Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SM PC300-8 SN01983-01
Uploaded by
aldy yasiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SM PC300-8 SN01983-01
Uploaded by
aldy yasiCopyright:
Available Formats
05:01-01
Issue 1.1 en
Gearbox
GR801
GR900
GRS890
GRS900
GRS920
GRSH900
GRSO900
Function Description
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
1 714 640
Contents
Contents
Function Description GR801....................................................................... 3
GR900....................................................................... 4
GRS900 .................................................................... 5
GRS890 .................................................................... 6
GRS920 .................................................................... 6
GRSO900 ................................................................. 7
Operation .................................................................. 8
Main gearbox............................................................ 9
Synchromesh .......................................................... 13
Planetary gear ......................................................... 18
Selector housing ..................................................... 22
Gearshift housing.................................................... 23
Range and splitter gears.......................................... 24
Neutral position valve (3/2 valve) .......................... 29
Splitter gear interlock valve.................................... 29
Inductive rotation speed sensor with overspeed
protection................................................................ 30
Gear lever knob ...................................................... 31
Lubrication system ................................................. 32
Gear changing......................................................... 33
Power flow for different gears, main gearbox ........ 35
Specifications Ratios...................................................................... 39
Power take-off ........................................................ 43
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
2 05:01-01
GR801
Function Description
GR801
GR801 is an 8-speed gearbox which comprises Gears are changed by first stepping through all
a 4-speed main gear section and a planetary the main gears with the planetary gear low gear
gear section. engaged (low range), after which the procedure
is repeated with the planetary gear high gear
The gearbox is a range-type gearbox, which engaged (high range).
means that the main gear section has close gear
steps and the planetary gear has a low-speed The gearbox can be used together with CS
and a high-speed range. (Comfort Shift) or CAG (Computer Aided
Gear change). With CS, only seven of the eight
gears on the gearbox are used.
1 Input shaft 6 Planetary gear
2 Synchromesh, third and fourth gear 7 Oil pump
3 Mainshaft 8 Layshaft
4 Synchromesh, first and second gear 9 Reverse gear shaft
5 Selector housing
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 3
GR900
GR900
GR900 is a 9-speed gearbox which comprises a Gears are changed by first stepping through all
4-speed main gear section and crawl gear as the main gears with the planetary gear low gear
well as a planetary gear section. engaged (low range), after which the procedure
is repeated with the planetary gear high gear
The gearbox is a range-type gearbox, which engaged (high range).
means that the main gear section has close gear
steps and the planetary gear has a low-speed In low range a crawl gear is also available
and a high-speed range. resulting in a total of nine gears.
1 Input shaft 4 Planetary gear section
2 Gearshift housing 5 Layshaft
3 Mainshaft
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
4 05:01-01
GRS900
GRS900
GRS900 is a 14-speed gearbox which Gears are changed by first stepping through all
comprises a 3-speed main gear section with the main gears with the planetary gear low gear
integrated splitter gear and crawl gear as well as engaged (low range), after which the procedure
a planetary gear section. is repeated with the planetary gear high gear
engaged (high range).
The gearbox is a range-splitter type gearbox,
which means that the main gear section has Each gear in turn can then be split again by
close gear steps and the planetary gear has a means of the splitter gear, which means that 12
low-speed and a high-speed range. gears are available. In low range, a crawl gear is
also available which can be split via the splitter
gear, resulting in a total of 14 gears.
1 Planetary gear section 5 Layshaft
2 Mainshaft 6 Power take-off
3 Gearshift housing 7 Range gear
4 Input shaft
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 5
GRS890, GRS920
GRS890
GRS890 is a close-ratio 12-speed gearbox The differences are found in the mainshaft;
which is derived from GRS900 but has no GRS900 has a gear wheel with a needle
crawl gear. bearing for the crawl gear, whereas GRS890
has a spacer sleeve (see illustrations).
GRS900
GRS890
102141
Difference between GRS900 and GRS890
GRS920
GRS920 is identical to GRS900, but designed The difference between GRS900 and GRS920
to cope with the ever-increasing torque levels is in the gear wheels for 1st, 2nd and 3rd gears,
produced by modern engines. where the manufacturing method and the
material are different.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
6 05:01-01
GRSO900
GRSO900
Z 36
Z 32
Z 31
Z 34
1
133 809
1 High split
Oil collector
2 Low split
GRSO is a gearbox with overdrive, which means places on it. The number of teeth on the input
that at least one gear has a gear ratio lower than shaft has been increased to 36 and the number of
1:1. teeth on the layshaft gear has been reduced to
31. This has changed the gear ratio from 1.23:1
This results in the output shaft rotating faster to 0.81:1 (overdrive).
than the input shaft in top gear, and this makes it
possible to drive faster at lowers engine speeds. In addition, an oil collector has been added to
ensure lubrication of the splitter gear wheels.
GRSO900 is basically the same gearbox as
GRS900 but low and high split have changed
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 7
Operation
Operation
The main gearbox unit has synchromesh on all
forward gears apart from the crawl gear. The
main gears and the crawl and reverse gear are
selected manually with a lever.
See also service information for "Gearshift
housing".
Gearshift housing
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
8 05:01-01
Main gearbox
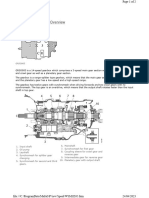
Main gearbox
The main gearbox has four shafts: Input shaft, mainshaft, layshaft and reverse gear shaft. All the gear
wheels in the gearbox are bevel cut.
