Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ceng5404 Assignment 1 Envrtl Eng
Uploaded by
ashe zinabCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ceng5404 Assignment 1 Envrtl Eng
Uploaded by
ashe zinabCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2 - Environmental Engineering (CENG5404)
1. A settling tank is used to remove suspended solids from wastewater. The rate of flow of
wastewater into the tank is 10 L/s, and the influent concentration of suspended solids (SS) is 200
mg/L. The removal efficiency of the settling tank for suspended solids is 60%. Calculate the
amount of suspended solids (sludge) accumulating in the sludge zone each day.
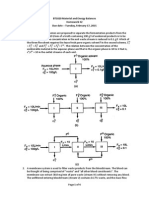
2. A sanitary landfill has available space of 16.2 ha at an average depth of 10 m. 765 cubic meters
of solids are dumped at the site 5 days per week. This waste is compacted to twice its delivery
density. Draw a mass-balance diagram and estimate the expected life of the landfill in years.
3. A mixing tank contains 1 m3 of water. a waste stream containing 32 kg/m3 of pollutant A flows
into the tank at a flow rate of 1.4 L/s. Liquid flows from the tank at a rate of 0.47 L/s. Assume
that the tank is completely mixed (i.e., the effluent concentration is equal to the tank
concentration of pollutant A). Calculate the concentration of A in the effluent when the tank
contains 1.4 m3 of solution. Assume that the pollutant is nonreactive.
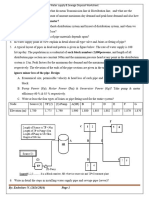
4. Dust is removed from the airstream of a municipal incinerator by four dust collectors operating in
parallel, each handling one-fourth of the total airflow of 200 m3/min. the airstream contains 10
g/m3 of suspended solids and collector efficiency is 98% decreasing linearly to 74 % as the air
flow is doubled. if the maximum permissible solids concentration from the combined stack
discharge is 1.0 g/m3, can one collector be temporarily taken out of service (a) by overloading
the other three units; (b) by not treating one-fourth of the air-flow?
5. A lake with constant volume 10 x 106 m3 is fed by a pollution-free stream with flow rate 50 m3/s.
A factory dumps 5 m3/s of a nonconservative waste with concentration 100 mg/L into the lake.
The pollution has a reaction rate coefficient K of 0.25/day. Assuming the pollution is well mixed
in the lake, find the steady-state concentration of pollution in the lake.
6. An ocean outfall diffuser that discharges treated wastewater into the Indian Ocean is 5,000 m
from a public beach. The wastewater contains 105 coliform bacteria per milliliter. The
wastewater discharge flow rate is 0.3 m3/s. The coliform first-order death rate in seawater is
approximated 0.3 h-1. The current carries the wastewater plume toward the beach at a rate of 0.5
m/s. The ocean current may be approximated as a pipe carrying 600 m3/s of seawater. Assume
that the current behaves as a plug-flow reactor and that the wastewater is completely mixed in the
current at the discharge point.
a. Determine the coliform concentration at the beach
b. If the concentration of coliform at the beach should not exceed 5 coliform bacteria per
milliliter, by how much should the treatment efficiency increase?
7. A liquid reaction is carried out in a batch reactor at constant temperature. A 50 % conversion is
achieved in 20 min. How long will it take to achieve the same conversion in (a) in a PFTR; (b) in
a CSTR?
8. If biodegradable organic matter, oxygen, and microorganisms are placed in a closed bottle, the
microorganisms will use the oxygen in the process of oxidizing the organic matter. The bottle
may be treated as a batch reactor and the decay of oxygen may be treated as a first-order reaction.
Write the general mass balance equation for the bottle. Using a computer spreadsheet calculate
and then plot the concentration of oxygen each day for a period of 5 days starting with a
concentration of 8 mg/L. Use a rate constant of 0.35 d-1.
