Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015
Uploaded by
Rovz GC BinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015
Uploaded by
Rovz GC BinCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s.
2015)
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
The fact or condition of Remembering identify, retrieve, recognize, duplicate, list,
knowing something The learner can recall information and retrieve relevant knowledge from long-term memorize, repeat, describe, reproduce
with familiarity gained memory
through experience or interpret, exemplify, classify, summarize,
association
Understanding
The learner can construct meaning from oral, written and graphic messages infer, compare, explain, paraphrase,
discuss
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The ability and capacity The learner can use information to undertake a procedure in familiar situations or in a dramatize, interpret, solve, use, illustrate,
acquired through new way convert, discover
deliberate, systematic, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare,
and sustained effort to The learner can distinguish between parts and determine how they relate to one contrast, organize, outline, attribute,
smoothly and another, and to the overall structure and purpose deconstruct
adaptively carryout coordinate, measure, detect, defend,
complex activities or
Evaluating
The learner can make judgments and justify decisions judge, argue, debate, describe, critique,
the ability, coming from appraise, evaluate
one's knowledge, generate, hypothesize, plan, design,
practice, aptitude, etc., Creating
The learner can put elements together to form a functional whole, create a new develop, produce, construct, formulate,
to do something assemble, devise
product or point of view
Attitude Categories: List of Attitudes:
Growth in feelings or 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention Self-esteem, Self-confidence, Wellness,
emotional areas. Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Respect, Honesty, Personal discipline,
A settled way of name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Perseverance, Sincerity, Patience, Critical
thinking or feeling 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. thinking, Open-mindedness, Interest,
about someone or Attends and reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize Courteous, Obedience, Hope, Charity,
something, typically compliance in responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding Fortitude, Resiliency, Positive vision,
one that is reflected in (motivation). Acceptance, Determined, Independent ,
a person’s behavior Gratitude, Tolerant, Cautious, Decisive,
Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help,
Self-Control, Calmness, Responsibility,
label, perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write
Accountability, Industriousness, Industry,
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges
Cooperation, Optimism, Satisfaction,
from simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is
Persistent, Cheerful, Reliable, Gentle,
based on the internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values
Appreciation of one’s culture, Globalism,
are expressed in the learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable.
Compassion, Work Ethics, Creativity,
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, Entrepreneurial Spirit, Financial Literacy,
form, initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Global, Solidarity, Making a stand for the
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, good, Voluntariness of human act,
resolving conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The Appreciation of one’s rights, Inclusiveness,
emphasis is on comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Thoughtful, Seriousness, Generous,
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, Happiness, Modest, Authority,
explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, Hardworking, Realistic, Flexible,
relate, synthesize Considerate,
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their Sympathetic, Frankness
behavior. The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly,
characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's
general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional).
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform,
practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify
Values Categories: List of Values:
A learner's principles or 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention 1. Maka-Diyos
standards of behavior; Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Love of God, Faith, Trusting, Spirituality,
one's judgment of what name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Inner Peace, Love of truth, Kindness,
is important in life. 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Humble
Attends and reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize 2. Maka-tao
Go beyond learner’s life compliance in responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding Concern for Others, Respect for human
on earth, include more (motivation). rights, Gender equality, Family Solidarity,
than wealth and fame, Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, Generosity, Helping, Oneness
and would affect the label, perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write 3. Makakalikasan
eternal destiny of 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges Care of the environment, Disaster Risk
millions from simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based Management, Protection of the
on the internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are Environment, Responsible Consumerism,
expressed in the learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable. Cleanliness, Orderliness, Saving the
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, ecosystem, Environmental sustainability
form, initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study 4. Makabansa
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, Peace and order, Heroism and
resolving conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis Appreciation of Heroes, National Unity,
is on comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Civic Consciousness, Social responsibility,
Harmony, Patriotism,
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, Productivity
explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare,
relate, synthesize
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their
behavior. The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly,
characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's
general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional).
