Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Constituents: The Chemistry of Plants
Uploaded by
NeanderthanPisdashioStuartOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Constituents: The Chemistry of Plants
Uploaded by
NeanderthanPisdashioStuartCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Constituents: The Chemistry of Plants
To a pharmacist, these are the active ingredients of the plant, the chemicals that have a marked,
definable physiological and therefore, possibly medical activity upon the body. These constituents and
their actions within the body are also referred to as their pharmacology.
These active ingredients are not of immense interest to a medical herbalist, because the focus is on
using whole plants for whole people. Knowing chemical components and actions in isolation from the
rest of the plant, does not tell us much about the activity of the plant itself. This does not deny the value
of studying such plant constituents, as long as it takes its place within a holistic context of therapeutics.
Plant chemistry includes the miracle of photosynthesis, plant respiration, structure, growth,
development, and reproduction. Much of the chemical basis of life is common to both plants and
animals. From a holistic perspective the whole of the plant must be respected as an integrated
biologically evolved unit that is beyond the analytical comprehension of science.
Plant Constituents
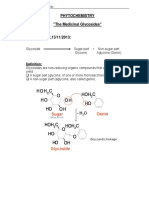
Physiologically active plant constituents are usually classified by their chemical structure rather than
specific actions. The list here will assumes a certain degree of chemical knowledge:
Acids
Alcohols
Carbohydrates
Phenols & phenolic glycosides
Tannins
Coumarins & their glycosides
Anthraquinones & their glycosides
Flavones & Flavonoid glycosides
Volatile Oils
Saponins
Cardioactive glycosides
Cyanogenic glycosides
“Bitter Principles”
Alkaloids
Recommended Resources:
Lisa Ganora, Herbal Constituents
Dr. Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants
Dr. Kerry Bone, The Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy
You might also like
- The Comprehensive Guide to Herbalism for Beginners: (2 Books in 1) Grow Medicinal Herbs to Fill Your Herbalist Apothecary with Natural Herbal Remedies and Plant Medicine: Herbology for BeginnersFrom EverandThe Comprehensive Guide to Herbalism for Beginners: (2 Books in 1) Grow Medicinal Herbs to Fill Your Herbalist Apothecary with Natural Herbal Remedies and Plant Medicine: Herbology for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- MoutainRoseHerbs - Herbal - Preparations.ebookDocument33 pagesMoutainRoseHerbs - Herbal - Preparations.ebooksmashdwarf100% (10)
- Your Guide for Herbal Medicine: Discover 56 Powerful Medicinal Herbs and Their Essential Oils that Will Boost Your Body and Mind HealthFrom EverandYour Guide for Herbal Medicine: Discover 56 Powerful Medicinal Herbs and Their Essential Oils that Will Boost Your Body and Mind HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Modern Herbal Dispensatory: A Medicine-Making Guide - Complementary MedicineDocument4 pagesThe Modern Herbal Dispensatory: A Medicine-Making Guide - Complementary Medicinenamyfipy0% (7)
- Native American’s Herbalist’s Guide: The Ultimate Herbal Medicine Encyclopedia. Create Your Apothecary Table and Discover Ancient Remedies to Improve Your Overall Well-BeingFrom EverandNative American’s Herbalist’s Guide: The Ultimate Herbal Medicine Encyclopedia. Create Your Apothecary Table and Discover Ancient Remedies to Improve Your Overall Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Guide To Blending Liquid Herbs: Herbal Formulations For The Individual Patient - Kerry BoneDocument4 pagesA Clinical Guide To Blending Liquid Herbs: Herbal Formulations For The Individual Patient - Kerry Bonedyfakyry33% (3)
