of Tagetes Minuta Terpenes by A ChemicalDocument9 pagesAllelopathic Potential of Tagetes Minuta Terpenes by A ChemicalbiologiaufbaNo ratings yet
- WS3Document2 pagesWS3dextercitomanNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Practical Booklet 2020-2021: NAME: - CLASS - TEACHERDocument9 pagesAs Chemistry Practical Booklet 2020-2021: NAME: - CLASS - TEACHERPaul MurrayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2Document41 pagesChapter 3 2jerrica thomasNo ratings yet
- Zahid Husain M.Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Faculty of Pharmacy, IU, LucknowDocument24 pagesZahid Husain M.Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Faculty of Pharmacy, IU, LucknowQA Dhq OkaraNo ratings yet
- Spectrex UV IR 20 20LBDocument2 pagesSpectrex UV IR 20 20LBGustavo Alejandro Flores GarriNo ratings yet
- T06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Document66 pagesT06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Zitouni LamineNo ratings yet
- A 826 - A826m - 95 Qtgyni05nqDocument5 pagesA 826 - A826m - 95 Qtgyni05nqsachinguptachdNo ratings yet
- Panduan Troli EmergencyDocument3 pagesPanduan Troli EmergencyTukiyemNo ratings yet
- CVDocument2 pagesCVyadse100% (1)
- Small STNTechnical ManualDocument8 pagesSmall STNTechnical ManualMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Energy and FluctuationDocument10 pagesEnergy and Fluctuationwalid Ait MazouzNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeDocument45 pagesInterpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeAnnisa RizqiaNo ratings yet