You might also like
- Chapter 8 (Principle of Chemical Engineering) 1Document9 pagesChapter 8 (Principle of Chemical Engineering) 1Edmark Sienes Icalina50% (2)
- Problems Mass BalanceDocument2 pagesProblems Mass BalanceKofi DanielNo ratings yet
- 2512 Tutorial Sheet 01Document2 pages2512 Tutorial Sheet 01aggrey noahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Final Exam Part IDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Final Exam Part IVaasha Ramnarine100% (1)
- Chapter One: IntroductionDocument4 pagesChapter One: IntroductionManandhar SomeshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Anonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- Himmelblue 168-169Document2 pagesHimmelblue 168-169Daniela Mora MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Victor Megong JakiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1SITI NADHIRAH AzmiNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance Practice Problems F04Document1 pageMass Balance Practice Problems F04KZS1996No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Pratik Babu GhimireNo ratings yet
- CE384 Homework PacketDocument57 pagesCE384 Homework PacketRenika Baruah0% (1)
- Materials and Energy Balance PDFDocument8 pagesMaterials and Energy Balance PDFStephanie Grace QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Exam Examples Water TreatmentDocument38 pagesExam Examples Water TreatmentBinyam Kebede100% (1)
- Astewater Reatment Lant DesignDocument2 pagesAstewater Reatment Lant Designas3ateNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: InstructionsDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam: InstructionsRainelda C. CruzNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filters PDFDocument16 pagesTrickling Filters PDFJohnclaude ChamandiNo ratings yet
- Advance Waste Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesAdvance Waste Water TreatmentEr Govind Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ee IiDocument10 pagesEe IiKrithikaVenkatNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Sesame Dehulling Wastewater Utilization For Biogas ManufacturingDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Sesame Dehulling Wastewater Utilization For Biogas ManufacturingAhmed WagihNo ratings yet
- 3rd BTech 2022-23civil EE Ses-K2Document7 pages3rd BTech 2022-23civil EE Ses-K2Telugu films and technical INo ratings yet
- ETP UpgradationDocument7 pagesETP UpgradationYogesh DhekaleNo ratings yet
- 2504 - Tutorial No 01 and 2Document23 pages2504 - Tutorial No 01 and 2ALEX NDIRANGUNo ratings yet
- The F To M RatioDocument6 pagesThe F To M Ratiojokish100% (2)
- 1996Document4 pages1996Cheuk Yin NGNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-CH2402 - 2019Document4 pagesTutorial 1-CH2402 - 2019Naduni RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 SolutionDocument4 pagesProblem Set 2 SolutionKaram Jaradat100% (2)
- Secondary Treatment (Biological)Document51 pagesSecondary Treatment (Biological)Girish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamJohnNo ratings yet
- All NumericalsDocument14 pagesAll NumericalsSarthakNo ratings yet
- Assignment IV PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment IV PDFAmit KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment1-ESM 2024Document1 pageAssignment1-ESM 2024Fast TrackNo ratings yet
- ASCE PE Exam Review 3-14-17 QUESTIONSDocument5 pagesASCE PE Exam Review 3-14-17 QUESTIONSNoe H. MoralesNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filters 2Document23 pagesTrickling Filters 2Aafaque HussainNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Secondary Treatment of Wastewater PDFDocument7 pagesAerobic Secondary Treatment of Wastewater PDFdanndiamond100% (3)
- HW3Document1 pageHW3Ashna WaseemNo ratings yet
- Trickling FiltersDocument16 pagesTrickling FiltersGunnar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetArega GenetieNo ratings yet
- Enlikes FinalDocument5 pagesEnlikes FinalBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2022Document1 pageAssignment 1 2022Myguitarjam GoNo ratings yet
- Assignment II Group: MEDocument1 pageAssignment II Group: MEJenisha karkeeNo ratings yet
- PFT Practice Excercise 11Document4 pagesPFT Practice Excercise 11Biniyam haileNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheet 2Document1 pageTut Sheet 2Anandu KBNo ratings yet
