Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technological Institute of The Philippines Quezon City Civil Engineering Department Ce407Earthquake Engineering Prelim Examination
Uploaded by
GerardoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technological Institute of The Philippines Quezon City Civil Engineering Department Ce407Earthquake Engineering Prelim Examination
Uploaded by
GerardoCopyright:
Available Formats
Technological Institute of the Philippines
Quezon City
Civil Engineering Department
CE407EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING
PRELIM EXAMINATION
(09January 2018)
NAME: _________________________________________________SECTION: ____________
INSTRUCTIONS: Read the question carefully. Discuss/calculate in detail and clearly the
following questions mentioned below. Use a clear letter size bond paper and do not write at the
back of your answer sheet. Any personal electronic devices (i.e. Mobile phone, Laptop
computers, etc.) are considered cheating devices and are therefore not allowed to be with the
examinees during the examination. Anyone caught with the above mentioned will his or her
examination results be given a transmuted grade below fifty (50). Good Luck!
Question:
1. Defines the type of seismic sources in the Philippines?
2. Defines the Soil Profile Types in the Philippines?
3. How many seismic zones in the Philippines? What are seismic zone factor?
4. Discuss the seismic coefficients for Ca & Cv as per seismic zone category in the
Philippines?
5. Distinguish the static force design base shear equation in the Philippines?
Mark-up with circle the correct answer
1. With which of the following is an increase in earthquake magnitude correlated?
A. An increase in acceleration
B. An increase in duration
C. A decrease in acceleration and duration
D. Magnitude, accelerated, and duration are not necessarily correlated
2. Which of the following characteristics influence the effect of an earthquake?
A. Frequency
B. Duration
C. Ground acceleration
D. All of the above
3. Liquefaction is best described as
A. A sudden drop in the shear strength of a soil
B. A decrease in pore water pressure of a soil
C. An increase in the bearing capacity of a soil
D. An increase in the effective stress of a soil
4. When liquefaction occurs, which of the following soil conditions are likely to exist?
A. The soils are made of saturated
B. The soils have zero shear strength and the soils are made of cohesion particles
C. The soils are made of cohesion particles
D. The soils have zero shear strength and the soils are made of saturated
5. Which of the following sites is most likely to amplify ground motion?
A. a dense soil site
B. a rock site
C. a stiff clay site
D. a soft clay site
6. Spectral velocity is best described as
A. The velocity of seismic energy
B. The velocity of a secondary wave
C. The velocity of a structure
D. The velocity of a structure relative to the ground
7. For a single-degree-of freedom system, the natural period, T1is
A. The inverse of the natural frequency
B. Equivalent to the linear natural frequency
C. Expressed in Hz
D. The inverse of the natural frequency and Expressed in Hz
8. What is the spectral acceleration of a single-degree-of-freedom system?
A. It is the minimum acceleration experienced by the system in response to a
perturbation.
B. It id the average acceleration experienced by the system in response to a
perturbation.
C. It is the maximum acceleration experience by the system in response to a
perturbation.
D. It is the absolute acceleration experienced by the system in response to a
perturbation.
9. For the following harmonic oscillator, how is the stiffness best described?
A. As the force acting on the ideal linear spring
B. As the force deflecting the spring a distance of 1 unit
C. As the magnitude of the spring deflection
D. As the reciprocal of deflection
10. When does the natural building period coincide with the earthquake period?
A. When the natural frequency is at its maximum
B. When the acceleration is at its maximum
C. When the displacement is at its maximum
D. All of the above
11. The period of a structure is correlated with the
A. Mass of the structure
B. Stiffness of the structure
C. Mass of the structure and Stiffness of the structure
D. All of the above are true
12. What is the maximum considered earthquake motion at a site?
A. It is the motion intensity with a 10% probability of being exceeded in a 100-year
time period.
B. It is based on presently available data and knowledge of the site.
C. It is the maximum level of earthquake ground motion expected at the site.
D. All of the above are true
13. Consider the natural period, T, and acceleration, a, of a single-degree-of-freedom system.
When the mass, m, of the system increase, how are T and a affected?
A. T increases and a increases
B. T increases and a decreases
C. T decreases and a increases
D. T decreases and a decreases
14. Where K is the stiffness and ∆ is the deflection, which of the following relationships best
describes the rigidity, R?
