Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report #2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Experimentation MDE Department 4 Year
Uploaded by
OmaroMohsenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report #2: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Experimentation MDE Department 4 Year
Uploaded by
OmaroMohsenCopyright:
Available Formats
Cairo University Experimentation MDE Department
Faculty of 4th year
Engineering
Report #2
Submitted By Omar Mohsen Abd Submission Date:
El Azim 20/11/2018
Checked By Dr. Shaltout
Abstract
This report is a result from the lab of pneumatic lab experiments. Firstly the components
were introduced to our group and after discussing about the components there were
applied pneumatic circuits that were required to know how it works and the group was
aided by Doctor Mohamed Shaltout. So this report requirement to write about components,
circuits and applications of the pneumatic components in Industry.
Contents
Abstract ................................................................................................................................................... 2
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 4
Main Components................................................................................................................................... 5
Air Service Component ....................................................................................................................... 5
Directional Control Valve .................................................................................................................... 5
Types: .............................................................................................................................................. 5
Cylinders.............................................................................................................................................. 6
Types ............................................................................................................................................... 6
Cushioning........................................................................................................................................... 7
Table of Contents
Figure 1( Pneumatic circuit) .................................................................................................................... 4
Figure 2(Air Service unit)......................................................................................................................... 5
Figure 3(ISO symbol of the air service unit) ............................................................................................ 5
Figure 4(Solenoid Control Valve) ............................................................................................................ 5
Figure 5(Mechanical directional control Valve) ...................................................................................... 6
Figure 6(pneumatic directional control valve) ........................................................................................ 6
Figure 7(Single acted cylinder) ................................................................................................................ 6
Figure 8(Double acting Cylinder) ............................................................................................................ 7
Figure 9( Cylinders used in labs) ............................................................................................................. 7
Introduction
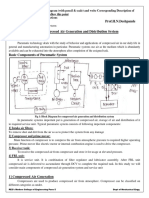
Pneumatic circuits are an essential circuit for motion transmission it is used as an applied
circuit for controlling and automation. So in order to be able to study this circuit, the circuit
must be divided into components (Air service, valves, cylinder….etc.) .Also there are a pure
pneumatic circuits for simple applications but the majority of the system is electro-
pneumatic as the precision of the circuit and high controllability. Some cautions must be
taken while designing there are control techniques and circuits that are suitable for each
application (Meter-in, Meter out, bleed off), moreover documentation must be clear while
designing this circuits.
Figure 1( Pneumatic circuit)
Main Components
Air Service Component
First of all it is a component that contains (air filter, pressure control valve, pressure gage)
So it is a component that its main function of is to provide the pneumatic system with a well
cleaned, lubricated and regulated compressed air. Figure 3 is a schematic drawing of the air
service according to the ISO.
Figure 3(ISO symbol of the air service unit)
Figure 2(Air Service unit)
Directional Control Valve
Types:
There are types of the directional control valve:
1-Solenoid Control Valve
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device in which the solenoid uses an electric
current to generate a magnetic field and thereby operate a mechanism which regulates the
opening of fluid flow in a valve.
Figure 4(Solenoid Control Valve)
2-Mechanical directional Control Valve
Mechanically directional control valve is a valve that must be subjected to force to change
the direction of the flow control valve
Figure 5(Mechanical directional control Valve)
3-Pneumatic directional control Valve
It is directional control valve that is operated by air
Figure 6(pneumatic directional control valve)
Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinder(s) (sometimes known as air cylinders) are mechanical devices which use
the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion.
Types
1- Single acting Cylinder:
A single acting cylinder is one where the thrust or output force is developed in only one
direction.
The piston is returned by a fitted spring, or by some other external means such as a weight,
mechanical movement, gravity or an external spring. They have a single port to allow
compressed air to enter the cylinder to move the piston to the desired position
Figure 7(Single acted cylinder)
2-Double acting Cylinder
A double acting pneumatic cylinder is one where the thrust, or output force, is developed in
both extending and retracting directions. Double acting cylinders have a port at each end
and move the piston forward and back by alternating the port that receives the high-
pressure air, necessary when a load must be moved in both directions such as opening and
closing a gate.
Figure 8(Double acting Cylinder)
Cushioning
In the lab there were some cylinders that used cushioning in order to increase the entire pneumatic
system, improve cycle time and reduce the size of the components, as good end position cushioning
decreases the impact forces generated by changing loads.
