Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ws ch04 e PDF
Uploaded by
6B - 06 招芷澄 CHIU TSZ CHINGOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ws ch04 e PDF
Uploaded by
6B - 06 招芷澄 CHIU TSZ CHINGCopyright:
Available Formats
Class: Name: ( ) Date:
4 Enzymes and metabolism
4.1 Metabolism (Book 1A, p. 4-3)
(1) _______________ (新陳代謝) is the sum of chemical reactions that take place in an
organism. It includes (2) _______________ (分解代謝) and (3) _______________ (合成代謝).
Catabolism Anabolism
energy energy
complex molecule simple molecules simple molecules complex molecule
The (4) ______________ (breaking-down / The (6) ______________ (breaking-down /
building-up) reactions in an organism. building-up) reactions in an organism.
Energy is (5) _______________ (released / Energy is (7) _______________ (released /
required). required).
4.2 The role of enzymes in metabolism (Book 1A, p. 4-4)
For every reaction, a certain amount of energy must be supplied to the reactants before the
reaction can occur. This is called the (1) _______________ _______________ (活化能).
In our body, (2) _______________ (酶) are present which function as biological catalysts (催化劑).
They help (3) _______________ (raise / lower) the activation energy so that chemical reactions
can take place at body temperature at a faster rate.
activation energy
(without enzyme)
activation energy
energy level
reactants (with enzyme)
products
◄ Enzymes work by lowering
the activation energy
progress of reaction
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 28 -
Go to
Practical 4.1 Demonstration of the breaking-down action of enzymes
(Book 1A, p. 4-5; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-1)
Practical 4.2 Demonstration of the building-up action of enzymes
(Book 1A, p. 4-6; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-4)
4.3 Actions and properties of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-7)
A How do enzymes work? (Book 1A, p. 4-7)
On each enzyme molecule, there is an (1) _______________ _______________ (活性部位). An
enzyme molecule only binds to (2) _______________ (受質) molecules that fit the shape of its
active site.
A metabolic reaction begins when the substrate molecule(s) bind to the active site of an
enzyme to form an (3) _______________-_______________ _______________ (酶受質複合物).
Its formation (4) _______________ (raises / lowers) the activation energy of the reaction.
The substrate(s) are converted into product(s). The enzyme molecule is released in its
(5) _______________ form.
Catabolic reactions
enzyme-substrate
complex
substrate shapes fit products
together
enzyme enzyme
unchanged
active site
enzyme can be reused
Anabolic reactions
enzyme-substrate
substrates
complex
shapes fit product
together
enzyme enzyme
active site unchanged
enzyme can be reused
▲ Enzyme action in metabolic reactions
The specificity of enzyme actions can be explained by the (6) ___________- _____________ -
_____________ _______________ (鎖鑰假說).
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 29 -
B What are the properties of enzymes? (Book 1A, p. 4-8)
Property Description
Enzymes are biological Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering the
(7) _______________. (8) _______________ energy of the reactions.
The actions of enzymes are An enzyme only acts on substrates that fit into its
(9) _______________. (10) _______________ _______________.
Enzymes are The structures and hence the activity of enzymes are easily
(11) _______________. affected by temperature and pH. Most enzymes are
(12) _______________ (變性) at high temperatures.
Enzymes are Enzymes remain unchanged after reactions. They can bind to
(13) _______________. other substrate molecules after the reaction is complete.
Enzymes are needed in relatively Since enzymes can be (15) _______________, they are
(14) _______________ amounts. usually needed in small amounts only.
4.4 Factors affecting the rate of enzymatic reactions
(Book 1A, p. 4-10)
A Temperature (Book 1A, p. 4-10)
maximum rate
reaction rate
enzymes are
enzymes are denatured
inactive
temperature (℃)
10 20 30 40 50 60
optimum temperature
for this enzyme
▲ Effect of temperature on the rate of an enzymatic reaction
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 30 -
At low temperatures, enzymes are (1) ______________ (不活躍). The enzyme and substrate
molecules move slowly and the chance for them to (2) _______________ with each other is low.
Therefore, the reaction rate is (3) _______________.
As the temperature rises, both enzyme and substrate molecules move around more rapidly and
collide with each other more (4) ______________. This increases the chance of forming
(5) _____________-_____________ ______________. As a result, the rate of the enzymatic
reaction (6) _______________.
The rate of enzymatic reaction will eventually reach a maximum at (7) _______________
_______________ (最適溫度).
High temperatures may cause (8) _______________ change (i.e. a change in shape) in the
active site of the enzyme molecule. The enzyme is said to be (9) _______________. The
substrate molecule can no longer fit into the active site of the enzyme. As a result, the rate of
the enzymatic reaction (10) _______________.
