Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 4 - Summary: The Three Laws of Motion of Isaac Newton
Uploaded by
Dilip KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 4 - Summary: The Three Laws of Motion of Isaac Newton
Uploaded by
Dilip KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 4 - summary
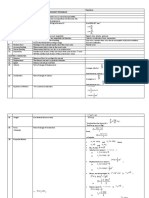
The Three Laws of Motion of Isaac Newton (1642 – 1727):
1. Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform These laws can be used to solve real
motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that engineering problems
state by forces impressed upon it.
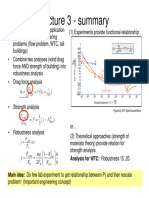
Example: Fall of the WTC towers N = 110
2. The change of motion is proportional to the motive force
impresses, and is made in the direction of the right line in on 9/11 2001
which that force is impressed. = 96 V0
3. To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction: M = 80
or, the mutual action of two bodies upon each other are
always equal, and directed to contrary parts. Photograph of towers removed
due to copyright restrictions.
pp. 37-48 in manuscript
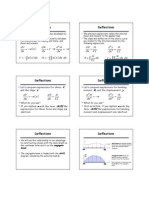
Test 2 hypotheses:
1) Free fall
2) Kausel’s model – discrete mass formulation
Instantaneous
m0 ,V0 m2 = m0 + 2m Conservation of linear
m1 = m0 + m V2 = ?
momentum under
V1 = ?
h changing mass
m
δ p i = 0 ⇒ Vi = i−1 Vi−1
mi
Vi −Vi−1
Δti =
g
Discrete
Free fall mass model Measurement
North Tower: 10.9 s ≈ 10 s
South Tower: 8.9 s
You might also like
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 4: Stresses and Strength Stresses and Equilibrium Discrete ModelDocument16 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 4: Stresses and Strength Stresses and Equilibrium Discrete ModelDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Quick SheetDocument1 pagePhyiscs Quick SheetEJ PosseliusNo ratings yet
- 18033578841st Sec Revision OnenanDocument32 pages18033578841st Sec Revision Onenanozops4ozoNo ratings yet
- F = m γ = m dv dt ,: Math 250 ADocument3 pagesF = m γ = m dv dt ,: Math 250 AjdgharibNo ratings yet
- FDS 2023 Theory-2Document1 pageFDS 2023 Theory-2Omkar WatpadeNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.50 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem 2.50 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Homework AssignmentDocument15 pagesChapter 06 Homework AssignmentMohammed ElnaggarNo ratings yet
- Heat 1 JeeDocument29 pagesHeat 1 JeeBrijesh BhartiNo ratings yet
- 17 Heat-2Document53 pages17 Heat-2Aman KeltaNo ratings yet
- The Finite Element Method for Dynamic AnalysisDocument33 pagesThe Finite Element Method for Dynamic AnalysispriyankarNo ratings yet
- Momentum & Collision (Impulse)Document5 pagesMomentum & Collision (Impulse)bat.laugh100% (1)
- Ia Dyn Chapter5Document5 pagesIa Dyn Chapter5WarishaNo ratings yet
- ECS455!5!4 - Cyclic PrefixDocument21 pagesECS455!5!4 - Cyclic Prefixali AlinezhadNo ratings yet
- PHY DEF Half-UpdtedDocument13 pagesPHY DEF Half-Updted'Aqilah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document141 pagesChapter 3Ahmad KarimNo ratings yet
- MSE3207 Lec18Document5 pagesMSE3207 Lec18Kasu NiNo ratings yet
- Physics Note Dynamic Force 02Document30 pagesPhysics Note Dynamic Force 02Tapendra BistNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document33 pagesLecture 13Jarom SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulaeDocument49 pagesPhysics FormulaeAll Rounder தமிழன்No ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULAS: 71 Equations for Kinematics, Forces, Energy, Momentum, and MoreDocument3 pagesPHYSICS FORMULAS: 71 Equations for Kinematics, Forces, Energy, Momentum, and MoreJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 1 (Kinematics)Document5 pagesPhysics Module 1 (Kinematics)Nancy AndrawesNo ratings yet
- Applying Newtons LawDocument6 pagesApplying Newtons Lawminh hoàng nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field With Time As A Dynamical Variable PosterDocument1 pageQuantum Field With Time As A Dynamical Variable PostergilyauNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS MOTION EQUATIONSDocument2 pagesMECHANICS MOTION EQUATIONSIan Neil LaenoNo ratings yet
