Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Haematology
Uploaded by
Annisa Jasmine NugrahaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Haematology
Uploaded by
Annisa Jasmine NugrahaCopyright:
Available Formats
8 FOCUS – 1 HAEMATOLOGY Veterinary Times
A review of basic haematology
WHETHER you are already
using an in-house laboratory,
thinking of setting one up, or
JACKIE CASEY
BVetMed, MRCVS, and
using a commercial laboratory,
it is always worth reviewing the
processes used in haematology
PETRA WESCHE
DVM, MSc, MRCVS
to make sure you are getting
the best from your samples. of Greendale Veterinary Diagnostics, review the processes used
to ensure that you get the best results possible from your
Blood collection
samples in the first part of this week's special feature on
haematology
Correct blood collection and
handling is critical: improper deteriorate very quickly in transit. blood cells may swell, which raises
technique can result in inaccurate This will severely compromise the PCV and MCV and lowers
blood cell counts and morphological interpretation of morphology. MCHC);
artifacts. Sample quality is the major Red cells show increased • excessive time at room
contributor to analytical errors. susceptibility to Iysis after 24 hours temperature can cause autolysis;
Where possible, it is advisable to in EDTA. • platelet counts are most affected
use jugular puncture to minimise Sodium citrate is required for some by delays in processing - platelets
cell damage during sampling. 21 platelet - and all coagulation - have short lifespans and tend to
gauge needles should be used in studies. clump over time, even in the
dogs and 23 gauge in cats; remove presence of anti-coagulants; and
EDTA tubes should be filled to their
needle first and avoid rapid
capacity. Underfilled tubes have an • blood samples should be mixed
aspiration and transfer of blood into
excessive amount of EDTA relative again several times immediately
the sample tube which can result in
to the blood volume and can cause before a portion is removed for
cell Iysis.
shrinkage of RBCs, resulting in a testing - avoid excessive mixing to
For haematology you need liquid reduction in the MCV. prevent physical trauma to cells (roll
blood, so it is vital that blood or use a mechanical blood mixing
Invert the tube several times after
should be drawn into tubes or device.
filling to ensure thorough mixing,
syringes that contain anticoagulant-
but do not shake.
EDTA is the anti-coagulant of
choice for most haematology, Note that blood from some exotic Blood films
although it can cause platelet species haemolyse in EDTA - Well-prepared blood films are vital
clumping in cats. Heparin can cause contact a specialist laboratory. to allow accurate assessment of the
clumping and poor staining of haemogram.
leukocytes, so should not be used Handling samples If you suspect blood parasites, for
routinely for haematology. When handling samples, be aware of example Mycoplasma spp, it is vital
Smears should be prepared as soon the following: that a smear is made immediately
after collection as possible; • label each tube clearly, even if after collection as the organisms
prolonged exposure to EDTA testing in-house; quickly detach themselves from the
produces artifacts in neutrophils cells (the gold standard in this case
• blood should be processed as is PCR analysis).
and platelets.
soon as possible after collection;
If you are using a commercial Use only new, clean slides. Handle
• blood films should be made slides by the edges to avoid
laboratory it is advisable to submit
immediately - if delay is anticipated fingerprints.
a freshly-made, unstained smear.This
before processing further, the blood
is especially important for bloods
should be refrigerated at 4°C (if
obtained from birds and reptiles, as
kept at room temperature the red
all cells are nucleated and
25th July 2005 Veterinary Times 9
Finally, make two haemogram suggests anaemia. Heinz
Figure 1. smears from each bodies are seen in a number of
sample. Label clearly conditions and represent oxidative
and, when air-dried, denaturation of haemoglobin;
submit in special slide further evaluation of the patient and
containers if not history would be required to
evaluating them establish the cause in each case.
yourself. A well-formed Be aware that Heinz bodies can be
smear has a flame seen routinely in low numbers in
shape (Figure 3). Bear cat red blood cells. Other
in mind the following Romanovsky-type stains such as
Figure 2. precautions: May-Grunwald/Giemsa are
• do not blot or wipe commonly used in diagnostic
dry, as this introduces laboratories to accommodate the
scratches; need to evaluate different species
• do not refrigerate, as and specific disease problems.
the condensation that
forms on cold slides Common artifacts/issues
can Iyse cells; • poor fixation;
• keep away from • stain precipitate - a stain that is
formalin; and old, or has been left open over a
Figure 3.