Figure 9( Cylinders used in labs)
You might also like
- Pneumatic Trainer KitDocument19 pagesPneumatic Trainer Kitfidianty hutasoitNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Report Mem 665 1Document13 pagesPneumatic Report Mem 665 1Nazif NazriNo ratings yet
- Mel 215 - Operation of Single Acting Cylinde-1Document8 pagesMel 215 - Operation of Single Acting Cylinde-1Aliyu omeiza YusufNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Pneumatic System & It's Components Marks 14Document14 pagesUNIT-IV Pneumatic System & It's Components Marks 14Chaitanya YengeNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics System: Operation of A Single Acting Cylinder Controlled by 3-Way ValveDocument14 pagesPneumatics System: Operation of A Single Acting Cylinder Controlled by 3-Way ValveMubarak ShehuNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics and Hydraulics: IndexDocument8 pagesPneumatics and Hydraulics: IndexescriboalprofeNo ratings yet
- Manual Bi Folding Gate PRINTCOPY SBDDocument50 pagesManual Bi Folding Gate PRINTCOPY SBDChockalingam AthilingamNo ratings yet
- Ueb1208620 - Mechanical Engineering - Hydraulics & PneumaticsDocument5 pagesUeb1208620 - Mechanical Engineering - Hydraulics & PneumaticsJoshua GrantNo ratings yet
- Atm1122 Hydraulics Module 1Document20 pagesAtm1122 Hydraulics Module 1Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Pneumatic Press For Various AttachmentsDocument16 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Pneumatic Press For Various AttachmentsSWAPNIL PATILNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lab 3Document20 pagesFluid Lab 3Wong Wei HaoNo ratings yet
- ElectroPneumatics TextbookDocument224 pagesElectroPneumatics TextbookLoforte Salomão Rapoio100% (1)
- Unit-Iv Pneumatic Systems: 4.2. Types of Motion Performed by Pneumatic ComponentsDocument17 pagesUnit-Iv Pneumatic Systems: 4.2. Types of Motion Performed by Pneumatic ComponentsJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ViceDocument30 pagesPneumatic ViceBoopathi KalaiNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Pneamatic ViceDocument26 pagesFabrication of Pneamatic Vicesselva20823No ratings yet
- Syn Button TestDocument12 pagesSyn Button TestDeepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic & HydraulicDocument10 pagesPneumatic & HydraulicAliArababadiNo ratings yet
- Course Code: ME 421 Course Title:: Class Day: Thursday Timing: 03:00 PM To 04:30 PMDocument19 pagesCourse Code: ME 421 Course Title:: Class Day: Thursday Timing: 03:00 PM To 04:30 PMNiaz Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Technology: Faculty of Engineering Technology Universiti Malaysia PahangDocument21 pagesFluid Power Technology: Faculty of Engineering Technology Universiti Malaysia PahangAniq AmirahNo ratings yet
- Flow Analysis of Upstream Fluid Flow Using Simulation For Different Positions of Optimized Inlet Guide Vane in Centrifugal Air CompressorDocument9 pagesFlow Analysis of Upstream Fluid Flow Using Simulation For Different Positions of Optimized Inlet Guide Vane in Centrifugal Air CompressorAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Unit 4& 5Document9 pagesUnit 4& 5hariharanbook0% (1)
- Mechatronic Lab ManualDocument23 pagesMechatronic Lab ManualTeaching ClubNo ratings yet
- Design and Implement A Semi-Automatic Clutch System For Automobiles Using DCV and The Link Mechanism To Reduce Human Effort While IncreasingDocument6 pagesDesign and Implement A Semi-Automatic Clutch System For Automobiles Using DCV and The Link Mechanism To Reduce Human Effort While IncreasingIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Pneumatic SystemDocument19 pagesChapter 1 Pneumatic Systemdivien rajNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document3 pagesActivity 2ron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- Cooking ManualDocument12 pagesCooking ManualathreyanjaneyaNo ratings yet
- Lab - 2 WriteupDocument8 pagesLab - 2 WriteupRuby ShajiNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Catalog: Compressed Air SystemsDocument28 pagesBest Practice Catalog: Compressed Air SystemsHamoNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydralics and Pneumatics 2 MarksDocument10 pagesApplied Hydralics and Pneumatics 2 MarksVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- PneumaticDocument6 pagesPneumaticIzzhan nasir100% (1)
- Design of Simple Pneumatics SystemsDocument5 pagesDesign of Simple Pneumatics SystemsRiya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Actuators and Their ApplicationDocument24 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic Actuators and Their ApplicationsarkrassNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Actuators and Their Application AreasDocument24 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic Actuators and Their Application AreasKart01No ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Airbrake System Using Engine Exhaust GasDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Airbrake System Using Engine Exhaust Gassv lyricsNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ViseDocument18 pagesPneumatic ViseSaravanan SaranNo ratings yet
- Circuit ApplicationsDocument65 pagesCircuit ApplicationsAman Baviskar100% (1)
