Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics, Hydrology, Water
Uploaded by
Adonis C. Bibat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views7 pageshydraulics :)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthydraulics :)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views7 pagesFluid Mechanics, Hydraulics, Hydrology, Water
Uploaded by
Adonis C. Bibathydraulics :)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Fluid Mechanics,
Hydraulics, Hydrology,
Water Supply
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
Properties of Fluids
1. When analyzing rockets,
spacecraft, and other systems
that involve high-speed gas
flows , the flow speed is often
expressed in terms of the
dimensionless Mach number
defined as
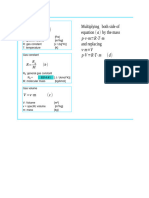
C= 𝑘𝑅𝑇
k=specific heat ratio
• sonic when Ma = 1 T=temp in Kelvin
• subsonic when Ma < 1
• supersonic when Ma > 1
• hypersonic when Ma >> 1
• Transonic when Ma approx.
equal to 1.
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
Properties of Fluids
2. Weight = mass x gravity 3. Work = Force x Distance
Unit: Unit:
Force = mass x acceleration
mass, m = kg S.I.
= (kg)*(m/s2)
= slug English System
= Newton
Gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2 S.I.
Hence;
= 32.2 ft/s2 English
System Work = (Newton)*(meters)
Hence; = N.m
Weight = (kg)*(m/s2) = Newton, (N) = Joule, (J) S.I.
= (slug)*(ft/s2)=Pound, (lb) Energy:
• the energy unit is the Btu (British thermal unit)
• 1 Btu = 1.0551 kJ (kilo-Joule)
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
Properties of Fluids
4. Power = Work/Time 5. Density, ρ = mass/unit volume
= Force x Velocity ρ = m/V (kg/m3)
Unit:
Power = (N.m)/(seconds) = watt, (W) 6. Specific volume, v = reciprocal of density
= (N)*(m/s) = watt, (W) S.I. v = 1/ρ
= Volume/mass (m3/kg)
= (lb.ft)/(seconds) = horsepower, (hp) 7. Specific gravity:
= (lb)*(ft/s) = horsepower, (hp) english s.g.= ρLIQUID/ ρW (unitless)
Note: commonly used unit of power is horsepower ρW = 1000 kg/m3
1 hp = 746 watts 8. Specific weight or Weight density:
1 hp = 550 (lb-ft)/sec ɣ = ρ*g
ɣ = (kg/m3)*(m/s2) = N/m3
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
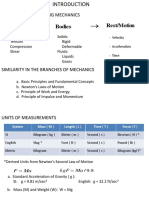
9. Density of Ideal Gases
Properties of Fluids Pabs*v = R*T
Pabs= ρ*R*T
Where:
Pabs = absolute pressure
v= specific volume , (1/ρ)
T=thermodynamic (absolute) temperature
R= gas constant
R=(universal gas constant)/(molar mass or
molecular weight)
***The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa.m3/kg.K.
***Universal gas constant, Ru=8.314 kJ/kmol.K
=1.986 Btu/lbmol.R
T=C+273 in Kelvin S.I.
T=F+460 in Rankine english
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
Properties of Fluids
10. Ideal Gas
Pabs*V=m*R*T
where;
m=N*M – (eq.1)
m=mass of gas
V=volume of gas
N=no. of moles
M=molar mass
Ru=MR – (eq.2)
Ru = Universal gas constant
R = gas constant
equating M:
m*R=N*Ru
Hence,
Pabs*V=N*Ru*T
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
Properties of Fluids
11. Ideal gas at two different states 13. Coefficient of Volume Expansion
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
12. coefficient of compressibility, k :
(also called the bulk modulus of compressibility or **volume expansion coefficient of an ideal gas
bulk modulus of elasticity)
Correlation Lecturer: Engr. Adonis C. Bibat, CE
You might also like
- Thermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyDocument38 pagesThermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyAron H OcampoNo ratings yet
- I. FLUID MECHANICS I.1 Basic Concepts & Definitions: Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesI. FLUID MECHANICS I.1 Basic Concepts & Definitions: Fluid Mechanicsdprao196750% (2)
- Ideal Gas Law. Application To AirDocument11 pagesIdeal Gas Law. Application To AirvyrgoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties and Conversion UnitsDocument12 pagesThermodynamic Properties and Conversion UnitsM MNo ratings yet
- MAE 261 Fundamental Dimensions and Consistent UnitsDocument2 pagesMAE 261 Fundamental Dimensions and Consistent UnitsLeilani OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and energy conversion basicsDocument16 pagesThermodynamics and energy conversion basicsNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-١١ في ٨.٣٧.١٧ صDocument34 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-١١ في ٨.٣٧.١٧ صabdollahali2004No ratings yet