A. 1/K B. K∆ C. ∆ D. 1/∆
15. A mass hangs on two ideal springs as shown. What is the total composite spring constant
for the system?
A. K1 + K2
B. K1K2
C. 1/K1 + 1/K2
𝐾1 𝐾2
D.
𝐾1 +𝐾2
16. Each of the following pendulums (equal in mass) are hanging on an
ideal spring. The periods of vibration for the pendulums are 1.73 sec and 3.0 sec,
respectively. Assume the pendulums are on frictionless
pivots. What is the stiffness of the second pendulum’s
spring?
A. 1/3 K1
B. 1/2K1
C. K1
D. 1.33K1
17. Each of the following columns supports a block of identical mass, m. The columns are fixed
at the bottom and free at the top. The height of the second column is twice the height of the
first column. The modulus of elasticity, E, and moment of
inertia, I, for both columns are the same. The system has
natural periods of vibration of T1 and T2, respective. Neglecting
the weight of the columns, what is the natural period of
vibration for the second system?
A. 0.5T1
B. 2T1
C. 3T1
D. 4T1
18. A force is acting at the top of a building
frame as shown. The supporting columns
are equal height and are fixed at the base.
The modulus of elasticity, E, is the same
for each column. Assuming the top place is
1 1
rigid and 𝐼1 = 3 𝐼2 = 6 𝐼3 , what is the shear
distributed to the first column?
A. 1/10 F
B. 1/5 F
C. 2/3 F
D. 1/3 F
19. How is the term damping described?
A. The ratio of one cycle’s amplitude to the subsequent cycle
B. The dissipation of energy from an oscillating system
C. The ratio of one cycle’s amplitude to the subsequent cycle and the dissipation of
energy from an oscillating system
D. The dynamic magnification factor and the dissipation of energy from an
oscillating system
20. How is the term flexibility define?
A. Stiffness
B. The reciprocal of stiffness
C. Rigidity
D. Static deflection
21. Which of the following terms describe the location of an earthquake? Epicenter; Focal
depth; Dip angle
A. Epicenter
B. Focal depth
C. Epicenter & Focal depth
D. Epicenter &Dip angle
22. There is a footwall facing a hanging wall prior to an earthquake. The hanging wall moves
up during the earthquake. Which type of fault occurred?
A. Strike-dip fault
B. reverse fault
C. normal fault
D. oblique fault
23. The process where an oceanic plate slides beneath a continental plate is known
A. Lithosphere
B. Mantle
C. Subduction
D. Strike-slip
24. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Compression, shear, and surface waves are seismic waves
B. S-waves are at right angles to the compression waves
C. S-waves can be expressed as horizontal and vertical components
D. None of the above are incorrect
25. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. S-waves travel more slowly than P-waves
B. S-waves transmit more energy than P-waves
C. S-waves cause less damage to structures than P=waves
D. All of the above are incorrect.
26. Which of the following activities occurs as seismic sea wave approach land?
A. Waves velocity increases
B. Waves height decreases
C. Both wave velocity and height increase.
D. Wave velocity decreases and wave height increases.
27. How are seismic waves generated?
A. by volcanic eruptions & by deep artificially induced explosions
B. by deep artificially induced explosions & by sudden dislocations within the earth’s
crust
C. by volcanic eruptions & by sudden dislocations within the earth’s crust
D. by volcanic eruptions; by deep artificially induced explosions &.by sudden
dislocations within the earth’s crust
28. What does a seismometer measure?
A. components of ground motion
B. reference points
C. attenuation
D. actual displacement
29. What is a tsunami?
A. a seismic sea waves
B. a tidal wave
C. a surface-water wave
D. all of the above
30. Which of the following statements are correct?
A. The Richter scale measures earthquake strength & The magnitude of an
earthquake can be determined from the logarithm of the recorded amplitude.
B. The Richter scale measures earthquake strength & The magnitude of an
earthquake does not depend on the length of the fault slip.
C. The magnitude of an earthquake can be determined from the logarithm of the
recorded amplitude & The magnitude of an earthquake does not depend on the
length of the fault slip.
