Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Pathophysiology Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
jesa_oliveOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Pathophysiology Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
jesa_oliveCopyright:
Available Formats
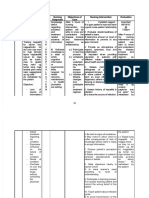
ASSESSMENT PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Px: Communication, A thyroidectomy is STO: Dx: STO:
verbal impaired the partial or After 3 hours Goal will be
complete removal of nursing > Assess energy >Fatigue and/or met if patient will
Subjective: of the thyroid interventions the level. shortness of breath be able to
gland. Partial patient will be can make establish method of
“nahihirapan akong
thyroidectomy able to establish communication communication in
magsalita” (lobectomy) is method of difficult or which needs can be
used to treat communication in impossible. understood.
Objectives:
individual, this needs can be > Assess for
>Difficulty localized nodules understood. presence and > Patients who are
or tumors, whereas history of dyspnea. experiencing
vocalizing words
complete (total) breathing problems
>Unable to speak thyroidectomy may may reduce or cease
be performed in verbal
>difficulty
cases of thyroid communication that
expressing thoughts enlargement, may complicate
metabolic > Assess speech their respiratory
verbally
dysfunction, and periodically efforts.
>refusal to speak primary cancer of
the thyroid. > Hoarseness and
>Difficulty of
A safe procedure, sore throat may
forming words or
a Thyroid Surgery occur secondary to
sentences.
generally has no tissue
>Use of non- verbal complications or edema or surgical
cues. side effect; apart Tx: damage to recurrent
from some swelling laryngeal nerve
Ax: and discomfort >Anticipate patient and may last
that is which are needs and pay several days.
Communication, expected after any attention to
impaired verbal may surgery procedure. nonverbal cues.
be related to Pain and stiffness
Vocal cord of the neck are >The nurse should
injury/laryngeal also common during set aside enough
nerve damage, the recovery time to attend to
Tissue edema; period, which can all of the details
pain/discomfort be anywhere from >Place important of patient care.
2-3 weeks. During objects within Care measures may
the recovery reach. take longer to
period, difficulty complete in the
while speaking, >Keep communication presence of a
hoarse voice, an simple; ask yes/no communication
irritated questions. deficit.
windpipe,
difficulty in >Use short >This maximizes
swallowing and sentences and ask patient’s sense of
neck tenderness only one question independence.
are common. at a time.
>Reduces demand for
>Provide response; promotes
alternative methods voice rest.
of communication as
appropriate >This allows the
patient to stay
>Anticipate needs focused on one
as possible. Visit thought.
patient frequently.
>Give the patient >Facilitates
ample time to expression of
respond. needs.
>Reduces anxiety
and patient’s need
to communicate.
>Maintain quiet >It may be
environment. difficult for
patients to respond
under pressure;
they may need extra
time to organize
Edx: responses, find the
correct word, or
>instruct patient make necessary
on voice language
limitations, translations.
>Enhances ability
to hear whispered
>encourage voice communication and
rest. reduces necessity
for patient to
raise/strain voice
to be
heard
>Prevents patient
>Encourage patient from straining
to socialize with voice to make needs
family and friends.
Known/summon
assistance.
.>Permanent nerve
damage can
occur (rare) that
causes paralysis of
vocal cords and/or
compression of the
trachea.
>Communication
should be
encouraged despite
impairment.
You might also like
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- NCP Hip FractureDocument5 pagesNCP Hip FractureCherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Drug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursingDocument1 pageDrug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursinghahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - Lupus and Blood DonationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - Lupus and Blood DonationMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- Ineffectuve Breathign PatternDocument2 pagesIneffectuve Breathign PatternDiana Marie Magango FranciaNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- NCP ImpairedDocument3 pagesNCP ImpairedLyka NgayanNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessDocument8 pagesSubjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- NCP Knowledge Deficit PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficit PDFskylertNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Planaprilrosehibaya100% (1)
- Assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation for Parkinson's patientDocument2 pagesAssessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation for Parkinson's patientBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PrioritizationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan PrioritizationKASIA SyNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentjisooNo ratings yet
- Code Green Introduction Reviewer - RedDocument4 pagesCode Green Introduction Reviewer - RedJamieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Comfort—pruritisBondan PalestinNo ratings yet
- Managing Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaDocument3 pagesManaging Electrolyte Imbalances: A Case of Self-Induced HyperkalemiaPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionPebbles PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MMMCDocument14 pagesDrug Study MMMCKathleen Pagulayan Intalan-GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationastersisk1121No ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- NCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument3 pagesNCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisVencel Mae Famas Villahermosa50% (2)