• do not fix until ready longer period of time, may deposit
to stain, but keep precipitate on the slide that can be
covered. mistaken for haemoparasites (for
example Mycoplasma spp),
Staining therefore, keep stain fresh and
There are several rapid always covered when not in use and
staining kits available regularly filter or replace to
for in-practice use. minimise precipitate;
Figures 1 to 3. Blood Smear preparation.
These consist of a • overstaining - in overstained
Blood smear preparation three-stage staining slides, all cells are deeply coloured
procedure, based on a Wright stain, with important cell details being
The procedure for blood smear
which can be varied in intensity lost, the red cells appear to be
preparation is shown in Figures I
according to requirements. more dense and more basophilic
to 3.
(blue) than normal.
First, place one small drop of blood These stains contain both an acid
• understaining - in understained
(approximately 3 µl) near the end of stain (usually eosin) and a basic stain
(such as methylene blue). Structures slides all the cells are pale, cellular
a clean glass slide. Place another
details of the leukocytes are barely
slide at an angle of about 30-45~ to rich in basic compounds, such as
distinguishable and red cells are
the first. Draw back until it touches eosinophil granules, bind the acidic
very faint, however, this should not
the drop of blood in the acute angle dye and are stained red.
Acidic structures, such as be confused with hypochromia.
between the slides (Figure 1).
Practice with staining procedures to
Then, after the blood has spread (by DNA/RNA or basophil granules, are avoid overstaining or understaining.
capillary action) to within 2-3mm of stained blue by the basic stain.
Neutral structures stain purple. Figure 4 shows some examples of
the edge, push the second slide
New methylene blue is used for poorly-prepared slides.
quickly and smoothly across the
full-length of the first to produce a reticulocyte counts and to stain
thin smear (Figure 2). For anaemic Heinz bodies.
blood make the smear more quickly, Reticulocyte counts are helpful in
for thick or polycythaemic blood assessing the regenerative response
make the smear more slowly. of the bone marrow when the
25th July 2005 Veterinary Times 10
Sample evaluation RBC.WBC or platelet aggregation. number. A minimum of six to 10
Blood cell counts alone are not which can cause errors in cell platelets per high power field is
sufficient to adequately evaluate the counts in most automated counters. classed as "adequate" (average
haemogram. This will allow you to find the most microscope with wide held of view).
suitable area for the cell count. If platelets appear to be low, check
for clumping (this occurs frequently
in cats): look in the tail of the smear
Figure 4. using low power magnification.
Large platelets are called
macroplatelets and can suggest
accelerated regeneration in dogs.
Examine leukocyte morphology
(abnormalities and inclusions).
Perform differential leukocyte count
if not using automated equipment. A
minimum of 100 consecutively
encountered cells are counted in a
systematic manner using the
customary "battlement" pattern
within the counting area.These are
classified into their individual
categories, with a category for
Figure 4 Examples of poorly-prepared The size nature and condition of "other'' if required.The total
slides. cells and platelets provide vital leukocyte count is then multiplied
information when investigating by the percentage of each fraction
disease. to give the absolute count.