D. The Richter scale measures earthquake strength; The magnitude of an
earthquake can be determined from the logarithm of the recorded amplitude &
The magnitude of an earthquake does not depend on the length of the fault slip
31. What does the modified Mercalli Intensity scale measure?
A. Magnitude & Apparent severity at particular location.
B. Apparent severity at particular location &Intensity
C. Magnitude &Intensity
D. Magnitude, Apparent severity at particular location & Intensity
32. How many levels of intensity are associated with the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale?
A. 8 B. 10 C. 12 D. 14
33. What is the definition of the term attenuation?
A. ground motion
B. a decrease in seismic energy
C. a geologic formation
D. the orientation of a fault
34. Attenuation is not influenced by
A. Path line and length
B. Geologic formation
C. Focal depth
D. Earthquake magnitude.
35. Which of the following periods share the same definition?
A. The period of an earthquake & the period of a site
B. The period of an earthquake & the period of a building
C. the period of a site & the period of a building
D. none of the above.
36. Which of the following characteristic influence the amount of structural damage caused by
an earthquake?
A. Peak ground acceleration and duration of motion & soil condition at the site and
period of the site
B. Distance between the epicenter and the structure & natural period and damping
of the structure
C. Peak ground acceleration and duration of motion, soil condition at the site and
period of the site & distance between the epicenter and the structure
D. All of the above.
37. When does resonance occur?
A. When the building period coincides with the earthquake period & when the
earthquake period coincides with the site period
B. When the building period coincides with the earthquake period & when the site
period coincides with the building period
C. when the earthquake period coincides with the site period &when the site period
coincides with the building period
D. When the building period coincides with the earthquake period, when the
earthquake period coincides with the site period & when the site period coincides
with the building period
38. Permanent, heavy air-condition equipment is installed on top of a building. How will affect
the fundamental period of the building?
A. It will increase
B. It will decrease
C. It will remain the same
D. It will increase the acceleration
39. How are seismic waves generated?
A. by volcanic eruptions & by deep artificially induced explosions
B. by deep artificially induced explosions & by sudden dislocations within the earth’s
crust
C. by volcanic eruptions & by sudden dislocations within the earth’s crust
D. by volcanic eruptions; by deep artificially induced explosions &.by sudden
dislocations within the earth’s crust
40. What does a seismometer measure?
A. components of ground motion
B. reference points
C. attenuation
D. actual displacement
PROBLEMS:
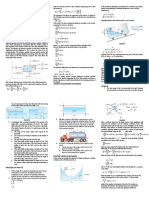
1. Determine the fundamental period of vibration of the two-story frame, which is located in an
area with a value forSD1 exceeding 0.4. The force system shown in the following illustration
may be used; the effective seismic weight at each level and the total stiffness of each story
are indicated.
Using NSCP or ASCE/SEI7 𝑇 = 2𝜋√∑ 𝑤𝑖 𝛿𝑖2 /𝑔 ∑ 𝑓𝑖 𝛿𝑖 = 𝑜. 32√∑ 𝑤𝑖 𝛿𝑖2 /𝑔 ∑ 𝑓𝑖 𝛿𝑖
The fundamental period, in accordance with NSCP or ASCE/SEI7 Sec. 12.8.2, is limited to
𝑇 = 1.4𝑇𝑎
F
i
g
u
r
e
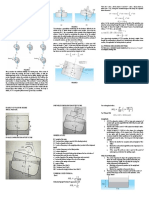
2. The two-story, reinforced concrete, special moment resisting frame is used for a residential
building. Calculate the seismic response coefficient by using the alternative value for the
fundamental period shown.
𝑆𝐷𝑆 = 1.0𝑔 ; 𝑆𝐷1 = 0.7𝑔 ; 𝐼𝑒 = 1.0; 𝑇 = 0.479 𝑠𝑒𝑐 ; 𝑇𝑠 = 𝑜. 70𝑔; 𝑅 = 8; ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 = 15 𝑓𝑡.