- Thermo DyDocument18 pagesThermo Dykeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgA0RIEvHiwraZxPlfKRr-98U6nP43O3VMAPyrV1wQLfMhyweFQJAH10C8bqPaHiL og8lCA2xqWk6nSJoRxRmWE35 zhcE2Ff1em 530-WQLwUFEdsQXuHanu3cu mipcQMYWxLHaRs4YBtDocument6 pagesACFrOgA0RIEvHiwraZxPlfKRr-98U6nP43O3VMAPyrV1wQLfMhyweFQJAH10C8bqPaHiL og8lCA2xqWk6nSJoRxRmWE35 zhcE2Ff1em 530-WQLwUFEdsQXuHanu3cu mipcQMYWxLHaRs4YBtElly John ReliquiasNo ratings yet
- Dimensions, Units, and Significant Digits: Primary Dimensions Basic DimensionsDocument5 pagesDimensions, Units, and Significant Digits: Primary Dimensions Basic DimensionsAce Heart Rosendo AmanteNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas. Ideal Gas Law Application To AirDocument12 pagesIdeal Gas. Ideal Gas Law Application To AirhasanNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1 Thermodynamic Systems Tutorial 1: Unit 43: Plant and Process PrinciplesDocument30 pagesOutcome 1 Thermodynamic Systems Tutorial 1: Unit 43: Plant and Process Principlesأيمن الكزةNo ratings yet
- ThermofluidsDocument103 pagesThermofluidsKarthikeyan ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Data - Sheet - 1 - Carbon Dioxide Capture From Internal Combustion Engine Exhaust Using Temperature Swing AdsorptionDocument10 pagesData - Sheet - 1 - Carbon Dioxide Capture From Internal Combustion Engine Exhaust Using Temperature Swing AdsorptionKhadija RAISSINo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids ADocument43 pagesProperties of Fluids AGlenn Frey LayugNo ratings yet
- LessonsDocument58 pagesLessonsMarvin CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Thermo 1Document31 pagesThermo 1Mharjon D. BacallaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Applying Newton's Second Law To The Weight Force GivesDocument6 pagesAnalysis Applying Newton's Second Law To The Weight Force GivesZumaflyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Fluid PropertiesDocument71 pagesBasic Concepts Fluid PropertiesAbed Alrahman QaddourNo ratings yet
- Handouts PPE Day 1Document7 pagesHandouts PPE Day 1Raziel SalasibarNo ratings yet
- Conversion UnitsDocument4 pagesConversion UnitsAngelo IntiaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesConversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringElma CruzNo ratings yet
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 pagesUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaNo ratings yet
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 pagesUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Fluid Properties GuideDocument4 pagesPhysics Fluid Properties GuideKarl HendrixNo ratings yet
- Out 2 T 1Document16 pagesOut 2 T 1Lilo IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Heat Calculation ReferenceDocument5 pagesHeat Calculation ReferenceCham SurendNo ratings yet
- Appendix G - Units and ConversionsDocument1 pageAppendix G - Units and Conversionskim haksongNo ratings yet
- Fluid 9ed Solution ManualDocument919 pagesFluid 9ed Solution ManualAmr f100% (1)
- CH 01Document54 pagesCH 01Larissa Albunio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Unit Systems: C C C 2 CDocument4 pagesUnit Systems: C C C 2 CAndre alexander dos santosNo ratings yet
- Formulas - PipeDocument34 pagesFormulas - PipeReuben Madera DabaNo ratings yet
- L-9 Pure Substance Ideal Gases-IDocument25 pagesL-9 Pure Substance Ideal Gases-IShailin SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Numerical Values Made SimpleDocument64 pagesFundamental Numerical Values Made SimpleFaiz Daud100% (1)
- MASS BALANCE DICTATE UNITS AND DIMENSIONSDocument22 pagesMASS BALANCE DICTATE UNITS AND DIMENSIONSFakri 'L' MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Summary of CH-1 (Fluid Properties) : Water Resources Engineering Department Third Class Year Elementary of Fluid MechanicsDocument33 pagesSummary of CH-1 (Fluid Properties) : Water Resources Engineering Department Third Class Year Elementary of Fluid Mechanicsمنتظر المدريديNo ratings yet
- Thermo Module 1Document4 pagesThermo Module 1Isshi Briones BuhayNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document72 pagesThermodynamics 1Victor CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Thermo FormulaDocument16 pagesThermo FormulaJomillenah JazminNo ratings yet
- Energy FormsDocument9 pagesEnergy FormsAlaa ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Prelim ModuleDocument6 pagesThermo Prelim ModuleredleatherwolfNo ratings yet
- NMAT MUST KNOW FORMULAS CHEMISTRY PHYSICS FORMULASDocument2 pagesNMAT MUST KNOW FORMULAS CHEMISTRY PHYSICS FORMULASCatNo ratings yet