1 Input shaft 5 Oil pump
2 Gearshift housing 6 Layshaft
3 Mainshaft 7 Reverse gear shaft
4 Selector housing
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 9
Main gearbox
Input shaft
The input shaft is seated in two tapered roller
bearings. The front one is supported by the front
end plate of the gearbox housing and the rear
one by the front end of the mainshaft. The shaft
is also supported by a ball bearing in the centre
of the flywheel.
The shaft is fitted with two piston rings on the
cross-drilled oilway in order to minimize
pressure drops in the lubrication system. The
needle bearing is lubricated via drilled channels
from the inside of the shaft.
On gearboxes with a splitter gear, the splitter
gear synchromesh hub is connected to the shaft
via a splined joint. The high split gear wheel on
GRSO900 and the low split gear wheel for other Input shaft. The arrows show the piston rings.
splitter gearboxes is seated on a needle bearing.
Reverse gear shaft
The reverse gear shaft is located to the left of the
layshaft. The shaft is firmly fixed in a bracket in
the gearbox housing and in the rear end plate of
the gearbox housing.
The reverse shaft gear, which provides the
mainshaft with the reverse direction of rotation
when reverse gear is engaged, is located on the
shaft. The gear wheel is seated on a needle
bearing and is splash lubricated. Earlier versions
have an oilway in the shaft.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
10 05:01-01
Main gearbox
Mainshaft
The front end of the mainshaft is seated in a
tapered roller bearing in the input shaft and the
rear end is seated in a tapered bearing in the
rear end plate of the gearbox housing. The
mainshaft gear wheels are seated on needle
bearings. The low split gear wheel on
GRSO900 and the high split gear wheel on
other splitter gearboxes are seated on two
tapered roller bearings on the mainshaft. Mainshaft, gearbox without splitter gear
The synchromesh hubs for the synchromesh
gears and the driver for the crawl and reverse
gears are connected to the mainshaft via a
splined joint. The sun wheel and the
synchromesh cone for the planetary gear are
fitted at the rear end of the mainshaft with a
splined joint to the shaft.
05_5433
The gear wheel bearings are lubricated through
drilled channels in the shaft.
Mainshaft, gearbox with splitter gear
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 11
Main gearbox
Layshaft
On GR gearboxes the gear wheels for reverse
and crawl gears are milled directly on the shaft.
The wheels for 1st gear, 2nd gear, 3rd gear and
the input shaft are press-fitted on the shaft,
using locking compound in the joints.
On GRS gearboxes the gear wheels for reverse
and crawl gears as well as 1st gear are milled Layshaft, gearbox without splitter gear
directly on the shaft. The 2nd gear wheel and
the gear wheels for the input shaft, low and
high split are press-fitted on the shaft, using
locking compound in the joints.
The layshaft is seated on tapered bearings at
the front and rear walls of the gearbox. A
square drive for the oil pump is fitted at the
05 5545
front end of the shaft. The square drive is
machined directly on the shaft.
Layshaft, gearbox with splitter gear
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
12 05:01-01
Synchromesh
Synchromesh
The main gearbox is equipped with two or three The purpose of the synchromesh is to rapidly
synchromesh units according to the type of bring the gear wheel for the gear concerned to
gearbox. the same speed as that of the mainshaft.
Reverse and crawl gears have no synchromesh This also means that the layshaft, input shaft
and thus only have one coupling sleeve, with clutch disc and other gear wheels on the
engaging directly with the coupling teeth on the mainshaft are brought to a speed which is
respective gear wheel when changing gear. appropriate for the current gear.
05_5649
Gearbox without splitter gear, GR900
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 13
Synchromesh
Single synchromesh
The synchromesh unit for all gears apart from
1st is known as single synchromesh. The driver
with locking roller, plunger and spring, shift
sleeve and latch cone are fitted directly on the
mainshaft.
They always rotate at the same speed as the
mainshaft. However, the synchromesh cones
are fitted via a splined joint on to the mainshaft
gear wheel of the gear concerned.
The shift sleeve has internal splines and can be
adjusted on the driver. The sleeve splines have
a locking unit which fits the teeth of the
synchromesh cone, so that the gear is retained
when torque is applied.
The shift sleeve has an internally turned groove
for the locking rollers. The rollers have two
functions, on the one hand to hold the shift
sleeve in neutral and on the other when 1 Synchromesh cone
synchromesh begins to press the latch cone
towards the synchromesh cone to adjust the 2 Spring
speed of the gear wheel to that of the shaft. 3 Plunger
The synchromesh cone has a ground friction 4 Latch cone
surface with a half-moon shaped groove for 5 Locking roller
draining oil on the cone surface. The latch cone 6 Shift sleeve
has a flame-sprayed friction surface with an oil
7 Driver
drainage groove on the cone surface.
8 Gear wheel
The latch cone and the synchromesh cone have 9 Mainshaft
externally pointed splines, known as locking or
coupling teeth. The latch cone has four external
lugs which mesh with the corresponding
recesses in the driver.
The recesses in the driver are slightly wider
than the lugs on the latch cone. The latch cone
can then be turned slightly so that the teeth of
the shaft sleeve and synchromesh cone do not
coincide, but provide a locking function. This
means that the gear cannot be engaged until the
shift sleeve and the synchromesh cone have the
same speed.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
14 05:01-01
Synchromesh
Double synchromesh
The synchromesh for 1st gear, which is
normally the hardest to engage, is known as
double synchromesh. With double
synchromesh the friction surface is larger,
resulting in more effective synchronisation.
The synchromesh cone, which is fitted on the
synchromeshes of the other forward gears, is
replaced by a coupling disc and an intermediate
cone. Two cone surfaces, one between the latch
cone and the intermediate cone and the other
between the intermediate cone and the inner
cone, make it easier to engage the gear.
