Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Lawliet RyuzakiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Lawliet RyuzakiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4:
Marginal Costing and Cost Volume Costing Analysis
Academic Areas of Competence
*Basic Principles of Marginal Costing *CPV Sensitivity Analysis
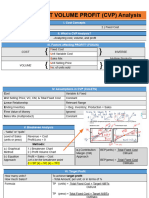
*Basic assumption within the relevant range *BEP Graph and CVP graph
*Understanding the Marginal Income Statement *The Indifference point
*Relevant Formulas in Marginal Costing *Operating leverage computation and analysis
Basic Principles
Cost and expenses are segregated into fixed and variable elements.
Profit = Sales – Cost and Expenses
Profit = Sales – Fixed Cost – Variable Costs*
(*The term cost means costs and expenses)
Activities and operations are made within the relevant range.
Basic Assumptions within the relevant range
Linearity – The behavior of sales and cost is linear
Behavior of sales, costs and expenses:
Sales – it changes directly in relation to the level of units sold.
Fixed Costs – Total fixed cost is constant without regard to the change in the level of units of
production and sales; unit fixed cost changes (I.e., unit foxed cost decreases as the level of
production increases, and vice-versa).
Variable Costs – Total variable costs change in direct proportion with the level of units produced
and sold; unit variable cost is constant.
Selling Price – assumed to be constant.
WIP inventory – disregarded, there is no WIP inventory
FG inventory – no charge in the FG inventory (i.e., production = sales).
Product(s) and sales mix:
There is only one product, or
If there are 2 or more products produced and sold, the sales mix is assumed to be constant
The Marginal income statement (or variable income statement)
The condensed format The expanded format
Sales Px Sales Px
-Variable costs and expenses x -Variable costs of goods sold x
Contribution margin x Manufacturing Margin x
-Fixed cost and expenses x -Variable Expenses x
Income before income tax Px Contribution margin x
-Direct fixed costs and expenses x
Direct margin (or segment margin) x
-Indirect fixed costs and expenses x
Income before income tax Px
Variable Production costs refer to direct materials direct labor, and variable overhead
Examples of variable expenses are delivery expenses, salesmen’s commission, and packing supplies
Direct fixed costs and expenses are those that are directly related to the segment (i.e., division,
department, or product line); these costs are directly identified with the segment that once the segment
is discontinued, these costs are avoided.
Indirect fixed costs and expenses = sometimes called as allocated costs or unavoidable costs
Summary of costs and expenses behavior within the relevant range.
Production and sales volume Unit sales price
↑ ↓ ↑ ↓
Variable cost
Per total ↑ ↓ Ne Ne
Per unit constant constant Ne Ne
Variable cost
Per total Constant Constant Ne Ne
Per unit ↓ ↑ Ne Ne
(ne = no effect)
Relevant Formulas
Contribution Margin
CM = Sales - Variable Cost CM = Fixed Cost + IBIT
CM = Sales x CMR CM = Quantity sold x UCM
Contribution Margin Ratio
CMR = 100% - VC Ratio CMR = CM/SALES
CMR = UCM/UCP CMR = NPR/MSR
CMR = △EBIT/△SALES (if FC
remains the same)
Unit Contribution Margin
UCM = USP - UVC
UCM = FC/BEP (units)
UCM = CM/Quantity Sold
Profit
Profit = CM – Fixed Cost
Profit = Sales x MS Ratio x CM Ratio
Profit = Sales x NP Ratio
△Profit = △CM – ↑ in FC
△Profit = △CM + ↓ in FC
Break Even Point
BEP (units) = FC/UC Margin
BEP (pesos)= FC/CM Ratio
Comp. BEP (units) = FC/Average UCM
Comp. BEP (pesos)= FC/Average CMR
BEP (units) = Actual sales x (1 - MS Ratio)
At BEP: Profit (loss) = 0
Sales = Total costs
Contribution margin = total fixed costs
Fixed Costs
FC = CM (at BEP)
FC = CM = Profit
FC = BEP (units) x UCM
Variable Cost Ratio
VC Ratio = VC/Sales
VC Ratio = UVC/USP
VC Ratio = 100% - CMR
VC Ratio = △Costs/△Sales
VC Ratio = (△Costs – ↑ in FC)/ △Sales
VC Ratio = (△Costs – ↓ in FC)/ △Sales
Margin of Safety
MS = Actual Sales – Actual Breakeven Sales
MS = Budgeted Sales – Budgeted Breakeven Sales
MS = Sales x MS Ratio
MSR = MS/Actual (or Budgeted) Sales
MSR = NPR/CMR
MSR = [1 – (BE Sales/Actual Sales)]
Net Profit Ratio
Unit Profit Margin / USP
NP Ratio = MSR x CMR
Degree f Operating Leverage (DOL)
DOL = CM/EBIT
DOL = % △ in EBIT / % △ in Sales
% △ in EBIT = % △ in Sales x DOL
You might also like
- Strat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressDocument17 pagesStrat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressAerwyna AfarinNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis and Marginal CostingDocument5 pagesCVP Analysis and Marginal CostingKJKSZPJ LXGIWYLNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis HandoutDocument24 pagesCVP Analysis HandoutAlexis RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument51 pagesCost-Volume-Profit AnalysisKalash SinghalNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume Profit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCost-Volume Profit AnalysisVianca MaquilanNo ratings yet