B pH (Book 1A, p. 4-12)
Most enzymes work in a (11) _______________ (wide / narrow) range of pH. They work best
at their (12) _______________ pH.
Similar to the effect of high temperatures, an unsuitable pH will cause (13) _______________
of the enzyme. Therefore the rate of the enzymatic reaction (14) _______________.
many enzymes in mammals
(e.g. salivary amylase)
pepsin pancreatic lipase
reaction rate
pH
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
optimum optimum optimum
pH pH pH
▲ Different enzymes have their own optimum pH
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 31 -
C Inhibitors (Book 1A, p. 4-15)
(15) _______________ (抑制劑) are chemicals that can decrease the rate of enzymatic
reactions. Cyanides and (16) _______________ _______________ (重金屬) such as mercury
ions, lead(II) ions and copper(II) ions are examples of inhibitors.
Go to
Practical 4.3 Investigation of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity
(Book 1A, p. 4-11; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-8)
Practical 4.4 Design an investigation of the effect of pH on enzyme activity
(Book 1A, p. 4-13; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-12)
Practical 4.5 Investigation of the effect of inhibitors on enzyme activity
(Book 1A, p. 4-15; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-17)
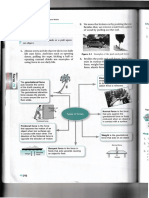
4.5 Applications of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-18)
Enzymes produced by organisms also work well outside the organisms. They are extracted and
used to produce various commercial products.
Examples of products and the enzymes used:
Product Enzyme used
I Biological washing powders a Protease
II Stonewashed jeans (石磨藍牛仔褲) b Lipase
III Contact lens cleaners c Cellulase
IV Meat tenderizers d Papain (木瓜酶)
V Cheese e Pectinase (果膠酶)
VI Fruit juices
I: (1) _______ & (2) _______ II: (3) _______ III: (4) ______
IV: (5) _______ V: (6) _______ VI: (7) ______
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 32 -
Advantages and limitations of using enzymes in the production of commercial products:
Advantage Limitation
Enzymes can speed up chemical Enzymes are sensitive to
reactions. This (8) _______________ the (15) _______________ and
production time and allows the (16) ________ changes. High
(9) _______________ production of temperatures and unsuitable pH can cause
products. (17) _______________ of enzymes.
Enzymes are (10) _______________ in Enzymes are easily affected by
action. This can reduce the production (18) _______________. All containers
of (11) _______________ products. that are used in the production processes
Enzymes are (12) _______________ and have to be (19) _______________. This
are needed in small amounts only. This prevents the containers from
lowers the (13) ______________ of (20) _______________ with inhibitors.
production.
Many enzymes work at
(14) _______________ conditions. Using
enzymes in the production processes does
not require extreme conditions.
Go to
Practical 4.6 Investigation of the effectiveness of different biological washing powders
(Book 1A, p. 4-20; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-20)
Practical 4.7 Design an investigation of protease activities in different fruit juices
(Book 1A, p. 4-21; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-24)
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 33 -
Answers
Ch 4 Enzymes and metabolism
4.1
1 Metabolism 2 catabolism 3 anabolism 4 breaking-down 5 released
6 building-up 7 required
4.2
1 activation energy 2 enzymes 3 lower
4.3
1 active site 2 substrate 3 enzyme-substrate complex 4 lowers
5 original 6 lock-and-key hypothesis 7 catalysts 8 activation
9 specific 10 active site 11 proteins 12 denatured 13 reusable
14 small 15 reused
4.4
1 inactive 2 collide 3 low 4 frequently
5 enzyme-substrate complexes 6 increases 7 optimum temperature
8 conformational 9 denatured 10 decreases 11 narrow 12 optimum
13 denaturation 14 decreases 15 Inhibitors 16 heavy metals
4.5
1 a 2 b 3 c 4 a 5 d
6 a 7 e 8 shortens 9 mass 10 specific
11 unwanted 12 reusable 13 cost 14 moderate 15 temperature
16 pH 17 denaturation 18 inhibitors 19 clean 20 contaminating
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2014
(Second Edition) - 34 -
You might also like
- Plants absorb minerals and exchange gasesDocument8 pagesPlants absorb minerals and exchange gasessafbadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerDocument12 pagesChapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerZhu Jiankun100% (1)
- Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis (Less than 40 chars: 35 charsDocument38 pagesRedox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis (Less than 40 chars: 35 charsミーチェルNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To In-Text Activities and Unit-End Exercises Topic 3 Unit 12Document21 pagesSuggested Answers To In-Text Activities and Unit-End Exercises Topic 3 Unit 12ミーチェルNo ratings yet
- MC - 05 The EcosystemDocument9 pagesMC - 05 The Ecosystemapi-3822784No ratings yet
- Material Specification: Document Number 1Pl030Document7 pagesMaterial Specification: Document Number 1Pl030Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Writing Complete Word EquationsDocument2 pagesWriting Complete Word EquationsSan (Alex) LimNo ratings yet