• Initial low-power examination: Some diseases - blood parasites and
Microscopic examination of a blood If using automated equipment it is
certain neoplasms – can be helpful to estimate the differential
smear is an essential part of any diagnosed directly from examination
haematological evaluation, count on the smear and compare to
of the blood film. that reported by the instrument.
regardless of the methodology to
be used for cell counting. The usual Estimate the total number of Note that it is possible for
site for examination of the stained leukocytes and develop a mental automated cell counters to give
smear is the small area of image of the appearance of typical erroneous results on occasions: if
monolayered cells between the leukocytes of each cell line any doubt about the result it is
thick body of the smear and the (neutrophil, eosinophil, Iymphocyte, advisable to check manually or
feathered edge. Leukocytes in this Monocyte, basophil). submit to a commercial laboratory.
area are flattened and not Evaluate the red cells for evidence • Packed cell volume
overlapping or touching and their of polychromasia, anisocytosis, (microhaematocrit):The packed cell
morphology can be easily Hypochromasia, poikilocytosis, etc. volume is used to estimate
recognised. Note any unusual findings such as erythroid mass. It is measured after
A systematic approach to evaluation atypical cells or parasites. high speed centrifugation of a
of the blood smear is essential to • Oil immersion magnification: column of blood (in a
obtain accurate and complete Once the counting area has been microhaematocrit tube) and
results. A common error is to begin selected examine erythrocytes and subsequently a tube reading device.
to identify and count the white cells confirm observations made at low Three distinct layers are produced:
immediately at high magnification. magnification (size, shape, colour, the plasma column. A small white
Failing to observe the abnormalities and any inclusions). band known as the buffy coat
characteristics of the leukocytes This will aid in interpretation of any (consisting of nucleated cells and
erythrocytes and platelets. Always anaemia and some specific disease platelets) and the packed
precede any cell counting by processes. erythrocytes (Figure 5).
scanning at low magnification (I0x) Examine platelet morphology and The appearance of plasma in
for rouleaux formation and for distribution and estimate relative haematocrit tubes can also provide
25th July 2005 Veterinary Times 11
important information: icterus
haemolysis and lipaemia may all be
detected.
Micro-haematocrit are accurate and
repeatable. Instrumentation and
supplies are inexpensive and
suitable for all practices.
Do not try to save time by not
allowing the sample to spin for long
enough.This produces an
overestimate of the PC\/: as the
plasma and cells are not fully
separated. Haematocrits may also
be computed and reported by in-
clinic automated analysers. However
these are calculated and may not
reflect the true picture in all cases.
Commercial laboratories
Many commercial laboratories offer
haematology services at reasonable
prices to veterinarians. Leading Figure 5. Serum Samples Figure 6. A centrifuge
laboratories have state-of-the-art
equipment as they are able to
and are best submitted for expert EDTA samples - check with your
spread the cost over a large
confirmation; reference laboratory and confirm
number of samples (Figure 6).
• they can provide additional that blood smears are at least
Counts are performed on scanned by trained professionals;
commentary on unusual findings
automated equipment,
and consultation with veterinary • automated haematology
supplemented by microscopic
clinical pathologists; equipment must be re-calibrated for
examination by trained personnel.
• they often have several trained each species or it will produce
In order to get the best from a inaccurate results;
personnel to discuss or interpret
commercial laboratory it is always
results; • persons evaluating blood smears
advisable to give full details of
• veterinary advice is offered on must be familiar with species
clinical history and medication when
further tests and investigations that differences or they may misclassify
submitting the samples.
may assist in a particular case; and white blood cell types and may
The advantages of using a misinterpret normal variation as a
commercial laboratory are: • trained personnel are more likely
to pick up faults with the equipment disease condition;
• well-run laboratories are enrolled • the largest laboratories have many
and often have back-up analysers or
in quality control programmes for technicians each of whom evaluates
manual facilities to compensate for
example RIQUAS,VLA to ensure blood films differently meaning a
problems.
accuracy; veterinarian cannot assume that all
The limitations associated with
• films are evaluated by personnel slides are evaluated in the same
employing a commercial laboratory
who process hundreds of smears way; and
are:
daily and are therefore more likely • not all laboratories are familiar
to notice and diagnose rare and • time - results are not usually
available for several hours (or the with evaluating veterinary samples
unusual abnormalities; and have veterinary
next day) which can be an issue for
• identification of bizarre or pathologists on staff you need to
time-sensitive cases or pre-
neoplastic cells is a job for an find this out or use a veterinary
anaesthetic screening;
expert; reference laboratory.
