Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan For Hypertension
Uploaded by
Franco Razon100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagessample NCP for HPN
Original Title
Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsample NCP for HPN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertension
Uploaded by
Franco Razonsample NCP for HPN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
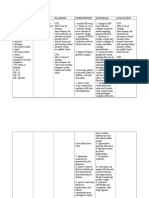
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR HYPERTENSION
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Decreased STG: 1.monitor BP every1-2 1. changes in BP may indicates STG:
“madalas ako Cardiac Output After 6 hrs of hours, or every5 changes in patient status After 6 hrs of nursing
mahilo”, as verbalized r/t malignant nursing minutes during active requiring prompt attention. interventions, the client had
by the patient. hypertension as interventions, the titration of vasoactive no elevation in blood
manifested by client will have no drugs. pressure above normal limits
Objective: decreased stroke elevation in blood 2. monitor ECG for 2. decrease in cardiac output and will maintain blood
>lethargic volume. pressure above dysrhythmias, may result in changes in pressure within acceptable
>decreased cardiac normal limits and conduction defects and cardiac perfusion causing limits.
output will maintain blood for heart rate. dysrhythmias. Goal was met.
>decreased stroke pressure within
volume acceptable limits. 3. suggest frequent 3. it may decrease peripheral LTG:
>increased peripheral position changes. venous pooling that may be After 5 days of nursing
vascular resistance LTG: After 5 days potentiated by vasodilators interventions, the client
>VS taken as follows: of nursing and prolonged sitting or maintained an adequate
T: 37.2 interventions, the standing. cardiac output and cardiac
PR: 83 client will maintain 4.encourage patient to 4. caffeine is a cardiac index.
RR: 18 adequate cardiac decrease intake of stimulant and may adversely Goal was met.
BP: 180/100 output and cardiac caffeine, cola and affect cardiac function.
index. chocolates.
5. observe skin color, 5. peripheral vasoconstriction
temperature, capillary may result in pale, cool,
refill time and clammy skin, with prolonged
diaphoresis. capillary refill time due to
cardiac dysfunction and
decreased cardiac output.
6.auscultate heart 6. hypertensive patients often
tones. have S4 gallops caused by
atrial hypertrophy.
7. administer 7. to promote wellness.
medicines as
prescribed by the
physician.
8. instruct client 8. restrictions can assist with
&family on fluid and decrease in fluid retention and
diet requirements and hypertension, thereby
restrictions of sodium. improving cardiac output.
9. instruct client and 9. promotes knowledge and
family on medications, compliance with drug regimen
side effects,
contraindications and
signs to report.
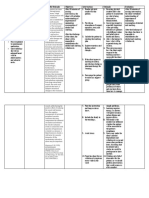
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Ineffective Tissue STG: After 8 hrs 1. monitor VS at least 1.to monitor baseline STG: After 8 hrs of
“ Laging sumasakit ang Perfusion: of nursing q 1-2 hrs and prn. data. nursing interventions,
aking ulo at parang Cardiopulmonary, interventions, 2. encourage patient blood pressure
nanlalabo ang aking Gastrointestinal blood pressure to decrease intake of 2. caffeine is a cardiac maintained within set
paningin”, as verbalized by and Peripheral r/t will be within caffeine, cola and stimulant and may parameters for the
the patient. hypertension and set parameters chocolates. adversely affect cardiac client.
decreased for the client. function. Goal was met.
Objective: cardiac output as LTG: After 6 3. administer LTG: After 6 days of
Tachycardia manifested by days of nursing vasoactive drugs and 3. these drugs have rapid nursing interventions,
Shortness of breath blurred vision interventions, titrate as ordered to action and may decrease the client had an
Rales and increased the client will maintain pressures at the blood pressure too adequate tissue
Restlessness blood pressure. have an set parameters for rapidly, resulting in perfusion to his body
Cool, clammy skin adequate tissue patient. complications. systems.
Optic disc perfusion to his 4. observe for Goal was met.
papilledema body systems. complaints of blurred 4. may indicate cyanide
vision, tinnitus or toxicity from increasing
confusion. intracranial pressure.
5. monitor I&O
status. 5. I&O will give an
indication of fluid balance
or imbalance, thus
allowing for changes in
treatment regimen when
required.
6. monitor for sudden 6. may indicate dissecting
onset of chest pain. aortic aneurysm.