- Sample WW QuestionsDocument10 pagesSample WW QuestionsKrishna Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- HW #2Document4 pagesHW #2Rohit ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module-80A: Sub: Environmental Engineering Topic: Waste Water EngineeringDocument3 pagesModule-80A: Sub: Environmental Engineering Topic: Waste Water EngineeringjhacademyhydNo ratings yet
- Work SheeetDocument3 pagesWork SheeetasregidhaguNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Biological Process Design For Wastewater Management CE-5160 Assignment No: 4Document4 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Biological Process Design For Wastewater Management CE-5160 Assignment No: 4vishuNo ratings yet
- Quality and Treatment of Waier and Wastewater: Answer Briefly (3 or 4 Sentences) or SolveDocument3 pagesQuality and Treatment of Waier and Wastewater: Answer Briefly (3 or 4 Sentences) or SolveDurgesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1567598084691Document10 pagesOrca Share Media1567598084691Kobe AcobNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment and Nanofiltration of Denim Textile Wastewater For ReuseDocument7 pagesBiological Treatment and Nanofiltration of Denim Textile Wastewater For ReuseOmaya TariqNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering Introduction To Biochemical Engineering Worksheet 2Document3 pagesHaramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering Introduction To Biochemical Engineering Worksheet 2workisaNo ratings yet
- Aplicacion de MBBR en Agua Residual de Lavanderias ComercialesDocument6 pagesAplicacion de MBBR en Agua Residual de Lavanderias ComercialesJulio Cesar Lopez UrregoNo ratings yet
- Problemario de Biorreactores Cap 14Document5 pagesProblemario de Biorreactores Cap 14Nycte Nava0% (1)
- Anarebic PondsDocument5 pagesAnarebic Pondsunitechwater6517100% (2)
- Final Exam (Year of 2021) 2Document3 pagesFinal Exam (Year of 2021) 2Sha Far97No ratings yet
- Print T TTTTTDocument17 pagesPrint T TTTTTashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Presented by Tanmay Kumar MishraDocument29 pagesPresented by Tanmay Kumar Mishraashe zinabNo ratings yet
- AssgfgDocument34 pagesAssgfgashe zinabNo ratings yet
- LLLDocument14 pagesLLLashe zinabNo ratings yet
- 13 Chapter2Document57 pages13 Chapter2ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Course OutlineDocument1 pageAddis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Course Outlineashe zinab100% (1)
- Presentation On Determination of Water Potential of The Legedadi CatchmentDocument25 pagesPresentation On Determination of Water Potential of The Legedadi Catchmentashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Eia Modified AssignmentDocument8 pagesEia Modified Assignmentashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Chapter 1Document11 pagesHydrology Chapter 1ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Air Pollution Part1Document19 pagesCh5 Air Pollution Part1ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Filtration & Softening: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)Document3 pagesAssignment 4: Filtration & Softening: Water Treatment (Ceng 5403)ashe zinab100% (1)
- ch4 Water Quality Engineering PDFDocument26 pagesch4 Water Quality Engineering PDFashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Good TeacherDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of A Good Teacherashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Filtration EgDocument4 pagesFiltration Egashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Modeling Assignment by Ashenafi ZinabieDocument48 pagesModeling Assignment by Ashenafi Zinabieashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting 2Document8 pagesDemand Forecasting 2ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Demand-Side Water Strategies and The Urban Poor: Gordon McgranahanDocument70 pagesDemand-Side Water Strategies and The Urban Poor: Gordon Mcgranahanashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Water Demand Management MeasuresDocument6 pagesPresentation On Water Demand Management Measuresashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Water: Reservoirs, Capacity and LocationDocument5 pagesDistribution of Water: Reservoirs, Capacity and Locationashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Group Project - Group1Document37 pagesGroup Project - Group1ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- MLWChapter05 PDFDocument18 pagesMLWChapter05 PDFashe zinabNo ratings yet