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform,
practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify
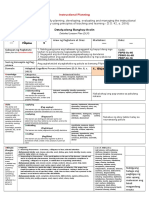
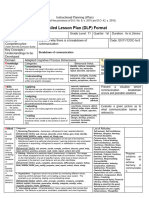
4. Procedures
4.1 Introductory Activity (____ minutes). This part introduces the lesson content. Although at times optional, it is usually included to serve as a warm-up activity to
give the learners zest for the incoming lesson and an idea about what it to follow. One principle in learning is that learning occurs when it is conducted in a pleasurable and
comfortable atmosphere.
4.2 Activity (____ minutes). This is an interactive strategy to elicit learner’s prior learning experience. It serves as a springboard for new learning. It illustrates the
principle that learning starts where the learners are. Carefully structured activities such as individual or group reflective exercises, group discussion, self-or group
assessment, dyadic or triadic interactions, puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics exercise, gallery walk and the like may be created. Clear instructions should be
considered in this part of the lesson.
4.3 Analysis (____ minutes). Essential questions are included to serve as a guide for the teacher in clarifying key understandings about the topic at hand. Critical points
are organized to structure the discussions allowing the learners to maximize interactions and sharing of ideas and opinions about expected issues. Affective questions are
included to elicit the feelings of the learners about the activity or the topic. The last questions or points taken should lead the learners to understand the new concepts or
skills that are to be presented in the next part of the lesson.
4.4 Abstraction (____ minutes). This outlines the key concepts, important skills that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude that should be emphasized. This is
organized as a lecturette that summarizes the learning emphasized from the activity, analysis and new inputs in this part of the lesson.
4.5 Application (____ minutes). This part is structured to ensure the commitment of the learners to do something to apply their new learning in their own environment.
4.6 Assessment (___ minutes). For the Teacher to: a) Assess whether learning objectives have been met for a specified duration, b) Remediate and/or enrich
with appropriate strategies as needed, and c) Evaluate whether learning intentions and success criteria have been met. (Reminder: Formative Assessment may be
given before, during, or after the lesson). Choose any from the Assessment Methods below:
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role Play, Oral Presentation, Dance, Musical Performance, Skill Demonstration, Group Activity
(Formal and informal observations of (e.g. Choral Reading), Debate, Motor & Psychomotor Games, Simulation Activities, Science Experiment
learners’ performance or behaviors are
recorded, based on assessment criteria)
b) Talking to Learners / Hands-on Math Activities, Written Work and Essay, Picture Analysis, Comic Strip, Panel Discussion, Interview,
Think-Pair-Share, Reading
Conferencing
(Teachers talk to and question learners about
their learning to gain insights on their
understanding and to progress and clarify
their thinking)
c) Analysis of Learners’ Worksheets for all subjects, Essay, Concept Maps/Graphic Organizer, Project, Model, Artwork, Multi-media
Presentation, Product made in technical-vocational subjects
Products
(Teachers judge the quality of products
produced by learners according to agreed
criteria)
d) Tests Skill Performance Test, Open-Ended Question, Practicum, Pen and Paper Test, Pre and Post Test, Diagnostic
(Teachers set tests or quizzes to determine Test, Oral Test, Quiz
learners’ ability to demonstrate mastery of a
skill or knowledge of content)
4.8 Concluding Activity (____ minutes).
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a short song, an anecdote, parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do
something to practice their new learning.
5. Remarks Indicate below special cases including but not limited to continuation of lesson plan to the following day in case of re-teaching or lack of
time, transfer of lesson to the following day, in cases of class suspension, etc.
6. Reflections Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this week. What works? What else needs to
be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can
ask them relevant questions. Indicate below whichever is/are appropriate.
A. No. of learners
who earned 80%
in the evaluation.
B. No. of learners
who require
additional
activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No.
of learners who
have caught up
with the lesson.
D. No. of learners
who continue to
require
remediation.
E. Which of my
learning strategies
worked well? Why
did these work?
F. What difficulties
did I encounter
which my
principal or
supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation
or localized
materials did I
use/discover
which I wish to
share with other
teachers?