You might also like
- 2023 Diagnostic Test For Grade 8 1Document31 pages2023 Diagnostic Test For Grade 8 1Annica Mae De LeonシNo ratings yet
- Edited STM 003 ReviewerDocument10 pagesEdited STM 003 ReviewerGian PelenioNo ratings yet
- ESAS Objectives 2Document15 pagesESAS Objectives 2Jayven VillamaterNo ratings yet
- S8 Q2 TQDocument8 pagesS8 Q2 TQRaniel LacuarinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 1 Earthquake and Fault Summative TestDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Module 1 Earthquake and Fault Summative TestJomar Rafil0% (1)
- PHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDDocument19 pagesPHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDhs6077074No ratings yet
- Grade 8Document4 pagesGrade 8Rhisia NoelNo ratings yet
- S8 - 2ND Periodical ExamDocument8 pagesS8 - 2ND Periodical ExamDonna T. Duaso100% (2)
- Grade 8 PretestDocument3 pagesGrade 8 PretestAvrìl Labrador SaquinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Foundations of Earth Science 7th 0321811143 9780321811141Document25 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Earth Science 7th 0321811143 9780321811141JoshuaGuerreropxmqg100% (30)
- Science 8 Key Answer 2ndDocument11 pagesScience 8 Key Answer 2ndAljeanNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Pretest2023 24Document4 pagesPretest2023 24arlene aliporo100% (1)
- Science8 Diagnostic 1 60Document5 pagesScience8 Diagnostic 1 60Annica Mae De LeonシNo ratings yet
- Dungtse Cluster Trial Examination 2018 Paper I PhysicsDocument17 pagesDungtse Cluster Trial Examination 2018 Paper I PhysicsRigzean Thinley Lhendrup100% (1)
- Grade 8Document3 pagesGrade 8JENY VEV GAYOMANo ratings yet
- Science G8 EA Test QuestionsDocument7 pagesScience G8 EA Test QuestionsMarlene Tubieros - InducilNo ratings yet
- Midterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111Document7 pagesMidterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111mhadd071100% (2)
- S8 - Q2 - TQ FinalDocument6 pagesS8 - Q2 - TQ FinalRaniel Lacuarin100% (1)
- John Vincent T. Villamor First Prelim in Conceptual PhysicsDocument5 pagesJohn Vincent T. Villamor First Prelim in Conceptual PhysicsJVVillamor100% (1)
- Phys 2A Sample FinalDocument14 pagesPhys 2A Sample FinalMichelleNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 8Document107 pagesReviewer 8junatasnadine1No ratings yet
- Quiz Bee-Grade8Document8 pagesQuiz Bee-Grade8Ma. Lorena Machitar100% (1)
- +1 Model 2011Document4 pages+1 Model 2011Xavier KattukulamNo ratings yet
- Physics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFDocument9 pagesPhysics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFsuan_143100% (6)
- SCIENCE Diagnostic 2020 - Gr10Document5 pagesSCIENCE Diagnostic 2020 - Gr10migaramNo ratings yet
- NDA Physics QuestionsDocument30 pagesNDA Physics QuestionsJerry JerryNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Periodical TestDocument4 pages2nd Grading Periodical TestEvelyn PabuaNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledHazel FrondaNo ratings yet
- Question 4 of 4Document10 pagesQuestion 4 of 4Anton_Young_1962No ratings yet
- AKU EB - Physics - XI - Paper I - 2014 - MayDocument8 pagesAKU EB - Physics - XI - Paper I - 2014 - MayEman VirkNo ratings yet
- Earth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test BankDocument38 pagesEarth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test Bankhaodienb6qj100% (26)
- Periodic Test Third Grading ScienceDocument4 pagesPeriodic Test Third Grading ScienceJaylordPalattaoNo ratings yet
- Nat Like Test in SciencDocument2 pagesNat Like Test in SciencIrene BaquiranNo ratings yet
- DP2 SL QPDocument19 pagesDP2 SL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam Science 8Document5 pages1st Quarter Exam Science 8Marvin Obra100% (1)
- 8th Grade Science Exam ReviewDocument5 pages8th Grade Science Exam ReviewMich100% (1)
- Phys 1011 Final SAMPLEDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 Final SAMPLEJonah the mixerNo ratings yet
- Summative Test No. 5Document3 pagesSummative Test No. 5Stephanie BorjaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument10 pagesQuestionsPatricia BugayongNo ratings yet