The latch cone and the inner cone are
connected via a driver plate. The intermediate
cone is connected to the coupling disc by eight
pins on which the cone can move axially.
1 Shift sleeve
Braking torque is obtained by the latch cone
being pressed against the intermediate cone, 2 Locking roller, 4 off
which is in turned pressed against the inner 3 Latch cone
cone. The intermediate cone, which is 4 Intermediate cone
connected to the coupling disc, is braked and
gear changing is then possible. 5 Pin, 8 off
6 Inner cone
In addition to this, the information provided
about single synchromesh also applies to 7 Coupling disc
double synchromesh. 8 Driver plate
9 Plunger, 4 off
10 Spring, 4 off
11 Driver
12 Mainshaft
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 15
Synchromesh
Gear changing
The illustration on the next page shows in eight
steps how a gear is engaged via synchromesh.
1 A gear change begins when the shift sleeve
is moved towards the latch cone.
2 The shift sleeve presses the cylindrical
roller towards the latch cone. (The
cylindrical roller has another function
which means that it has to centre the shift
sleeve in neutral.)
3 When the cones are pressed towards each
other, the latch cone will follow the
synchromesh cone in one or the other
direction depending on whether the gear is
to be shifted up or down.
The latch cone can only move half a tooth's
width in one or the other direction before it
is prevented from doing so by its four lugs
which run into the corresponding recesses
in the driver. When the shift sleeve has
come so far that the sleeve teeth are resting
with their locking flanks against the
locking flanks on the latch cone teeth, axial
force is transferred to the synchromesh
cone which starts to brake.
4 The shift sleeve can now be moved further
to mesh between the latch cone teeth. This
is possible because the latch cone is turned
out of the way. Since there is still contact
between the cones, when it turns the entire
box will turn.
5 The shift sleeve is moving towards
meshing with the synchromesh cone. The
latch cone has released.
6 When the shift sleeve reaches the
synchromesh cone teeth, the synchromesh
cone turns so that it can start to engage.
7 The shift sleeve can then be moved
onwards so that it meshes with the
synchromesh cone.
8 Gear changing has been completed. Since
both the shift sleeve and the synchromesh
cone have some tapered teeth, the gear is
kept engaged via the locking unit.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
16 05:01-01
Synchromesh
The function of synchromesh during gear changing
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 17
Planetary gear
Planetary gear
General
The planetary gearbox is 2-speed and is combined with the rear section of the main gearbox. Both
high and low gears have synchromesh.
The planetary gear comprises an adjustable internal ring gear with internal teeth and coupling teeth, a
sun wheel which is attached to the mainshaft in the main gearbox and five planet wheels between the
ring gear and sun wheel. The planet wheels are mounted on the output shaft which acts as a planet
wheel carrier at the same time.
Planetary gear, main components
1 Output shaft, main gearbox 6 Synchromesh cone, low
2 Synchromesh cone, high 7 Output shaft, planetary gear
3 Internal ring gear 8 Latch cone
4 Planet wheel (5 off) 9 Sun wheel
5 Selector fork
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
18 05:01-01
Planetary gear
Low range
When driving in the low speed range, the sun
wheel drives the planet wheels. The internal ring
gear, which is stationary, is locked to the planet
gear housing via a fixed coupling disc in the
housing. Since the internal ring gear is
stationary, the planet wheels and planet wheel
carrier with output shaft are forced to rotate,
resulting in the gear being shifted down.
High range
When driving in the high speed range, the
internal ring gear is locked to the sun wheel via
the synchromesh cone which is attached to the
sun wheel via a splined joint. The entire
planetary gear will then rotate as a unit and the
gear will not be shifted down.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 19
Planetary gear
Synchromesh
The planetary gearbox is equipped with a cone-
type synchromesh, whose function is in
principle the same as that of the main gearbox.
The purpose of the synchromesh is to bring the
main gearbox output shaft (mainshaft) to the
same speed as that of the planetary gear output
shaft when high speed range (high range) is
engaged and then low speed range (low range)
is engaged.
The synchromesh comprises two latch cones,
two synchromesh cones and the internal ring
gear which acts as a shift sleeve. One of the
synchromesh cones is attached to the sun wheel
and the other is fitted in the planetary gear
housing. In the internal ring gear there are 12
spring-loaded latch balls, six on each side,
whose task is to adjust the cones to each other
in the initial stage of the synchronisation.
The latch cones can only move half a tooth's
width in one direction in the internal ring gear
and therefore perform the same task as the latch
cones in the gearbox synchromesh. The friction
surfaces of the latch cone and synchromesh
cone are of the same design as those in the
gearbox. 1 Internal ring gear
The internal ring gear, finally, acts as a shift 2 Latch cone
sleeve at the same time. The internal ring gear 3 Synchromesh cone
has coupling teeth on each side to mesh with
the appropriate synchromesh cone. For the 4 Latch ball
synchromesh function, refer to gearbox
synchromesh.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
20 05:01-01
Planetary gear
Operation
During gear changing, the internal ring gear is
moved by means of two diametrically
positioned control cylinders. The control
cylinder selector shafts are connected to each
other via a lever. In a torque-free condition, the
gear is held by two catches which actuate the
lever.