- 1 Description of The Study AreaDocument29 pages1 Description of The Study Areaashe zinabNo ratings yet
- MLWChapter10 PDFDocument7 pagesMLWChapter10 PDFashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Management: Executive SummaryDocument22 pagesStormwater Management: Executive Summaryashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Fieldcrest Division of Fieldcrest MillsDocument3 pagesFieldcrest Division of Fieldcrest Millsmayur2510.20088662No ratings yet
- Lib Burst GeneratedDocument37 pagesLib Burst GeneratedIgnacio Del RioNo ratings yet
- Mentor Graphics Corporation, SystemVerilog-VHDL Assistant Reference Manual, Release v2018.2Document454 pagesMentor Graphics Corporation, SystemVerilog-VHDL Assistant Reference Manual, Release v2018.2dupipiNo ratings yet
- DLL Araling Panlipunan 3 q4 w3Document3 pagesDLL Araling Panlipunan 3 q4 w3Jessica Agbayani CambaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Summative Test - Org'n & Mgt. 2nd SemesterDocument4 pages2nd Summative Test - Org'n & Mgt. 2nd SemesterDo FernanNo ratings yet
- Berna1Document4 pagesBerna1Kenneth RomanoNo ratings yet
- чек лист IELTS speaking September-December 2021Document2 pagesчек лист IELTS speaking September-December 2021Елена КуликоваNo ratings yet
- 0401110Document66 pages0401110HomeNo ratings yet
- Toeic 1Document28 pagesToeic 1Jordan Antoneo ToelleNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation in NursingDocument24 pagesTheoretical Foundation in NursingJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greece Tic-Tac-ToeDocument2 pagesAncient Greece Tic-Tac-Toeapi-277969821No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FRS651 Mac-July 2020Document2 pagesAssignment 1 FRS651 Mac-July 2020aizatNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloy - SeminarDocument15 pagesShape Memory Alloy - SeminarGeorgeMThomas33% (3)
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument20 pagesBarriers To Effective CommunicationGladys Mae GuerreroNo ratings yet
- R1 CH5 Encoder Decoder Mux DemuxDocument44 pagesR1 CH5 Encoder Decoder Mux DemuxChang BillyNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFDocument6 pagesSolutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFMichael Christian BaysauliNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Development in A Mayan Sign Language-Austin German-CILLA - IXDocument26 pagesGrammatical Development in A Mayan Sign Language-Austin German-CILLA - IXAustin Allen GermanNo ratings yet
- 3 Flowserve CatalogueDocument268 pages3 Flowserve CatalogueSudherson JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Intel (R) ME Firmware Integrated Clock Control (ICC) Tools User GuideDocument24 pagesIntel (R) ME Firmware Integrated Clock Control (ICC) Tools User Guidebox.office1003261No ratings yet
- Class 31: Outline: Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions - Possible Exam Questions Hour 2Document46 pagesClass 31: Outline: Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions - Possible Exam Questions Hour 2akirank1No ratings yet
- Ngo ProjectDocument11 pagesNgo ProjectcancelcancelNo ratings yet
- S3 4 SEMM21 22 Understanding Sports FansDocument98 pagesS3 4 SEMM21 22 Understanding Sports FansAj StylesNo ratings yet
- Bcpp6e TB Ch01Document32 pagesBcpp6e TB Ch01tnguyen194No ratings yet
- New Maths Frameworking: Matches The Revised KS3 FrameworkDocument232 pagesNew Maths Frameworking: Matches The Revised KS3 FrameworkMerihane Naguib100% (2)
- A SF Study of Field Marketing Across Europe P IDocument17 pagesA SF Study of Field Marketing Across Europe P IMasud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions: 8.1. Review of Bode PlotsDocument8 pagesChapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions: 8.1. Review of Bode PlotsjaronjerNo ratings yet
- Iteh Standard Preview (Standards - Iteh.ai) : SIST EN 837-1:1997 Slovenski StandardDocument13 pagesIteh Standard Preview (Standards - Iteh.ai) : SIST EN 837-1:1997 Slovenski StandardJAMSHIL.T JjNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Failon Ngayon: Kalamidad Sa Pabahay Failon Ngayon: Barangay Health StationsDocument4 pagesReaction Paper Failon Ngayon: Kalamidad Sa Pabahay Failon Ngayon: Barangay Health StationsRomeo Chavez BardajeNo ratings yet
- SwatiDocument23 pagesSwatiShashankNo ratings yet
- Bridge Embankment FailuresDocument13 pagesBridge Embankment Failuresirmreza68No ratings yet