- ConstantsDocument2 pagesConstants3 stacksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document15 pagesLesson 1 and 2Ian Arnold Fami50% (2)
- BME 2210: Supplementary Notes Basic Constants and Conversion FactorsDocument1 pageBME 2210: Supplementary Notes Basic Constants and Conversion FactorsJessica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Dimensional AnalysisDocument10 pagesDimensional AnalysisXyra P. KujoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document12 pagesLecture 2Samaseen PrabhatNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Concept of A FluidDocument11 pages1.1 The Concept of A FluidKhan Nawaz AliNo ratings yet
- Useful ConstantsDocument1 pageUseful ConstantsFarhan HalimNo ratings yet
- Presented By: John Lester D. MonesDocument26 pagesPresented By: John Lester D. Monesmark louie colandogNo ratings yet
- Matter Exercises2Document6 pagesMatter Exercises2Camila PrzNo ratings yet
- Factores de ConversionesDocument1 pageFactores de Conversioneschef Sergio rojasNo ratings yet
- THERMO1 - 1 Introductory Concepts and Definition - Sample Problems PDFDocument25 pagesTHERMO1 - 1 Introductory Concepts and Definition - Sample Problems PDFEdmark AldeaNo ratings yet
- ConversionbyEngrProfPH PDFDocument4 pagesConversionbyEngrProfPH PDFCALICA RYAN ANTHONY V.No ratings yet
- Intro. Chem. Eng. II Energy ConceptsDocument9 pagesIntro. Chem. Eng. II Energy ConceptskaledNo ratings yet
- Paul Norton "Appendices" Ed. Jan F. Kreider Boca Raton, CRC Press LLC. 2001Document27 pagesPaul Norton "Appendices" Ed. Jan F. Kreider Boca Raton, CRC Press LLC. 2001nascasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Ch2Document13 pagesFluid Mechanics Ch2AVCNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and DefinitionDocument8 pagesThermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and DefinitionHENRICK IGLENo ratings yet
- Unit HydrographDocument49 pagesUnit HydrographAdonis C. Bibat67% (3)
- Water Chap 9Document20 pagesWater Chap 9Adonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- ISO 50001:2011 Energy Management System: Inspiring ExcellenceDocument32 pagesISO 50001:2011 Energy Management System: Inspiring ExcellenceAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- 98860-Salmon ISM CH06 PDFDocument18 pages98860-Salmon ISM CH06 PDFAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Brandl PDFDocument17 pagesBrandl PDFRodneyXerriNo ratings yet
- Excel SolverDocument6 pagesExcel SolverdboyszNo ratings yet
- Construction of Multi-Level ParkingDocument13 pagesConstruction of Multi-Level Parkingdunknown15No ratings yet
- Operations Research: Assignment Problems and Network OptimizationDocument56 pagesOperations Research: Assignment Problems and Network OptimizationAdonis C. Bibat0% (1)
- Leveling MethodsDocument12 pagesLeveling MethodsAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Tle Plumbing LMDocument131 pagesTle Plumbing LMAdrian Goze Reformina92% (13)
- Measuring Earth's Shape & FeaturesDocument30 pagesMeasuring Earth's Shape & FeaturesAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- ISE 330 MidtermDocument11 pagesISE 330 MidtermAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Three-Wire and Reciprocal LevelingDocument13 pagesThree-Wire and Reciprocal LevelingAdonis C. Bibat50% (2)
- Som PDFDocument195 pagesSom PDFSonu Kumar100% (1)
- Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument43 pagesThin-Walled Pressure VesselsAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document26 pagesCH 12Adonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserDocument145 pagesSolution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserManuull71% (49)
- m2l13 PDFDocument17 pagesm2l13 PDFAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- UscDocument6 pagesUscAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- ch4 PDFDocument31 pagesch4 PDFAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Ftool PDFDocument25 pagesFtool PDFAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Theory Ii: (Statically Indeterminate Structure)Document16 pagesStructural Analysis Theory Ii: (Statically Indeterminate Structure)Adonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Physics General NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics General NotesAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- 2016ERDTBrochure PDFDocument2 pages2016ERDTBrochure PDFAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- 5S Usep 012717Document174 pages5S Usep 012717Adonis C. Bibat100% (1)