- Herbalism 101: How to Grow Herbs, Learn About Holistic Health, and Become a Herbalist From A to ZFrom EverandHerbalism 101: How to Grow Herbs, Learn About Holistic Health, and Become a Herbalist From A to ZNo ratings yet
- Herbal Medicine, Healing & Cancer - Donald YanceDocument4 pagesHerbal Medicine, Healing & Cancer - Donald YancenefixedaNo ratings yet
- Everything Elderberry: How to Forage, Cultivate, and Cook with this Amazing Natural RemedyFrom EverandEverything Elderberry: How to Forage, Cultivate, and Cook with this Amazing Natural RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Apothecary GuideDocument72 pagesApothecary GuideMoBiqueNo ratings yet
- The Organic Medicinal Herb Farmer: The Ultimate Guide to Producing High-Quality Herbs on a Market ScaleFrom EverandThe Organic Medicinal Herb Farmer: The Ultimate Guide to Producing High-Quality Herbs on a Market ScaleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Leonurus Cardiaca MonographDocument5 pagesLeonurus Cardiaca MonographDian Fitri ChairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Planting the Future: Saving Our Medicinal HerbsFrom EverandPlanting the Future: Saving Our Medicinal HerbsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Book of Herbal Wisdom - Matthew WoodDocument5 pagesBook of Herbal Wisdom - Matthew Woodmediliso8% (13)
- Energetic Herbalism: A Guide to Sacred Plant Traditions Integrating Elements of Vitalism, Ayurveda, and Chinese MedicineFrom EverandEnergetic Herbalism: A Guide to Sacred Plant Traditions Integrating Elements of Vitalism, Ayurveda, and Chinese MedicineRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Herbal Education Guide & Schools DirectoryDocument81 pagesHerbal Education Guide & Schools DirectoryStacey Diane100% (1)
- Bergner Adaptogens and Tonics 2017Document62 pagesBergner Adaptogens and Tonics 2017Virág Mezei100% (1)
- Medical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal MedicineFrom EverandMedical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal MedicineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Tincture Instruction HandoutDocument5 pagesTincture Instruction HandoutD_ChaosNo ratings yet
- The Business of Botanicals: Exploring the Healing Promise of Plant Medicines in a Global IndustryFrom EverandThe Business of Botanicals: Exploring the Healing Promise of Plant Medicines in a Global IndustryNo ratings yet
- Herbal Formularies For Health Professionals, Volume 4: Neurology, Psychiatry, and Pain Management, Including Cognitive and Neurologic Conditions and Emotional Conditions - Jill StansburyDocument5 pagesHerbal Formularies For Health Professionals, Volume 4: Neurology, Psychiatry, and Pain Management, Including Cognitive and Neurologic Conditions and Emotional Conditions - Jill Stansburyxinebere0% (3)
- How To Start Your Herbal CareerDocument100 pagesHow To Start Your Herbal Careeradrians3852100% (4)
- Women Healers of the World: The Traditions, History, and Geography of Herbal MedicineFrom EverandWomen Healers of the World: The Traditions, History, and Geography of Herbal MedicineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Alchemy of Herbs: Transform Everyday Ingredients Into Foods and Remedies That Heal - Rosalee de La ForetDocument4 pagesAlchemy of Herbs: Transform Everyday Ingredients Into Foods and Remedies That Heal - Rosalee de La Foretxinebisu0% (3)
- Workbook 1 March 9Document5 pagesWorkbook 1 March 9cora4eva5699100% (1)
- Herbal Formularies For Health Professionals, Volume 1: Digestion and Elimination, Including The Gastrointestinal System, Liver and Gallbladder, Urinary System, and The Skin - Dr. Jill StansburyDocument5 pagesHerbal Formularies For Health Professionals, Volume 1: Digestion and Elimination, Including The Gastrointestinal System, Liver and Gallbladder, Urinary System, and The Skin - Dr. Jill Stansburygahyduga0% (4)
- The Artisan Herbalist: Making Teas, Tinctures, and Oils at HomeFrom EverandThe Artisan Herbalist: Making Teas, Tinctures, and Oils at HomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Nourishing Herbal Infusions Ebookv2Document43 pagesNourishing Herbal Infusions Ebookv2Anything_Nottaken100% (13)
