Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Educ Tech 2 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
SerryAlbercaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Educ Tech 2 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
SerryAlbercaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 2
TECHNOLOGY IN TEACHING AND LEARNING
Dajotoy, Joey / Cavity, Arcelie / Hitalia, tiny Roselyn / Carmen, Flora Mae
Salvador, Niño / Paredes, Mernalyn / Balaba, Shielarose
This chapter introduces the standards that administrator, teachers, and students should observe in the use and integration of
technology in education. This chapter also explains how one entity of Tech – PACK is connected and interfaced with the other
entities. Likewise, it shows how the Tech – PACK process works in integrating technology in education.
Intended Learning outcome
At the end of this chapter, you are expected to :
Design a plan assisting teachers in the integration of technology in instruction
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR TECHNOLOGY IN EDUCATION (ISTE)
In every project that we need to accomplish, we specifically design and enumerate the guidelines, criteria, or specification
which meet our standards and eventually say,”Most like the way I want it” and It turns out to be perfect for us.
Like in constructing your dream house, you would ask the architect to design you according to your needs and likes, you
would choose a materials that are quality , you make sure that the carpenters and workers are thinking their job well to meet
you standards and acquiring beautiful furniture that will beautify in-doors of house this in the end will give you contenmentand
comfort for living our own house.
In choosing catering service for your party, you would select the one that serves savory dishes, with clean serving utensils
and crew that are alert and respectful. In this way, you do not satisfy yourself in terms of the entirety of the party but also your guests.
Another example is children being sent to school by their parents. The parents would see it that the school gives quality
education that will highly benefit their children. Quality education encompasses teaching strategies and pedagogies, assessments and
the facilities that support children’s learning. Having standard in teaching and learning help meet the needs and improvement of
children’s knowledge and skills.
Setting standards helps us achieve quality output may it be in house, office, and school. This in turn will give us fulfillment in
our activities for our family, friends, staff, heads, people in the society and the community.
In education, administrator and teachers with the support of the national educational departments and organizations define
their standards that would guide and help the students in possessing the knowledge and skills that are required of them to make them
successful learners and professionals in the future.
The use of technology in education is likewise guided by standards to develop among learners the skills that they need to
possess for the 21st century for them to be able to serve not only themselves but the world. This is where the International society for
Technology in Education (ISTE) comes in. ISTE is a nonprofit organization that promotes the use of technology to support and enhance
teaching and learning.
There are three standards that we have been developed by ISTE for better connection and empowerment among
administrators, teachers and students:
Standards for administrators
Standards for Teachers
Standards for students
To better understand these standards set by ISTE, let us first define the term standard.
According to Merriam – Webster’s Learner’s Dictionary, “Standards is an idea or thing used as a measure, norm, or
model in comparative evaluations.” It can also be defined as a level of quality, achievement that is considered acceptable or
desirable; something that is very good and that is used to make judgment about the quality of other things; or something
established by authority, custom, or general consent as a model or example.
According to Dictionary.com,” Standards is a rule or principle that is used as a basis for judgment.”
In other words, “Standards” in incorporating the use of technology in education would mean something that would
serve a guide to assist the administrators, teachers, and learners in achieving quality and excellence in teaching and learning.
Below are the following ISTE standards for administrators, teachers, and students. For more information on ISTE
standards, visit http://www.iste.org/standards.
ISTE Standards for Administrators
Administrators are the lead supporters of digital and technology-rich teaching and learning environment. They lead in the
transformation of educational system with the affirmation that these technologies make teaching and learning more engaging,
interesting, inspiring, reflecting and empowering.
Visionary Leadership. Being visionary leaders, they inspire and engage stakeholders in the development, communication,
and implementation of educational transformation with the use of digital and technological resources which are aligned
with the shared vision.
Digital age learning culture. Education administrators lead in creating, promoting, and upholding digital age educational
environment culture. They ensure the effective use of digital tools and technological resources in meeting the diverse needs
of learners and help them to be more innovative, creative, and efficient in learning.
Excellence in professional practice. Educational administrator ensure healthy and professional growth in technology fluency
and integration among educators to help enhance students’ learning. Further, educational administrator keeps themselves
informed with the changes and updates in technology that are beneficial in teaching and learning.
Systematic improvement. Educational administrators also extend leadership in the improvement of the department,
organization, and school through the promotion and effective use of information and technology resources which make the
daily operations easy and efficient.
Digital citizenship. Educational administrators ensure, promote, and model ethical use of information and communication
technology following policies and legalities of technology.
ISTE Standards for Students
Acquisition of knowledge is not the only reason why students go to school. Developing and improving of skills are
likewise the goals of the learners. Teachers facilitate student’s cognitive, effective, and psychomotor learning to enable the
students to be life-ready and world-ready. With the ISTE Standards, students are more guided in learning both knowledge and
skills that will soon make a big contribution to the community and society.