- Mas 06-03 Cost Volume Profit (CVP)Document7 pagesMas 06-03 Cost Volume Profit (CVP)xernathanNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic Univesity of The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesPolytechnic Univesity of The PhilippinesJewel AmponinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument7 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementIris FenelleNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CVP and Breakeven AnalysisDocument4 pagesModule 3 CVP and Breakeven Analysiskhaireyah hashimNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument18 pagesCVP Analysiskhyla Marie NooraNo ratings yet
- Công TH CDocument19 pagesCông TH Ckim oanhNo ratings yet
- Cost and management accounting: Marginal costing & CVP analysisDocument25 pagesCost and management accounting: Marginal costing & CVP analysisJyotsna JhaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing Formulae: Contribution Sales (Sales - Variable Cost) SalesDocument1 pageMarginal Costing Formulae: Contribution Sales (Sales - Variable Cost) SalespratiknkNo ratings yet
- Element of Costing Unit 4 and 5Document30 pagesElement of Costing Unit 4 and 5best video of every timeNo ratings yet
- MMM MMMMMMMMMMMMDocument48 pagesMMM MMMMMMMMMMMMgojjamnhialpalNo ratings yet
- Equation and FormulaDocument6 pagesEquation and FormulaNgọc Minh Đỗ ChâuNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument2 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisBloodyapplesNo ratings yet
- 1491820614costing by CA Jitender Singh (Overhead, Labour, Material, Marginal, Ratio, Machine Hour RateDocument311 pages1491820614costing by CA Jitender Singh (Overhead, Labour, Material, Marginal, Ratio, Machine Hour RateRam IyerNo ratings yet
- Summary FinalDocument28 pagesSummary FinalJackNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Managerial Accounting Chapter 5Document2 pagesFormulas of Managerial Accounting Chapter 5Shahinul KabirNo ratings yet
- Five Important Factors Influence Cost Volume Profit Analysis AreDocument9 pagesFive Important Factors Influence Cost Volume Profit Analysis Aresuraj banNo ratings yet
- Cost Behaviour & Decision Making - HodDocument65 pagesCost Behaviour & Decision Making - Hodsrimant100% (2)
- Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesMarginal CostingSandhya Darshan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Cost AccountingDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Cost AccountingManika SharmaNo ratings yet
- ACAUD 3139 Strategic ManagementDocument31 pagesACAUD 3139 Strategic ManagementchxrlttxNo ratings yet
- 2-CVP Analysis, Use & RelationshipsDocument1 page2-CVP Analysis, Use & RelationshipsDana Beatrice RoqueNo ratings yet
- Product costing methods & variance analysisDocument3 pagesProduct costing methods & variance analysisPrakhar SharmaNo ratings yet
- MS - Until WCM HeyheiDocument16 pagesMS - Until WCM Heyheimisonim.eNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis and ABC ChapterDocument63 pagesCost-Volume-Profit Analysis and ABC ChapterGizachewNo ratings yet
- Summary 2Document9 pagesSummary 2Eman El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting FormulasDocument6 pagesManagerial Accounting FormulasKristine Esplana ToraldeNo ratings yet
- SC Class 2Document54 pagesSC Class 2rodrigo.felix17012002No ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument79 pagesCVP AnalysisMRIDUL GOELNo ratings yet
- Profit Modelling Variable Costing Absorption CostingDocument17 pagesProfit Modelling Variable Costing Absorption CostingLeslie Beltran ChiangNo ratings yet
- MAC Summary of FormulasDocument25 pagesMAC Summary of FormulasRuNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - Marginal CostingDocument2 pagesCost Accounting - Marginal CostingS Usama SNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument6 pagesBreak Even Analysisemmanuel Johny100% (1)
- CVP Copy 4Document2 pagesCVP Copy 4BloodyapplesNo ratings yet
- Understand Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) AnalysisDocument39 pagesUnderstand Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) AnalysisVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- CIMA P1 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCIMA P1 Cheat Sheetasamy3010100% (1)
- Cost VolumeDocument22 pagesCost Volume2023-2-95-013No ratings yet
- Persys Midterms FormulasDocument2 pagesPersys Midterms Formulaslingat airenceNo ratings yet
- Analy CDocument52 pagesAnaly CMiriam Ubaldo DanielNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Elements of Cost and Classification of CostDocument11 pagesTopic 11 Elements of Cost and Classification of CostCarry KelvinsNo ratings yet
- CVP NotesDocument7 pagesCVP NotesKerrice RobinsonNo ratings yet
- CH - 13Document39 pagesCH - 13divya kalyaniNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument5 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document24 pagesLecture 5neri biNo ratings yet
