Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HDPE Bolt Torque Flanged Joints HIERRO DUCTIL
Uploaded by
Renato BarretoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HDPE Bolt Torque Flanged Joints HIERRO DUCTIL
Uploaded by
Renato BarretoCopyright:
Available Formats
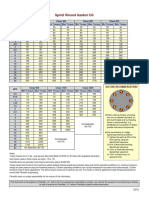
TABLE 3
Examples of Estimated Bolt Torque to “Seat” the HDPE Flange Face To
A Butterfly-Valve, Steel Pipe Flange, or Ductile Iron Flange.
The engineer of record is usually responsible for establishing each flange joint criteria, and
performing the required calculations to determine the initial and residual torque values.
These estimated liberally lubricated torque values assume the flanged joint connects one HDPE
flange-adapter to a Butterfly-Valve or Steel Pipe flange of Schedule 40 ID, or a Ductile-Iron flange.
For bolting to steel flanges or butterfly valves, the flange face contact area is just over half that of
HDPE to HDPE flanges, so calculated bolt torque for this flange pair will be measurably less than the
values listed in Table #2.
Dimensional flange data should be obtained for each case from the pipe flange suppliers, so as to
be able to calculate the face contact area.
These estimated values are based on non-plated bolts and studs, using a K=0.16 for lightly greased
bolts and nuts. These calculations use an HDPE material minimum and maximum compressive
seating stress of 1200-psi to 1800-psi.
IPS LJF Initial Minimum Initial Maximum HDPE
Nominal Bolt Dia. Number Lubed Lubed Flange OD
Pipe Size (inches) of Bolts Torque (Ft-Lbs) Torque (Ft-Lbs) Steel Pipe ID
( inches)
2” 0.625 4 22 32 3.90 / 2.067
3” 0.625 4 30 45 5.00 / 3.068
4” 0.625 8 30 45 6.60 / 4.026
5” 0.75 8 44 66 7.50 / 4.40
6” 0.75 8 44 66 8.50 / 6.06
8” 0.75 8 58 88 10.63 / 7.98
10” 0.875 12 58 88 12.75 / 10.02
12” 0.875 12 75 114 15.00 / 11.94
14” 1.000 12 140 210 17.50 / 13.13
16” 1.000 16 140 210 20.00 / 15.00
18” 1.125 16 140 210 21.12 / 16.88
20” 1.125 20 140 210 23.50 / 18.81
22” 1.25 20 160 240 25.60 / 21.25
24” 1.25 20 180 270 28.00 / 23.25
26” 1.25 24 180 270 30.00 / 25.25
28” 1.25 28 180 270 32.30 / 27.25
30” 1.25 28 180 270 34.30 / 29.25
32” 1.50 28 240 360 36.50 / 31.00
34” 1.50 32 240 360 38.50 / 33.00
36” 1.50 32 260 390 40.80 / 35.00
40” 1.50 36 310 465 46.00 / 39.00
42” 1.50 36 310 465 47.50 / 41.00
48” 1.50 44 310 465 54.00 / 47.00
54” 1.75 44 365 550 60.00 / 53.00
Train and supervise the bolting personnel. Tell the crew what is to be accomplished, why, and explain that
good results are not automatically achieved. Skill and care are essential. Bolted Joint assembly is a
technical skill that is not common in the construction and maintenance profession, being considered more
like a specialty. There is no universally accepted testing, nor certification, of bolted-joint assembly
mechanics. With no common training, certification, nor standards, it is no surprise there is +/- 25%
variability in assembly torque. Specifications and instructions by the engineer, followed by trained
mechanics, help to solve the dilemma. (Note: Consult ASME PCC-1, Appendix A)
11
You might also like
- Tabla de Torque - HdpeDocument3 pagesTabla de Torque - HdpeDevi SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Torque Values Graphite Laminate (B16.5)Document2 pagesTorque Values Graphite Laminate (B16.5)Gonçalo Cortez50% (2)
- Rubber Gasket (Full Face in Flat Face Flanges) Installation & TorqueDocument4 pagesRubber Gasket (Full Face in Flat Face Flanges) Installation & Torquecavillalobosb8167No ratings yet
- Flange Torque Recommendations GF PDFDocument2 pagesFlange Torque Recommendations GF PDFTulioLopezJNo ratings yet
- Acsr SPLN 41-7 PDFDocument2 pagesAcsr SPLN 41-7 PDFDharta Wira100% (1)
- Bolt Torque Chart - Astm A325Document1 pageBolt Torque Chart - Astm A325MoanquileNo ratings yet
- Bolt torque requirements for gasketsDocument2 pagesBolt torque requirements for gasketsrached100% (2)
- Torque Chart For ASTM A193 Grade B7 StudsDocument3 pagesTorque Chart For ASTM A193 Grade B7 Studssarip83100% (3)
- ASME PCC-1 Bolted Flange Joint AssemblyDocument1 pageASME PCC-1 Bolted Flange Joint Assemblykhaireddin75% (4)