The cylinders are pressurised only in neutral in
the main gearbox. 1 Internal ring gear
2 Lever
3 Selector shaft
4 Control cylinder
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 21
Selector housing
Selector housing
The selector housing is equipped with three or Three spring-loaded plungers are fitted on the
four pivoting forks which are mounted in two top of the selector housing which are intended to
brackets. The main gearbox pivoting forks are hold the relevant gearshift rod when the gear is
actuated from the gearshift housing via selector engaged or disengaged during a torque-free
plates. condition. When torque is applied the gear is
retained by the synchromesh shift sleeve, whose
splines are equipped with a locking unit.
Selector housing, GR gearboxes Selector housing, GRS gearboxes
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
22 05:01-01
Gearshift housing
Gearshift housing
A selector shaft seated on a needle bearing with
a gear selector to operate the main gearbox unit
is fitted in the gearshift housing. A neutral
position valve for operating the planetary gear
is located at the front edge.
At one end of the selector shaft there is a lateral
stroke spring to prevent crawl and reverse gears
from being unintentionally engaged when
driving forwards. There are no lateral stroke
springs between the main gears.
The gear selector, which is screwed on to the
shaft, works in a coulisse to prevent more than
one gear from being engaged.
The neutral position valve is actuated directly
by the gear selector and is designed so that air
is released to the planetary gear's 4/2 valve
when the gear selector is in neutral.
The control cylinder for the splitter gear is
fitted in the rear part of the selector housing
and activates the pivoting fork via a selector
shaft. A 4/2 valve is screwed on to the control 1 Lateral stroke spring
cylinder.
2 Coulisse
A spring-loaded latch ball, which actuates the 3 Neutral position valve
gearshift rod directly from the split cylinder, is 4 Selector shaft
fitted in the reinforcing rib on the underside of
the selector housing. The function of the latch 5 Reversing light switch
ball is to prevent a gear from being disengaged Gearshift housing, gearbox without splitter
during a torque-free condition. When the clutch gear
pedal is released, the control cylinder is
unpressurised.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 23
Range and splitter gears
Range and splitter gears
Wiring diagram and pneumatic diagram for range gear
+L
(−H)
H L
9
5 Range
H L
Range
Range
8
H
L (NO)
7
4
3
+24V
−H
2
1 +24V
05_5648
7 bar
6
= A
= B
= C
1 Output shaft A Air line, pressurised/not pressurised
2 Rotation speed sensor B Air line, pressurised
3 Overspeed protection C Electric cable
4 Splice
5 Range switch
6 Air tank
7 Shift fork
8 Neutral position valve
9 Two range cylinders with one control valve
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
24 05:01-01
Range and splitter gears
Wiring diagram and pneumatic diagram for range and splitter gears, GRS900, GRS890 and
GRS920
+L
(−H)
Split H L
13
6 Range
H L
Range
5
Range Split
12
H H
L L (NO)
11
4
3
Split
H L
+24V
−H
2 10
+L
+24V (−H)
1
9
+
(NC)
7 bar 8
7
05 5168
−NO
+24V
A
1 Output shaft 12 Neutral position valve
2 Rotation speed sensor 13 Two range cylinders with control valve
3 Overspeed protection A Air line, pressurised/not pressurised
4 Splice B Air line, pressurised
5 Range switch C Electric cable
6 Split switch
7 Air tank
8 Clutch pedal switch
9 Solenoid valve (split interlock valve)
10 Split cylinder with control valve
11 Shift fork
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 25
Range and splitter gears
Wiring diagram and pneumatic diagram for range and splitter gears, GRSO900
1 Output shaft 12 Neutral position valve
2 Rotation speed sensor 13 Two range cylinders with control valve
3 Overspeed protection A Air line, pressurised/not pressurised
4 Splice B Air line, pressurised
5 Range switch C Electric cable
6 Split switch
7 Air tank
8 Clutch pedal switch
9 Solenoid valve (split interlock valve)
10 Split cylinder with control valve
11 Shift fork
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
26 05:01-01
Range and splitter gears
Split/range control valve
The control valve, which is of the 4/2 type At the same time the other side of the control
valve, essentially comprises two parts; the cylinder is vented through connections 22 and
valve housing itself with all air connections and 24 on the valve housing and out through the
the magnetic part with electrical connections. vent on the control valve.
There is a spring-loaded valve plunger in the In the actuated condition, the valve plunger is
valve housing which distributes supply air to moved by means of the operating air,
the control cylinder. connection 12, towards the venting side of the
valve housing.
In the unactuated condition, it is therefore the
spring which holds the valve plunger against The supply air passes out in connections 22 and
the magnet side of the valve housing. The 24. Now connections 21 and 23 can be vented
supply air can pass out in connections 21 and instead.
23.
1 Pressure in 22 Pressure out
3 Venting 23 Pressure out
12 Pressure in (pilot) 24 Pressure out
21 Pressure out
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 27
Range and splitter gears
The operating air, which controls the valve In the unactuated condition the operating air is
plunger, is controlled in turn by the magnetic vented through the magnetic part.
part. Inside the magnetic part there is a small
valve cone, which is actuated by the The unactuated control valve provides in any
electromagnet. When the electromagnet case one additional high gear regardless of
operates, the cone opens a connection to the whether it is split or range. The exception is
valve housing. The operating air then GRSO900, on which the unactuated control
counteracts the spring force on the valve valve provides low split.
plunger and moves it towards the venting side
of the valve housing.
Low gear position High gear position
1 Supply air
3 Supply air return
12 Operating air
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
28 05:01-01
Neutral position valve, Splitter gear interlock valve
Neutral position valve
(3/2 valve)
The neutral position valve is actuated
mechanically from a cam which is fitted on the
selector shaft in the gear selector housing.
When the gear is in neutral, operating air can
pass from connection 1 through the valve and
out through connection 2 and on to the range
control valve.
