Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Self-Study Guide: BGP Protocol Terminologies: Isp-A
Uploaded by
Mahdi AlseddahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Self-Study Guide: BGP Protocol Terminologies: Isp-A
Uploaded by
Mahdi AlseddahCopyright:
Available Formats
Self-Study Guide: BGP Protocol Terminologies
BGP Stands for Border Gateway Protocol. It is one of the most important protocols to make Internet
work the way it works. It is used mainly in two scenarios:
Between ISP (Internet Service Provider) – ISP connect with at least one or more of other ISPs
and exchange all of their Public IP Routing information. This makes possible the connectivity
around the globe for all the internet users.
ISP-A
ISP-D ISP-B
ISP-C
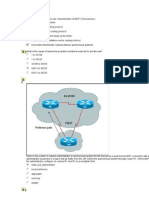
Between ISP and Enterprise Network – Enterprises sometimes host some servers and services
within their premises which they want people to access using Internet. In such a scenario if they
want to advertise their Public IP network to 2 different ISP so that even if one ISP fails people
can come in to access the services from the second ISP. Note that it is not required if enterprise
wants to just use two connections for failover purpose when people inside the enterprise are
accessing internet.
I-MEDITA LEARNING SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
Enterprise
Customer ISP-A
ISP-B
ISP-C
BGP is one the most fine tunable protocol and can handle very large number of routes as required by
most ISPs. It is one of the major topics for CCNP and CCIE Certification. Hence, we summarized few of
the most commonly used Acronyms of BGP Protocol for you.
1. BGP:
Border Gateway Protocol; it is a protocol for Inter-AS communication.
2. ASN:
Autonomous System Number represents a group of devices under a single administration. ASN
can be any number from 1 to 65535.
3. BGP Peer:
A BGP speaking router that has established the neighbor relationship with other BGP Speaking
Router.
4. FSM:
Finite State Machine; BGP use FSM to make decisions with peers. FSM has six states.
5. BGP Speaker:
A BGP Running router is known as BGP Speaker.
6. eBGP:
BGP neighbor relationship between two different ASN is known as external BGP peering.
7. iBGP:
BGP neighbor relationship between two same ASN is known as internal BGP peering.
I-MEDITA LEARNING SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
8. BGP Synchronization Rule:
A BGP router should not use, or advertise to an external neighbor, a route learned by IBGP,
unless that route is local or is learned from the IGP.
9. Neighbor Table:
A table created in BGP that keeps all the BGP speaking neighbor information.
10. BGP Table:
Also considered as forwarding database. It contains list of networks learned from each neighbor,
BGP Attributes and some other information.
11. NLRI:
Network layer reachability Information: A list of Length, prefix tuples.
12. Single Homed:
When a router is connected with only one ISP, it is known as Single Homed connectivity.
13. Dual Homed:
When there are more than one connection from ISP terminating on a single customer, it is
known as Dual Homed.
14. Multihomed:
Connections from different ISPs can terminate on single customer site router.
15. Dual Multihomed:
Multiple edge routers, connecting to multiple ISP is known as Multihomed connection.
16. Path Attributes:
Set of metrics describing the path to the network.
17. Router Reflectors:
A technique used in IBGP to avoid full mesh neighbor relationship with other peers which is
necessary.
18. Communities:
BGP Communities are tags that can be used by BGP to achieve some task. Communities can be
applied on incoming and outgoing prefixes.
19. MED:
Multi-Exit Discriminator; an attribute defining preferred path among multiple entry points into
an AS.
I-MEDITA LEARNING SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
20. AS-Path List:
A list of autonomous systems that a prefix crosses to reach the destination. BGP maintain an AS-
Path list for loop avoidance.
21. Open Message:
It includes a set of parameters that have to be agreed upon before a full BGP adjacency can be
established. After successful exchange of Open Message, updates can be sent.
22. Notification Message:
Message sent when neighbor relationship is tiered down because of some error.