- Notes 08bDocument5 pagesNotes 08bViệt Vớ VẩnNo ratings yet
- 97 PhysDocument22 pages97 PhysLani Lizza BuelaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics DynamicsDocument5 pagesEngineering Mechanics DynamicsReggy SeptaNo ratings yet
- 15.1 - Introduction - Physics LibreTextsDocument1 page15.1 - Introduction - Physics LibreTextsjlrnr1991No ratings yet
- Formula Fizik Pecutan SPM 2019Document4 pagesFormula Fizik Pecutan SPM 2019athirah razallyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Dynamics, Statics, Strength)Document15 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Dynamics, Statics, Strength)Shan BarbastroNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument10 pagesMomentumBatisane Kantsu MathumoNo ratings yet
- 6.mites2010 Solution2Document14 pages6.mites2010 Solution2Catherine WhitewoodNo ratings yet
- Tipos de Fluidos No NewtonianosDocument2 pagesTipos de Fluidos No NewtonianosIsabellaNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and Collisions ExplainedDocument25 pagesLinear Momentum and Collisions ExplainedArie HNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 OkDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Okwaelabood51No ratings yet
- Review Module 18 - Hydraulics 3 (Part 1)Document1 pageReview Module 18 - Hydraulics 3 (Part 1)Alexander P. BelkaNo ratings yet
- Xi Ach-4th Feb Phy SoluDocument10 pagesXi Ach-4th Feb Phy Solupuraosohamsandip01No ratings yet
- Solving for the critical bending moment of a reinforced concrete beamDocument2 pagesSolving for the critical bending moment of a reinforced concrete beamSamantha VillaltaNo ratings yet
- Rotating Unbalance Free Vibration Principal of Virtual WorkDocument3 pagesRotating Unbalance Free Vibration Principal of Virtual WorkVincent KohNo ratings yet
- MP 06Document2 pagesMP 06l Faris lNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 EquationsDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 EquationsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Tien Duc: Unofficial SolutionDocument4 pagesTien Duc: Unofficial SolutionMinh DuyNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument248 pagesThermodynamicssnehaeslate100% (1)
- Phy MomentumDocument11 pagesPhy MomentumKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- In-Class Problems 11-13: Uniform Circular Motion SolutionsDocument8 pagesIn-Class Problems 11-13: Uniform Circular Motion SolutionsSarthakNo ratings yet
- 13.kinetic Theory of Gases and ThermodynamicsTheoryDocument25 pages13.kinetic Theory of Gases and ThermodynamicsTheorymaqboolansari.jaunpurNo ratings yet
- Walter Lewin Notes 11Document12 pagesWalter Lewin Notes 11Romesor Apol100% (1)
- Problem 1.12 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 1.12 PDFWallace AbreuNo ratings yet
- 2 PanjangGelombang DeBroglie Termal Dan PengantarDocument8 pages2 PanjangGelombang DeBroglie Termal Dan PengantarRustan RuslanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument36 pagesDynamics Notestayyab10ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 - Contact InteractionsDocument14 pagesChapter 04 - Contact InteractionsPeterNo ratings yet
- MATH151 BASIC PHYSICS KEY TERMSDocument2 pagesMATH151 BASIC PHYSICS KEY TERMSGabriel BettinelliNo ratings yet
- Quals 2013 Sec 1Document15 pagesQuals 2013 Sec 1paimoNo ratings yet
- LEC ThermoI 2 ConservationMassEnergy1Document16 pagesLEC ThermoI 2 ConservationMassEnergy1Aldrin Jesril BascoNo ratings yet
- What Happen Ed To This Picture ? ?Document20 pagesWhat Happen Ed To This Picture ? ?Soni Idawaty SihombingNo ratings yet
- KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesKTG & ThermodynamicsAkshaan Khan100% (1)
- Formula+data Sheet For Edexcel Ial MathDocument4 pagesFormula+data Sheet For Edexcel Ial Mathlinda heatherNo ratings yet