- ASME StampsDocument3 pagesASME StampsDushyant BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Torque Values KlingerDocument1 pageTorque Values KlingerSầu ĐờiNo ratings yet
- Guía de Evaluación AWS G1.10MDocument45 pagesGuía de Evaluación AWS G1.10MDaniel Jimenez100% (1)
- Torqueo Bridas FRP PDFDocument1 pageTorqueo Bridas FRP PDFGianny RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Torqueo Pikotek PDFDocument4 pagesTorqueo Pikotek PDFjast111100% (1)
- Torque Values For EPDM-GasketsDocument1 pageTorque Values For EPDM-GasketsfaizanAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Torque FlexitallicDocument2 pagesTorque FlexitallicLuis Arturo Ramirez EstebanNo ratings yet
- Skidmore Instructions Model MS ManualsDocument15 pagesSkidmore Instructions Model MS ManualsbwbrockNo ratings yet
- 2.1 WPS - PipingDocument13 pages2.1 WPS - PipingSheri DiĺlNo ratings yet
- Comparison Pe4710 Pe3608Document1 pageComparison Pe4710 Pe3608Rene CALLIRI MAQUERANo ratings yet
- ASTM A53 (Steel Pipe)Document21 pagesASTM A53 (Steel Pipe)romi_hamdani100% (1)
- Formato de ITP-estructuras Metalicas BOLT TORQUE TESTDocument1 pageFormato de ITP-estructuras Metalicas BOLT TORQUE TESTkrlitos24100% (1)
- ANSI B 16.1 CLASS 125 Slip On FlangesDocument2 pagesANSI B 16.1 CLASS 125 Slip On FlangesEdimilson LanaNo ratings yet
- ASME RTP-1–2007 Nozzle Flange Dimensions for Class 150 BoltingDocument1 pageASME RTP-1–2007 Nozzle Flange Dimensions for Class 150 BoltingAndres Camilo Galvis Espinel100% (1)
- Pfi Es 3Document2 pagesPfi Es 3EstefaníaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Schedule PDFDocument1 pagePipe Schedule PDFSrinivasan SeenuNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Chart G16667 (Pressure Rating For ASTM A53-40 ERW Type E)Document2 pagesTechnical Data Chart G16667 (Pressure Rating For ASTM A53-40 ERW Type E)polysourceNo ratings yet
- 316 316l Data SheetDocument2 pages316 316l Data SheetDiman Aditya KardiNo ratings yet
- Flange Bolt Tightening ProcedureDocument5 pagesFlange Bolt Tightening ProcedureArya100% (1)
- Tabla de Equivalencias Pulgadas DiametralesDocument7 pagesTabla de Equivalencias Pulgadas DiametralesPaul Paredes Flores100% (1)
- ASTM A312 A312M Standard Specification For Seamless Welded and Heavily Cold Worked Austenitic Stainless Steel PipesDocument12 pagesASTM A312 A312M Standard Specification For Seamless Welded and Heavily Cold Worked Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipesessai expertiseNo ratings yet
- Astm D 2657 - 97Document9 pagesAstm D 2657 - 97Walther LaricoNo ratings yet
- INSPECTION AND TEST PLAN FOR 7.6 KM 4Document7 pagesINSPECTION AND TEST PLAN FOR 7.6 KM 4Farhan100% (1)
- Stainless - 304 Vs F593C ArticleDocument2 pagesStainless - 304 Vs F593C ArticleOswaldo Leyva R100% (8)
- Torque Values RTJ (B16.5)Document3 pagesTorque Values RTJ (B16.5)Dave Donohue100% (9)
- Fitting - ASTM A 197Document4 pagesFitting - ASTM A 197yajuNo ratings yet
- Astm C 582Document7 pagesAstm C 582Tanktech TanktechNo ratings yet
- Not For Production Use (For Reference Only) : ASTM A778-01Document1 pageNot For Production Use (For Reference Only) : ASTM A778-01Abu Bakr AsharefNo ratings yet
- Pipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Document1 pagePipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Jorge GarciaNo ratings yet
- Welder'S Work Record Log Sheet Welder's Name: S.M.W. Membership#Document1 pageWelder'S Work Record Log Sheet Welder's Name: S.M.W. Membership#satnamNo ratings yet
- PSV 430066 PDFDocument41 pagesPSV 430066 PDFErikikoNo ratings yet
- Weldolet DimensionDocument4 pagesWeldolet DimensionabhishekNo ratings yet
- PVC & HDPE Backing Flange Dimensions ChartDocument1 pagePVC & HDPE Backing Flange Dimensions ChartKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Pipe fitting material bill of quantitiesDocument3 pagesPipe fitting material bill of quantitiesSalim BakhshNo ratings yet
- Motor Starter Ready ReckonerDocument2 pagesMotor Starter Ready ReckoneranandpurushNo ratings yet
