Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Text in English
Uploaded by
ugi lestariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Text in English
Uploaded by
ugi lestariCopyright:
Available Formats
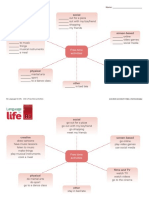
PROCEDURE 2.
Complication ( a problem arises and followed by
other problems)
Social function: To help us do a task or make 3. Resolution ( provide solution to the problem)
something. They can be a set of instructions or Language features:
directions. 1. Use of noun phrases ( a beautiful princess, a huge
Text organization: temple)
1. Goals ( the final purpose of doing the instruction) 2. Use of adverbial phrases of time and place ( in
2. Materials ( ingredients, utensils, equipment to do the garden, two days ago)
the instructions) 3. Use of simple past tense ( He walked away from
3. Steps ( a set of instruction to achieve the final the village)
purpose) 4. Use of action verbs ( walked, slept)
Language features : 5. Use of adjectives phrases ( long black hair)
Use of imperative ( Cut…….., Don’t mix……..)
Use of action verbs (turn, put) DESCRIPTION
Use of connectives(first, then, finally)
Social Function: To describe a particular person,
place or thing.
RECOUNT
Generic Structure:
1. Identification (identify phenomenon to be
Social function: To tell the readers what happened
described)
in the past through a sequence of events.
2. Description (describe parts, qualities,
Generic Structure:
characteristics)
1. Orientation ( who were involved, when and
Language features:
where was it happened)
2. Events ( tell what happened in a chronological Focus on specific participants
order) Use of attributive and identifying processes
3. Re-orientation ( optional – closure of events) Frequent use classifiers in nominal groups.
Language features: Use of the Simple Present Tense
Use of pronouns and nouns ( David, he, she)
Use of action verbs in past (went, studied) NEWS ITEM
Use of past tense ( We went for a trip to the zoo)
Social function: To inform readers or listeners about
Use of adverbial phrases
events of the day which are considered newsworthy
Use of adjectives or important.
Generic structure:
NARRATIVE 1. News worthy event ( tells the event in a summary
form)
Social function: To amuse or entertain the readers
2. Background events ( elaborate what happened,
with actual or imaginary experience in different
tell what caused the incident)
ways. Narrative always deals with some problems
3. Sources ( comments by participants, witnesses,
which lead to the climax and then turn into a
authorities and experts involved in the event)
solution to the problem.
Language features:
Generic Structure:
Information on the use of head lines.
1. Orientation ( who was involved, when and where
was it happened) Use of action verbs( hit, attack)
Use of saying verbs( said, added, claimed) Words that qualify statements such as: usual
Use of passive sentences ( Aceh was hit by probably
Tsunami in 2004) Words that link arguments such as: firstly, however,
Use of adverbs in passive sentences (The victims on the other hand, therefore.
were badly injured) Usually present tense
Compound and complex sentences
REPORT
SPOOF
Social function: To describe the way things are (for
example: a man -made thing, animals, plants). The Social function: To tell an event with a humorous
things must be a representative of their class. twist.
Text organization: Generic structure:
1. General classification (introduces the topic of the 1. Orientation (who were involved, when and where
report/tells what phenomenon under discussion is.) was happened)
2. Description (tell the details of topic such as 2. Events ( tell what happened in a chronological
physical appearance, parts, qualities, order)
habits/behaviour). 3. Twist (provide the funniest part of the story)
Language features: Language features:
Use of general nouns ( Whales, Kangaroo, Use of connectives (first, then, finally)
Computer) Use of adverbial phrases of time and place (in the
Use of present tense(Komodo dragons usually garden, two days ago)
weigh more than 160 kg) Use of simple past tense (he walked away from the
Use of behavioural verbs (Snakes often sunbathe in village)
the sun)
Use of technical terms ( Water contains oxygen and HORTATORY EXPOSITION
hydrogen)
Use of relating verbs (is, are, has) Social function: To persuade the readers or the
listeners that something should or should not be the
ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION case.
Generic structure:
Social function: To persuade the readers or the 1. Thesis ( stating an issue of concern)
listeners that something in the case, to analyze or to 2. Arguments ( giving reasons for concern, leading
explain. recommendation)
Generic Structure: 3. Recommendation (stating what ought or ought
1. Thesis (usually includes a preview argument. It not to happen)
introduces topics and indicates the writer’s Language features:
position.) Emotive words: alarmed, worried
2. Arguments (consists of a point and elaboration Words that qualify statements: usual probably
sequence. The number of points may vary, but each Words that link arguments: firstly, however, on the
must be supported by discussion and evidence). other hand, therefore
3. Reiteration (restates the position more forcefully
Usually present tense
in the light of the arguments presented).
Language features: Compound and complex sentences
Emotive words such as : alarmed, worried. Modal auxiliary: can, may, should, must
EXPLANATION opinion, or recommendation. It can consist of more
Social function: To explain the process involved in than one.
the formation or working of natural or socio cultural 3. Interpretative Recount ( summary of an art works
phenomena. including characters and plot).
Generic structure: 4. Evaluative summation: the last opinion consisting
1. A general statement to position the reader the appraisal or the punch line of the art works
2. A sequenced explanation of why or how being criticized.
something occurs. Language features:
3. Closing Focus on specific participants
Language features: Use of adjectives
Focus on generic, non-human participants. Use of long and complex clauses
Use mainly of general and abstract nouns, action Use of metaphor
verbs, simple present tense, passive voice, Reviews are used to summarize, analyze and
conjunction of time and cause, noun phrases, respond to art works. They may include: movie, TV
complex sentences, and technical language. shows, books, plays, concerts, etc.
