Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tax 5.2 - Fringe Benefits and Fringe Benefit Tax
Uploaded by
elizabeth angelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tax 5.2 - Fringe Benefits and Fringe Benefit Tax
Uploaded by
elizabeth angelCopyright:
Available Formats
TAX 5.
2 – FRINGE BENEFITS AND FRINGE BENEFIT TAX
Definition of terms
Fringe benefit – an employee’s benefit supplementing a money wage or salary
Managerial employees – one who is vested with powers or prerogatives to lay down and
execute management policies and/or to hire, transfer, suspend, lay-off, recall, discharge, assign
or discipline employees.
Supervisory employees – those who, in the interest of the employer, effectively recommend
such managerial actions if the exercise of such authority is not merely routinary or clerical in
nature but requires the use of independent judgment
Rank and file employees – all employees who are holding neither managerial nor supervisory
position
Fringe Withholding Tax
Fringe benefit tax is a final tax
Imposed on the grossed-up monetary value
It is imposed on the grossed-up monetary value of fringe benefits furnished granted or paid by
employer to employee except rank and file employees
Withheld by employer
It shall be treated as a final tax on employee, which shall be withheld and paid by the employer
on a calendar quarterly basis
Taxable Fringe Benefits
Any good and other benefit furnished or granted by an employer in cash or in kind, in addition
to basic salaries to employees (except rank and file) such as, but not limited to the following:
- Housing
- Expense account
- Vehicle of any kind
- Housing personnel, such as maid, driver, and others
- Interest on loan at less that market rate to the extent of the difference between the market
rate and the actual (12%benchmark rate)
- Membership fee to professional organization (social and athletic club or other similar
organizations)
- Expenses for foreign travel
- Holiday and vacation expense
- Educational assistance to the employee or his dependents
- Life or health insurance and other non-life insurance premium or similar amount in excess of
what the law allows
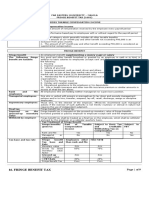
Tax base and tax rate
Fringe benefit tax Employees other NRA-NETB Special alien
base and rate than rank and file (including Filipino
Counterparts) and
employees in special
economic zone**
Monetary value PXX PXX PXX
Divide by Gross 68% (TRAIN Law 65%) 75% 85% (TRAIN Law 65%)
monetary value factor
Grossed-up monetary PXX PXX PXX
value
X FBT Rate 32% (TRAIN Law 35%) 25% 15% (TRAIN Law 35%)
Fringe Benefit Tax PXXX PXXX PXXX
Basic Rules on Fringe Benefit and Fringe Benefit Tax
- Fringe benefit given to rank and file employee is not subject to FBT
- Fringe benefit is given to a supervisory or managerial employee and subject to FBT
- De minimis benefit, whether given to rank and file employee or to a supervisory or
managerial employee is not subject to the FBT
- Any excess in de minimis benefit, whether given to rank and file employee or to a
supervisory or managerial employee part of other 13th month pay and other benefits
Valuation of fringe benefits
- If money, the value is the amount granted
- If property, and ownership is transferred to the employee, the value is the fair market value
of the property
- If property, but ownership is not transferred to the employee, the value is equal to the
depreciation value of the property
Computation of Monetary Value of Benefit of Housing Privilege and Motor Vehicle
- In case of housing privilege and motor vehicles:
o If there is no transfer of ownership, the monetary value of benefit is 50% of the
value of the benefit
o If there is transfer of ownership, the monetary value of the benefit is the same as
the value of the benefit
- In case of other fringe benefits > the monetary value of the benefit is the same as the value
of the benefit
Deductible expense of the employer
-If the fringe benefit is given to a rank and file employee, or to a supervisory or managerial
employee, but is not subject to fringe benefit tax, the deduction for the employer is the
monetary value of the fringe benefit
- If the fringe benefit is given to a supervisory or managerial employee and is subject to fringe