You might also like
- DLL Perdev GenogramDocument7 pagesDLL Perdev GenogramJoy Ontangco PatulotNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 10Document2 pagesLearning Task 10Jexter Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cadawinonan Elementary School Character Evaluation FormDocument1 pageCadawinonan Elementary School Character Evaluation FormArjix HandyManNo ratings yet
- Grade-3-Exemplar in EnglishDocument10 pagesGrade-3-Exemplar in EnglishTEODERICK B. MACATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- LAC PLAN Tve 1Document1 pageLAC PLAN Tve 1Alma Tomas-CafeNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Remembering: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP)Document4 pagesKnowledge Remembering: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP)billy jane ramosNo ratings yet
- The Process of Systematically Planning, Developing, Evaluating and Managing The Instructional Process by Using Principles of Teaching and Learning - D.O. 42, S. 2016Document4 pagesThe Process of Systematically Planning, Developing, Evaluating and Managing The Instructional Process by Using Principles of Teaching and Learning - D.O. 42, S. 2016Ronieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in CGPDocument2 pagesNarrative Report in CGPJohn Dale Evangelio50% (2)
- DLP FormatDocument2 pagesDLP Formatrudy rex mangubat0% (1)
- Grading System in The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesGrading System in The PhilippinesRose Chua100% (1)
- DLP English 7Document7 pagesDLP English 7Rey NonNo ratings yet
- DLP in Filipino For Observation RevisedDocument4 pagesDLP in Filipino For Observation RevisedLissa Mae Macapobre100% (1)
- Q1 Form 14 (Pre & Post Test) - SHSDocument8 pagesQ1 Form 14 (Pre & Post Test) - SHSArthur LegaspinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On IMsDocument7 pagesPresentation On IMsGlenn E. DicenNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 English c0t 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesGrade 2 English c0t 2nd QuarterKrissa Ann Espino FloresNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasCecille HernandoNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan Aringin High School 9 Jennilyn A. Paloma English February 18, 2020 4 (Fourth) TuesdayDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan Aringin High School 9 Jennilyn A. Paloma English February 18, 2020 4 (Fourth) TuesdayPalomaJudelNo ratings yet
- Weekly STEM Home Learning PlanDocument2 pagesWeekly STEM Home Learning PlanGinno OsmilloNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Substances and MixturesDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Substances and MixturesNonie Beth CervantesNo ratings yet
- Ippd Form 3: Self Monitoring Check: SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020Document2 pagesIppd Form 3: Self Monitoring Check: SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020Lilian Laurel CariquitanNo ratings yet
- Pertinent Papers: Aplication To Teacher-I PositionDocument1 pagePertinent Papers: Aplication To Teacher-I Positionjulie ann gustiloNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 English Lesson on Summarizing Information, Problem-Solution Texts, and Compound-Complex SentencesDocument10 pagesGrade 6 English Lesson on Summarizing Information, Problem-Solution Texts, and Compound-Complex SentencesedelbertoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status FormDocument1 pageNutritional Status Formmelda_bunquin90% (10)
- Table of Specification for Fourth Quarter Examination in TLE 6 - Entrepreneurship and ICTDocument8 pagesTable of Specification for Fourth Quarter Examination in TLE 6 - Entrepreneurship and ICTTholitzDatorNo ratings yet
- Catch UP Friday DLLDocument3 pagesCatch UP Friday DLLRechelle Almazan100% (2)
- English 5 Lesson on Signal Words and Following DirectionsDocument7 pagesEnglish 5 Lesson on Signal Words and Following Directionskate apitongNo ratings yet
- EPP 6 Summative Test Score SheetDocument1 pageEPP 6 Summative Test Score Sheetshai24No ratings yet
- Lesson Planning 2Document28 pagesLesson Planning 2AltheaGuanzonNo ratings yet
- FS1 Journey Reflection and InsightsDocument3 pagesFS1 Journey Reflection and InsightsLoren MonarcaNo ratings yet