- Mechatronics Module 2 - HydraullicsDocument33 pagesMechatronics Module 2 - HydraullicsRahul DasNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Lab 1Document11 pagesHydraulic Lab 1pokok assam100% (1)
- Best Practice Compressed Air PDFDocument28 pagesBest Practice Compressed Air PDFfestradavNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED PNEUMATICS ReviewerDocument4 pagesADVANCED PNEUMATICS ReviewerLeanne Mae PaduaNo ratings yet
- A Project On Pneumatic ViceDocument13 pagesA Project On Pneumatic ViceKumar Gk50% (2)
- Automation of Pneumatic Press With Clamping DeviceDocument6 pagesAutomation of Pneumatic Press With Clamping Deviceivan bernardNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Module2 Student VersionDocument13 pagesHydraulics Module2 Student VersionvozoscribdNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power DME 6TH SEMDocument58 pagesFluid Power DME 6TH SEMAman Ahmed MokamiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 (Me160p-2, Bellen)Document14 pagesLab Report 2 (Me160p-2, Bellen)AndreNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATİCDocument13 pagesPNEUMATİCAyşenur ÇetinNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Auto Feed Punching and Riveting Machine: A.S. Aditya Polapragada, K. Sri VarshaDocument7 pagesPneumatic Auto Feed Punching and Riveting Machine: A.S. Aditya Polapragada, K. Sri VarshaAkgec BoschNo ratings yet
- Flow Control ValveDocument5 pagesFlow Control Valvezakaria100% (1)
- Pneumatic System - 1Document12 pagesPneumatic System - 1Ikram NajihuddinNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument83 pagesControl EngineeringAbdulmajid AbusittaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 HydraulicDocument9 pagesLab 1 Hydraulicohoodalfowdaie123No ratings yet
- Attitude IndicationDocument69 pagesAttitude IndicationdinNo ratings yet
- ME 1305 - Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument7 pagesME 1305 - Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsUva ShruthikaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4actuation System For MechatronicsDocument62 pagesPresentation 4actuation System For MechatronicswabdushukurNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Water Pumping SystemDocument46 pagesPneumatic Water Pumping SystemAjithNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Two Mark Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit - I: Two Mark Questions & Answerssmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Asi 04 00034 v2Document20 pagesAsi 04 00034 v2OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- A Smart Tool Wear Prediction Model in Drilling ofDocument13 pagesA Smart Tool Wear Prediction Model in Drilling ofOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- K Mat 9mmDocument1 pageK Mat 9mmOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Applsci 12 02979 v2Document8 pagesApplsci 12 02979 v2OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- art3A10.10072Fs11668 016 0113 2Document16 pagesart3A10.10072Fs11668 016 0113 2OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Aerospace 08 00130Document13 pagesAerospace 08 00130OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- A Note On Mori-Tanakas MethodDocument12 pagesA Note On Mori-Tanakas MethodneerajNo ratings yet
- RIndustry Certificates NREA - 2Document43 pagesRIndustry Certificates NREA - 2OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Definition of EDM Electrode Passing Charge Role of Fluid Types of Wire EDMDocument2 pagesDefinition of EDM Electrode Passing Charge Role of Fluid Types of Wire EDMOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Cutting Data Corrax EngDocument58 pagesCutting Data Corrax EngOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Precision Instrumentation Amplifier: Data SheetDocument25 pagesPrecision Instrumentation Amplifier: Data SheetKaren MendozaNo ratings yet
- Oil + Air-Lubrication SystemDocument52 pagesOil + Air-Lubrication SystemOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Design of Filament Winding MachineDocument19 pagesDesign of Filament Winding MachineOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Robot SpecsDocument7 pagesRobot SpecsOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Faulty Product Detection and Separation System: ComponentsDocument2 pagesFaulty Product Detection and Separation System: ComponentsOmaroMohsen100% (1)
- Cutting Data Corrax EngDocument5 pagesCutting Data Corrax Engstanalina00No ratings yet