Creativity and innovation. Students exhibit constructive learning by generating new ideas out of the existing knowledge. They
create, explore, develop, and innovates products with the help of technology.
Communication and collaboration. Students make use of a variety of technological tools and digital media to effectively converse,
interact, disseminate information, communicate, and collaborate with their peers to work on their school projects and other
tasks.
Research and information fluency. Students utilize digital and technological tools to search and select for data and information,
organize process, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information. Students likewise produce the processed reports with the aid of
the digital and technological tools.
Critical thinking, problem solving, and decision making. Students use appropriate digital and technological tools in practicing
their creative and critical thinking skills to identify problems, plan, investigate, collect, process, analyze information in developing
solutions to help in decision making.
Digital citizenship. Students practice ethical, legal, and responsible use of information, communication, and technology in learning
and production of outputs.
Technology operations and concepts. Students exhibit awareness and knowledge in the effective selection and usage of
technology which allow them to learn, improve, and innovate.
The Significance of Standards
Standards are criteria that define what is expected from the administrator, teachers, and learners.
How to lead teachers and learners in the effective use of technology in teaching and learning; how to create a
Administrator culture of innovation to achieve excellence in education ; how to promote the positive integration of technology
into teaching and learning.
Content to teach; meeting the requirements of the curriculum; how to teach the lessons; how to assess the
Teachers learners; hoe to integrate technologies into teaching.
How learners learn; how learners acquire knowledge and skills; how well learners perform; how learners create,
Learners innovate, collaborate and communicate with the use of technologies; how to integrate technologies into
learning.
The set standards would be futile if these are not demonstrated by
the people involved in the implementation. The administrators,
teachers and learners must be compliant with the standards to
achieve high quality service, teaching, and learning. Moreover,
being compliant or noncompliant is associated with consequences.
This is the question of what will be done to those who have
complied and failed to comply with the standards – (compliant)
Teachers’
Learners’
giving of incentives and positive remarks; and (noncompliant)
giving of remedial instructions and delays or limited opportunities.
It is just enough to remember that having standards like of the
technology standards of ISTE, provides expectation from the
administrators, teachers and technology regarding the knowledge
and skills that each one should acquire while performing
competency in technology integration within the teaching and
learning process. Study Figure 2.1. Discuss the relationship of
Administrator
Figure 2.1 Standards of the Integration of technology standards with the teaching and learning process.
Technology in Teaching and Learning Standards
Standards
ator
TECHNOLOGICAL PEDAGOGICAL CONTENT KNOWLEDGE (TPACK) AND TECHNOLOGY INTEGRATION PLANNING (TIP)
Teaching can be associated with soldiers who go to war. Soldiers are being trained and they make a lot of preparation.
Before going to war, they plan for the tactics and strategies to be done; they make sure that they are complete with their
stockpile of ammunition and protection. No soldier will go to war without enough bullets in his pockets. Same with
teaching, teachers are trained on how to teach and manage a class. Before stepping inside the classroom, they have made
their lessons plan on what to teach and how to teach, they make sure that they have all the materials needed for the
lesson. The use of technology is one of the materials that teachers make use to deliver the lesson successfully to their
learners. However, sometimes the use of technology becomes ineffective because of insufficient knowledge on the true
purpose and proper use of such technology. This is why the Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK) by
Mishra, P. & Koeler, M. and Technology Integration Planning (TIP) by Roblyer, M.D & Doering, A.H. came into existence,
to guide teachers on hoe to integrate technology into teaching.
Tech – PACK, previously known as TPCK, later TPACK,
is a framework that integrates technology in education to
help encapsulate the complex interactions among
content, pedagogy, and technology. TPACK provides a
picture of the entire process of technology integration
that helps identify what is essential and what is not in any
discussions of teacher using technology for teaching
subject matter.
According to Mishra & Koehler (2006), the TPACK
Framework which is shown in Figure 2.2, “emphasizes the
connections, intercations, affordances, and constarints
between and among content, pedagogy, and technology.
In this model, it shows that content (C), pedagogy (P), and
Technology (T) are the three main components of
tecahers knowledge. Looking at the model closely, it
shown the interactions between and among the bodies of
knowledge: PCK (Pedagogical Content Knowledge), TCK
Figure 2.2 TPACK and its Knowledge Components (Technological Content Knowledge), TPK (Technological
Source:www.tpack.org Pedagogical knowledge), and TPACK (Technological
Pedagogical Content Knowledge) which are significant in
making teaching and learning with the use of technology a success.