23. Weight:
A Cisco proprietary attribute for path selection. It has the value from 0 to 65535 and is
completely locally significant.
24. Hard Reset:
Event that completely re-initializes the routing table on one or more BGP sessions.
25. Soft Reset:
Re-establishing the neighbor relationship on per neighbor basis without clearing the BGP
session. It doesn’t stop the flow of the traffic.
You may also like:
Self-Study Guide: OSPF Routing Protocol Terminologies
Popular Cisco CCNA, CCNP and CCIE Trainer’s in India
Basic CCNA Networking Interview Questions & Answers
How to pass CCNA Exam in First Attempt
To know more about Cisco Training and Certifications, call +91-8750004411 or email us at
info@imedita.com
I-MEDITA LEARNING SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
You might also like
- Forensic Science From The Crime Scene To The Crime Lab 2nd Edition Richard Saferstein Test BankDocument36 pagesForensic Science From The Crime Scene To The Crime Lab 2nd Edition Richard Saferstein Test Bankhilaryazariaqtoec4100% (25)
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewDocument4 pagesBGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewAmit DongreNo ratings yet
- Change Management in British AirwaysDocument18 pagesChange Management in British AirwaysFauzan Azhary WachidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: BGP: BGP Terminology, Concepts and OperationDocument12 pagesChapter 6: BGP: BGP Terminology, Concepts and OperationJordi KlerigaNo ratings yet
- Cis185 ROUTE 6 EnterpriseInternetConnectivityDocument83 pagesCis185 ROUTE 6 EnterpriseInternetConnectivityHung Phan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Cis185 ROUTE 7 BGP ImplementingBGPDocument98 pagesCis185 ROUTE 7 BGP ImplementingBGPNILTON RUBEN AVENDAÑO AGUEDONo ratings yet
- CIS 185 CCNP ROUTE Ch. 6 Border Gateway Protocol Solution for ISP Connectivity – Part 1Document98 pagesCIS 185 CCNP ROUTE Ch. 6 Border Gateway Protocol Solution for ISP Connectivity – Part 1Luiz CahueNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3-ODC112029 BGP Multi-Homed ISSUE1Document24 pagesModule 3.3-ODC112029 BGP Multi-Homed ISSUE1jorgevargasmNo ratings yet
- BGP QuestionDocument45 pagesBGP Questionashok nagNo ratings yet
- BGP Fundamentals: Part 1: Facebook22TwitterlinkedinpinterestwhatsappDocument7 pagesBGP Fundamentals: Part 1: Facebook22Twitterlinkedinpinterestwhatsappramchandnnnnn waghNo ratings yet
- BGP Autonomous SystemDocument2 pagesBGP Autonomous Systembasawaraj900No ratings yet
- ON Current BGP Problems and Suggested Solutions CS526-Assignment# 4Document7 pagesON Current BGP Problems and Suggested Solutions CS526-Assignment# 4Sai Kyaw HtikeNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNP ROUTE BGP Quick ReferenceDocument64 pagesCisco CCNP ROUTE BGP Quick ReferencePiya ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Internet Service ProvidersDocument26 pagesInternet Service ProviderssyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- BGP Introduction - Understanding the Border Gateway ProtocolDocument15 pagesBGP Introduction - Understanding the Border Gateway ProtocolPankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: BGP: Instructor MaterialsDocument73 pagesChapter 11: BGP: Instructor MaterialskanthyadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BGPDocument105 pagesChapter 3 BGPMike TNo ratings yet
- Simulate BGP/OSPF Routing ProtocolsDocument10 pagesSimulate BGP/OSPF Routing ProtocolsRukmini GhantiNo ratings yet
- Border Gateway ProtocolDocument4 pagesBorder Gateway ProtocolKashif BakshNo ratings yet
- ROUTE Chapter 6 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document11 pagesROUTE Chapter 6 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (4)
- IT221 T Project Template (BGP)Document12 pagesIT221 T Project Template (BGP)1021shiroe1021No ratings yet