When a gear is engaged, the plunger in the valve
is pressed in and connection 1 closes. At the
same time connection 2 is vented through vent
3. The supply air line is then unpressurised.
Splitter gear interlock
valve
The interlock valve is a conventional solenoid
valve, 3/2 valve. The same type is used on the
solenoid valve shelf for power take-off,
differential lock etc. There is a connector on the
clutch component which provides current to the
interlock valve when the pedal is depressed. The
interlock valve then passes supply air to the
control valve and only then can gear changing
take place in the split valve. When the clutch
pedal is released, the supply air line is
unpressurised.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 29
Rotation speed sensor
Inductive rotation speed sensor with overspeed
protection
The rotation speed sensor sends impulses to the
overspeed protection. At speeds above
approximately 30 km/h (depending on the rear
axle gear ratio) the rotation speed sensor sends
impulses to the overspeed protection. It then
breaks the circuit to the magnetic part of the
range control valve. It is not possible to change
to low range preventing overspeeding of the
clutch and engine.
At speeds below approximately 30 km/h the
circuit is closed in the overspeed protection.
The magnetic part on the control valve can then
actuate the operating air which then moves the
valve plunger to the low gear position.
The overspeed protection has a built-in
monitoring feature which means that when the
protection detects certain faults in the sensor
circuit, it prevents low gear from being 1 Road speed sensor
engaged. These faults are: 2 Rotation speed sensor for overspeed
1 Short circuit to earth protection
2 Short circuit to battery voltage
3 Open circuit in sensor circuit
Limp-home mode may be engaged when there
is a fault on the overspeed protection if the
protection is replaced by a standard relay (e.g.
243 460).
Newer designs of overspeed protection do not
have the monitoring feature. Only the new
design is available as a spare part.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
30 05:01-01
Gear lever knob
Gear lever knob
Two designs of gear lever knob are available, the
old and the new one. They both have a switch
for range gear or range and splitter gears.
Range gear
A switch is provided on the gear lever knob. In
low range the switch closes the circuit to the
magnetic part of the control valve and the
operating air therefore actuates the valve
plunger.
The above will apply provided that the circuit is
127 939
also closed in the overspeed protection
136 202
Older version Newer version
Range and splitter gears
There are two switches on the gear lever knob;
one for the splitter gear and one for range. In a
situation where both switches are in the low gear
position, they close the circuit to the magnetic
part of the control valve and the operating air
therefore actuates the valve plunger. The above
will apply to range provided that the circuit is
also closed in the overspeed protection.
127 938
136 201
Older version Newer version
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 31
Lubrication system
Lubrication system
Lubrication is provided via a combination of There is another overflow valve, known as a
splash and force-feed lubrication. Splash dumping valve, in the system and it is intended
lubrication is carried out by the teeth of the to protect the oil pump against excessive back
layshaft reaching down under the oil level in pressure, e.g. when the gearbox oil is extremely
the gearbox housing and acting as an impeller. cold. The dumping valve, which is mounted in
the gearbox housing immediately behind the oil
Force-feed lubrication is provided by means of filter, will then open and oil is dumped directly
an oil pump, pipes and drilled channels in the into the gearbox again.
shafts. The lubrication system is also equipped
with an oil filter and overflow valve. Oil is pressed from the oil filter on either via
the input shaft through the mainshaft away to
The oil pump is a rotor-type pump which is the planetary gear, or through an internal oil
fitted in the clutch housing and is driven by the pipe away to the planetary gear.
layshaft. The pump draws oil through a strainer
in the bottom of the gearbox housing. The oil is There are drilled channels in the mainshaft
pushed from the oil pump on through a filter which supply the different bearings and the
with a built-in overflow valve and is then different gear wheels for the planetary gear
distributed through various ducts in the clutch through the sun wheel with oil. The internal oil
housing. pipe supplies the output shaft bearing with oil
through the spray nozzles.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
32 05:01-01
Gear changing
Gear changing
Main gearbox Range gear
The main gearbox has three or four gears and a The range gear is a synchromesh planetary gear
reverse gear. Some versions also have a crawl which is located behind the main gearbox. The
gear. The gears of the main gearbox have range gear doubles the gear steps in the main
synchromesh, but those of the crawl and gearbox into a low and a high range. It is
reverse gears do not. Operation is by moving operated via a switch on the gear lever.
the gear lever to each gear position.
The gearbox is equipped with overspeed
protection which prevents low range from
Splitter gear being engaged at speeds above approximately
30 km/h.
The splitter gear is located in the front part of
the main gearbox. The splitter gear splits each The gear ratio between low and high range is
gear step, 1-3, into low and high. In this way 6 3.75.
gear steps can be obtained. In addition, the
crawl and reverse gears can also be split into
low and high split.
The splitter gear is selected using a rocker
switch on the gear lever.
The gear ratio between low and high split is
approximately 23%.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 33
Gear changing
Gear changing, gearbox with splitter gear Gear changing, gearbox without splitter gear
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
34 05:01-01
Power flow
Power flow for different gears, main gearbox
Refer to booklet "Gearbox GR/GRS, Planetary gear section" for power flow through the planetary
gear.