Content Knowledge (CK)
Teacher’s knowledge about the subject matter
Includes concepts, theories, ideas, organizational, frameworks, evidences, and proofs, stablished, practices and
approaches toward developing such knowledge (Shulman, 1986)
Having no comprehensive knowledge in content may cause erroneous information to learners, thus may develop
misconceptions about the subject matter.
Pedagogical Knowledge (PK)
Teacher’s deep knowledge about the process and practices or methods of teaching and learning.
This includes lesson planning, classroom management skills, understanding how students learn, and student
assessment.
A teacher with profound pedagogical knowledge facilitates student’s construction of knowledge and acquisition of
skills, and helps students in developing habits of mind and positive dispositions toward learning.
Therefore, understanding of cognitive, social, and developmental theories of learning and how they apply to
students in the classroom are requisites of pedagogical knowledge.
Pedagogical content knowledge (PCK)
Covers conditions that promote learning: teaching, learning, curriculum, assessment, reporting, and pedagogy.
There is transformation of the subject matter for teaching which happens when teacher interprets the subject
matter.
Technology knowledge (TK)
The definition of TK is fluid due to its fast updates and upgrades that happen from time to time. However,
technology applies to all technological tools and resources.
Understanding of technology which is beyond the definition of computer literacy is a must in TK. Thus, essential
appreciation and mastery of information technology for information processing, communication, and problem
solving are important.
Technology Content Knowledge (TCK)
TCK is an understanding of the way in which technology and content affect and restrict one another.
This overlap explains that teaching is more than the subject matter they teach; they must also have a profound
knowledge on the way how subject matter can be taught through the use of particular technologies.
Teachers need to figure out which specific technologies are appropriate in delivering the subject-matter to have a
better understanding and appreciation of the lesson.
This allows us to determine the suitable pairing of appropriate technology to the content or vice versa.
Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK)
TPK is an understanding of how teaching and learning can change when particular technologies are used in
particular method.
The fucos of this TPK is to have an understanding of the affordances of technology and how they can influence
differently the context and intentions of teaching.
Teachers have to look beyond the normal functions of techonology, they have to be creative and think of other
possible things that this technologies can do to achieve advancement in the learning and understanding of the
students.
Technological Pedagogical Content knowledge (Teck-PACK)
Tech-PACK shows interactions among the main components of knowledge-content, pedagogy, and knowledge.
Tech-PACK is the basis of effective teaching with technology.
The relationship among the components of knowledge are interfaced with one another to have a stronger
content, more effective pedagogy and efficient technology that may remedy difficulties in teaching and learning
to develop higher comprehension and better learning.
“Context”
This is the outer-dotted circle which highlights the understanding that technology, pedagogy, and content do
not exist in a vacuum, but rather, are represented in specific learning and teaching context.
Technology integration planning (TIP)
Technology integration planning (TIP) is a model created for teachers as a guide that ensures the effeciency of
integration of technology in education. TIP gives teachers a systematic way to indentify and address challenges involved
in integrating technology into teaching practices (Roblyer & Doering, 2013, p. 52)
Further, TIP Model shows teachers how to establish a milieu in which technology can effetually enrich learning.
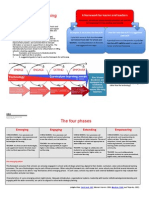
In the earlier editions of TIP model, there were five to six phases to enable the teachers successfully integrate
technology in instruction. In the recent edition (6th), it boils down into three phases with sub steps in each phase (as
shown in Figure 2.3).
Phase1: Analysis of learning and teaching
Needs
Step 1: Determine the relative advantage
Focus: will a technology-based method
offer relative advantage?
Heraclitus once said that nothing is
permanent in this world except change. But,
some people resist to change things that they
are used to doing because according to them
they still able to deliver well using the hold
method even if there are new better
approaches to achieve the task. However,
change may be acceptable if they would
understand the advantages of the new
method over the old one. This is seeing a”
relative advantage” as mentioned by Everett
Rogers ( Diffusion of innovation, (1995).
Below are the measures to see relative
advantage easier:
1. Compatibility- method consistent with
their cultural values and beliefs and others
adopted in the past. For example, teachers
see using technology as compatible with
their views of being an updated teacher.
2. Complexity- easy enough for them to
learn and to carry out on a frequent basis.
Teachers who use technology-based
method feel no fear and find difficulties in
understanding and learning something new.
3. Triability- being able to try out a little
before making a final decision. Teachers have the courage to try using and applying technology-based methods
than saying no to it outhright.
4. Observability- seeing others they respect or emulate using the method successfully. Observation is one of the
many ways to help teachers decide whether technology-based method will be helpful or not or if it is effective
or not.