- Educational Administration in PerspectiveDocument4 pagesEducational Administration in PerspectiveЛеиа АморесNo ratings yet
- IPCRF (2018 - 2019) - LongDocument22 pagesIPCRF (2018 - 2019) - LongHidari SonoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Grade 10 English Lesson on Responding to Natural PhenomenaDocument4 pagesPhilippine Grade 10 English Lesson on Responding to Natural PhenomenaGrace Cristobal100% (1)
- Sample Space DLPDocument2 pagesSample Space DLPAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance Learners Development Assessment Junior High School 1Document3 pagesHomeroom Guidance Learners Development Assessment Junior High School 1LalaineNo ratings yet
- CERA Reflection On Making A Lesson Plan Using Inquiry-Based Approach and Interdisciplinary ContextualizationDocument1 pageCERA Reflection On Making A Lesson Plan Using Inquiry-Based Approach and Interdisciplinary ContextualizationFely Magkilat100% (1)
- I. Objectives: Grades 11 / 12 Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: Grades 11 / 12 Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterChe RaveloNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Cost of Production)Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Cost of Production)Glenda Javier100% (1)
- Journeying The Teaching Profession: Myself and My CareerDocument13 pagesJourneying The Teaching Profession: Myself and My CareerJasoel Joshua MarinoNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF) Teacher I-IiiDocument10 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF) Teacher I-IiiGiesselle Bulos-Felipe MindoNo ratings yet
- I. TITLE: Basic Baking Breads and Pastries II. OBJECTIVES: The Student Demonstrates Understanding Of/onDocument4 pagesI. TITLE: Basic Baking Breads and Pastries II. OBJECTIVES: The Student Demonstrates Understanding Of/onRaymund PatricioNo ratings yet
- DLL Entrep-12Document3 pagesDLL Entrep-12MALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- DLL HE Week 10Document4 pagesDLL HE Week 10Eunice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers (PPST)Document11 pagesPhilippine Professional Standards For Teachers (PPST)Krystal Gail De VeraNo ratings yet
- Mr. Ruel B. EstoresDocument3 pagesMr. Ruel B. EstoresWawa MooreNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 SF8 (G5)Document4 pagesSchool Form 8 SF8 (G5)Melieza Melody AmpanNo ratings yet
- DLL-JULY 22-25 Fact Vs OpinionDocument5 pagesDLL-JULY 22-25 Fact Vs Opinionerrol rustiaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanJisbert Pablo Ampo100% (1)
- School Form 5 Report On Promotion and Learning Progress AchievementDocument4 pagesSchool Form 5 Report On Promotion and Learning Progress Achievementbernaflor pacantaraNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Group ActivityDocument2 pagesRubrics For Group ActivitySarah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- FS 2 Activity 5Document7 pagesFS 2 Activity 5Mharesa ParagasNo ratings yet
- Course 3: The Deped TeacherDocument14 pagesCourse 3: The Deped TeacherPrincess SolarioNo ratings yet
- Performance Task For The 2nd Quarter g8Document6 pagesPerformance Task For The 2nd Quarter g8marife gupaal100% (1)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDocument12 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesMacky CometaNo ratings yet
- Narrative CUF Feb 2 2024Document5 pagesNarrative CUF Feb 2 2024Ernesdyne SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Shs e Class Record G11farrimondDocument8 pagesShs e Class Record G11farrimondElma QuiselNo ratings yet
- Buenlag National High School: Region I Schools Division Office I Pangasinan Calasiao District IIDocument3 pagesBuenlag National High School: Region I Schools Division Office I Pangasinan Calasiao District IIMaria Joy Domulot100% (1)
- Implementing Daily Curriculum in the ClassroomDocument17 pagesImplementing Daily Curriculum in the ClassroomAriell EmraduraNo ratings yet
- IPLan TemplateDocument5 pagesIPLan TemplateSigrid Therese CañeteNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- ANSWER SHEET in DRRDocument2 pagesANSWER SHEET in DRRRovz GC Bin100% (2)
