Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maylynn Renal Lasix Monograph
Uploaded by
AORN20080 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views1 pageMaylynn Renal Lasix Monograph
Uploaded by
AORN2008Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
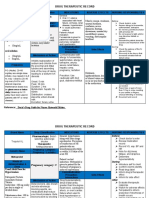
MAYLYNN ACOSTA RENAL (FUROSEMIDE -LASIX) MONOGRAPH
GENERIC NAME: FUROSEMIDE
PHARMACOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION: BRAND NAME: Lasix THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION:
Loop diuretics. Diuretics.
ACTION: Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle & distal
renal tubule. Increases renal excretion of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, hydrogen
& calcium. May have renal and peripheral vasodilatory effects. Effectiveness persists in
impaired renal function.
THERAPEUTIC EFFECT:
Diuresis & subsequent mobilization of excess fluid (edema, pleural effusion).
Decreased blood pressure.
SIDE/ADVERSE EFFECTS ROUTE/DOSAGE/ONSET
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:OF ACTION/PEAK/DURATION:
Excess Fluid volume.
Pregnancy Category C Available in Tablets, IM, IV.
CNS: dizziness, encephalopathy, headache, Route/Dosage: Edema – 20-80 mg.day as single dose initially,
insominia, nervousmess may repeat in 6-8 hrs.Hypertension – 40mg twice daily initially
EENT: hearing NURSING INTERVENTIONS: DO NOT CONFUSE
loss, tinnitus (when FUROSEMIDE
added to regimen,WITHdecrease
TORSEMIDE. dosage of other
CV:hypotensionAssess fluid status during therapy. Monitor daily weight, I&O, edema, lung sounds, skin
antihypertensive by 50%). Hypercalcemia turgor and
– 120mg/day mucous
I 1-3
membranes. Notify physician
GI: constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia,if thirst, dry mouth,
doses. lethargy, weakness, hypotension or oliguria occurs.
Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and
nausea, vomiting during administration.
PO/Onset30-60min. Peak: 1-2In geriatric patients,
hrs.Duration: diuretic use is
6-8 hrs.
associated
GU: excessive urination with increased risk for falls in older adults. Assess falls risk and implement
Mostly metabolized by the liver. Use cautiously in fall prevention
severe liver
strategies.
F&E: dehydration, Administer
hypochloremia, medication in the morning
hypokalemia, to prevent disruption of sleep cycle. Administer
disease. May precipitate hepatic coma; concurrent use with orally with
food or
hypomagnesemia, milk to minimize
hyponatremia, gastric irritation. Tablets
hypovolemia, may be crushed if patient has difficulty
potassium sparing diuretics may be necessary. Geriatric swallowing. Do
not administer discolored solution or tablets.
metabolic alkalosis When using furosemide for hypercalcemia, replace
patients may have increased risk of side effects, especially
HEMAT: blood extracellular
dyscrasia volume and sodium chloride hypotension to maintain fluid
andvolume andimbalance.
electrolyte increase calcium excretion
effectively. Instruct
METAB: hyperglycemia, hyperurecemia patient to take furosemide as directed. Take missed
Drug-drug interaction: Increased does as soon aswith
hypotension possible. Do not
double up doses. Caution
MS:arthralgia, muscle cramps, myalgia patient to change antihypertensives, nitrates or acute ingestion of alcohol. Caution
positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
patient
MISC.: increased BUN to use sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent
Increased photosensitivity.
risk of ototoxicity Advise patient to contact
with aminoglycosamides. May
health care professional immediately if muscle weakness, cramps, nausea, dizziness,numbness
increase the effectiveness of warfarin, thrombolytic agents or tingling
or
of extremities occurs. Advise diabetic patients to monitor blood glucose closely, may cause increased
anticoagulants.
blood glucose levels.