At this phase, teachers do curriculum review and assessment of teaching methods, then, they determine
problems in instruction and find out which technology may be helpful to remedy the problem.
Summary of issues to address the step 1
1. Are there any topics or curriculum objectives I have difficulty teaching?
2. Do any of these instructional problem areas have technology-based solution?
3. What is the relative advantage of the technology-based solutions?
4. Is the relative advantage sufficient to justify the effort involved?
Step 2: Assess tech-pack
Focus: what is my technological pedagogical content knowledge (tech-PACK)?
Teachers have to be proficient in content, pedagogy and technology before the day of instruction comes.
The teacher has to spend time in understanding all the components of knowledge to have a better and
successful delivery of the lesson. Being knowledgeable of the content, pedagogy and technology will make the
teacher confident in the entire process of teaching and of learning. This Tech-PACK helps to emphasize
technology contribution to teaching. (Review the Tech-PACK discussed earlier in this chapter)
Summary of issues to Address in Step 2:
1. Do I have the mastery of the subject matter, both the content and its context?
2. Is the pedagogy I am planning to employ appropriate for the subject matter, my learners and technology?
3. Is the technology I am planning to use appropriate for the subject matter, pedagogy, and my learners?
4. Have I reviewed my TPACK?
Phase 2: Planning for integration
Step 3: Decide on objective, assessments
Focus: How will I know students have learned? Teachers define the skill they want their students to possess
upon learning the lesson and create ways to measure the authenticity of students’ learning and how successful
the activities have been carried out by them.
The problems that have been identified in phase 1 must be addressed successfully by defining observable and
measureable outcomes. Then, teachers design activities or performance tasks to measure the outcomes.
Teachers must remember that having more than the multiple choice activities is better to effectively see
authentic learning among learners.
Summary of issues to addressed in step 3
1. What kind of performances do I expect from students to show they learned?
2. What is the best way for me to assess student learning progress and products?
3. Do the desired instrument exist or do I have to develop them?
4. What other method could gauge success? (eg.g observations, attitude, instruments)
Step 4: Design integration Strategies
Focus: what teaching strategies and activities will work best? Teachers decide on pedagogies and study its execution.
In deciding on the instructional course of action, the characteristics of the topic and the needs of the students
are being taken into consideration whenever teachers create an instructional design for technology integration.
With this, teachers make decision on:
1. Instructional approaches- traditional or constructivist approach
2. Curriculum approaches- single subject approach or interdisciplinary approach
3. Grouping- from individual to pair or group learning
4. Sequence- must have acquired technology prerequisite skills to successfully learn from the resources
Summary of issues to addressed in step 4
1. Should instruction be directed, constructivist, or a combination of both?
2. Will the instruction be single subject or interdisciplinary?
3. Should activities be individual, paired, small group, or whole class?
4. What strategies should I use to encourage female and minority student to be integrally involved with the
technologies?
5. What sequence of activities should I teach?
6. Have I built in demonstrations of the skills students will need to use both equipment and the specific software?
7. Have I allowed students enough time to get used to materials before beginning a graded activity?
Step 5: Prepare instructional Environment
Focus: are essentials conditions in place to support teaching and learning? Teachers establish the educational
environment to carry out effectively the plan of using technology in teaching and learning.
With the support of international society for technology in education (ISTE) the teachers will be guided in setting
the essential standards to unleash at its level best the potential of technology tools and method when used in
teaching and learning. Teachers have to remember the integration of technology in education would only be
successful if there is an adequate hardware, software, and technical support available.
Summary issues to address in step 5
1. What are the technological needs necessary to carry out the activities (e.g. computer software, printer,ect.)?
2. Is the supply of the computers and copies of software enough to carry out the activities?
3. When and how long when the technology resources be needed?
4. Do I need to set the schedule for occupancy of laboratory or media center?
5. Will projection devices or large screens be needed for demonstrations?
6. Have I checked out the legalities of the uses of technology I want to make?
7. Have I looked into students’ privacy and safety in carrying out the activities?
8. Have I considered the necessary provisions for students with physical disabilities in carrying out the activities?
9. Am I knowledgeable in troubleshooting if ever problems arise during the activity?
10. Have I set and tested everything that is needed before the student to the activity?
11. Do student already have the knowledge in using the technologies that they will be using for the activity?
12. Am I already with a backup plan whenever the plan resources fail to work?
Phase 3: post instruction analysis and Revisions
Step 6: Analyze results
Focus: what work well? What could be improved? Teachers have to spend time reflecting and assessing themselves to
determine whether the integration of technology and if all processes in teaching and learning went on smoothly
and have been successful in the delivery.