benefit tax, the deduction is the grossed-up monetary value of the fringe benefit which
compose to the fringe benefit expense and fringe benefit tax
Fringe Benefits Explained
- Housing
o Employer leases residential property for the use of the employee
Value: Rental paid
Monetary value: 50% of the value of the benefits
o Employer owns residential property which was assigned to an officer for his use as
residence
Value: 5% of the (FMV in the real property declaration or Zonal Value, whichever is
higher) of the land and improvements
MV: 50% of the value of the benefits
o Employer purchases residential property on the installment basis and allows the
employee to use the same as his residence
Value: 5% of the acquisition cost exclusive of interest
MV: 50% of the value of the benefits
o Employer purchases a residential property and transferred the ownership in the
name of the employee
Value: The higher between the acquisition cost or FMV
MV: Entire value of the benefit
o Employer purchases a residential property and transfer ownership to his employee
for the latter’s residential use at a price less than the employer’s acquisition
Value: FMV less payment by employee (Higher between the assessed value and
zonal value as determined by the CIR)
MV: Entire value of the benefit
You might also like
- Fringe Benefits TaxationDocument12 pagesFringe Benefits TaxationKaila Mae Tan DuNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits TaxDocument38 pagesFringe Benefits Taxkeisha santosNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit TaxDocument30 pagesFringe Benefit Taxrav danoNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerangel ciiiNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax - Nov 06Document27 pagesFringe Benefit Tax - Nov 06Renievave TorculasNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit TaxDocument37 pagesFringe Benefit TaxAna Marie CuerboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Fringe BenefitsDocument21 pagesChapter 4-Fringe BenefitsAlyssa Camille DiñoNo ratings yet
- FBT GuideDocument62 pagesFBT GuideDiapera, Rhina LynNo ratings yet
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Cpa ReviewDocument11 pagesExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Cpa ReviewKuro HanabusaNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No 3-98Document9 pagesRevenue Regulations No 3-98Anonymous MikI28PkJcNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No. 3-98Document14 pagesRevenue Regulations No. 3-98Angela Magbanua100% (1)
- Revenue Regulations No 3-98 FBTDocument15 pagesRevenue Regulations No 3-98 FBTeric yuulNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax!!!!Document4 pagesFringe Benefit Tax!!!!Claire ZafraNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax GuideDocument24 pagesFringe Benefit Tax GuidelcNo ratings yet
- De Minimis and Fringe BenefitsDocument14 pagesDe Minimis and Fringe BenefitsCza PeñaNo ratings yet
- Material F - Fringe Benefit DiscussionDocument10 pagesMaterial F - Fringe Benefit Discussion21100698No ratings yet
- RR 03-98Document5 pagesRR 03-98Ayvee BlanchNo ratings yet
- RR 3-98Document13 pagesRR 3-98Althea Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- IT Part 2Document95 pagesIT Part 2Virgilio E Aranas JrNo ratings yet
- Fringe BenefitDocument9 pagesFringe BenefitKim BarriosNo ratings yet
- Fringe BenefitsDocument22 pagesFringe BenefitsMariel BerdigayNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax Train LawDocument27 pagesFringe Benefit Tax Train LawJoyce Leeann Manansala75% (4)
- Bam031 Income Taxation P2 NotesDocument8 pagesBam031 Income Taxation P2 NotesRyan Malanum AbrioNo ratings yet
- Bsa1202 FS2122 Incometax 04Document9 pagesBsa1202 FS2122 Incometax 04Katring O.No ratings yet
- Tax Tax TaxDocument7 pagesTax Tax TaxClaire ZafraNo ratings yet
- Northern CPAR: Taxation - Fringe Benefit Taxation: Rex B. Banggawan, Cpa, MbaDocument7 pagesNorthern CPAR: Taxation - Fringe Benefit Taxation: Rex B. Banggawan, Cpa, MbaLouiseNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No. 3-1998Document10 pagesRevenue Regulations No. 3-1998Brian BaldwinNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No. 3-98 - Fringe Benefit TaxDocument14 pagesRevenue Regulations No. 3-98 - Fringe Benefit TaxNikki BinsinNo ratings yet