- Acctg 402Document9 pagesAcctg 402Marriah Izzabelle Suarez RamadaNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis Explained: Cost-Volume-Profit RelationshipsDocument9 pagesCVP Analysis Explained: Cost-Volume-Profit RelationshipsgishaNo ratings yet
- CHP 14. Marginal Costing - CAPRANAVDocument28 pagesCHP 14. Marginal Costing - CAPRANAVAYUSH RAJNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis (CVP Analysis) : Incremental Contribution"Document14 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis (CVP Analysis) : Incremental Contribution"Corin Ahmed CorinNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument2 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingLaura OliviaNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument28 pagesCVP AnalysisSurender SinghNo ratings yet
- Costram - Midterm Reviewer PDFDocument8 pagesCostram - Midterm Reviewer PDFliliNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing: Types of Product Costing MethodDocument2 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing: Types of Product Costing MethodKuya ANo ratings yet
- Cost Behaviour and Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) AnalysisDocument21 pagesCost Behaviour and Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) AnalysisEugene TeoNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument9 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisAryh Grace Tan100% (1)
- CVP AnalysisDocument21 pagesCVP AnalysisDaksh AnejaNo ratings yet
- Bii - Factors Influencing Performance of Dairy Farming Projects in Cherangani Sub County, Transnzoia County, KenyaDocument68 pagesBii - Factors Influencing Performance of Dairy Farming Projects in Cherangani Sub County, Transnzoia County, KenyaGirmaTeklehanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Building TrustDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Building TrustSally GarasNo ratings yet
- Receipt: MRS Astrid Hairasani MakkarumpaDocument1 pageReceipt: MRS Astrid Hairasani MakkarumpaAzhari NugrahaNo ratings yet
- FTU Thesis on Impacts of Info Asymmetry on Cost of EquityDocument79 pagesFTU Thesis on Impacts of Info Asymmetry on Cost of EquityLớp Cao họcNo ratings yet
- Current Scenario of Financial ServicesDocument8 pagesCurrent Scenario of Financial Servicessureshsen80% (5)
- MGT 1115 REVIEW PROBLEM SETS CHAPTERS 10-17Document11 pagesMGT 1115 REVIEW PROBLEM SETS CHAPTERS 10-17Maryrose Sumulong100% (2)
- Revenue Recognition Under PFRS 15Document14 pagesRevenue Recognition Under PFRS 15Jenver BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 SolDocument17 pagesCHP 2 SolZakiah Abu KasimNo ratings yet
- Draft Red Hearing Prospectus of Lemon Tree PDFDocument572 pagesDraft Red Hearing Prospectus of Lemon Tree PDFShankar SanyalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document3 pagesExercise 2Sebastian AcostaNo ratings yet
- On Competitive StrategiesDocument33 pagesOn Competitive Strategiesmmjmmj100% (1)
- Financial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition Mishkin Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition Mishkin Solutions Manualmichaelkrause22011998gdj100% (31)
- Digital Marketing Impact on Consumer BehaviorDocument3 pagesDigital Marketing Impact on Consumer Behavioranusha100% (1)
- Practice Final Bus331 Spring2023Document2 pagesPractice Final Bus331 Spring2023Javan OdephNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 1 OverviewDocument18 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 1 OverviewSiambeNo ratings yet
- Importance and Salience of Customer BenefitsDocument19 pagesImportance and Salience of Customer BenefitsKunal JainNo ratings yet
- Jaearmntk PDFDocument272 pagesJaearmntk PDFMalavika SivagurunathanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Chinese Dumping in India PPT Sem5 GRP No. 6Document10 pagesEffects of Chinese Dumping in India PPT Sem5 GRP No. 6akanksha parabNo ratings yet
- What Is Otcei ??? - Shares & Stock Forum - Chartered Accountants ..Document7 pagesWhat Is Otcei ??? - Shares & Stock Forum - Chartered Accountants ..kelvin_king222No ratings yet
- Bar Graph Unit MonthDocument2 pagesBar Graph Unit MonthshrikantNo ratings yet
- PR Emet 2 PDFDocument2 pagesPR Emet 2 PDFgleniaNo ratings yet
- Cengage Eco Dev Chapter 13 - The Environment and Sustainable Development in AsiaDocument32 pagesCengage Eco Dev Chapter 13 - The Environment and Sustainable Development in AsiaArcy LeeNo ratings yet
- Break Even Point No Profit No Loss Sales - Variable Contribution - Fixed Cost ProfitDocument10 pagesBreak Even Point No Profit No Loss Sales - Variable Contribution - Fixed Cost ProfitShilpan ShahNo ratings yet
- Avca Avca Venture Capital in Africa Report v13Document40 pagesAvca Avca Venture Capital in Africa Report v13Mr PenZoNo ratings yet
- 1343 Kaustubh IFMDocument11 pages1343 Kaustubh IFMKaustubh ShilkarNo ratings yet
- Trading Hub 3.0Document36 pagesTrading Hub 3.0Báu Lương Văn100% (12)
- NR4 IbDocument44 pagesNR4 IbspringsnowNo ratings yet
- BA500 MarketingDocument32 pagesBA500 Marketingarshdeep1990No ratings yet
- FMS 5,6Document19 pagesFMS 5,6Upen DudiNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument65 pagesSyllabusSannu VijayeendraNo ratings yet