- Herbs-Sam CoffmanDocument9 pagesHerbs-Sam CoffmanSilambarasu Karuppiah0% (1)
- Herbal Medicine : Simples Approved for Modern Uses of CureFrom EverandHerbal Medicine : Simples Approved for Modern Uses of CureNo ratings yet
- Herbal Tea Blending NOTESDocument9 pagesHerbal Tea Blending NOTESAna Lopes100% (2)
- Making Liquid Herbal Extracts or TincturesDocument2 pagesMaking Liquid Herbal Extracts or TincturesAbdul Samad100% (1)
- Grow Your Own Medicine: Handbook for the Self-Sufficient HerbalistFrom EverandGrow Your Own Medicine: Handbook for the Self-Sufficient HerbalistNo ratings yet
- Farming HerbsDocument161 pagesFarming Herbsplessiosaurus100% (4)
- Making Plant Medicinez - Richo CechDocument253 pagesMaking Plant Medicinez - Richo CechAquarian88% (8)
- Tea of Tranquility: Making Herbal Teas That Support Tranquility and Nervous System Function: BeWell Bohemia Herbs and Things, #1From EverandTea of Tranquility: Making Herbal Teas That Support Tranquility and Nervous System Function: BeWell Bohemia Herbs and Things, #1No ratings yet
- Herbal Gifts BookDocument14 pagesHerbal Gifts BookSarah Orndorff100% (1)
- The Complete Herbal Guide: A Natural Approach to Healing the Body NaturallyFrom EverandThe Complete Herbal Guide: A Natural Approach to Healing the Body NaturallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Calendula: Nature's Wound HealerDocument26 pagesCalendula: Nature's Wound Healeranon_910582813100% (1)
- Healing Herbal Teas: A Complete Guide to Making Delicious, Healthful BeveragesFrom EverandHealing Herbal Teas: A Complete Guide to Making Delicious, Healthful BeveragesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Demistifying Herbal TincturesDocument10 pagesDemistifying Herbal Tincturesmiadelfior100% (3)
- Backyard Medicine For All: A Guide to Home-Grown Herbal RemediesFrom EverandBackyard Medicine For All: A Guide to Home-Grown Herbal RemediesNo ratings yet
- Amy K. Fewell, Joel Salatin - The Homesteader's Herbal Companion - The Ultimate Guide To Growing, Preserving, and Using Herbs-Lyons Press (2018) PDFDocument321 pagesAmy K. Fewell, Joel Salatin - The Homesteader's Herbal Companion - The Ultimate Guide To Growing, Preserving, and Using Herbs-Lyons Press (2018) PDFVL100% (23)
- Plant HealerDocument153 pagesPlant HealerTrismegiste100% (10)
- The Wild Medicine Solution: Healing with Aromatic, Bitter, and Tonic PlantsFrom EverandThe Wild Medicine Solution: Healing with Aromatic, Bitter, and Tonic PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assange's Extradition Hearing Continues Amid Covid-19 PandemicDocument3 pagesAssange's Extradition Hearing Continues Amid Covid-19 PandemicNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- The Ecology of Herbal Medicine: A Guide to Plants and Living Landscapes of the American SouthwestFrom EverandThe Ecology of Herbal Medicine: A Guide to Plants and Living Landscapes of the American SouthwestNo ratings yet
- New Freedoms Post-Corona: GPS Trackers, Forced Selfies, and "Shoot Them DeadDocument3 pagesNew Freedoms Post-Corona: GPS Trackers, Forced Selfies, and "Shoot Them DeadNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- How To Make an Herbal Salve: An Introduction To Salves, Creams, Ointments, & MoreFrom EverandHow To Make an Herbal Salve: An Introduction To Salves, Creams, Ointments, & MoreRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- NHS Corruption - Cover Up Davis DavisDocument4 pagesNHS Corruption - Cover Up Davis DavisNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- The Art of Herbal Healing: Herbalism for BeginnersFrom EverandThe Art of Herbal Healing: Herbalism for BeginnersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- HypnotherapyDocument3 pagesHypnotherapyNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- An Herbalist's Guide to Formulary: The Art & Science of Creating Effective Herbal RemediesFrom EverandAn Herbalist's Guide to Formulary: The Art & Science of Creating Effective Herbal RemediesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Corona World OrderDocument1 pageCorona World OrderNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Fromm and NarcissismDocument12 pagesFromm and NarcissismNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Exposing NHS England CorruptionDocument2 pagesExposing NHS England CorruptionNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Plant Spirit Medicine: Using An Ancestral Meditation to Connect with the Medicine of Plants: Living Grace Meditation, #1From EverandPlant Spirit Medicine: Using An Ancestral Meditation to Connect with the Medicine of Plants: Living Grace Meditation, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assange's Extradition: Covid-19 Brings Death Sentence To Free SpeechDocument3 pagesAssange's Extradition: Covid-19 Brings Death Sentence To Free SpeechNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- The NHS Is Corrupt-I Was Raped: - Michelle Torez, in Reference To Roycroft IncidentDocument2 pagesThe NHS Is Corrupt-I Was Raped: - Michelle Torez, in Reference To Roycroft IncidentNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- NHS Staff in 214million FraudDocument2 pagesNHS Staff in 214million FraudNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Beatport Feb 2020 House ChartDocument28 pagesBeatport Feb 2020 House ChartNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- NHS Corrupt - 20 Years of Hell Started This Day in 1998Document5 pagesNHS Corrupt - 20 Years of Hell Started This Day in 1998NeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- 31 New Angelic PowersDocument4 pages31 New Angelic PowersNeanderthanPisdashioStuart100% (10)
- Application For TrainingDocument5 pagesApplication For TrainingNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Psoriasis ResearchDocument34 pagesPsoriasis ResearchNeanderthanPisdashioStuart100% (1)
- Bullying and Harassment at Work A Guide For EmployeesDocument16 pagesBullying and Harassment at Work A Guide For EmployeesIonelia PașaNo ratings yet
- The Ancient British Goddess: New, Revised, Updated, Expanded!Document13 pagesThe Ancient British Goddess: New, Revised, Updated, Expanded!NeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Application For TrainingDocument5 pagesApplication For TrainingNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- GriffinDocument8 pagesGriffinNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Psychic Predictions of Frederick DaviesDocument2 pagesPsychic Predictions of Frederick DaviesNeanderthanPisdashioStuart100% (1)
- SinusitusDocument1 pageSinusitusNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Eye Colour PsychologyDocument6 pagesEye Colour PsychologyNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Christos ExpDocument15 pagesChristos ExpNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Estrogen Actions in The Brain and The Basis For Differential Action in Men and WomenDocument69 pagesEstrogen Actions in The Brain and The Basis For Differential Action in Men and WomenNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Leader Narcissism and Outcomes in OrganizationsDocument32 pagesLeader Narcissism and Outcomes in OrganizationsNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Plant Constituents: The Chemistry of PlantsDocument1 pagePlant Constituents: The Chemistry of PlantsNeanderthanPisdashioStuart0% (1)
- Narcissistic Leaders and Their VictimsDocument28 pagesNarcissistic Leaders and Their VictimsNeanderthanPisdashioStuartNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Glycosides Presentation on VanillaDocument13 pagesAldehyde Glycosides Presentation on VanillaarmymanNo ratings yet
- Pharmsem PPT With Answers Pharmacognosy 2Document344 pagesPharmsem PPT With Answers Pharmacognosy 2MERVI CHRAINBERLY ZOLETANo ratings yet