- 3tane3tan30 : Do Kftot or (Pil MG Sine+Document1 page3tane3tan30 : Do Kftot or (Pil MG Sine+Shyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Hw. 3Document4 pagesHw. 3MySunNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Summary17 PDFDocument1 pageSummary17 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Summary: Topic: How To Measure and Describe DeformationDocument1 pageLecture 16 - Summary: Topic: How To Measure and Describe DeformationDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12-Summary: Mohr-Coulomb Strength Criterion Physical Meaning: StrengthDocument1 pageLecture 12-Summary: Mohr-Coulomb Strength Criterion Physical Meaning: StrengthDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary2 PDFDocument1 pageSummary2 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Summary: Structural Scale (H, B, D..) REV Molecular ScaleDocument1 pageLecture 5 - Summary: Structural Scale (H, B, D..) REV Molecular ScaleDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - summary of Pi-theorem applications and analysesDocument1 pageLecture 3 - summary of Pi-theorem applications and analysesDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary10 PDFDocument1 pageSummary10 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary10 PDFDocument1 pageSummary10 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear Deformation Theory SummaryDocument1 pageLinear Deformation Theory SummaryDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Summary: Review: Continuum ModelDocument1 pageLecture 6 - Summary: Review: Continuum ModelDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Stress distribution in foundation on two soilsDocument1 pageStress distribution in foundation on two soilsDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13-Summary: Beam Section Strength CriterionDocument1 pageLecture 13-Summary: Beam Section Strength CriterionDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14-Summary: Beam Section Strength Criterion: Coupled Moment and Normal LoadDocument1 pageLecture 14-Summary: Beam Section Strength Criterion: Coupled Moment and Normal LoadDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary19 PDFDocument1 pageSummary19 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary1 PDFDocument1 pageSummary1 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Strength Models 3D Model - Mohr-Coulomb Model Application To Sand PilesDocument6 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Strength Models 3D Model - Mohr-Coulomb Model Application To Sand PilesDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Example - Detailed StepsDocument7 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Example - Detailed StepsDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics I: Beam Elasticity - Problem Solving Technique and ExamplesDocument6 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics I: Beam Elasticity - Problem Solving Technique and ExamplesDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Isotropic ElasticityDocument19 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Isotropic ElasticityDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Beam Elasticity - Derivation of Governing EquationDocument7 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Beam Elasticity - Derivation of Governing EquationDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- General Solution Procedure: D W DDDocument6 pagesGeneral Solution Procedure: D W DDDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics I: Beam Elasticity - Problem Solving Technique and ExamplesDocument6 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics I: Beam Elasticity - Problem Solving Technique and ExamplesDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Stresses and EquilibriumDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Stresses and EquilibriumDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Stresses and EquilibriumDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Stresses and EquilibriumDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 6: Stresses and Equilibrium Application: Hoover DamDocument8 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 6: Stresses and Equilibrium Application: Hoover DamDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 2: Dimensional Analysis and Atomic ExplosionDocument12 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 2: Dimensional Analysis and Atomic ExplosionDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec9 PDFDocument5 pagesLec9 PDFDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 3: Dimension Analysis and Application To Engineering StructuresDocument6 pages1.050 Engineering Mechanics: Lecture 3: Dimension Analysis and Application To Engineering StructuresDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Stresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsDocument6 pagesStresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsMark Louies Mago VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their Rates of ChangeDocument234 pagesFunctions and Their Rates of ChangePeter JonesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: MRA and Inference: Dr. Yundan GongDocument52 pagesLecture 2: MRA and Inference: Dr. Yundan GongVIKTORIIANo ratings yet
- Bs 4360Document2 pagesBs 4360notZm62F67% (3)
- Calculating Density and Pressure for Circus ActsDocument4 pagesCalculating Density and Pressure for Circus ActsKaiswan GanNo ratings yet
- SK Duggal Vol 1Document658 pagesSK Duggal Vol 1Deepak YadavNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument126 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmsMalliNo ratings yet
- Lingo 11 Users ManualDocument714 pagesLingo 11 Users ManualMathi3u100% (3)
- Optimun Bahaviour FactorDocument23 pagesOptimun Bahaviour FactorFernando AdurizNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Self-Consolidating Concrete - Statistical Modelling, Mixture Design and Performance EvaluationDocument417 pagesLightweight Self-Consolidating Concrete - Statistical Modelling, Mixture Design and Performance Evaluationshak543No ratings yet
- Periodic Review Inventory Model WithDocument18 pagesPeriodic Review Inventory Model WithDr-Mohammed FaridNo ratings yet
- Research On K-Value Selection Method of K-Means Clustering AlgorithmDocument10 pagesResearch On K-Value Selection Method of K-Means Clustering AlgorithmabhishekNo ratings yet
- ICT Presentation 3rd QuarterDocument28 pagesICT Presentation 3rd QuarterJeanette Bonifacio CorpuzNo ratings yet
- F2 2016 Jun (IAL)Document4 pagesF2 2016 Jun (IAL)Candice WangNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Plan (Sept. 18)Document4 pagesGrade 7 Plan (Sept. 18)Michael SkiesNo ratings yet
- Qin2000 Article GeneralMatrixRepresentationsFoDocument10 pagesQin2000 Article GeneralMatrixRepresentationsFoCamel HhNo ratings yet
- One Sample T TestDocument5 pagesOne Sample T TestAre Meer100% (1)
- KHDA - Uptown School 2016-2017Document27 pagesKHDA - Uptown School 2016-2017Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document11 pagesWeek 8yawahabNo ratings yet
- Math Siop Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath Siop Lesson Planapi-35496503350% (2)
- Generating Polyphase Voltages in AlternatorsDocument7 pagesGenerating Polyphase Voltages in AlternatorsDreian Calaoagan PalalayNo ratings yet
- Partition function insights for statistical mechanicsDocument23 pagesPartition function insights for statistical mechanicsRiya MathurNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas and Volumes CalculatorDocument53 pagesSurface Areas and Volumes CalculatorShubham SaksenaNo ratings yet
- Fields Rings and Modules Lecture NotesDocument43 pagesFields Rings and Modules Lecture Notesrahulmnnit_csNo ratings yet
- Q3 Math 6 Module 6Document11 pagesQ3 Math 6 Module 6mangande.perlaNo ratings yet
- Brane WorldDocument34 pagesBrane WorldPriyanko ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 2012 Menu-Based Choice (MBC) For Multi-Check Choice Experiments (Bryan Orme - Sawtooth)Document141 pages2012 Menu-Based Choice (MBC) For Multi-Check Choice Experiments (Bryan Orme - Sawtooth)Kevin WiryawanNo ratings yet
- 2004 Modeling Wood Gasification in A Countercurrent Fixed Bed ReactorDocument14 pages2004 Modeling Wood Gasification in A Countercurrent Fixed Bed ReactorJean Carlos Gonzalez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Intro Parent FcnsDocument22 pagesIntro Parent FcnsDrew StrauchNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurDocument37 pagesEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurShreyaNo ratings yet