- Tablas para El Calculo de Tuberias de Distribucion en EdificacionesDocument7 pagesTablas para El Calculo de Tuberias de Distribucion en Edificacionesalex reyes gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aaac PDFDocument1 pageAaac PDFAnonymous 9Tdyr1No ratings yet
- AaacDocument1 pageAaacAnonymous 9Tdyr1No ratings yet
- ALL ALUMINUM ALLOY CONDUCTOR (AAAC) SPECIFICATIONSDocument1 pageALL ALUMINUM ALLOY CONDUCTOR (AAAC) SPECIFICATIONSAkbar Nicko RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Aaac PDFDocument1 pageAaac PDFAkbar Nicko RamadhanNo ratings yet
- USP Mechanical Joint Fittings C153 Submittal DigitalDocument20 pagesUSP Mechanical Joint Fittings C153 Submittal DigitalAbdel Mongy AhmedNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors ChartDocument1 pageConversion Factors ChartManuel MontañezNo ratings yet
- PVC SCH80 Price ListDocument1 pagePVC SCH80 Price Listbig lasagnaNo ratings yet
- Refuerzo Nylon PDFDocument1 pageRefuerzo Nylon PDFMilena JimenezNo ratings yet
- CV10 CV15 Brochure 09.01.2021Document4 pagesCV10 CV15 Brochure 09.01.2021hamadaNo ratings yet
- Accesorios Junta MecanicaDocument9 pagesAccesorios Junta MecanicaZaira LorenaNo ratings yet
- Tap Drill SizesDocument2 pagesTap Drill SizespriecsNo ratings yet
- P5 CPLG NPTDocument2 pagesP5 CPLG NPTdandi zlkNo ratings yet
- End Caps ANSI B16.9Document1 pageEnd Caps ANSI B16.9Thappatla IndurNo ratings yet
- MATERIALES INDUSTRIALES CODOS ACERODocument1 pageMATERIALES INDUSTRIALES CODOS ACEROcesarasmNo ratings yet
- Tabla Tuberia GalvanizadaDocument5 pagesTabla Tuberia GalvanizadaJuliia Mariia Chamorro VergaraNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Certification, ASNT SNT TC 1A, 2011Document1 page9.0 Certification, ASNT SNT TC 1A, 2011Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- AB-511 Impact Testing EnigmaDocument16 pagesAB-511 Impact Testing Enigmajoseca59No ratings yet
- 32K31S00 - CB250 Twister MC250 2017 ESPDocument107 pages32K31S00 - CB250 Twister MC250 2017 ESPFerdinand Raul StoneNo ratings yet
- Aws WJ 201306 PDFDocument170 pagesAws WJ 201306 PDFRenato Barreto100% (1)
- RT Level I BasicDocument290 pagesRT Level I Basicpraveentien100% (11)
- Aws WJ 201602 PDFDocument147 pagesAws WJ 201602 PDFRenato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Bonney Forge BrochureDocument22 pagesBonney Forge BrochureAnonymous dvrhf5No ratings yet
- Standard For Blasting ISO 8501 1Document2 pagesStandard For Blasting ISO 8501 1Roberto Silva100% (3)
- Aws WJ Esp 201701Document7 pagesAws WJ Esp 201701Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Aws WJ Esp 201701Document7 pagesAws WJ Esp 201701Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Selenium 75, Ir 192 and X-RaysDocument5 pagesSelenium 75, Ir 192 and X-RaysLei LaniNo ratings yet
- SENTINEL High Resolution Catalog May 2006Document47 pagesSENTINEL High Resolution Catalog May 2006Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- CFR 2011 Title49 Vol3 Part178Document251 pagesCFR 2011 Title49 Vol3 Part178Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- E1079Document2 pagesE1079Renato Barreto100% (1)
- E1079Document2 pagesE1079Renato Barreto100% (1)
- CFR 2011 Title49 Vol3Document689 pagesCFR 2011 Title49 Vol3parmindersinNo ratings yet
- DOT pressure relief requirements for portable tanksDocument1 pageDOT pressure relief requirements for portable tanksRenato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Radiography in Modern IndustryDocument212 pagesRadiography in Modern IndustryMohammed Abdul Sayeed50% (2)
- DOT pressure relief requirements for portable tanksDocument58 pagesDOT pressure relief requirements for portable tanksRenato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Sspc-Pa9 1311669483Document5 pagesSspc-Pa9 1311669483mrreach100% (1)
- 982-983 49 CFRDocument2 pages982-983 49 CFRRenato BarretoNo ratings yet
- CFR 2011 Title49 Vol3 Part178Document251 pagesCFR 2011 Title49 Vol3 Part178Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- Process ManualDocument183 pagesProcess ManualAnonymous UoHUag100% (5)
- Preparing and Using Protective Coating SpecificationsDocument38 pagesPreparing and Using Protective Coating SpecificationsRenato Barreto100% (1)