- Report #1: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering GENN327 Selections of Life Long SkillsDocument9 pagesReport #1: Cairo University Faculty of Engineering GENN327 Selections of Life Long SkillsOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- file:///C:/Users/user/Downloads/iot-gateway-nexcom-robotic-systems-brief - PDF DriveDocument1 pagefile:///C:/Users/user/Downloads/iot-gateway-nexcom-robotic-systems-brief - PDF DriveOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Setting Goals: Class FourDocument10 pagesSetting Goals: Class FourOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- READMEDocument1 pageREADMEOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- PLC Based Paper Cutting Machine: ComponentsDocument2 pagesPLC Based Paper Cutting Machine: ComponentsOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Cairo University Faculty of EngineeringDocument15 pagesCairo University Faculty of EngineeringOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- ME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedDocument4 pagesME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgmentDocument9 pagesAcknowledgmentOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Presented By: 1-Omar Mohsen (113526) 2-Mahmoud Sayed Zaghlool (1135487) Presented To: Dr. Said Megahed Eng. ImanDocument9 pagesPresented By: 1-Omar Mohsen (113526) 2-Mahmoud Sayed Zaghlool (1135487) Presented To: Dr. Said Megahed Eng. ImanOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- ME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedDocument4 pagesME307 091 Old-Exam Final-Exam SolvedOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training MDE Department Year 4Document12 pagesCairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training MDE Department Year 4OmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Coursework For ResumeDocument7 pagesCoursework For Resumeafjwdxrctmsmwf100% (2)
- Immovable Sale-Purchase (Land) ContractDocument6 pagesImmovable Sale-Purchase (Land) ContractMeta GoNo ratings yet
- CEC Proposed Additional Canopy at Guard House (RFA-2021!09!134) (Signed 23sep21)Document3 pagesCEC Proposed Additional Canopy at Guard House (RFA-2021!09!134) (Signed 23sep21)MichaelNo ratings yet
- Woodward GCP30 Configuration 37278 - BDocument174 pagesWoodward GCP30 Configuration 37278 - BDave Potter100% (1)
- Incoterms 2010 PresentationDocument47 pagesIncoterms 2010 PresentationBiswajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- S200 For Sumber RezekiDocument2 pagesS200 For Sumber RezekiIfan JayusdianNo ratings yet
- Revenue Management Session 1: Introduction To Pricing OptimizationDocument55 pagesRevenue Management Session 1: Introduction To Pricing OptimizationDuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mix Cases UploadDocument4 pagesMix Cases UploadLu CasNo ratings yet
- Usha Unit 1 GuideDocument2 pagesUsha Unit 1 Guideapi-348847924No ratings yet
- Seminar Report of Automatic Street Light: Presented byDocument14 pagesSeminar Report of Automatic Street Light: Presented byTeri Maa Ki100% (2)
- Toshiba Satellite L200 M200 M203 M206 KBTIDocument59 pagesToshiba Satellite L200 M200 M203 M206 KBTIYakub LismaNo ratings yet
- Municipality of Boliney: Republic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Province of AbraDocument7 pagesMunicipality of Boliney: Republic of The Philippines Cordillera Administrative Region Province of AbraErnest Aton100% (1)
- Analysis of Brand Activation and Digital Media On The Existence of Local Product Based On Korean Fashion (Case Study On Online Clothing Byeol - Thebrand)Document11 pagesAnalysis of Brand Activation and Digital Media On The Existence of Local Product Based On Korean Fashion (Case Study On Online Clothing Byeol - Thebrand)AJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management ModelsDocument4 pagesStrategic Management ModelsBarno NicholusNo ratings yet
- SCHEDULE OF FEES - FinalDocument1 pageSCHEDULE OF FEES - FinalAbhishek SunaNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument4 pagesCasesNaveen Stephen LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Enumerator ResumeDocument1 pageEnumerator Resumesaid mohamudNo ratings yet
- Computer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorDocument44 pagesComputer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorJess QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- Cinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Document8 pagesCinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Social Scientists' AssociationNo ratings yet
- Emco - Unimat 3 - Unimat 4 LathesDocument23 pagesEmco - Unimat 3 - Unimat 4 LathesEnrique LueraNo ratings yet
- DFUN Battery Monitoring Solution Project Reference 2022 V5.0Document50 pagesDFUN Battery Monitoring Solution Project Reference 2022 V5.0A Leon RNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesDrug Study TemplateKistlerzane CABALLERONo ratings yet
- BSL-3 Training-1Document22 pagesBSL-3 Training-1Dayanandhi ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Gogte Institute of Technology: Karnatak Law Society'SDocument33 pagesGogte Institute of Technology: Karnatak Law Society'SjagaenatorNo ratings yet
- Type BOQ For Construction of 4 Units Toilet Drawing No.04Document6 pagesType BOQ For Construction of 4 Units Toilet Drawing No.04Yashika Bhathiya JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Planas V Comelec - FinalDocument2 pagesPlanas V Comelec - FinalEdwino Nudo Barbosa Jr.100% (1)
- Ks 1609Document5 pagesKs 1609krish dabhiNo ratings yet
- 01 Eh307 Crimpro Case Digests Part 1Document214 pages01 Eh307 Crimpro Case Digests Part 1Kimberly PerezNo ratings yet
- CENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFDocument22 pagesCENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFsabrina rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Company Law Handout 3Document10 pagesCompany Law Handout 3nicoleclleeNo ratings yet