Summary issues to address in step 6
1. Was there a change in the behavior of the student upon learning the subject matter?
2. Were the students engaged in the instruction and task given?
3. Did the technological work well as expected?
4. Did the student work deeply and thoroughly in the teaching and learning environment?
5. Is the integration of the technology in education, instructions, strategies, activities, assessments work well in the
entire teaching and learning process?
Step 7: Make revisions
Focus: should I make the revision? After analyzing the result, it is important to determine the necessary areas which
need improvement for better execution of instruction with technology integration the next time around.
Summary issues to address in step 7
1. What pedagogy should I do to make the instruction more interesting and engaging?
2. What technology resources should I used next time for better understanding of the lesson?
STRATEGIES OF TECHNOLOGY INTEGRATION IN TEACHING AND LEARNING
In every cycle, anything and everything begins with the first stage. Before a butterfly begins to spread its wings
to fly, it passes through different stages from a tiny egg to a beautiful insects with wings. A teacher likewise passes
through different stages of teaching from novice to proficient, to distinguished or expert teacher. A teacher move on
from one stage to another based on his experiences, achievement, increased knowledge and skills, and developing
characteristics. Same is true when it experiment on how technology can be integrated in instruction until he understand
fully the appropriate use of technology in instruction.
The following are the different stages of technology integration
Beginning stage Developing Stage Proficient stage Transformative stage
Teachers will make use of Teachers plan, manage, Teachers demonstrate and model Teachers engaged with
chalkboards, textbooks, and facilitate student effective use of a variety of existing students to explore and
workbooks, handout, understanding of and emerging technology-based determine appropriate uses
worksheets, in their technologies and other resources to encourage in a range of existing and emerging
instructions and activities resources best suited to of learning experiences. technology-based resources
despite the presence of the support specific learning so that student may
selected technologies and experiences. effectively plan, manage, and
other resources that support evaluate their learning
student learning experience. experiences.
Teachers research and Teachers facilitate and Teachers model creativity and Teachers collaborate with and
discuss strategies students guide students as they knowledge construction and involve students as leads
can use to promote employ strategies to enable students to demonstrate learners to engage with
knowledge construction and construct knowledge and creativity and innovation. activities to promote in
demonstrate creativity. They promote creative thought; Teachers advocate for and creativity and innovation and
monitor safe, ethical, legal, they model safe, ethical effectively instruct students in the explore complex issues. They
and healthy use of legal, and healthy use of safe, legal, ethical, and healthy use engage students as active
technology and information technology and of technology and information participants in the safe ,
resources information resources and resources including emerging ethical, legal, and healthy use
help student address policies and practices related to of technology and
threat to security of issues such as security, intellectual information resources by
technologies, data and property , and personal rights encouraging them to establish
information policies and procedures for its
use and determining methods
to address its misuse
Teachers use and modify the Teachers adapt or create Teachers design and customized teachers collaborate with
existing learning resources to instructional activities that instructional activities in response students to identify and
redesign instructional and allow student to collect and to student learning styles, develop personalized
learning activities for student report information through preferences, and abilities so that instructional activities that
learning. a variety of products and student develop questions, allow student to formulate,
formats. Teachers and propose solutions, and, elicit evaluate, and test hypotheses
develop and conduct feedback on their learning. to address complex problems
formative and summative Teachers provide students with that address real-world local
assessment to inform various opportunities to and global issues with their
teaching learning. demonstrate skills and knowledge teachers, other students,
to adapt future teaching and outside expert and share their
learning opportunities. information for real world
application
You might also like
- Ethics IntroductionDocument33 pagesEthics IntroductionExekiel Albert Yee Tulio100% (1)
- Portfolio Part3cDocument13 pagesPortfolio Part3capi-579167947No ratings yet