- 1527Document1 page1527Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- SSPC Pa1Document12 pagesSSPC Pa1Bladimir SantacruzNo ratings yet
- Process ManualDocument183 pagesProcess ManualAnonymous UoHUag100% (5)
- Aws WJ 201306 PDFDocument170 pagesAws WJ 201306 PDFRenato Barreto100% (1)
- 58 A2016 Lpg-Aaa SD PcresponsesDocument275 pages58 A2016 Lpg-Aaa SD PcresponsesRenato BarretoNo ratings yet
- PreschoolerDocument18 pagesPreschoolerapi-59739555No ratings yet
- Internal Communication Assignment - Communicating Strategy: Starting PointDocument4 pagesInternal Communication Assignment - Communicating Strategy: Starting PointNiaNo ratings yet
- Termination and Adoption PetitionDocument4 pagesTermination and Adoption Petitionjuakin12350% (4)
- Judgment Sheet in The Lahore High Court Multan Bench Multan Judicial DepartmentDocument14 pagesJudgment Sheet in The Lahore High Court Multan Bench Multan Judicial DepartmentMehtab Gul JunejoNo ratings yet
- Admin Law Prefinal NotesDocument14 pagesAdmin Law Prefinal NotesSanson OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The RequirementsDocument6 pagesThesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirementsbk4h4gbd100% (1)
- 031 Pre Admission ScreeningDocument1 page031 Pre Admission Screeningdohtrc pototanNo ratings yet
- Branton - The Dulce Book PDFDocument433 pagesBranton - The Dulce Book PDFnityapriya.meNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate Diploma in International Trade PgditDocument13 pagesPost Graduate Diploma in International Trade PgditNeekhar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Maloto v. CADocument2 pagesMaloto v. CAMariella Grace AllanicNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 Biologi - HalDocument29 pagesContoh Soal C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 Biologi - HalTaufik Bumika100% (1)
- Radio PharmaceuticalsDocument48 pagesRadio PharmaceuticalsKris Joy EbonNo ratings yet
- Identity, Self and Gender (Document10 pagesIdentity, Self and Gender (hayrunnisa kadriNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2468243Document18 pagesSSRN Id2468243Bhawani ShankerNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Kuby Immunology 7th Edition Judy OwenDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Kuby Immunology 7th Edition Judy OwenJosephGonzalezqxdf100% (48)
- Application Letter and ResumeDocument2 pagesApplication Letter and ResumeLindon Jay EnclunaNo ratings yet
- EdTPA SES Planning Commentary Danielle WilsonDocument4 pagesEdTPA SES Planning Commentary Danielle WilsonDanielle Wilson70% (10)
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Y. El Mghouchi, A. El Bouardi, Z. Choulli, T. AjzoulDocument13 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Y. El Mghouchi, A. El Bouardi, Z. Choulli, T. AjzoulAyde Taype SENo ratings yet
- Benedicts and Acetic Acid Urine TestsDocument12 pagesBenedicts and Acetic Acid Urine TestsUALAT STELLA MARIENo ratings yet
- Team Assignment 1 - Composing An Informational EmailDocument1 pageTeam Assignment 1 - Composing An Informational EmailHuỳnh Hồ Diễm NgọcNo ratings yet
- Fairytale PretestDocument3 pagesFairytale Pretestapi-339190123No ratings yet
- Section 1004Document14 pagesSection 1004djbechtelnlNo ratings yet
- How I Created The Theory of RelativityDocument4 pagesHow I Created The Theory of RelativityEric TseNo ratings yet
- IBISWorld - Database & Directory Publishing in The US - 2019Document31 pagesIBISWorld - Database & Directory Publishing in The US - 2019uwybkpeyawxubbhxjyNo ratings yet
- Why is sample size importantDocument98 pagesWhy is sample size importantLaura RossiNo ratings yet
- Engleza Bilingv Admitere CL IX Var.1 2012Document2 pagesEngleza Bilingv Admitere CL IX Var.1 2012AaliceMcDonaldNo ratings yet
- Critical EssaysDocument6 pagesCritical EssaysFaisal GhousNo ratings yet
- ELazar of Worms British Library MS 27199Document3 pagesELazar of Worms British Library MS 27199TaviNo ratings yet
- Indian Political SystemDocument25 pagesIndian Political SystemAyeza AmerNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles ExplainedDocument4 pagesLearning Styles ExplainedAisyah Nauli SihotangNo ratings yet