7. monitor ECG for 7. decreased perfusion
changes in rate, may result in dysrhythmias
rhythm, dysrhythmias caused by decrease in
and conduction oxygen.
defects.
8. observe 8.Bedrest promotes
extremities for venous statis which can
swelling, erythema, increase the risk of
tenderness and pain. thromboembolus
Observe for formation. If treatment is
decreased peripheral too rapid and aggressive in
pulses, pallor, decreasing the blood
coldness and pressure, tissue perfusion
cyanosis. will be impaired and
ischemia can result.
9. instruct client in
signs/symptoms to 9. promotes knowledge
report to physician and compliance with
such as headache treatment. Promotes
upon rising, increased prompt detection and
blood pressure, chest facilitates prompt
pain, shortness of intervention.
breath, increased
heart rate, visual
changes, edema,
muscle cramps and
nausea and vomiting.
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Prepared By: Maria Theresa S. TalplacidoDocument115 pagesPrepared By: Maria Theresa S. TalplacidoFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DISORDERSDocument9 pagesPsychiatric DISORDERSNilay Bhatt100% (1)
- Divine Word College of Legazpi College of Nursing: Franco L. Razon, Man, RNDocument91 pagesDivine Word College of Legazpi College of Nursing: Franco L. Razon, Man, RNFranco Razon100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical DrugsDocument92 pagesPharmaceutical DrugsFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies and Methodologies For Teaching and LearningDocument39 pagesTeaching Strategies and Methodologies For Teaching and LearningFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- 36clinical Neuropsychology A Pocket Handbook For Assessment, 3 Edition PDFDocument768 pages36clinical Neuropsychology A Pocket Handbook For Assessment, 3 Edition PDFEstebanGira100% (2)
- Blood Disorders Seminar No 7Document142 pagesBlood Disorders Seminar No 7Hysum Mushtaq100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertensionmariejo89% (82)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideDocument137 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DM Type 2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan DM Type 2Jay V. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anemia N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageAnemia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Managing Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesManaging Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac Outputanon_9189425950% (2)
- Drugs - Icu (Group)Document7 pagesDrugs - Icu (Group)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Examples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepDocument24 pagesExamples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepJatro100% (1)
- Acute Kidney Injury: Causes, Stages, and ManagementDocument62 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Causes, Stages, and ManagementApidha KartinasariNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocument2 pagesKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 pagesETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Document7 pagesNursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Rosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (3)
- Body WeaknessDocument1 pageBody Weaknessnymphaaugustus100% (3)
- Nasal PolypsDocument43 pagesNasal PolypsManasa anonymous100% (2)
- CHED Memorandum Order # 5 (2008)Document121 pagesCHED Memorandum Order # 5 (2008)wiredpsyche100% (69)
- Managing Arteriosclerosis with Nursing CareDocument6 pagesManaging Arteriosclerosis with Nursing CareANCHAL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Pathology of Hemodynamic Disorders 1 and 2 Practice Questions-1Document26 pagesPathology of Hemodynamic Disorders 1 and 2 Practice Questions-1JCNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- School Health ProgramDocument27 pagesSchool Health ProgramFranco Razon100% (1)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanAsylla PajijiNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 pagesMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP HPNDocument5 pagesNCP HPNGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- NCP Heart BlockDocument3 pagesNCP Heart BlockEköw Santiago Javier33% (3)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 pagesCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- Managing Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesDocument1 pageManaging Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesChristian Daayata0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: Independentzebzeb STEMANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionJessy MalloNo ratings yet
- Nursing As A ProfessionDocument38 pagesNursing As A ProfessionFranco Razon100% (1)
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoNo ratings yet
- NCP Hypertension 2Document3 pagesNCP Hypertension 2Roseben Somido50% (2)
- Nursing Leadership and Management StaffingDocument66 pagesNursing Leadership and Management StaffingJay Soriano100% (1)
- Assessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver DiseaseDocument1 pageAssessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver Diseasehaniehaehae100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainDocument3 pagesNursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care Plangeng gengNo ratings yet
- 5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for HypertensionDocument7 pages5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for Hypertensionmelerine16No ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension and Knee PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension and Knee PainEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDrug Study Dopamine HCLA.No ratings yet