- Ws ch05 eDocument10 pagesWs ch05 eJoesy ChanNo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans: 8.1 The Human Transport SystemDocument11 pagesTransport in Humans: 8.1 The Human Transport SystemPhylliscccNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK4 NotesDocument20 pagesMastering Biology BK4 NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK1A NotesDocument26 pagesMastering Biology BK1A NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesThe Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeOlivia LinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Change of State: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument63 pagesChapter 3 Change of State: Multiple-Choice Questionssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- 3 Cellular Organization: 3.1 Cells As The Basic Units of LifeDocument6 pages3 Cellular Organization: 3.1 Cells As The Basic Units of LifeVenice Lo100% (1)
- % Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument32 pages% Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsK C100% (1)
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 The Human Breathing SystemDocument11 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 The Human Breathing SystemKat100% (1)
- Biodiversity Classification and the Six KingdomsDocument41 pagesBiodiversity Classification and the Six KingdomsAlva WongNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCh5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsYing Hei NgNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 3Document6 pagesBiology Paper 3Nyakweba Denis100% (1)
- HKDSE Biology S5 Exam (2020)Document28 pagesHKDSE Biology S5 Exam (2020)FuchingAuntie100% (1)
- F4CD1 英國語文Document1 pageF4CD1 英國語文ミーチェルNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK2 NotesDocument44 pagesMastering Biology BK2 NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- Nms Utest04 L1 Trial eDocument10 pagesNms Utest04 L1 Trial eHugo CheungNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 1 Introducing BiologyDocument33 pagesSuggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 1 Introducing BiologyCharmine Holmes100% (1)
- Nms Utest04 L2 Trial eDocument11 pagesNms Utest04 L2 Trial eHugo CheungNo ratings yet
- Oxford Lesson Ws 1 02 eDocument9 pagesOxford Lesson Ws 1 02 eZhu JiankunNo ratings yet
- Saraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 MinsDocument2 pagesSaraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 Minsnehru09No ratings yet
- CH 3Document15 pagesCH 3Choi MingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 QuestionDocument31 pagesChapter 04 Questionapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Integrated Science Notes Ch8 ElectricDocument3 pagesIntegrated Science Notes Ch8 ElectricAngel LiNo ratings yet
- Biology CH.41Document56 pagesBiology CH.41yanaaNo ratings yet
- MSS 1718MockPaper2Document8 pagesMSS 1718MockPaper2Kelvin ChowNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Form 3 Final ExaminationDocument23 pagesChemistry: Form 3 Final Examinationjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 3 Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesSuggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 3 Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneHarry Leung100% (2)
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument20 pagesConcentration of SolutionsRyanNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions and Answers New Syllabus 016Document19 pagesBiology Questions and Answers New Syllabus 016Khaled Dabour100% (1)
- F2 Science C8 Force and Motion TextDocument15 pagesF2 Science C8 Force and Motion TextAlex LowNo ratings yet
- Measure pH Using IndicatorsDocument20 pagesMeasure pH Using IndicatorsRyanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC I Paper I (2019)Document12 pagesChemistry HSSC I Paper I (2019)Tayyib Khan100% (1)
- Nutrition in humans: Modes and processesDocument9 pagesNutrition in humans: Modes and processesCHIU KEUNG OFFICIAL PRONo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QP PDFDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QP PDFSyakir Fahmie100% (2)
- Revision Acid and Alkali and Simple ReactionsDocument10 pagesRevision Acid and Alkali and Simple Reactionsvictorwu.uk100% (1)
- Cell Structure As Biology Questions OCR AQA EdexcelDocument4 pagesCell Structure As Biology Questions OCR AQA EdexcelAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transfer Processes: ConductionDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Transfer Processes: ConductionZhu JiankunNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7Document4 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7HansyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and gas exchange in plantsDocument28 pagesNutrition and gas exchange in plants4B21 Renee Sin Yat HeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 6Document130 pagesUnit 12 6Lai BryanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Microscopic World IDocument15 pagesTopic 2 Microscopic World IBelladonna LeeNo ratings yet
- Class: Name: ( ) Date: Reproduction in flowering plantsDocument11 pagesClass: Name: ( ) Date: Reproduction in flowering plantsada lumNo ratings yet
- New Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - e - AnsDocument7 pagesNew Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - e - AnsChun Kit LauNo ratings yet
- F3 Challenging Exercise 11Document3 pagesF3 Challenging Exercise 11pgkbgjrh5pNo ratings yet
- S 495160Document4 pagesS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Chap 2Document72 pagesChap 2miguel0angel0ramos-1100% (6)
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Document12 pagesPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziNo ratings yet
- Hkdse Chemistry - A Modern View: (Second Edition) (Reprinted With Minor Amendments 2019)Document25 pagesHkdse Chemistry - A Modern View: (Second Edition) (Reprinted With Minor Amendments 2019)Tat LNo ratings yet
- Human Biology Part 1 FBDocument56 pagesHuman Biology Part 1 FBJayjayjay 5No ratings yet
- Corrosion of Metals and Their Protection: Learning GoalDocument36 pagesCorrosion of Metals and Their Protection: Learning GoalRyanNo ratings yet
- Express Each of The Following Ratio in Its Simplest Form 1 RM25: RM40 2Document8 pagesExpress Each of The Following Ratio in Its Simplest Form 1 RM25: RM40 2Mr Ling Tuition CentreNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsDocument5 pagesCells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper - Core (By Topic)Document15 pagesExam Paper - Core (By Topic)Henry Leung100% (1)
- Fortron PPS PDFDocument57 pagesFortron PPS PDFkfaravNo ratings yet
- Romero Diaz Albert 2018-19 PDocument183 pagesRomero Diaz Albert 2018-19 PLuiz Rodrigo AssisNo ratings yet
- HX HX230E Liebherr D934SDocument4 pagesHX HX230E Liebherr D934Smiguel sousaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chapter 17 - Organometallic ReactionsDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chapter 17 - Organometallic ReactionsSairille ManejaNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN FB Biobase BK Mini 200.EN Rev2022.07.26Document3 pagesApplication Note AN FB Biobase BK Mini 200.EN Rev2022.07.26Amine AmineNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Biological MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Biological Macromoleculesion1barangaNo ratings yet
- 1103 Paper PDFDocument26 pages1103 Paper PDFAryan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Yabatech Post Utme Past QuestionDocument25 pagesYabatech Post Utme Past QuestionFaithNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Electronic Theory, VBT and Hybridization)Document23 pagesChemical Bonding (Electronic Theory, VBT and Hybridization)Noor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- Formulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument19 pagesFormulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPveronica burlacuNo ratings yet
- Softening water processesDocument20 pagesSoftening water processesHassan AliNo ratings yet
- A2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20632Document4 pagesA2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20632Cosmescu Mario FlorinNo ratings yet
- Transfer Printing: Transfer of Design From One Substrate To Another First Substrate Paper Second Substrate FabricDocument15 pagesTransfer Printing: Transfer of Design From One Substrate To Another First Substrate Paper Second Substrate FabricAmdeworkNo ratings yet
- CO Capture by Absorption With Potassium CarbonateDocument23 pagesCO Capture by Absorption With Potassium CarbonatekumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy Experiment No: 3: Anum Hanif Faculty of Pharmacy Hajvery University (HU)Document12 pagesPhysical Pharmacy Experiment No: 3: Anum Hanif Faculty of Pharmacy Hajvery University (HU)Raja Hamood KhanNo ratings yet
- Managing Risks of Storing Chemicals in The Workplace - 0Document18 pagesManaging Risks of Storing Chemicals in The Workplace - 0qamar sayedNo ratings yet
- Form 2Document20 pagesForm 2Murtaza ÇakaloğluNo ratings yet
- Free Radical PharmacologyDocument5 pagesFree Radical PharmacologySANJAY K GOWDANo ratings yet
- POM FatigueDocument6 pagesPOM FatigueMustapha BelloNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument115 pagesThe Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Multiple Choice QuestionsJing LiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions in Biological and Industrial ProcessesDocument10 pagesChemical Reactions in Biological and Industrial ProcessesMary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-Cuadra100% (1)
- Theory: Mechanism of SaponificationDocument4 pagesTheory: Mechanism of SaponificationA/P MARICHELVAN PRADEBANo ratings yet
- Ink compositions reduce smearing when highlighting printed imagesDocument9 pagesInk compositions reduce smearing when highlighting printed imagesJoyce Abegail De PedroNo ratings yet
- Surface Operations in Petroleum Production IDocument847 pagesSurface Operations in Petroleum Production Ingoxuandang93% (14)
- MoscharDocument33 pagesMoscharggooppaall ppuullaakkaallaaNo ratings yet
- Catalog G-1 Chem, Lubricants and AccDocument32 pagesCatalog G-1 Chem, Lubricants and AccBrayan MejiaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual for Pharmaceutical Engineering Laboratory BP308PDocument52 pagesLaboratory Manual for Pharmaceutical Engineering Laboratory BP308PArghadeep BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Chemicals StatusDocument1 pageChemicals StatusfahadullahNo ratings yet