- RR 3-98Document6 pagesRR 3-98matinikkiNo ratings yet
- FringeDocument7 pagesFringeJoyce Anne TilanNo ratings yet
- RR 2-98 and 3-98Document103 pagesRR 2-98 and 3-98Ria Camille de JesusNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No. 3-98 - Fringe Benefit TaxDocument14 pagesRevenue Regulations No. 3-98 - Fringe Benefit TaxRaiza Radoc100% (1)
- Fringe BenefitsDocument31 pagesFringe BenefitsClang Santiago100% (1)
- Fringe Benefits and Withholding TaxDocument7 pagesFringe Benefits and Withholding TaxXiaoyu KensameNo ratings yet
- Tax SemiDocument18 pagesTax Seminodnel salonNo ratings yet
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Classification of EmployeesDocument12 pagesExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Classification of Employeesvane rondinaNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits TaxDocument6 pagesFringe Benefits TaxRandom VidsNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax 2Document20 pagesFringe Benefit Tax 2shpo.porras.uiNo ratings yet
- What Is A PerquisiteDocument8 pagesWhat Is A PerquisitesoujnyNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits TaxDocument5 pagesFringe Benefits TaxStanley Renz Obaña Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits Tax and de Minimis Benefits: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesFringe Benefits Tax and de Minimis Benefits: ObjectivesChristelle JosonNo ratings yet
- De Minimis Benefits: Taxability: Excluded From Gross Income Up To The Extent of 90,000 PesosDocument3 pagesDe Minimis Benefits: Taxability: Excluded From Gross Income Up To The Extent of 90,000 PesosKathNo ratings yet
- Continuation of Income Tax For IndividualDocument10 pagesContinuation of Income Tax For IndividualElla Mae VergaraNo ratings yet
- TAX 2306 - Fringe Benefits TaxDocument4 pagesTAX 2306 - Fringe Benefits TaxPurple KidNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit Tax PDFDocument9 pagesFringe Benefit Tax PDFLorraine TomasNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits - Income Tax NotesDocument3 pagesFringe Benefits - Income Tax NotesMa Terresa TejadaNo ratings yet
- Tax Treatments of Fringe BenefitsDocument14 pagesTax Treatments of Fringe BenefitsAdmNo ratings yet
- Tax Treatments of Fringe BenefitsDocument63 pagesTax Treatments of Fringe BenefitsAdmNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits TaxDocument4 pagesFringe Benefits TaxKathleen Jane SolmayorNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefits Tax PDFDocument8 pagesFringe Benefits Tax PDFBianca Margaret TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit TaxDocument9 pagesFringe Benefit TaxBusiness MatterNo ratings yet
- Cprefinal - Fringe BenefitsDocument35 pagesCprefinal - Fringe BenefitsRexell DepalacNo ratings yet
- 03 BAINCTAX - Individual de Minimis and FringeDocument15 pages03 BAINCTAX - Individual de Minimis and FringeCarmela PeducheNo ratings yet
- Fringe Benefit TaxDocument62 pagesFringe Benefit TaxALLIAH CLARISSE PACHECONo ratings yet
- RR 3-98Document7 pagesRR 3-98evelyn b t.No ratings yet
- Chapter No: 1 Introduction-SalaryDocument23 pagesChapter No: 1 Introduction-SalaryMrunali kadamNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Fringe Benefit TaxDocument45 pagesModule 5 Fringe Benefit TaxAjey MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Effective January 1, 2018Document7 pagesEffective January 1, 2018shimb tiuNo ratings yet
- 20107-1998-Implementing Section 33 of The National20180312-6791-1ui4ur4Document12 pages20107-1998-Implementing Section 33 of The National20180312-6791-1ui4ur4Deanna Clarisse HecetaNo ratings yet
- Cred Trans CodalDocument13 pagesCred Trans Codalelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17-Statement of Cash FlowsDocument4 pagesChapter 17-Statement of Cash Flowselizabeth angel100% (1)
- Cred Trans CodalDocument13 pagesCred Trans Codalelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- 2 Econimics052-017 AnswersDocument8 pages2 Econimics052-017 Answersרשע חוטאNo ratings yet