- NCP For HeadacheDocument1 pageNCP For HeadacheJohn MajanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJamie Haravata0% (1)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocument3 pagesNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNikai PabayoNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Cva NCP AnxietyDocument1 pageCva NCP AnxietyQueenElsaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Document2 pagesNcp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce67% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionRodel Yacas0% (1)
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation (AEPPIREDocument11 pagesAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation (AEPPIREGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageRationale EvaluationAshraf DalumaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonathan LiscanoNo ratings yet
- DirectingDocument111 pagesDirectingFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Types of LearnersDocument35 pagesTypes of LearnersFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- College: Program: Course Code: Credits: Class Days: Room: InstructorDocument9 pagesCollege: Program: Course Code: Credits: Class Days: Room: InstructorFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Personal Health-Emotional MentalDocument44 pagesPersonal Health-Emotional MentalFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Pricelist AppleDocument2 pagesPricelist ApplePeetsaNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument15 pagesMood DisordersFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Your Health Triangle AssessmentDocument48 pagesYour Health Triangle AssessmentFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- An Orientation: Franco L. Razon, RN, Man Clinical Intructor DWCL College of NursingDocument17 pagesAn Orientation: Franco L. Razon, RN, Man Clinical Intructor DWCL College of NursingFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process: Franco L. Razon, Man, RN Divine Word College of Legazpi College of NursingDocument72 pagesNursing Process: Franco L. Razon, Man, RN Divine Word College of Legazpi College of NursingFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid2Document24 pagesBasic First Aid2Franco RazonNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument15 pagesMood DisordersFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- 11th National Congress of NSTP Educators and ImplementersDocument41 pages11th National Congress of NSTP Educators and ImplementersFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CHP 1Document93 pagesAnatomy CHP 1Franco RazonNo ratings yet
- Franco L. Razon, RN, Man Divine Word College of LegazpiDocument42 pagesFranco L. Razon, RN, Man Divine Word College of LegazpiFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Cushings Syndrome and Addison Disease - BPTDocument45 pagesCushings Syndrome and Addison Disease - BPTAanchal GuptaNo ratings yet
- DementiaDocument1 pageDementiaidno1008No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The External GenitaliaDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The External GenitaliaNicole Xyza Junsay100% (1)
- Fever Without Source: Dr. Tiroumourougane Serane. VDocument29 pagesFever Without Source: Dr. Tiroumourougane Serane. VTirouNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot PDFDocument6 pagesDiabetic Foot PDFprisillia monicaNo ratings yet
- GERD Classification, Diagnosis and Management ReviewedDocument8 pagesGERD Classification, Diagnosis and Management Reviewedakhil fahri atalahNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Document2 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Prince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Nephrology Syllabus FinalDocument13 pagesPaediatric Nephrology Syllabus FinalClever BarbieNo ratings yet
- CA - Adult Health Nursing PDFDocument55 pagesCA - Adult Health Nursing PDFMarvin Heramis RyanNo ratings yet
- Acetylsalicilic Acid 250mg + Paracetamol 250mg + Caffeine 65mg (Acamol Focus, Exidol, Exedrin, Paramol Target)Document6 pagesAcetylsalicilic Acid 250mg + Paracetamol 250mg + Caffeine 65mg (Acamol Focus, Exidol, Exedrin, Paramol Target)asdwasdNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument6 pagesLumbar PunctureMitkoNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduDocument35 pagesUterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduAdu DolapoNo ratings yet
- Rare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceDocument2 pagesRare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceCharticha PatrisindryNo ratings yet
- 0-0010 PDFDocument11 pages0-0010 PDFAnonymous syRbQm6No ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage Causes and TypesDocument25 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage Causes and TypesdeangamaNo ratings yet
- Microwave DiathermyDocument19 pagesMicrowave DiathermyDale P. PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic Agents and Hematinics: PharmacologyDocument9 pagesHematopoietic Agents and Hematinics: PharmacologyAbi SulitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34:: Granuloma Annulare::: Julie S. PrendivilleDocument10 pagesChapter 34:: Granuloma Annulare::: Julie S. PrendivilleDavid HartantoNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers - UpToDateDocument40 pagesManagement of Diabetic Foot Ulcers - UpToDatePriscillaNo ratings yet
- 65 Stenoza GDDDocument7 pages65 Stenoza GDDGabriela MilitaruNo ratings yet
- Images,: Neurological Aspect Auditory HallucinationsDocument6 pagesImages,: Neurological Aspect Auditory HallucinationsSoulyogaNo ratings yet