GR801
1st and 5th gear 2nd and 6th gear
3rd and 7th gear 4th and 8th gear
Reverse gear
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 35
Power flow
GR900
Crawl gear 1st and 5th gear
05 5595
05 5596
2nd and 6th gear 3rd and 7th gear
05 5597
05_5598
4th and 8th gear Reverse gear
05 5599
05 5600
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
36 05:01-01
Power flow
GRS900, GRS920 and GRS890 except crawl gear
Crawl gear, low split Crawl gear, high split
05 5602
05 5603
1st and 4th gear, low split 1st and 4th gear, high split
05_5604
05 5605
2nd and 5th gear, low split 2nd and 5th gear, high split
05 5607
05 5606
3rd and 6th gear, low split 3rd and 6th gear, high split
05 5608
05_5609
Reverse gear, low split Reverse gear, high split
05 5610
05 5611
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 37
Power flow
GRSO900
Crawl gear, low split Crawl gear, high split
1st and 4th gear, low split 1st and 4th gear, high split
2nd and 5th gear, low split 2nd and 5th gear, high split
3rd and 6th gear, low split 3rd and 6th gear, high split
Reverse gear, low split Reverse gear, high split
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
38 05:01-01
Specifications
Specifications
Ratios
GR801
Gear Gear ratio
Manual/CAG CS
1 1 9.15
2 2 6.31
3 4.69
4 3 3.75
5 4 2.44
6 5 1.68
7 6 1.25
8 7 1.00
R R 8.21
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 39
Specifications
GR900
Gear Gear ratio
C 16.86
1 10.10
2 7.10
3 5.09
4 3.75
5 2.69
6 1.89
7 1.36
8 1.00
RL 16.42
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
40 05:01-01
Specifications
GRS900, GRS920 and GRS890 except crawl gear
Gear Gear ratio
CL 16,38
CH 13,28
1L 11,38
1H 9,23
2L 7,17
2H 5,81
3L 4,63
3H 3,75
4L 3,03
4H 2,46
5L 1,91
5H 1,55
6L 1,23
6H 1,00
L RL 14,74
L RH 11,95
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 41
Specifications
GRSO900
Gear Gear ratio 13,28
CL 13,28
CH 10,76
1L 9,23
1H 7,48
2L 5,81
2H 4,71
3L 3,75
3H 3,04
4L 2,46
4H 1,99
5L 1,55
5H 1,26
6L 1,00
6H 0,81
0,81
L RL 14,74
135 775
6L 5L 4L 3L 2L 1L CL
L RH 11,95
6H 5H 4H 3H 2H 1H CH
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
42 05:01-01
Specifications
Power take-off
All gearboxes can be equipped with power take-off from the EG600 series.
GR gearboxes
Power take-off Drive Gear ratio Torque
EG601 Direct drive 1.24 700 Nm
EG603 Direct drive 1.13 500 Nm
EG611 Single power take-off for propeller shaft drive 0.93 1200 Nm
EG612 Single power take-off for propeller shaft drive 0.92 1200 Nm
EG621 Double power take-off for propeller shaft drive 1.24 700 Nm
0.93 1200 Nm *
* The torque must not exceed 600 Nm if both power take-offs are used.
GRS gearboxes
Power take-off Drive Gear ratio Torque Splitter gear
EG600 Direct drive 1.45 600 Nm low split
1.78 500 Nm high split
EG604 Direct drive 1.12 500 Nm low split
1.37 500 Nm high split
EG606 Direct drive 1.16 500 Nm low split
1.44 500 Nm high split
EG610 Single power take-off for 0.94 1200 Nm low split
propeller shaft drive 1.15 1100 Nm high split
EG620 Double power take-off for 1.45 600 Nm low split
propeller shaft drive 1.78 500 Nm high split
0.94 1200 Nm * low split
1.15 1100 Nm * high split
* The torque must not exceed 600 Nm if both power take-offs are used.
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
05:01-01 43
© Scania CV AB 2005, Sweden
44 05:01-01
You might also like
- Grs 900rDocument11 pagesGrs 900rslipsittin92% (13)
- Scania Opticruse GRS905Document2 pagesScania Opticruse GRS905fugega100% (13)
- Scania Retarder 3Document33 pagesScania Retarder 3neilevcvr88% (34)
- GRS 890 900 GR 801 900Document28 pagesGRS 890 900 GR 801 900Osmar Franco Pires100% (24)
- Ejes Grs890, Grs900, Grs920 y OtrasDocument36 pagesEjes Grs890, Grs900, Grs920 y OtrasLucas Laporte75% (4)
- A2 Electrical DiagramDocument16 pagesA2 Electrical Diagramjacklyn ade putra100% (14)
- A2 Electrical DiagramDocument16 pagesA2 Electrical Diagramjacklyn ade putra100% (14)
- SEN01983-01 Shop Machine PC 300-8Document839 pagesSEN01983-01 Shop Machine PC 300-8jacklyn ade putra96% (26)
- Brake Diagram ScaniaDocument25 pagesBrake Diagram ScaniaPetrus Kanisius Wiratno91% (11)
- Scania Retarder PDFDocument39 pagesScania Retarder PDFGermainCampillay75% (4)
- enDocument30 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (3)
- SCANIA Work Description Engine - 12 Industrial and Marine EngineDocument76 pagesSCANIA Work Description Engine - 12 Industrial and Marine Enginemliugong82% (22)
- ScaniaDocument6 pagesScaniaGustavo Paez100% (2)
- en PDFDocument44 pagesen PDFAlex Renne Chambi100% (1)
- Clucth ScaniaDocument2 pagesClucth ScaniaNoeRtjahya Ahmad100% (1)
- SDP 3 User ManualDocument102 pagesSDP 3 User ManualTopo Susilo100% (7)
- SCANIA COO Fault Codes DTC-1Document15 pagesSCANIA COO Fault Codes DTC-1frank mutale100% (5)