- Introduction To BGPDocument13 pagesIntroduction To BGPkmadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Routing: Link StateDocument33 pagesBasics of Routing: Link StateJef BenNo ratings yet
- Route Chapter 6 CCNP 6Document5 pagesRoute Chapter 6 CCNP 6Walter SolisNo ratings yet
- BGP(Border Gateway ProtocolDocument23 pagesBGP(Border Gateway ProtocolJumput PurnomoNo ratings yet
- BGPDocument12 pagesBGPKesavarapuVaralababuNo ratings yet
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewDocument4 pagesBGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewBhanu Saini100% (1)
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers: Key Concepts ExplainedDocument5 pagesBGP Interview Questions and Answers: Key Concepts ExplainedprakashrjsekarNo ratings yet
- Networking and Scripting - BGP Q&ADocument4 pagesNetworking and Scripting - BGP Q&AMohammed ElyasNo ratings yet
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers - Basic and Advanced LevelsDocument6 pagesBGP Interview Questions and Answers - Basic and Advanced LevelsAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Network Level Multihoming and BGP Challenges: Li Jia Helsinki University of Technology Jili@cc - Hut.fiDocument5 pagesNetwork Level Multihoming and BGP Challenges: Li Jia Helsinki University of Technology Jili@cc - Hut.fijoaopualo_df52No ratings yet
- Connecting Networks Exam 3Document3 pagesConnecting Networks Exam 3Marce L YungaNo ratings yet
- 04 BGPDocument44 pages04 BGPducquang89No ratings yet
- Border Gateway Protocol ThesisDocument5 pagesBorder Gateway Protocol Thesiscandacedaiglelafayette100% (2)
- BGP StateDocument14 pagesBGP StateRakesh BadayaNo ratings yet
- Operation: Extensions NegotiationDocument15 pagesOperation: Extensions NegotiationBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3-ODC112023 BGP Overview ISSUE1Document24 pagesModule 3.3-ODC112023 BGP Overview ISSUE1Jorge VargasNo ratings yet
- Examen BGP 6.0Document9 pagesExamen BGP 6.0Angel AvilesNo ratings yet
- The Bryant Advantage CCNP ROUTE Study Guide: Back To IndexDocument57 pagesThe Bryant Advantage CCNP ROUTE Study Guide: Back To IndexTyler MillsNo ratings yet
- Why We Use BGP?Document7 pagesWhy We Use BGP?Guhan RkNo ratings yet
- Why We Use BGP?Document7 pagesWhy We Use BGP?Guhan RkNo ratings yet
- Introduction to BGP Routing ProtocolDocument14 pagesIntroduction to BGP Routing ProtocolAakash Goel100% (1)
- 2 - BGP Basics - HuaweiDocument44 pages2 - BGP Basics - HuaweinocNo ratings yet
- Ipi Internet Route ServerDocument8 pagesIpi Internet Route ServerNguyễn Phương LyNo ratings yet
- BGP Part IDocument42 pagesBGP Part IwaseemshaikNo ratings yet
- Routing Protocols Explained: PrefaceDocument3 pagesRouting Protocols Explained: PrefaceSai RamNo ratings yet
- MPLS Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)Document2 pagesMPLS Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)Habet MoshmoshNo ratings yet
- CCNP Quick Reference PDFDocument30 pagesCCNP Quick Reference PDFAditya BeheraNo ratings yet
- Cisco ExamDocument109 pagesCisco ExamBart WetzelsNo ratings yet
- Routers Guide - IP Networks, Routing Tables & ProtocolsDocument12 pagesRouters Guide - IP Networks, Routing Tables & ProtocolspravinuttamNo ratings yet
- Implementing BGP-4 Route Reflectors, Confederations, or BothDocument5 pagesImplementing BGP-4 Route Reflectors, Confederations, or BothAbdelaziz MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Stump The Chump Technical Screen Questions: October 12, 2012Document11 pagesStump The Chump Technical Screen Questions: October 12, 2012oltzerNo ratings yet
- BGP Short Notes: Key Concepts and Usage of the Border Gateway ProtocolDocument12 pagesBGP Short Notes: Key Concepts and Usage of the Border Gateway Protocolparveen_1974No ratings yet