- ISTE Standards for Educators: A Guide for Teachers and Other ProfessionalsFrom EverandISTE Standards for Educators: A Guide for Teachers and Other ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Difficulties in Learning VocabularyDocument3 pagesDifficulties in Learning Vocabularyguccirush297% (32)
- The Evolution of Instructional Technology: Overcoming Apprehension About the Use of Technology in the Classroom for InstructionFrom EverandThe Evolution of Instructional Technology: Overcoming Apprehension About the Use of Technology in the Classroom for InstructionNo ratings yet
- ArtifactsDocument45 pagesArtifactsapi-418341355100% (1)
- Sven Ove Hansson, Gertrude Hirsch Hadorn Eds. The Argumentative Turn in Policy Analysis Reasoning About Uncertainty PDFDocument354 pagesSven Ove Hansson, Gertrude Hirsch Hadorn Eds. The Argumentative Turn in Policy Analysis Reasoning About Uncertainty PDFakerrp100% (2)
- DELF B1 SyllabusDocument6 pagesDELF B1 SyllabusRaji RaviNo ratings yet
- Teacher of 21 Century: Characteristics and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesTeacher of 21 Century: Characteristics and DevelopmentRafsan WakanoNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Instructional MaterialDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Instructional MaterialJheramae SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Educational Technologies and Its Current ApproachesDocument55 pagesEvaluation of Educational Technologies and Its Current ApproachesMarinell Gamido100% (1)
- GrashaDocument9 pagesGrashaLisha LiuNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders Powerpoint MMCDocument220 pagesPersonality Disorders Powerpoint MMCEmilee Joice Rochelle Maluto100% (1)
- Nature of Educational TechnologyDocument43 pagesNature of Educational TechnologyJustin Kylo-Marc Manuben Orpia100% (1)
- Clil Activities Planing-1Document3 pagesClil Activities Planing-1Sonia Felipe MartínezNo ratings yet
- Transform Learning Through Technology: A Guide to the ISTE Standards for CoachesFrom EverandTransform Learning Through Technology: A Guide to the ISTE Standards for CoachesNo ratings yet
- Bsed 3 Technology For Teaching and Learning 2Document2 pagesBsed 3 Technology For Teaching and Learning 2Laarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- ISTE Standards for Students: A Practical Guide for Learning with TechnologyFrom EverandISTE Standards for Students: A Practical Guide for Learning with TechnologyNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Planning FrameworkDocument9 pagesE-Learning Planning Frameworkapi-240128777No ratings yet
- Education Reimagined: Leading Systemwide Change with the ISTE StandardsFrom EverandEducation Reimagined: Leading Systemwide Change with the ISTE StandardsNo ratings yet
- ICT IntergrationDocument16 pagesICT IntergrationWAGAYEN , MarvenNo ratings yet
- Iste StandardsDocument16 pagesIste StandardsCindy May Paguyan MolinaNo ratings yet
- The Seven Roles For Teachers Under The ISTE StandardsDocument8 pagesThe Seven Roles For Teachers Under The ISTE Standardskaren rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Background and MotivationDocument29 pagesBackground and MotivationAkash DidhariaNo ratings yet
- W Cordy Vision PaperDocument6 pagesW Cordy Vision Paperapi-253462692No ratings yet
- Nets-T (Matirces For Teachers' and Students' AssessmentDocument16 pagesNets-T (Matirces For Teachers' and Students' AssessmentLeidyaospinaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Digital Learning GuideDocument32 pagesTeacher Digital Learning GuideFredd Ivan Tipismana BecerraNo ratings yet
- Section ThreeDocument15 pagesSection Threeapi-365937447No ratings yet
- Practica SuplementDocument6 pagesPractica Suplementcarmen joseNo ratings yet
- EDLD 5398 ETL Reflections I-VIII Kimberly McKayDocument11 pagesEDLD 5398 ETL Reflections I-VIII Kimberly McKaykjmckay915No ratings yet
- National Educational Technology Standards (Tic) For Teachers (2008) (NESTS.T)Document16 pagesNational Educational Technology Standards (Tic) For Teachers (2008) (NESTS.T)noralba89No ratings yet
- Section 3 Part 2Document14 pagesSection 3 Part 2api-547409083No ratings yet
- Educ-205 Chapter6Document12 pagesEduc-205 Chapter6Marita TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Section Three - Artifact TwoDocument9 pagesPortfolio Section Three - Artifact Twoapi-419006824No ratings yet
- Allgood Shared Vision & RationaleDocument12 pagesAllgood Shared Vision & Rationaleapi-233678602No ratings yet
- 1 Running Head: Shared Vision & RationaleDocument8 pages1 Running Head: Shared Vision & Rationaletia reynoldsNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document16 pagesWeek 3api-287042551No ratings yet
- TTL 1-Lesson 1Document14 pagesTTL 1-Lesson 1Jenny HermosaNo ratings yet
- Technology Standards For School Administrators An Analysis of Practicing and ...Document17 pagesTechnology Standards For School Administrators An Analysis of Practicing and ...radhwamegannyNo ratings yet
- The Use of Instructional Materials in TeDocument3 pagesThe Use of Instructional Materials in TeOLIVEROS, Reiner Joseph B.No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Iste Standards For EducatorsDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Iste Standards For Educatorsapi-742477080No ratings yet