• fresh blood smears should be
• red cell parasites and inclusions
prepared in-clinic and sent with
can also be difficult to differentiate
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Virtual Microscope Lab 1Document6 pagesVirtual Microscope Lab 1Sama WahbaNo ratings yet
- CSF Analysis AFP 2021Document9 pagesCSF Analysis AFP 2021henry leonardo gaona pinedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Blood ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Blood ReviewerPhilline ReyesNo ratings yet
- Acne Urticata Associated With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: of Be of ofDocument4 pagesAcne Urticata Associated With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: of Be of ofGo McFlyNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Donating Blood: October 2017Document10 pagesThe Benefits of Donating Blood: October 2017MAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- Thalasemmia, Hemophilia & Blood Cancer at Hamza Foundation Peshawar Field Work Report by Fakhre Alam Mohmand Dept of Social Work University of PeshawarDocument26 pagesThalasemmia, Hemophilia & Blood Cancer at Hamza Foundation Peshawar Field Work Report by Fakhre Alam Mohmand Dept of Social Work University of PeshawarFakhrealamswNo ratings yet
- CS - Labs & CITWDocument9 pagesCS - Labs & CITWPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Hemocue WBC Diff: Operating ManualDocument84 pagesHemocue WBC Diff: Operating ManualLowayNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual and Review On Clinical Pathology: February 2014Document33 pagesLaboratory Manual and Review On Clinical Pathology: February 2014Muhammad JamalNo ratings yet
- General Pathology CoopDocument37 pagesGeneral Pathology CoopRaymondNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing School - IStudentNurse SiteDocument27 pagesMnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing School - IStudentNurse SiteCharity T.100% (1)
- Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (3g Is)Document34 pagesLimited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (3g Is)Vher John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Terminalia Catappa L. Extract Improves Survival, HematologicalDocument13 pagesTerminalia Catappa L. Extract Improves Survival, Hematologicalnicko.arya.dharmaNo ratings yet
- Training Resources: Unicel DXH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis System Training ResourcesDocument56 pagesTraining Resources: Unicel DXH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis System Training ResourcesHadi BitarNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 - Chap1Document78 pagesBiology Sem1 - Chap1kotaknotaku100% (1)
- Lab.5 WBCs CountingDocument4 pagesLab.5 WBCs CountingSarwar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis CompiledDocument76 pagesLeptospirosis CompiledTine Mendoza100% (1)
- Kova Glasstic Slide 10 With Grids: Instructions For UseDocument2 pagesKova Glasstic Slide 10 With Grids: Instructions For UsealvaroNo ratings yet
- AB-CD1700 Service Manual (1995-02 Rev 9140265A) Pp446-OCRDocument446 pagesAB-CD1700 Service Manual (1995-02 Rev 9140265A) Pp446-OCRTNo ratings yet
- Final Case (Postpartum)Document14 pagesFinal Case (Postpartum)KimJohnSanchoManeroNo ratings yet
- WBC AbnormalitiesDocument37 pagesWBC AbnormalitiesMajj MajjNo ratings yet
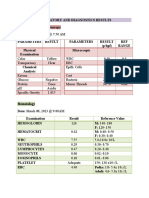
- Method: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMDocument10 pagesMethod: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMburela_naveenNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Malaria TesDocument5 pagesJurnal Malaria TesMaya RustamNo ratings yet
- BLG111Document7 pagesBLG111Manasseh LawrenceNo ratings yet
- TestresultDocument2 pagesTestresultaasirNo ratings yet
- Dengue Breakbone Fever Case StudyDocument53 pagesDengue Breakbone Fever Case StudyLeilani Rodriguez AmpoNo ratings yet
- Case Study For CellulitisDocument21 pagesCase Study For CellulitisMary Ann Lumbay Paye75% (4)
- Flagging and AlertsDocument12 pagesFlagging and AlertsLimNo ratings yet
- 1st MBBS PhysiologyDocument17 pages1st MBBS PhysiologyplsssssNo ratings yet