- NCP Acute Pain WDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain Wmiles sbNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short TermDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short Termgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Postpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestDocument8 pagesPostpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeDocument11 pagesNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- NCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Document3 pagesNCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Ma Kaye Gelizabeth Corpuz-DauloNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis Discharge PlanDocument1 pageCellulitis Discharge PlanJuvy Rose Tinga YeeNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleep PatternHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Oral Mucous MembraneDocument11 pagesNCP For Impaired Oral Mucous MembraneRYAN SAPLADNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Document2 pagesCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16No ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationErjohn Vincent Lim100% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageImpaired Physical MobilitySheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianNo ratings yet
- DiagnosisDocument7 pagesDiagnosisjhilltotNo ratings yet
- RLE III - A ENT MED Day 1Document14 pagesRLE III - A ENT MED Day 1Kristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Improve Communication for Child with Ear PainDocument7 pagesImprove Communication for Child with Ear PainKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planspumpkin21No ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For Breast FeedingDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan For Breast Feedingjesa_olive86% (7)
- Invitation CardDocument2 pagesInvitation Cardjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- Compiled Case Pres X Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pageCompiled Case Pres X Pa Tho Physiologyjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- Wish Ur My Love - T MaxDocument5 pagesWish Ur My Love - T Maxjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- Thinking of You LyricsDocument3 pagesThinking of You Lyricsjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- Invitation CardDocument2 pagesInvitation Cardjesa_oliveNo ratings yet
- 7t Pros ConsDocument12 pages7t Pros ConsFrancis NgNo ratings yet
- ObsernDocument1 pageObsernGobi NavaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Non-Communicating Congenital HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Non-Communicating Congenital HydrocephalusRose Lyn Camarista VelascoNo ratings yet
- SNC2D Cell NotesDocument17 pagesSNC2D Cell NotesBenjamin FallahyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocument57 pagesAssessment of The AbdomenKarylle Petil100% (1)
- Reproduction and Development: General OutcomesDocument34 pagesReproduction and Development: General OutcomesNavjot TiwanaNo ratings yet
- The New Armenian Medical Journal: in Honor of Dr. Nikolaes Tulp, "I Consume Myself Serving Others"Document5 pagesThe New Armenian Medical Journal: in Honor of Dr. Nikolaes Tulp, "I Consume Myself Serving Others"Сергей КутяNo ratings yet
- Handwriting Analysis IN C Ancer Patients Clinical - Radiological and Graphological CorrelationDocument28 pagesHandwriting Analysis IN C Ancer Patients Clinical - Radiological and Graphological Correlationveronica mediaNo ratings yet
- MRI of Acute Spinal TraumaDocument37 pagesMRI of Acute Spinal TraumashivaprakashbhNo ratings yet
- Why Is An EEG Performed?Document4 pagesWhy Is An EEG Performed?Sai MuraliNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma: Dr.R.Srivathsan Pg-IiDocument98 pagesAbdominal Trauma: Dr.R.Srivathsan Pg-IiddallasNo ratings yet
- Practice: Pituitary AdenomasDocument7 pagesPractice: Pituitary AdenomasujiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandHead PeacockNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in Radiology2015Document13 pagesFinal Examination in Radiology2015Ndor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Assessment GuideDocument47 pagesCervical Spine Assessment GuideMichelle Peters100% (2)
- 2020 Prep Self Assessment 2016309916Document884 pages2020 Prep Self Assessment 2016309916Female calm100% (2)
- Abstract Leftsidest SetDocument1,047 pagesAbstract Leftsidest Setpokharelriwaj82No ratings yet
- Skin PathologyDocument59 pagesSkin PathologyNeill CelesteNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : ObservationDocument10 pagesJournal Homepage: - : ObservationIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Brain Bee Study QuestionsDocument13 pagesBrain Bee Study QuestionsMartyna Petrulytė88% (25)
- Atenolol: Atenolol Is A Beta Blocker MedicationDocument6 pagesAtenolol: Atenolol Is A Beta Blocker MedicationAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Class 9-Biology-Lesson 11-Sense Organs-EarDocument10 pagesClass 9-Biology-Lesson 11-Sense Organs-EarShlok JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Art Therapy Relieves Cancer SymptomsDocument13 pagesArt Therapy Relieves Cancer SymptomsCyanNo ratings yet
- (FreeCourseWeb - Com) 0857013947 PDFDocument290 pages(FreeCourseWeb - Com) 0857013947 PDFSaad Ahmed Al Muhannadi100% (4)
- HematopoiesisDocument52 pagesHematopoiesisUNO RIPPERSNo ratings yet
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Adults (Printer-Friendly)Document37 pagesComplex Regional Pain Syndrome in Adults (Printer-Friendly)roooNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman AnatomyBabylove GoalsNo ratings yet
- BioPsych NotesDocument18 pagesBioPsych NotesGUTIERREZ, CRISHA ANDREA M.No ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Head InjuryDocument28 pagesCase Presentation On Head Injuryarchana verma83% (6)
- Diseases of The Small Intestine-1Document70 pagesDiseases of The Small Intestine-1ElvisNo ratings yet