- WSM 0000003 01Document52 pagesWSM 0000003 01Anderson Bombista90% (10)
- John Deere 772d 6wd GraderDocument6 pagesJohn Deere 772d 6wd GraderyaserattiaNo ratings yet
- Quiz MicrobiologyDocument65 pagesQuiz MicrobiologyMedShare98% (51)
- ScaniaDocument39 pagesScaniarowan100% (7)
- 120302en PDFDocument35 pages120302en PDFduongpn100% (2)
- Wabco ABS/TC "D" 4 and 6 Channel System: Issue 3Document34 pagesWabco ABS/TC "D" 4 and 6 Channel System: Issue 3user100% (10)
- Gearbox Scania BusDocument18 pagesGearbox Scania BusNoeRtjahya Ahmad88% (8)
- Scania Ralentizador 100507 PDFDocument39 pagesScania Ralentizador 100507 PDFGermainCampillayNo ratings yet
- SCANIA Suspension BT300 Work DescDocument44 pagesSCANIA Suspension BT300 Work DescHeri SuryoNo ratings yet
- WSM - 01!03!01 - En.11,12 and 16 Litre EngineDocument36 pagesWSM - 01!03!01 - En.11,12 and 16 Litre EngineSubkhi Fauzan94% (16)
- Sistema de Combustible Con Inyector Bomba PDE y EDC S6. Descripción de FuncionamientoDocument48 pagesSistema de Combustible Con Inyector Bomba PDE y EDC S6. Descripción de FuncionamientoFelipe Sierra97% (35)
- ZF TrainnigDocument132 pagesZF TrainnigNuno Pires100% (4)
- WA 470-5H 50051&upDocument1,297 pagesWA 470-5H 50051&upclaudio100% (14)
- PC300 LC - 350 LCDocument775 pagesPC300 LC - 350 LCDanielBarrazaTapia100% (1)
- HH150 Smanual - MasterDocument43 pagesHH150 Smanual - Masterjacklyn ade putra80% (5)
- HEProductGuide1 PDFDocument52 pagesHEProductGuide1 PDFaldy yasi100% (2)
- HEProductGuide1 PDFDocument52 pagesHEProductGuide1 PDFaldy yasi100% (2)
- JCB ExcavatorDocument275 pagesJCB Excavatoraldy yasi71% (7)
- M. J. T. Lewis - Surveying Instruments of Greece and Rome (2001)Document410 pagesM. J. T. Lewis - Surveying Instruments of Greece and Rome (2001)Jefferson EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Factoring Problems-SolutionsDocument11 pagesFactoring Problems-SolutionsChinmayee ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Movie ReviewDocument2 pagesMovie ReviewJohanna Gwenn Taganahan LomaadNo ratings yet
- enDocument84 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (11)
- B - Bledding Procedurre On Page 13Document35 pagesB - Bledding Procedurre On Page 13EndraNo ratings yet
- enDocument83 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (12)
- Scania Dismantling ManualDocument48 pagesScania Dismantling ManualTaqi Syed93% (15)
- Scania Opticruise Transmission Fault Codes DTC & TroubleshootingDocument84 pagesScania Opticruise Transmission Fault Codes DTC & Troubleshootingfrank mutale100% (10)
- Tacometro y Velocimetro ScaniaDocument48 pagesTacometro y Velocimetro ScaniaChristian Ramos Campos60% (5)
- Scania Skrzynia BiegówDocument67 pagesScania Skrzynia Biegówandrzej100% (1)
- Chequeo Frenos ScaniaDocument68 pagesChequeo Frenos ScaniaOmar Zerna100% (3)
- enDocument24 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (6)
- WSM - Maintenance Instruction Part - 1 Truk - en PDFDocument120 pagesWSM - Maintenance Instruction Part - 1 Truk - en PDFDul AdulNo ratings yet
- Hpi Function DescriptionDocument64 pagesHpi Function DescriptionHari50% (4)
- enDocument40 pagesenRegistr Registr91% (11)
- Communication ErrorDocument24 pagesCommunication Errorali wardana100% (1)
- Scania P, G, R and S Series Workshop Manual - Dismantling Information PDFDocument106 pagesScania P, G, R and S Series Workshop Manual - Dismantling Information PDFLuciana Silveira100% (3)
- enDocument30 pagesenRegistr RegistrNo ratings yet
- enDocument44 pagesenRegistr Registr90% (10)
- 030402en PDFDocument55 pages030402en PDFdaniel_jorge_10No ratings yet
- 16 1enDocument96 pages16 1enRegistr Registr78% (9)
- Ko OrdinatorDocument31 pagesKo Ordinatoruser100% (6)
- Scania Inter AxleDocument14 pagesScania Inter AxleKharis Mahfudz100% (2)
- enDocument72 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (4)
- enDocument17 pagesenRegistr Registr60% (5)
- Scania HelperDocument79 pagesScania HelperHenrique Gonçalves Abreu100% (19)
- enDocument60 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (2)
- Fact Sheet: SpecificationDocument2 pagesFact Sheet: SpecificationShane LinNo ratings yet
- V2009 Eng 01 1091Document2 pagesV2009 Eng 01 1091Shane LinNo ratings yet
- MTC - 316 - V1 (Teil 2) EN - MCSEEDocument32 pagesMTC - 316 - V1 (Teil 2) EN - MCSEEViệt ThắngNo ratings yet
- enDocument60 pagesenRegistr Registr100% (3)
- Gd663a 2 - Cen00472 01Document8 pagesGd663a 2 - Cen00472 01kazemiNo ratings yet
- Slides. Rear Axle RTS2370A. Texto PDFDocument16 pagesSlides. Rear Axle RTS2370A. Texto PDFYery Cruz100% (2)
- Overvier Gear BoxDocument2 pagesOvervier Gear BoxTristan YudaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.agb-Rgb 16112019Document32 pagesUnit 4.agb-Rgb 16112019motores4297No ratings yet
- PT2606 Eng 03 303855078Document2 pagesPT2606 Eng 03 303855078Shane LinNo ratings yet