- Licensure Examination For Teachers Practice TestDocument14 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachers Practice Testapi-286466377No ratings yet
- Science 8Document7 pagesScience 8RodaMaeNatividadNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTIC TEST For Grade 10 ScienceDocument7 pagesDIAGNOSTIC TEST For Grade 10 ScienceJOEL MONTERDENo ratings yet
- S10 Diagnostic Answer KeyDocument15 pagesS10 Diagnostic Answer KeyNanette MoradoNo ratings yet
- CANARVACANAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE EXAMDocument5 pagesCANARVACANAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE EXAMMike Guerzon100% (1)
- Class 11C - Physics Paper 1Document10 pagesClass 11C - Physics Paper 1St. Andrew's High School KarachiNo ratings yet
- Second Grading Summative TestDocument6 pagesSecond Grading Summative TestYeyeth Jabaybay TabolongNo ratings yet
- Dat Sci10Document7 pagesDat Sci10hendrixNo ratings yet
- Q2-Science 8Document6 pagesQ2-Science 8Reynalyn CalwitNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document4 pagesScience 10Kim Coleen CamasoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Examination in Sci 8 - 2023-2024Document4 pages1ST Quarter Examination in Sci 8 - 2023-2024Jonathan donanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics SGDocument3 pagesAP Physics SGAron WamNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR EXAm SCI 8Document6 pages2nd QTR EXAm SCI 8Benson CornejaNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice 2013 07 11 PDFDocument4 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice 2013 07 11 PDFYuusuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Science 8Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test Science 8Santisas Zai96% (24)
- Engineering exam questions and answersDocument6 pagesEngineering exam questions and answersRogelio Jr. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- g11 Physics Term IIDocument5 pagesg11 Physics Term IIsanthiyajosphinarrsNo ratings yet
- Open Open: Storage/Ee RM Ee RMDocument1 pageOpen Open: Storage/Ee RM Ee RMGerardoNo ratings yet
- Forces On Curved SurfacesDocument1 pageForces On Curved SurfacesGerardoNo ratings yet
- Fluids in static equilibrium with reference framesDocument4 pagesFluids in static equilibrium with reference framesGerardoNo ratings yet
- Handout For Stability of Floating BodiesDocument2 pagesHandout For Stability of Floating BodiesGerardoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech. 3Document2 pagesFluid Mech. 3GerardoNo ratings yet
- Handout For Stability of Floating BodiesDocument2 pagesHandout For Stability of Floating BodiesGerardoNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS - A Science That Deals With The Study of Fluids at Rest or inDocument1 pageFLUID MECHANICS - A Science That Deals With The Study of Fluids at Rest or inGerardoNo ratings yet
- FLD-FNDMNTLS-FLD-FLWDocument3 pagesFLD-FNDMNTLS-FLD-FLWGerardoNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS - A Science That Deals With The Study of Fluids at Rest or inDocument1 pageFLUID MECHANICS - A Science That Deals With The Study of Fluids at Rest or inGerardoNo ratings yet
- Gas On A Body or Surface, With The Force Acting at Right Angles To The Surface Uniformly in All DirectionsDocument4 pagesGas On A Body or Surface, With The Force Acting at Right Angles To The Surface Uniformly in All DirectionsGerardoNo ratings yet
- Handout For Stability of Floating Bodies PresentationDocument3 pagesHandout For Stability of Floating Bodies PresentationGerardoNo ratings yet
- Handout For Stability of Floating Bodies PresentationDocument3 pagesHandout For Stability of Floating Bodies PresentationGerardoNo ratings yet
- Example: Dead Load: 5 Kpa Live Load: 2 KpaDocument3 pagesExample: Dead Load: 5 Kpa Live Load: 2 KpaGerardoNo ratings yet
- Example: Dead Load: 5 Kpa Live Load: 2 KpaDocument3 pagesExample: Dead Load: 5 Kpa Live Load: 2 KpaGerardoNo ratings yet
- Soil EffectsDocument1 pageSoil EffectsGerardoNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument2 pagesDamsGerardoNo ratings yet
- Joh1 (1) .PdfaaDocument10 pagesJoh1 (1) .PdfaagreekseptuagintNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument94 pagesEARTHQUAKEGerardo100% (1)