- 01-09 Huawei AR Series - BGP ConfigurationDocument154 pages01-09 Huawei AR Series - BGP ConfigurationHarry Chan Putra. SP. MTCNA. MTCTCE. MTCRENo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Practical - 7: AIM - Implement The Concept of Dynamic Routing (RIP, OSPF, BGP)Document6 pagesComputer Networks Practical - 7: AIM - Implement The Concept of Dynamic Routing (RIP, OSPF, BGP)JeetNo ratings yet
- Explain BGP ?Document3 pagesExplain BGP ?Pravesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSFrom EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Krok2 - Medicine - 2010Document27 pagesKrok2 - Medicine - 2010Badriya YussufNo ratings yet
- Guiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test BankDocument16 pagesGuiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (29)
- Motor Master 20000 SeriesDocument56 pagesMotor Master 20000 SeriesArnulfo Lavares100% (1)
- CAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityDocument6 pagesCAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityPermalino Borja Rose AnneNo ratings yet
- Lifespan Development Canadian 6th Edition Boyd Test BankDocument57 pagesLifespan Development Canadian 6th Edition Boyd Test Bankshamekascoles2528zNo ratings yet
- 20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 EagDocument122 pages20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 Eagxie samNo ratings yet
- Survey Course OverviewDocument3 pagesSurvey Course OverviewAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Important Instructions To Examiners:: Calculate The Number of Address Lines Required To Access 16 KB ROMDocument17 pagesImportant Instructions To Examiners:: Calculate The Number of Address Lines Required To Access 16 KB ROMC052 Diksha PawarNo ratings yet
- Customer Perceptions of Service: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument27 pagesCustomer Perceptions of Service: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinKoshiha LalNo ratings yet
- NLL - Elementary - Coursebook 2019 PDFDocument24 pagesNLL - Elementary - Coursebook 2019 PDFgilmolto100% (1)
- AFNOR IPTDS BrochureDocument1 pageAFNOR IPTDS Brochurebdiaconu20048672No ratings yet
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDocument14 pagesInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisNo ratings yet
- MBO, Management by Objectives, Pooja Godiyal, Assistant ProfessorDocument20 pagesMBO, Management by Objectives, Pooja Godiyal, Assistant ProfessorPooja GodiyalNo ratings yet
- Wi FiDocument22 pagesWi FiDaljeet Singh MottonNo ratings yet
- Pre Job Hazard Analysis (PJHADocument2 pagesPre Job Hazard Analysis (PJHAjumaliNo ratings yet
- Sanhs Ipcrf TemplateDocument20 pagesSanhs Ipcrf TemplateStephen GimoteaNo ratings yet
- Moor, The - Nature - Importance - and - Difficulty - of - Machine - EthicsDocument4 pagesMoor, The - Nature - Importance - and - Difficulty - of - Machine - EthicsIrene IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyBunga Larangan73% (11)
- Unit 1 - Gear Manufacturing ProcessDocument54 pagesUnit 1 - Gear Manufacturing ProcessAkash DivateNo ratings yet
- Archlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Document16 pagesArchlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Goh Ka WeeNo ratings yet
- AsiaSat 7 at 105Document14 pagesAsiaSat 7 at 105rahman200387No ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyDocument20 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyHima Bindhu BusireddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Computer ScienceradNo ratings yet
- IoT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEMDocument18 pagesIoT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEMArunkumar Kuti100% (2)
- SEG Newsletter 65 2006 AprilDocument48 pagesSEG Newsletter 65 2006 AprilMilton Agustin GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Good Ethics Is Good BusinessDocument9 pagesGood Ethics Is Good BusinesssumeetpatnaikNo ratings yet
- 50 Years of Teaching PianoDocument122 pages50 Years of Teaching PianoMyklan100% (35)