- Sec08 Sebd0350Document54 pagesSec08 Sebd0350pmcisissengueNo ratings yet
- Catalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!Document241 pagesCatalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!aldy yasiNo ratings yet
- LOVOL User's HandbookDocument87 pagesLOVOL User's Handbookanibalwol100% (1)
- Catalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!Document241 pagesCatalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!aldy yasiNo ratings yet
- LOVOL User's HandbookDocument87 pagesLOVOL User's Handbookanibalwol100% (1)
- 1004TG Spec Sheet PDFDocument2 pages1004TG Spec Sheet PDFm50% (2)
- Catalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!Document14 pagesCatalogue: Professional Power Solution For Greater Value!Dhee DoodzNo ratings yet
- Torque Converter and TransmissionDocument16 pagesTorque Converter and Transmissionaldy yasiNo ratings yet
- Machine Model Serial Number: WA470-5 70001 and Up WA480-5 80001 and UpDocument82 pagesMachine Model Serial Number: WA470-5 70001 and Up WA480-5 80001 and Upaldy yasiNo ratings yet
- Sebm024300 (General S&F)Document268 pagesSebm024300 (General S&F)Joakim Indarno97% (30)
- Repari Manuaall PDFDocument216 pagesRepari Manuaall PDFaldy yasiNo ratings yet
- Shop Manual Wa500 PDFDocument1,046 pagesShop Manual Wa500 PDFaldy yasiNo ratings yet
- A4 SEBM024301 (T&a Troubleshooting)Document330 pagesA4 SEBM024301 (T&a Troubleshooting)nurdinzai100% (5)
- Sebm024300 (General S&F)Document268 pagesSebm024300 (General S&F)Joakim Indarno97% (30)
- CATALOGcat PDFDocument150 pagesCATALOGcat PDFaldy yasiNo ratings yet
- Komatsu 730EDocument4 pagesKomatsu 730EWahyuni Tri Sundari100% (1)
- S1-TITAN Overview BrochureDocument8 pagesS1-TITAN Overview BrochureصصNo ratings yet
- Letter Response From AG Rob Bonta's Office Re: Batmobile InvestigationDocument2 pagesLetter Response From AG Rob Bonta's Office Re: Batmobile InvestigationLeah WorthingtonNo ratings yet
- RBConcept Universal Instruction ManualDocument19 pagesRBConcept Universal Instruction Manualyan henrique primaoNo ratings yet
- Ad&d - Poison Costs & Poison CraftDocument4 pagesAd&d - Poison Costs & Poison Craftweb moriccaNo ratings yet
- Four Year Plan DzenitaDocument4 pagesFour Year Plan Dzenitaapi-299201014No ratings yet
- TLE ICT CY9 w4 PDFDocument5 pagesTLE ICT CY9 w4 PDFMichelle DaurogNo ratings yet
- Amit Singh RF EngineerDocument3 pagesAmit Singh RF EngineerAS KatochNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Steel and AccessoriesDocument4 pagesReinforcing Steel and AccessoriesTheodore TheodoropoulosNo ratings yet
- U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Miller 362-94-3108 DeaneDocument2 pagesU.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Miller 362-94-3108 DeaneKeith MillerNo ratings yet
- LPP-Graphical and Simplex MethodDocument23 pagesLPP-Graphical and Simplex MethodTushar DhandeNo ratings yet
- Project Definition and DescriptionDocument9 pagesProject Definition and DescriptionEileen VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusDocument16 pagesPyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusVã RãNo ratings yet
- 14 BibiliographyDocument22 pages14 BibiliographyvaibhavNo ratings yet
- MELSEC System Q: QJ71MES96 MES Interface ModuleDocument364 pagesMELSEC System Q: QJ71MES96 MES Interface ModuleFajri AsyukronNo ratings yet
- SoapDocument10 pagesSoapAira RamoresNo ratings yet
- Conflict Management and Negotiation - Team 5Document34 pagesConflict Management and Negotiation - Team 5Austin IsaacNo ratings yet
- Abb PB - Power-En - e PDFDocument16 pagesAbb PB - Power-En - e PDFsontungNo ratings yet
- Gothic Fiction Oliver TwistDocument3 pagesGothic Fiction Oliver TwistTaibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Pier Cap Corbel 30m SGDocument3 pagesPier Cap Corbel 30m SGSM ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- Tu 05Document23 pagesTu 05Yang ElvisQUNo ratings yet
- The SU Electric Fuel Pump Type Car Reference List AUA 214Document4 pagesThe SU Electric Fuel Pump Type Car Reference List AUA 214Anonymous aOXD9JuqdNo ratings yet
- Do or Does1.1.2Document4 pagesDo or Does1.1.2dzanardipintoNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Museum: History and Memory of Morocco, Jewish Life in FezDocument1 pageThe Invisible Museum: History and Memory of Morocco, Jewish Life in FezmagnesmuseumNo ratings yet
- Sajid, Aditya (Food Prossing)Document29 pagesSajid, Aditya (Food Prossing)Asif SheikhNo ratings yet
- King of Chess American English American English TeacherDocument6 pagesKing of Chess American English American English TeacherJuliana FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Securingrights Executive SummaryDocument16 pagesSecuringrights Executive Summaryvictor galeanoNo ratings yet