- Tech Integration Matrix 1Document7 pagesTech Integration Matrix 1api-307498864No ratings yet
- National Educational Technology Standards (Tic) For TEACHERS (2008) (NESTS.T)Document7 pagesNational Educational Technology Standards (Tic) For TEACHERS (2008) (NESTS.T)noralba89No ratings yet
- ISTE National Educational Technology Standards For Students (NETSFS)Document23 pagesISTE National Educational Technology Standards For Students (NETSFS)Shairon palmaNo ratings yet
- How Will you-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesHow Will you-WPS OfficeAngelica TalastasinNo ratings yet
- Pointers To ReviewDocument8 pagesPointers To ReviewNouriella RaquipoNo ratings yet
- Ed-Tech 2 - Module #2Document2 pagesEd-Tech 2 - Module #2Jhack SonNo ratings yet
- Saint Theresa College of Tandag, Inc.: Learning Module in Educ 11 - Educational Technology 2Document4 pagesSaint Theresa College of Tandag, Inc.: Learning Module in Educ 11 - Educational Technology 2Imelda Ombat RosarioNo ratings yet
- ICT Competencies and Standards For AdministratorsDocument16 pagesICT Competencies and Standards For AdministratorsKathrina Escarate FelicidarioNo ratings yet
- ICT Competencies and Standards For AdministratorsDocument16 pagesICT Competencies and Standards For AdministratorsKathrina Escarate FelicidarioNo ratings yet
- Standard 1Document2 pagesStandard 1api-370169875No ratings yet
- Copyright and Fairuse MatrixDocument8 pagesCopyright and Fairuse Matrixapi-299929193No ratings yet
- Artifact 8Document5 pagesArtifact 8api-515705518No ratings yet
- Et 247 Matrix 1Document11 pagesEt 247 Matrix 1api-316948987No ratings yet
- Blog Template t6-12Document8 pagesBlog Template t6-12api-291958931No ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToDocument11 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToSuga MinNo ratings yet
- Tech Integration Matrix 4Document9 pagesTech Integration Matrix 4api-316351511No ratings yet
- Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument28 pagesTechnology For Teaching and LearningNeilchoi MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Overview and ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOverview and Objectivesjonah julampongNo ratings yet
- Vision Paper RevisedDocument12 pagesVision Paper Revisedapi-364437018No ratings yet
- Tech Intergration Matrix - RecoverDocument8 pagesTech Intergration Matrix - Recoverapi-285302242No ratings yet
- Et347 Eportfolio MatrixDocument6 pagesEt347 Eportfolio Matrixapi-316927427No ratings yet
- Rethinking Education 2020Document18 pagesRethinking Education 2020Jose Jonathan Advincula BitoyNo ratings yet
- Et 247 Matrix 4Document8 pagesEt 247 Matrix 4api-299929193No ratings yet
- Apple Iste Nets TeachersDocument1 pageApple Iste Nets Teachersapi-302824565No ratings yet
- Education Aligned With TechnologyDocument13 pagesEducation Aligned With Technologyvigneshsri764No ratings yet
- Technology UtilizationDocument3 pagesTechnology UtilizationMary Cres Deguma OtazaNo ratings yet
- Case ProblemDocument1 pageCase ProblemSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- 1narrative 1 3rd Grading CulmanitionDocument1 page1narrative 1 3rd Grading CulmanitionSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Serry Javier Alberca Application LetterDocument1 pageSerry Javier Alberca Application LetterSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- All Over The WorldDocument5 pagesAll Over The WorldSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Masa Inc., #36 Kamias Road. Corner K-H Street Brgy. West Kamias, Quezon City Tel. 3515018Document1 pageMasa Inc., #36 Kamias Road. Corner K-H Street Brgy. West Kamias, Quezon City Tel. 3515018SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Aerial PlantsDocument1 pageAerial PlantsSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- What Is Plan ?Document2 pagesWhat Is Plan ?SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. FORUM & WEBINAR Objective: This Activity Will Allow The Students To Experience Some Communication Tools That Are UsefulDocument5 pagesActivity 1. FORUM & WEBINAR Objective: This Activity Will Allow The Students To Experience Some Communication Tools That Are UsefulSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Educ Tech 2 Chapter 9Document3 pagesEduc Tech 2 Chapter 9SerryAlberca0% (1)
- 9 1 18Document1 page9 1 18SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Alberca, PROGRESS CHARTDocument1 pageAlberca, PROGRESS CHARTSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Chart IN Fundamentals of Electricity: FIRST GRADING PERIOD, S.Y. 2018-2019Document1 pageAnalysis Chart IN Fundamentals of Electricity: FIRST GRADING PERIOD, S.Y. 2018-2019SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- A Synchronous Motor From A Hammond OrganDocument1 pageA Synchronous Motor From A Hammond OrganSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- 488075Document2 pages488075SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Iser 2012 SolarDocument7 pagesIser 2012 SolarSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Educ Tech 2 Chapter 8Document2 pagesEduc Tech 2 Chapter 8SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. FORUM & WEBINAR Objective: This Activity Will Allow The Students To Experience Some Communication Tools That Are UsefulDocument5 pagesActivity 1. FORUM & WEBINAR Objective: This Activity Will Allow The Students To Experience Some Communication Tools That Are UsefulSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- A Biological Definition of SelfDocument1 pageA Biological Definition of SelfSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Words With Multiple MeaningDocument2 pagesWords With Multiple MeaningSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Educ Tech 2 Chapter 12Document2 pagesEduc Tech 2 Chapter 12SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- A Biological Definition of Self PDFDocument5 pagesA Biological Definition of Self PDFSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Architecture: Successful Track Record in The Designing in Our BuildingDocument1 pageArchitecture: Successful Track Record in The Designing in Our BuildingSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Educ Tech 2 Chapter 6Document6 pagesEduc Tech 2 Chapter 6SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Name:Jayford Longos Date:Sept 26,2018 Year & Section:11 Galileo Galilei ScoreDocument1 pageName:Jayford Longos Date:Sept 26,2018 Year & Section:11 Galileo Galilei ScoreSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- A Voltage Regulator Is A System Designed To Automatically Maintain ADocument3 pagesA Voltage Regulator Is A System Designed To Automatically Maintain ASerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- 488075Document2 pages488075SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- 488075Document2 pages488075SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile Control Car1Document12 pagesSolar Mobile Control Car1SerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in T L EDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in T L ESerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- COYNODocument2 pagesCOYNOSerryAlbercaNo ratings yet
- 187294ad60250112ff9 83381519past Simple Story Half EditableDocument1 page187294ad60250112ff9 83381519past Simple Story Half EditableAnn SchwartzNo ratings yet
- How To Utilize Erc Tutorials EfficientlyDocument4 pagesHow To Utilize Erc Tutorials EfficientlyKashato BabyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Techniques of Paninian Grammar - Chetan PandeyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To The Techniques of Paninian Grammar - Chetan Pandeychetanpandey100% (4)
- Brochure RubricDocument1 pageBrochure RubricJulymar Gomez AngcogNo ratings yet
- Religion and Emotion Approaches and Interpretations PDFDocument366 pagesReligion and Emotion Approaches and Interpretations PDFskinnywonderfulmanNo ratings yet
- Whythedrive Theutilitaria Nand Hedonic Benefits of Self-Expression Through ConsumptionDocument6 pagesWhythedrive Theutilitaria Nand Hedonic Benefits of Self-Expression Through ConsumptionVinícius AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Self Activity 1 Do You Truly Know Yourself?Document17 pagesPhilosophical Self Activity 1 Do You Truly Know Yourself?Villanueva ,Samuel M.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Manging Peer PressureDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Manging Peer Pressureandreellina8486No ratings yet
- Silabus Advanced Grammar Semester Genap Tahun Akademik 2020Document7 pagesSilabus Advanced Grammar Semester Genap Tahun Akademik 2020Randi AnimxNo ratings yet
- LDT 4 - Samples of Teacher's LanguageDocument4 pagesLDT 4 - Samples of Teacher's LanguageKarla Rebecca Campos100% (2)
- Maranao Rido: Implicatiom To Education: Asnifah M. Mimbala Hidaya M. AsalanDocument1 pageMaranao Rido: Implicatiom To Education: Asnifah M. Mimbala Hidaya M. AsalanChem R. PantorillaNo ratings yet
- EMBA 7005 Editing ExerciseDocument3 pagesEMBA 7005 Editing ExerciseTara BakerNo ratings yet
- Komal Gidda Portfolio s1Document7 pagesKomal Gidda Portfolio s1api-291603309No ratings yet
- Techniques For Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument15 pagesTechniques For Teaching Listening and Speakingnur atikah IshakNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Prelim Quiz 2 To Prelim ExamDocument21 pagesNSTP 1 Prelim Quiz 2 To Prelim ExamJOSHUA PALMANo ratings yet
- Ethics l2Document34 pagesEthics l2James Maverick Medina CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ReadingDocument7 pagesBenefits of ReadingCeleste GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Foster LP#3. Thirteen Moons On Turtle's BackDocument6 pagesFoster LP#3. Thirteen Moons On Turtle's Backfostersds1No ratings yet
- A Project Report On Recruitment and SeleDocument73 pagesA Project Report On Recruitment and SeleOn Point management serviceNo ratings yet
- Ficha para Vacaciones InglésDocument7 pagesFicha para Vacaciones InglésSergio TupiñoNo ratings yet
- Data GeneralizationDocument5 pagesData GeneralizationRavindra Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- DLP Cot English-Q3Document8 pagesDLP Cot English-Q3dhinaNo ratings yet
- Passivity and MotivationDocument10 pagesPassivity and MotivationemysamehNo ratings yet