- Warm Bodies (Isaac Marion)Document4 pagesWarm Bodies (Isaac Marion)elizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- AfarDocument7 pagesAfarelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- Tax 5.2 - Fringe Benefits and Fringe Benefit TaxDocument7 pagesTax 5.2 - Fringe Benefits and Fringe Benefit Taxelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- Maceda LawDocument2 pagesMaceda LawcryziaNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Solutions Manual 2017 EditionDocument21 pagesAuditing and Assurance Solutions Manual 2017 EditionGerlyn Dasalla Claor50% (2)
- GamesDocument3 pagesGameselizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- Budget BreakdownDocument1 pageBudget Breakdownelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesPhysical Scienceelizabeth angelNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument6 pagesCompensationkanikasinghalNo ratings yet
- Ignou Mba Agri Business HRM Notes 2013Document43 pagesIgnou Mba Agri Business HRM Notes 2013DrPallati Sujendra100% (1)
- Role of Work Life BalanceDocument19 pagesRole of Work Life BalancePragya Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Perk Valuation of Motor CarDocument18 pagesPerk Valuation of Motor CarcapkaggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri: Inland Revenue BoardDocument17 pagesLembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri: Inland Revenue Boardlookiensang100% (2)
- Human Resource Management FunctionsDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management FunctionsvineethvijayNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitDocument11 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Gross Earnings Fed Taxable Gross Total Taxes Total Deductions Net PayDocument2 pagesGross Earnings Fed Taxable Gross Total Taxes Total Deductions Net PaybryansypNo ratings yet
- RetentionDocument35 pagesRetention4179309No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (HRM)Document56 pagesHuman Resource Management (HRM)Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Retention of Talent & Employee MotivationDocument4 pagesRetention of Talent & Employee MotivationHarshal TakNo ratings yet
- 4 Tip For Communication Your Compensation PlanDocument4 pages4 Tip For Communication Your Compensation Planeric_mdisNo ratings yet
- Induction ManualDocument4 pagesInduction Manualrajashree97No ratings yet
- Primer CnaDocument9 pagesPrimer CnaJuris ArrestNo ratings yet
- NTPC Human Resource Policies-21!10!08Document26 pagesNTPC Human Resource Policies-21!10!08SamNo ratings yet
- Employee State Insurance ActDocument14 pagesEmployee State Insurance ActPravin ChandanshiveNo ratings yet
- For Against Essay Being Your Own BossDocument1 pageFor Against Essay Being Your Own BossRoberto GramajoNo ratings yet
- UN Salary ScaleDocument8 pagesUN Salary Scalemaconny20No ratings yet
- Contract Review Report TemplateDocument19 pagesContract Review Report Templateraghacivil100% (1)
- Labour Cost and Systems of Wage PaymentDocument19 pagesLabour Cost and Systems of Wage PaymentAnusha_SahukaraNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Benefits at Reliance PowerDocument21 pagesCompensation and Benefits at Reliance Powersumit87rajNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Theories of Employee RemunerationDocument2 pagesMeaning and Theories of Employee RemunerationMaulikMakwana100% (2)
- Understanding Life Insurance and Imputed Income: Table 1 RatesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Life Insurance and Imputed Income: Table 1 RatesarbindokiluNo ratings yet
- Cash Balance PlansDocument11 pagesCash Balance Plansmphillips36111No ratings yet
- Compensation and BenefitsDocument44 pagesCompensation and BenefitsOnkar SawantNo ratings yet
- De Minimis and FringeDocument1 pageDe Minimis and FringeAlicia Jane NavarroNo ratings yet
- How Does Bright Horizons Family SolutionDocument2 pagesHow Does Bright Horizons Family SolutiontahirNo ratings yet
- Assignment of CompensationDocument3 pagesAssignment of CompensationSapan SuriNo ratings yet
- What Is Human Resource Management?: (1) (Need Quotation To Verify)Document1 pageWhat Is Human Resource Management?: (1) (Need Quotation To Verify)Saleh RehmanNo ratings yet
- Gabriel F Stellar - Rmi 3501 - CompleteDocument30 pagesGabriel F Stellar - Rmi 3501 - CompletestudentATtempleNo ratings yet