Bibliographic citation: Davis Drug Guide
Tenth Edition: pages 558-560
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Zamora - Colon Cancer 2Document25 pagesZamora - Colon Cancer 2Kristel PunoNo ratings yet
- Drug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyDocument57 pagesDrug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyMichelle Davis-JacksonNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsedmond callenNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument3 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- DTR PediaDocument3 pagesDTR PediaMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Record for Lasix and MetoprololDocument3 pagesDrug Record for Lasix and MetoprololMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionSheferely BayauaNo ratings yet
- JINANG's Drug Data SummaryDocument4 pagesJINANG's Drug Data SummaryiammaiaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesCebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesdnllsgrraNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilDocument9 pagesHydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilcotyboyNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Group-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesGroup-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyRen Mark CanlasNo ratings yet
- Chew, swallow or crush mebendazole tabletsDocument6 pagesChew, swallow or crush mebendazole tabletsDenvicNo ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Drug Study - DoxDocument3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study - Doxan naNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1.1Document2 pagesDrug Study 1.1Arianne Nicole PinuelaNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyshakiraNo ratings yet
- IndapamideDocument2 pagesIndapamideNovi Yuliana100% (1)
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: University of Northern PhilippinesDocument8 pagesCollege of Nursing: University of Northern PhilippinesSanti MooreNo ratings yet
- NJKFANFJKANSZJFNZDDocument4 pagesNJKFANFJKANSZJFNZDSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- Reduce cholesterol and triglycerides with CRESTORDocument2 pagesReduce cholesterol and triglycerides with CRESTORSunny Mae T. PuigNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIADocument8 pagesDRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIAKent Martin AmorosoNo ratings yet
- 37 Thyroid and Parathyroid AgentsDocument6 pages37 Thyroid and Parathyroid AgentssenyorakathNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action, Indications, Administration and Side Effects of RisperidoneDocument2 pagesMechanism of Action, Indications, Administration and Side Effects of RisperidoneLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesWinter HyuckNo ratings yet
- Simvastatin (Zocor)Document2 pagesSimvastatin (Zocor)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2nd SemDocument7 pagesDrug Study 2nd SemKyla CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Colon CancerDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Colon Cancerbea pegadNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsDocument7 pagesDiuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMagnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug Studyprog.ecleo.swuNo ratings yet
- MC HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesMC HydroxyzineCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Cebu Normal University College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Cebu Normal University College of Nursing Drug StudyLouie Danielle Segarra100% (1)
- Drug Study: ChlorthalidoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study: ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Anti PsychotisDocument21 pagesAnti Psychotissuresh sataguniNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Health AssessmentDocument8 pagesHealth AssessmentAORN2008No ratings yet
- Chart Transfused Blood ProductsDocument2 pagesChart Transfused Blood ProductsAORN2008No ratings yet
- Special Proc Test FormDocument7 pagesSpecial Proc Test FormAORN2008No ratings yet
- EEGDocument1 pageEEGAORN2008No ratings yet
- Pneumonia Key PointDocument2 pagesPneumonia Key PointAORN2008No ratings yet
- ABCs of Infection ControlDocument1 pageABCs of Infection ControlAORN2008No ratings yet
- DKA Vs HHNKDocument1 pageDKA Vs HHNKBetty Sanchez DiazNo ratings yet
- Aiapget 2020 QPDocument29 pagesAiapget 2020 QPGanesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Effective Lifting ProgramDocument30 pagesBenefits of Effective Lifting ProgramMoradeke OnasanyaNo ratings yet
- Ohio Prison Suicide ReportDocument26 pagesOhio Prison Suicide ReportPBS NewsHourNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chart: Warm UpDocument1 pageExercise Chart: Warm UpJeremy van der MerweNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative MatrixDocument42 pagesFundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative Matrixasifmdzakaria57% (7)
- The Lord of Lost Heart PDFDocument44 pagesThe Lord of Lost Heart PDFCouteron LaurentNo ratings yet
- Loxapine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesLoxapine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2016 3 23 9 12 47tapchi-Dhdn-So12 (97) .2015-Color-WebDocument128 pages2016 3 23 9 12 47tapchi-Dhdn-So12 (97) .2015-Color-WebThọ Nguyễn Văn100% (1)
- High Yield Surgery Compatible VersionDocument77 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version17kimpNo ratings yet
- Water, Sanitation and Hygiene in SchoolsDocument6 pagesWater, Sanitation and Hygiene in SchoolsDux Mercado100% (1)
- TB Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesTB Teaching PlanTrisha Fae Loyola Balagot100% (1)
- Experiment 5 EDTA Titration: Calcium in Calcium Supplements: Student HandoutDocument6 pagesExperiment 5 EDTA Titration: Calcium in Calcium Supplements: Student HandoutIbad MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Fundamentals and Fire Extinguisher ClassificationsDocument3 pagesFire Safety Fundamentals and Fire Extinguisher ClassificationsGangapuram SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Monthly Current Affairs Quiz - January 2023: Follow UsDocument244 pagesMonthly Current Affairs Quiz - January 2023: Follow UsSubhankar BasakNo ratings yet
- Q&A2Document3 pagesQ&A2Marv MarvNo ratings yet
- Surya Namaskar BenefitsDocument16 pagesSurya Namaskar BenefitsMillion Dollar KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Slide PPT PrismaDocument31 pagesSlide PPT PrismaUlul Azmi AdnanNo ratings yet
- Mary Law PEO Model PDFDocument15 pagesMary Law PEO Model PDFalepati29No ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Anxiety DisordersDocument66 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Anxiety Disordersnajaxx100% (2)
- Fire Retardant Research PaperDocument2 pagesFire Retardant Research Paperapi-318759920No ratings yet
- ACIDITY REMEDIESDocument3 pagesACIDITY REMEDIESYasmeen JafferNo ratings yet
- MedEx FAQDocument2 pagesMedEx FAQJee CHIUN CHENNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2772569323000026 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2772569323000026 MainAditya RizkyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ADocument3 pagesCardiovascular AAutumn AllisonNo ratings yet
- Referral Letter: Client Personal Details Client Identity DetailsDocument2 pagesReferral Letter: Client Personal Details Client Identity DetailsFlorence LinNo ratings yet
- Annex 2 7d PEMAPS QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesAnnex 2 7d PEMAPS QuestionnaireAlma PustaNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients ProteinsDocument2 pagesMacronutrients ProteinsEllice O. MonizNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument3 pagesArgumentative Essayapi-444150463No ratings yet
- PALLIATIVE CARE SYMPTOM MANAGEMENTDocument153 pagesPALLIATIVE CARE SYMPTOM MANAGEMENTrlinao100% (3)
- Human Kinetics Library Platform - Benefits and Values of Outdoor RecreationDocument17 pagesHuman Kinetics Library Platform - Benefits and Values of Outdoor RecreationMihail RonnyNo ratings yet