- 2 2-PharmacognosyDocument11 pages2 2-PharmacognosyDahlia Suello100% (1)
- GlycosidesDocument18 pagesGlycosidesAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Evaluation of MarchantiapolymorphamontivagansDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Evaluation of MarchantiapolymorphamontivagansjujuadrianNo ratings yet
- Screening On The Phytochemical Constituents in Luffa Acutangula (L.) Roxb. (Kha We)Document11 pagesScreening On The Phytochemical Constituents in Luffa Acutangula (L.) Roxb. (Kha We)ေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26 - Cyanophore Cyanogenic Glycosides (Compatibility Mode)Document9 pagesLecture 26 - Cyanophore Cyanogenic Glycosides (Compatibility Mode)ahsanonweb19830% (1)
- An Assessment of Some of The Poisonous Plant Species To Animals Found in Delta State, NigeriaDocument8 pagesAn Assessment of Some of The Poisonous Plant Species To Animals Found in Delta State, NigeriaAZOJETE UNIMAIDNo ratings yet
- GLYCOSIDES AND CHEMICAL TESTSDocument32 pagesGLYCOSIDES AND CHEMICAL TESTSCik ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Crude Drug ClassificationDocument22 pagesCrude Drug Classificationraj royel100% (1)
- Module 2 - Plant ChemistryDocument22 pagesModule 2 - Plant ChemistrySelena MoonNo ratings yet
- 2.review of LiteratureDocument20 pages2.review of LiteratureMjd ObiedNo ratings yet
- Lec 10 Drugs Containing Saponin GlycosidesDocument51 pagesLec 10 Drugs Containing Saponin GlycosidesSandhya Parameswaran100% (2)
- Phle Reviewer Module 2 - PharmacognosyDocument52 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 2 - PharmacognosyMayrigen Dominguez100% (1)
- PharmacognosyDocument101 pagesPharmacognosyimam mahdi tv officialNo ratings yet
- A Review On Balanites Aegyptiaca Del (Desert Date) - Phytochemical Constituents, Traditional Uses, and Pharmacological ActivityDocument12 pagesA Review On Balanites Aegyptiaca Del (Desert Date) - Phytochemical Constituents, Traditional Uses, and Pharmacological Activityshishir badve100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy II l6 Test For GlycosidesDocument8 pagesPharmacognosy II l6 Test For GlycosidesChinchillaNo ratings yet
- Saponins Properties Applications and ProcessingDocument29 pagesSaponins Properties Applications and ProcessingCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- Scope of PharmacognosyDocument6 pagesScope of PharmacognosyDr. Mussadiq Latif88% (16)
- Experiment Nos. 1 To 5 Student HandoutDocument7 pagesExperiment Nos. 1 To 5 Student HandoutEzra Lee NgatiyonNo ratings yet
- Chemo Taxonomy of Medicinal PlantDocument11 pagesChemo Taxonomy of Medicinal Plantshankul kumar89% (36)
- Medicinal Glycosides LectureDocument9 pagesMedicinal Glycosides LectureRamling PatrakarNo ratings yet
- GPAT - Pharmacognosy SectionDocument35 pagesGPAT - Pharmacognosy SectionBashar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cog Nosy I (Part 6)Document88 pagesPharma Cog Nosy I (Part 6)neerajchoudhary100% (1)
- Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Canthium Parviflorum by In-Vitro MethodDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Canthium Parviflorum by In-Vitro MethodYanie IsfahannyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy RevisedDocument14 pagesPharmacognosy RevisedYishka ZaireahNo ratings yet
- Area 2 PCOG LECTURE CARBS TO LIPIDS PDFDocument172 pagesArea 2 PCOG LECTURE CARBS TO LIPIDS PDFMishella OconNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Phytochemical Constituents and AntDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Phytochemical Constituents and AntJoseph BernardoNo ratings yet
- PCOGDocument3 pagesPCOGChester John SotomilNo ratings yet
- NATURAL DRUGS: ALKALOIDS, TERPENOIDS, GLYCOSIDES & OILSDocument48 pagesNATURAL DRUGS: ALKALOIDS, TERPENOIDS, GLYCOSIDES & OILSPreeti VermaNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (56)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)