DISCUSSION
Social function: To present information and
opinions about more than one side of an issue (“for”
points “against” points)
Generic structure:
1. Opening statement presenting the issue
2. Arguments or evidence for different points of
view ( pros and cons)
3. Concluding recommendation.
Language features:
Use of general nouns: alcohol, abortion, smoking,
etc.
Use of relating verbs: is, are, etc.
Use of thinking verbs: think, feel, hope believe, etc.
Use of additive connectives: addition, furthermore,
besides, etc.
Use of contrastive connectives: although, even, if,
nevertheless, etc.
Use of causal connectives: because, because of, etc.
Use of modal auxiliary: must, should, etc.
Use of adverbial manner: hopefully.
REVIEW
Social function: To critique an art work or event for
a public audience.
Generic structure:
1. Orientation ( background information on the text)
2. Evaluation ( concluding statement : judgment,
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Teacher's Book 4Document261 pagesTeacher's Book 4Fazee Khalid AlmuslimiNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani Presentation Dr. Nilak Datta HSS Department, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument15 pagesBITS Pilani Presentation Dr. Nilak Datta HSS Department, K K Birla Goa CampusbbbbbNo ratings yet
- ENGL 102 UNIT 2 - Spring 2022Document18 pagesENGL 102 UNIT 2 - Spring 2022AliNo ratings yet
- Intensivão To BeDocument98 pagesIntensivão To BeUIR4ZINNN FFNo ratings yet
- Language For Life b1 Mind MapsDocument20 pagesLanguage For Life b1 Mind MapsMarisol IaccinoNo ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Ashuddhi 1Document4 pages10 Cbse Ashuddhi 1praveen_nair35No ratings yet
- ConcordDocument16 pagesConcordHarum Dwi WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Claremont COURIER 8.21.10Document27 pagesClaremont COURIER 8.21.10Claremont CourierNo ratings yet
- OpenMind 1 Practice OnlineDocument10 pagesOpenMind 1 Practice OnlineClauCamarenaNo ratings yet
- Critical Discourse Analysis in Practice - Description by Group 5Document26 pagesCritical Discourse Analysis in Practice - Description by Group 5ZATA ISMAH Sastra InggrisNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument1 pageAction Planapi-476216257No ratings yet
- Quantifier Guide: Countable vs Uncountable NounsDocument4 pagesQuantifier Guide: Countable vs Uncountable Nounsmohamed mohamedNo ratings yet
- SEMASIOLOGY LECTURE 1 - APPROACHES AND TYPES OF MEANINGDocument24 pagesSEMASIOLOGY LECTURE 1 - APPROACHES AND TYPES OF MEANINGАнастасия ШутиковаNo ratings yet
- Common Names Examples:: Examples: A Man, A Goat, A Tree, A LakeDocument20 pagesCommon Names Examples:: Examples: A Man, A Goat, A Tree, A LakeHairmanb BustNo ratings yet
- 4A Ho Thanh An Functions of English Adjectives and Their Equivalents in Vietnamese LanguageDocument14 pages4A Ho Thanh An Functions of English Adjectives and Their Equivalents in Vietnamese LanguageTrúc Quỳnh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Catatan LIADocument15 pagesCatatan LIAichadelishaan100% (1)
- EnglishGrammercomposition 12 2018 03 04 108 PDFDocument332 pagesEnglishGrammercomposition 12 2018 03 04 108 PDFSony devi KeshriNo ratings yet
- Subjectverbagreement DietherDocument21 pagesSubjectverbagreement Dietherdiether pilapilNo ratings yet
- Noun functions in sentencesDocument23 pagesNoun functions in sentencescaren santosNo ratings yet
- Certain Nouns Possess A Singular Form But Still Represent Plurality and ThusDocument5 pagesCertain Nouns Possess A Singular Form But Still Represent Plurality and ThusasvenesekarNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument3 pagesCountable and Uncountable NounsEdison Pareja EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Grammar Structure of Modern EnglishDocument367 pagesGrammar Structure of Modern EnglishBranimira Troyanova100% (2)
- Arabic Influence in Ghomara Berber by J El HannoucheDocument294 pagesArabic Influence in Ghomara Berber by J El HannoucheAzurag ArrifNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument38 pagesBasic English GrammarAung HtunNo ratings yet
- 1 - F1 - Chilukuri Bhuvaneswar - THE SYNTAX OFTELUGU PROVERBS 1 THE SENTENCE - 06-07-14 PDFDocument48 pages1 - F1 - Chilukuri Bhuvaneswar - THE SYNTAX OFTELUGU PROVERBS 1 THE SENTENCE - 06-07-14 PDFbhuvaneswar Chilukuri100% (1)
- Compass Level 2 Scope and Sequence ChartDocument4 pagesCompass Level 2 Scope and Sequence ChartHasan BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Summary GMAT VerbalDocument21 pagesSummary GMAT VerbalGautam Popli100% (1)
- The Grammar of PerfumeryDocument11 pagesThe Grammar of PerfumeryMorne100% (1)
- TKT Module 1 Part 1 (Describing Language and Language Skills)Document40 pagesTKT Module 1 Part 1 (Describing Language and Language Skills)Jennefer AranillaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical GrammerDocument64 pagesTheoretical Grammermohtab100% (2)