- Name: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Students' Potential Gains from Perception StudyDocument3 pagesStudents' Potential Gains from Perception StudyRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- 4TH Summative TestDocument1 page4TH Summative TestRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST in Practical ResearchDocument4 pages1ST SUMMATIVE TEST in Practical ResearchRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Teacher-Made Learner'S Home Task (Q3-Week 3 - Week 4)Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Teacher-Made Learner'S Home Task (Q3-Week 3 - Week 4)Rovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: Explain How Typhoons Develop Code: S8ES - Iid-18Document1 pageDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: Explain How Typhoons Develop Code: S8ES - Iid-18Rovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Division Monitoring Evaluation and Assessment (Dsmea) 3Rd QuarterDocument4 pagesDivision Monitoring Evaluation and Assessment (Dsmea) 3Rd QuarterRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Roland Rolled Over The Floor in Order To Put Off The Fire That Caught Her Clothes. Which Principle Explains This?Document3 pagesRoland Rolled Over The Floor in Order To Put Off The Fire That Caught Her Clothes. Which Principle Explains This?Rovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Earthquake and Volcano HazardsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Earthquake and Volcano HazardsRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction Home TaskDocument10 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction Home TaskRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Division Monitoring Evaluation and Assessment (Dsmea) 3Rd QuarterDocument4 pagesDivision Monitoring Evaluation and Assessment (Dsmea) 3Rd QuarterRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Coastal Processes Lesson Exemplar Explains Erosion, Submersion & IntrusionDocument4 pagesCoastal Processes Lesson Exemplar Explains Erosion, Submersion & IntrusionRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Office/School/Clc Work Week Plan To: Mrs. Charito P. Velasco Principal Barrio Luz Elementary SchoolDocument5 pagesOffice/School/Clc Work Week Plan To: Mrs. Charito P. Velasco Principal Barrio Luz Elementary SchoolRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Office/School/Clc Work Week Plan To: Mrs. Charito P. Velasco Principal Barrio Luz Elementary SchoolDocument5 pagesOffice/School/Clc Work Week Plan To: Mrs. Charito P. Velasco Principal Barrio Luz Elementary SchoolRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- How Did Politics and Governance Evolve in The Philippines?Document1 pageHow Did Politics and Governance Evolve in The Philippines?Rovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order: Santa Filomena National High SchoolDocument2 pagesPurchase Order: Santa Filomena National High SchoolRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- District of Alegria: Lesson Plan in Diss Time 8:30-9:30 Year & Section 11-St. Joseph HUMMSSDocument1 pageDistrict of Alegria: Lesson Plan in Diss Time 8:30-9:30 Year & Section 11-St. Joseph HUMMSSRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- MNHS - Grade 11 Unpacking of MELCsDocument1 pageMNHS - Grade 11 Unpacking of MELCsRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 11Document13 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 11Rovz GC Bin83% (12)
- Summative TestDocument1 pageSummative TestRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- District of Alegria: Trace The Historical Foundations and Social Contexts That Led To The Development of Each DisciplineDocument2 pagesDistrict of Alegria: Trace The Historical Foundations and Social Contexts That Led To The Development of Each DisciplineRovz GC Bin100% (1)
- Philippine Literary History Geographic, Linguistic, Ethnic DimensionsDocument5 pagesPhilippine Literary History Geographic, Linguistic, Ethnic DimensionsRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- DLP 3.finalDocument2 pagesDLP 3.finalRovz GC Bin100% (3)
- Handout 1 Exogenic WeatheringDocument1 pageHandout 1 Exogenic WeatheringRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Epp 6 Ict and Entrepreneurship First Periodical Test Table of SpecificationsDocument1 pageEpp 6 Ict and Entrepreneurship First Periodical Test Table of SpecificationsJacqueline Acera Balingit95% (42)