- Calculating Stresses in Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument43 pagesCalculating Stresses in Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsAdonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserDocument145 pagesSolution Manual of Physics by Arthur BeiserManuull71% (49)
- ECE 470 Introduction To Robotics Alternative Lab 4 and 5 Manual Spring 2020Document22 pagesECE 470 Introduction To Robotics Alternative Lab 4 and 5 Manual Spring 2020SELVAKUMAR RNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Aeronautical-StructureDocument28 pagesB.Tech. Aeronautical-StructureSøūrã'v KūmãrNo ratings yet
- اheat Transfer ProblemDocument3 pagesاheat Transfer ProblemgrodeslinNo ratings yet
- Philips Affiniti 50 Ultrasound SystemDocument32 pagesPhilips Affiniti 50 Ultrasound SystemTuyen nguyen ngocNo ratings yet
- Paper - Stator Life of A Positive Displacement Down-Hole Drilling Motor - Por Majid S. Delpassand R&M Energy SystemsDocument11 pagesPaper - Stator Life of A Positive Displacement Down-Hole Drilling Motor - Por Majid S. Delpassand R&M Energy SystemsJuanNo ratings yet
- Minor02 QP DLP NEET17 (Pmtcorner - In)Document31 pagesMinor02 QP DLP NEET17 (Pmtcorner - In)Abir Dn100% (1)
- Setting Up A Case For Turbomachinery Problems: Openfoam Kurs 2009 Håkan Nilsson Olivier PetitDocument33 pagesSetting Up A Case For Turbomachinery Problems: Openfoam Kurs 2009 Håkan Nilsson Olivier PetitBryan ArcilaNo ratings yet
- ECC206 - Ch6 - Distributed Forces - Centroids and Centers of ForcesDocument36 pagesECC206 - Ch6 - Distributed Forces - Centroids and Centers of ForcesGravisNo ratings yet
- Refresher No.4 (MDSP)Document4 pagesRefresher No.4 (MDSP)chyno.kang08No ratings yet
- Physics Short Questions Notes (9th) EMDocument14 pagesPhysics Short Questions Notes (9th) EMUmair SarwarNo ratings yet
- Vibro Acoustic SimulationDocument28 pagesVibro Acoustic SimulationSharanNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Ae / Overseer/Jdo / Ri / Surveyor / Draftsman TRB Polytechnic / EnggDocument46 pagesTNPSC Ae / Overseer/Jdo / Ri / Surveyor / Draftsman TRB Polytechnic / Engggopala krishnanNo ratings yet
- Compressor Design, Triangle Velocity ExampleDocument26 pagesCompressor Design, Triangle Velocity Exampleilham dwi putraNo ratings yet
- Chapter V Beam Deflections 5.3Document8 pagesChapter V Beam Deflections 5.3Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis - IiiDocument11 pagesStructural Analysis - IiiDeepak Sah0% (1)
- Force Systems & ResultantsDocument55 pagesForce Systems & ResultantsJanina Christelle OrmitaNo ratings yet
- Q3 1ST Summative Test - Frictional and Gravitational ForceDocument2 pagesQ3 1ST Summative Test - Frictional and Gravitational ForceMa Cristina D. MagadiaNo ratings yet
- NavierDocument2 pagesNavierrusdanadityaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Mece5104 - Mechanical VibrationDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Mece5104 - Mechanical VibrationCedricNo ratings yet
- Tim1 KelasADocument5 pagesTim1 KelasARiatus SNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Jacking Forces During Microtunnelling in LimestoneDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Jacking Forces During Microtunnelling in Limestonetkm2004No ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures-II - U1 - L1 - T9 - Analysis of Unsymmetrical Bending of Beams - Principal Axis MethodDocument11 pagesAircraft Structures-II - U1 - L1 - T9 - Analysis of Unsymmetrical Bending of Beams - Principal Axis Methodsarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument42 pagesUnit IVabhijeetchaudhary7779No ratings yet
- Lateral-Torsional Vibration of A Side-Loaded Rotor With AsymmetriDocument101 pagesLateral-Torsional Vibration of A Side-Loaded Rotor With AsymmetriAgustín Erasmo Juárez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Fluid - Mechanics 04bDocument54 pagesFluid - Mechanics 04bjavi checaNo ratings yet
- Pad Foundation Design Example Eurocode 2Document5 pagesPad Foundation Design Example Eurocode 2tedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument10 pagesQuestion BankNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Plane Bending (Part 2)Document113 pagesChapter 6. Plane Bending (Part 2)Lam TranNo ratings yet
- Physics Key FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Key FormulasChidi BenedictNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion (JEE-SHM)Document4 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion (JEE-SHM)Unknown anonymous100% (1)