- Board ExamDocument1 pageBoard ExamGerardoNo ratings yet
- Piano PatternDocument2 pagesPiano PatternRonald Kharismawan100% (5)
- Mega Group StudyDocument1 pageMega Group StudyGerardoNo ratings yet
- Handout PDFDocument65 pagesHandout PDFmustakim79No ratings yet
- Dota BuildlistDocument81 pagesDota BuildlistMarcus Vinicius LovatoNo ratings yet
- Consolidation ExampleDocument1 pageConsolidation ExampleGerardoNo ratings yet
- Timber ProblemDocument1 pageTimber ProblemGerardoNo ratings yet
- Fade HairstylesDocument1 pageFade HairstylesGerardoNo ratings yet
- Max Shear ValuesDocument1 pageMax Shear ValuesGerardoNo ratings yet
- Face ShapesDocument1 pageFace ShapesGerardoNo ratings yet
- HairstylingDocument1 pageHairstylingGerardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 Static ElectricityDocument54 pagesChapter - 17 Static ElectricityNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Geography Hon.Document18 pagesGeography Hon.Bijay Krishna DasNo ratings yet
- Physics CapsuleDocument33 pagesPhysics CapsulepranodanNo ratings yet
- Wind TB GeneratorDocument26 pagesWind TB GeneratorbinhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: IntroductionDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology: IntroductionLyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pollution in Lebanon Grade 6Document2 pagesPollution in Lebanon Grade 6Amir Mershad100% (1)
- Bio ScrubberDocument10 pagesBio ScrubberSata AjjamNo ratings yet
- Wood Wide WebDocument6 pagesWood Wide WebGurleen Hora100% (1)
- Statements of the Second Law ExplainedDocument45 pagesStatements of the Second Law ExplainedSindhu KemburuNo ratings yet
- Bremsstrahlung X-RayDocument2 pagesBremsstrahlung X-RayYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer From Fin SurfacesDocument25 pagesHeat Transfer From Fin SurfacesAizaz HabibNo ratings yet
- The Planets of The Solar System With All Their DescriptionsDocument1 pageThe Planets of The Solar System With All Their DescriptionsMiranda SosaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsabdulhafizmy87100% (1)
- Thermo ChemistryDocument27 pagesThermo ChemistryhannahNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Air Track: Name: Akshat Date:12/15/20Document9 pagesStudent Exploration: Air Track: Name: Akshat Date:12/15/20Akshat Pant100% (8)
- Study On Solar Power PlantDocument26 pagesStudy On Solar Power PlantPrakash MarathiNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationtransDocument51 pagesSolar RadiationtransmrizqynugrahaNo ratings yet
- PMC - Module No 11Document17 pagesPMC - Module No 11TALHA ZAFAR72% (50)
- CH-HW-PH-115 MWAC BARAS SOLAR POWER PLANT CHANNEL LINING SOLUTION-Rev2-Jun22-ENDocument2 pagesCH-HW-PH-115 MWAC BARAS SOLAR POWER PLANT CHANNEL LINING SOLUTION-Rev2-Jun22-ENAmihan SantosNo ratings yet
- Project SynopsisDocument6 pagesProject Synopsislive userNo ratings yet
- FMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesFMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsBhavani Chandra Unique100% (1)
- Photoelectric Effect NotesDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Notesalex ewnuNo ratings yet
- Science Process Skills Examination 1ncv0kyDocument9 pagesScience Process Skills Examination 1ncv0kyInsar Damopolii TempoesekarangNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Chemical Fertilizers On Our Environment and EcosystemDocument19 pagesThe Impact of Chemical Fertilizers On Our Environment and EcosystemDiana DainaNo ratings yet
- NCSE 2015 Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesNCSE 2015 Integrated ScienceMath Class90% (10)
- 00 A07 - SiDocument2 pages00 A07 - SiAndrei Alexandru TulbureanuNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Fin Equations OverviewDocument12 pagesHeat Transfer Fin Equations OverviewRajeev RajeevNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Form 5 2020 BMDocument217 pagesModul Fizik Form 5 2020 BMPak TehNo ratings yet
- Relative Density of Gases Lab ReportDocument10 pagesRelative Density of Gases Lab ReportAnusha AnuNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety 5Document22 pagesFire Safety 5Lino CornejaNo ratings yet