- DLP 3.finalDocument2 pagesDLP 3.finalRovz GC Bin100% (3)
- Philippine Politics ExamDocument2 pagesPhilippine Politics ExamRovz GC Bin100% (1)
- 1st. DISSDocument2 pages1st. DISSRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Defence MechanismsDocument15 pagesDefence MechanismsSathish RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Pnu Recommendation Form-1Document2 pagesPnu Recommendation Form-1Danilo PadernalNo ratings yet
- Guided Meditation With Singing Bowl PDFDocument6 pagesGuided Meditation With Singing Bowl PDFasder444100% (1)
- Sound TherapyDocument2 pagesSound TherapyCarlo DamiãoNo ratings yet
- Clegg 1982 Simple Statistics A Course Book For The Social SciencesDocument105 pagesClegg 1982 Simple Statistics A Course Book For The Social SciencesMihaela Alina TiticaNo ratings yet
- A Course in Self ManagementDocument16 pagesA Course in Self ManagementMakarand PathakNo ratings yet
- TCNJ Lesson Plan: Title: Using Similar Triangles To Interpret Slope Unit # - 1 - Lesson # - 3 - Day # - 3Document12 pagesTCNJ Lesson Plan: Title: Using Similar Triangles To Interpret Slope Unit # - 1 - Lesson # - 3 - Day # - 3api-253005231No ratings yet
- No 2Document4 pagesNo 2ronaliza c. cerdenolaNo ratings yet
- InayanDocument2 pagesInayanRamon Lopez100% (1)
- Math 4 Week 6Document10 pagesMath 4 Week 6Julie Ann UrsulumNo ratings yet
- Theme of Lonliness in Robert FrostDocument2 pagesTheme of Lonliness in Robert FrostAbdulRehman100% (4)
- Tchoukball 10 Weeks Unit Plan (TBAS)Document9 pagesTchoukball 10 Weeks Unit Plan (TBAS)Louis WangNo ratings yet
- Barney SMCA3 03Document45 pagesBarney SMCA3 03Annisa MoeslimNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Manager PDFDocument2 pagesWarehouse Manager PDFAgus WitonoNo ratings yet
- Success Secrets For BA Mind PDFDocument122 pagesSuccess Secrets For BA Mind PDFThirumaleshwara M Shastry0% (1)
- AP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesDocument7 pagesAP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesBellony SandersNo ratings yet
- Mgt162 Fundamentals of Management Topic 5: Motivation (Assignment 5)Document4 pagesMgt162 Fundamentals of Management Topic 5: Motivation (Assignment 5)Valerie ColeNo ratings yet
- Review of - I - Juvenile Delinquency - Causes and Control - I - (2nd Ed PDFDocument4 pagesReview of - I - Juvenile Delinquency - Causes and Control - I - (2nd Ed PDFMike joshua telacas100% (1)
- Smartphone Addiction SymptonsDocument3 pagesSmartphone Addiction SymptonsSandeep SoniNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Success and Power Dynamics in SocietyDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Success and Power Dynamics in SocietyJane Yonzon-RepolNo ratings yet
- ST Sir Gems, Subhadip Sir Pivots and Explanation of IDF by DR - VivekDocument101 pagesST Sir Gems, Subhadip Sir Pivots and Explanation of IDF by DR - VivekUsha JagtapNo ratings yet
- Apa ch18 PDFDocument25 pagesApa ch18 PDFNBNo ratings yet
- EBIC Booklist2013Document7 pagesEBIC Booklist2013celinelbNo ratings yet
- Action Research Presentation On Reading ComprehensionDocument7 pagesAction Research Presentation On Reading ComprehensionEuropez AlaskhaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Evidence-Based Psychotherapy Case Formulation?: January 2011Document11 pagesWhat Is An Evidence-Based Psychotherapy Case Formulation?: January 2011Everline BedinNo ratings yet
- Start Now. Get Perfect Later (2018)Document240 pagesStart Now. Get Perfect Later (2018)Diah Diky100% (13)
- Behaviorism Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesBehaviorism Reflection PaperTrisha MenesesNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Reflection EssayDocument3 pagesPortfolio Reflection Essayapi-357755915No ratings yet
- Kunyit Asam Efektif Mengurangi Nyeri DismenoreaDocument6 pagesKunyit Asam Efektif Mengurangi Nyeri DismenoreaSukmawatiNo ratings yet
- MSC Language Sciences With Specialisation in Language Development - UCL Psychology and Language Sciences - UCL - London's Global UniversityDocument3 pagesMSC Language Sciences With Specialisation in Language Development - UCL Psychology and Language Sciences - UCL - London's Global UniversityBrenda MuñozNo ratings yet